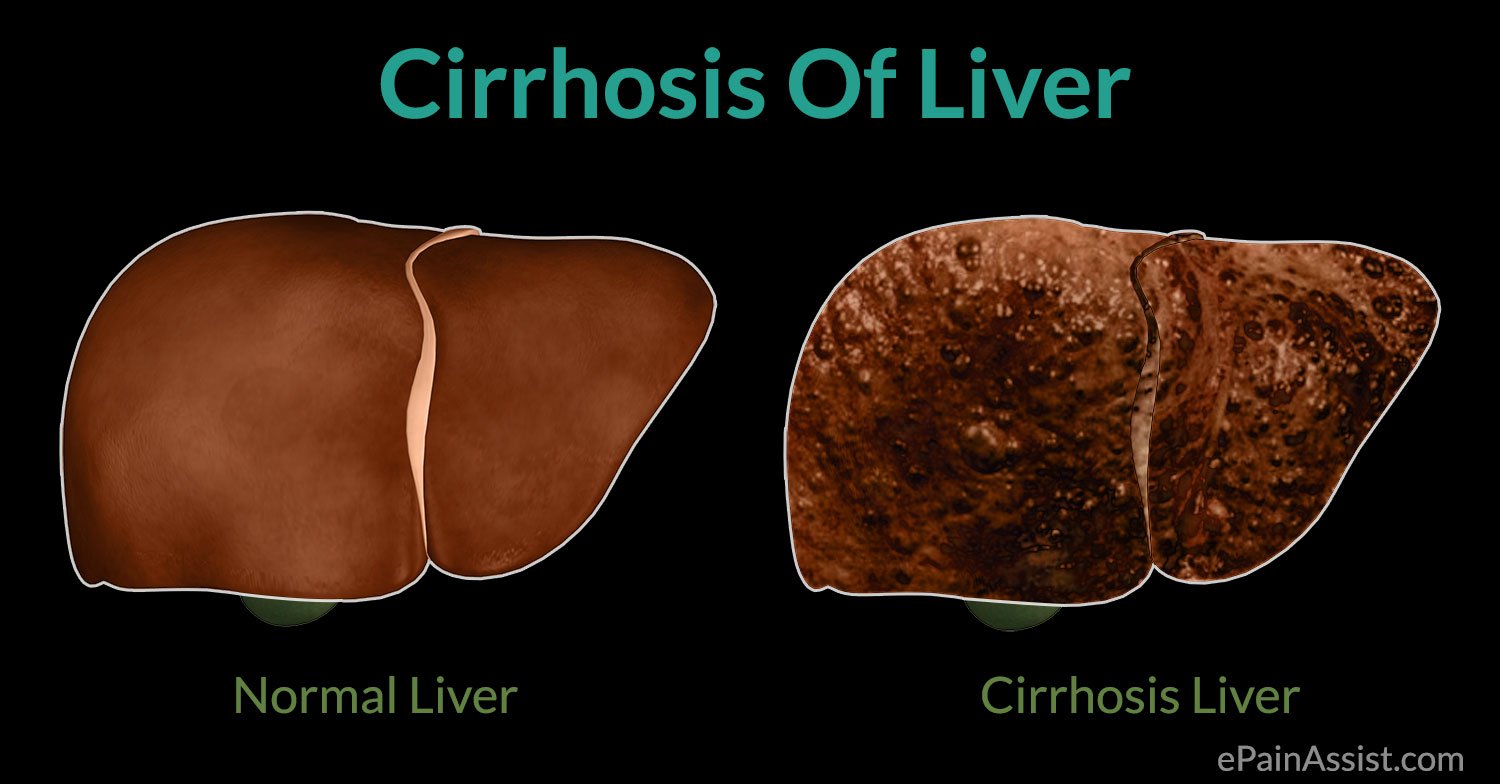
What Are The Stages Of Liver Cirrhosis
Typically, during stages of early liver damage there are no symptoms, and the liver still functions relatively well. These are called compensated stages. Decompensated stages occur as there is more liver damage and other signs of liver failure.
The chart below shows the different stages of liver cirrhosis:
| Clinical stage |
|---|
| More than one decompensating event |
When Should I Call 911 Or Go To The Emergency Room
If you have cirrhosis and experience the following, call 911:
- Your poop are black and tarry or contain blood .
- You are vomiting blood.
- You have muscle tremors or shakiness.
- You are confused, irritable, disoriented, sleepy, forgetful or foggy.
- You have a change in your level of consciousness or alertness you pass out.
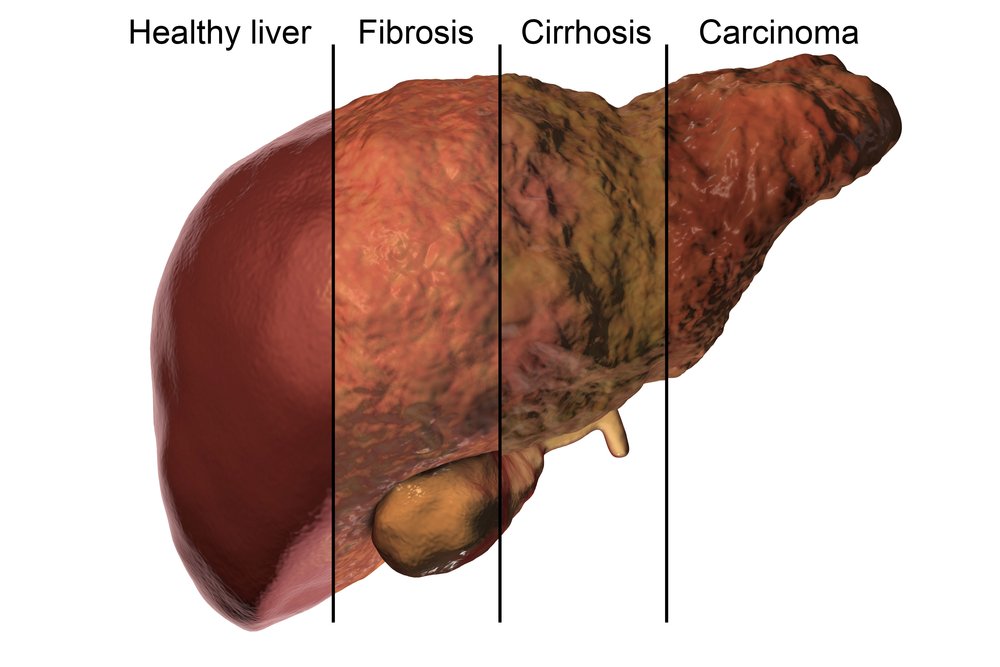
Complications Of Liver Cirrhosis
Without medical treatment, cirrhosis of the liver can lead to a range of potentially life-threatening complications including:
- bleeding from enlarged blood vessels in the oesophagus or stomach
- build-up of fluid within the abdominal cavity
- infection of the fluid found within the abdominal cavity
- liver failure loss of liver cells and disruption of blood flow through the liver by scar tissue can impair liver function
- impaired functioning of the brain caused by toxins that the liver has failed to remove .
- primary liver cancer the most common type of cancer caused by cirrhosis is hepatocellular carcinoma
- osteoporosis
Tests used to diagnose liver cirrhosis may include:
- medical history
- blood tests, including liver function tests
- urine tests
- imaging studies, including ultrasound, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging
- transient elastography , this test uses an ultrasound-based technique to detect liver cirrhosis. This test is less accurate in people with obesity issues unless specially designed XL probes are used.
- liver biopsy, obtaining liver tissue for laboratory examination.
Read Also: How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis B
How Is Cirrhosis Diagnosed
A healthcare provider will do a physical exam and run blood tests to check your complete blood count, including liver enzymes and bilirubin levels to determine liver function. A blood test that measures how well your blood clots, PT/INR, is also a reflection of liver function that’s used in diagnosing cirrhosis. Imaging tests such as a CT or MRI, along with a biopsy, are also used to diagnose cirrhosis.
What Is The Outlook If You Have Liver Cancer
Your outlook, also called your prognosis, depends on things like your overall health, the type and stage of your cancer, and how well you respond to treatment.
Liver cancer will be cured for the small number of people who are able to have a successful organ transplant. Liver cancer is also resolved for about one in three people who have surgery to remove tumors or parts of the liver. Liver cancer that is not treated successful is fatal, but researchers are working daily to find more effective treatments.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis B Virus
How To Prevent Cirrhosis
The best way to prevent alcohol-related cirrhosis is to drink within the recommended limits.
The guidelines recommend:
- men and women should not regularly drink more than 14 units of alcohol a week
- you should spread your drinking over 3 days, or more, if you drink as much as 14 units a week
Stop drinking alcohol immediately if you have alcohol-related cirrhosis. Drinking alcohol speeds up the rate at which cirrhosis progresses, regardless of the cause.
A GP can offer help and advice if you’re finding it difficult to cut down the amount you drink.
Primary Goals In Management Ofcompensated Cirrhosis
- Treatment of the etiology of the underlying liver disease, for example:
- Antiviral treatment of HCV or HBV
- Abstinence from alcohol
Recommended Reading: What Is Chronic Hepatitis B
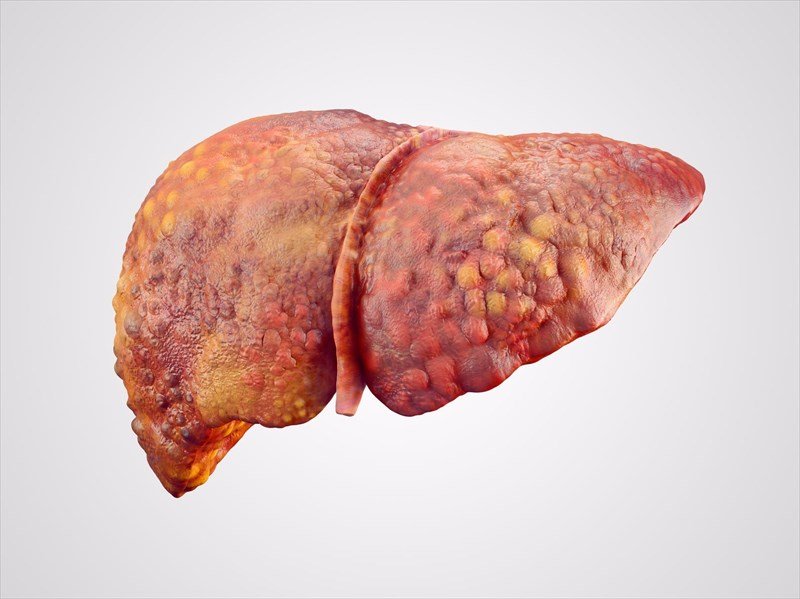
Symptoms Of Liver Cirrhosis
Symptoms depend on the severity of the cirrhosis, but may include:
- appetite loss
- spidery red veins on the skin
- easily bruised skin
- yellowing of the skin and eyes
- reddened palms
- fluid retention in the abdomen and legs
- internal bleeding presenting as dark-coloured stools or vomiting blood
- hormone disruptions that could cause a range of problems, including testicular atrophy and impotence in males or amenorrhoea in women
- disturbed sleep patterns
- cognitive problems such as memory loss, confusion or concentration difficulties.
How Are The Complications Of Cirrhosis Treated
Portal hypertension: Portal hypertension is mainly the result of chronic end-stage liver disease. Treatment consists of treating its many complications. Treatments of portal hypertension include:
- Giving beta blockers or nitrates to lower blood pressure in your veins.
- Cutting off blood flow through the varices to stop or reduce further bleeding with procedure using tiny elastic bands or with sclerotherapy.
- Redirecting blood from the portal vein to reduce pressure in the portal vein and to control variceal bleeding. This is achieved using either one of two techniques distal splenorenal shunt or transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
- Prescribing lactulose to absorb toxins in the blood that result from hepatic encephalopathy, which cause symptoms including confusion and other mental changes.
- Draining excess fluid in your abdomen in a procedure called paracentesis or taking a diuretic medication to decrease extra fluids in your legs and other areas of your body.
Bacterial peritonitis: Antibiotics and infusion of a protein will be prescribed. Typically patients are admitted to the hospital for treatment and monitoring. Following a diagnosis of bacterial peritonitis, an oral antibiotic will be prescribed for daily use to prevent recurrence of infection.
Kidney failure: Treatment may include medication, dialysis and kidney transplant, depending on the cause and extent of failure.
Recommended Reading: How Is Hepatitis C Spread
Cirrhosis And Chronic Liver Failure: Part I Diagnosis And Evaluation
JOEL J. HEIDELBAUGH, M.D., and MICHAEL BRUDERLY, M.D., University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, Michigan
Am Fam Physician. 2006 Sep 1 74:756-762.
This is part I of a two-part article on cirrhosis and chronic liver failure. Part II, Complications and Treatment, appears in this issue of AFP.
Patient information: See related handout on cirrhosis and chronic liver failure, written by the authors of this article.
Cirrhosis and chronic liver failure together were the 12th most common cause of death in the United States in 2002, accounting for 27,257 deaths , with a slight male predominance.1 Approximately 40 percent of patients with cirrhosis are asymptomatic, and the condition often is discovered during a routine examination with laboratory or radiographic studies, or at autopsy. In 2000, there were 360,000 U.S. hospital discharges related to cirrhosis and liver failure.1 This article, part I of a two-part series, outlines the diagnosis and evaluation of cirrhosis and chronic liver failure . Part II discusses complications and treatment.2
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Although no laboratory test can diagnose cirrhosis accurately, liver function tests, a complete blood count with platelets, and a prothrombin time test should be performed if a liver abnormality is suspected.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Diagnosis of Cirrhosis and Chronic Liver Failure
Figure 1.
Algorithm for the diagnosis of cirrhosis and chronic liver failure.
Figure 1.
Tracing Genetic Links: Is Cirrhosis Of The Liver Hereditary
Inherited liver disease, these are a team of metabolic and also genetic defects, which typically cause premature chronic involvement of the liver. Nearly all are because of a defect within a transport protein which alters metabolic pathways, exerting particularly a pathogenic position mainly within the liver. This prevalence is in fact variable, but the majority are uncommon pathologies. Several laboratory tests, centering on the position associated with molecular genetics have been performed. In reality, by way of recent developments in genetics, the molecular analysis allows for earlier, specific medical diagnosis for the majority of disorders and assists to relieve the invasive method that is liver biopsy.
It is postulated that several of those SNPs could possibly be in charge of the predisposition for producing cirrhosis. Once accurate, it may possibly be likely to determine these SNPs or assess ALR levels within the blood to assist in catching liver problems sooner. Highly effective treatment may be available to delay or counter continuing liver injury. Researchers intend to expand the study through the examination of how usually the SNPs ALR theyve distinguished takes place in patients having alcoholic liver disease when compared with people not having the disease.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis B Virus
Cancer And Other Causes Of Liver Disease
Cancers. Primary cancers of the liver arise from liver structures and cells. Two examples include hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma.
Metastatic cancer begins in another organ and spreads to the liver, usually through the bloodstream. Common cancers that spread to the liver begin in the lung, breast, large intestine, stomach, and pancreas. Leukemia and Hodgkin’s lymphoma may also involve the liver.
Blood flow abnormalities. Budd Chiari syndrome is a disease in which blood clots form in the hepatic vein and prevent blood from leaving the liver. This can increase pressure within the blood vessels of the liver, especially the portal vein. This pressure can cause liver cells to die and lead to cirrhosis and liver failure. Causes of Budd Chiari syndrome include polycythemia , inflammatory bowel disease,sickle cell disease, and pregnancy.
Congestive heart failure, where poor heart function causes fluid and blood to back up in the large veins of the body can cause liver swelling and inflammation.
Gallstones. Normally, bile flows from the liver into the gallbladder and ultimately into the intestine to help with the digestion of food. If bile flow is obstructed, it can cause inflammation within the liver. Most commonly, gallstones can cause an obstruction of the ducts that drains bile from the liver.
Other causes of liver disease
Formation And Secretion Of Vldl
In the fed state, -oxidation of fatty acids is not required as an energy source, and fatty acids delivered to the liver are mainly converted to TAG. Insulin regulates the metabolic path that fatty acids take in the liver. Without insulin, creatinine palmitoyl transferase-I commit fatty acids to mitochondrial -oxidation when insulin levels are high, glycerol-3-phosphate acetyltransferase commits fatty acids to the formation of TAG. This bulk of acetyl CoA entering the citric acid cycle, results in delivery of electrons to the respiratory chain, where they generate ROS.
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis A Vaccine A Live Virus
How Does Gynecomastia Affect My Body
Gynecomastia can be seen as a button-sized growth underneath the nipple. You may be able to see this as a breast lump or feel it when you press on the area. The lump may move easily within the breast tissue and may be tender to touch. Breast lumps and breast enlargement may occur in one or both breasts.
How Common Is Ascites
Fluid buildup rarely occurs in otherwise healthy people. It develops as a result of other diseases, most often cirrhosis. Ascites is the most common complication of cirrhosis. About half of people with decompensated cirrhosis will develop ascites. Cirrhosis accounts for about 80% of the cases of ascites.
Also Check: How Can Hepatitis B Be Transmitted
Treatment: Home Care Medications And Surgery
Your treatment depends on how badly your liver is injured. The goal is to protect the healthy tissue you have left.
The first step is to treat the condition that’s causing your cirrhosis to prevent any more damage. Some things you may need to do include:
- Stop drinking alcohol right away. Your doctor can suggest a treatment program for addiction.
- Lose weight if you are obese, especially if your cirrhosis is caused by fat buildup in your liver.
- Take medications if you have hepatitis B or C.
- Keep all your doctor’s appointments.
- Eat enough protein. People with cirrhosis need more than most folks.
- Get shots for flu, pneumonia, and hepatitis A and B.
- Practice good hygiene. Wash your hands often.
- Ask your doctor if it’s OK to take over-the-counter medicines like acetaminophen, aspirin, or ibuprofen. You cannot take these medications if you have ascites.
- Drink enough fluids, even if you have ascites, so you don’t get dehydrated.
- Eat a low-salt diet if you have ascites.
- Eat a high-protein, high-calorie diet.
- Take a diuretic if your doctor prescribes one to help manage ascites.
- Take medicine your doctor prescribes if you have constipation .
Your doctor will also want to treat any complications that can happen with cirrhosis. They may suggest things like:
Low-sodium diet. This can help control swelling. Your doctor may also ask you to take medications for this problem. If you have a severe fluid buildup, you may need to get it drained.
Pathogenesis Of Steatosis In Chronic Hepatitis C
IR emerges as a very important host factor, mainly because it has been related to steatosis development, fibrosis progression and non-response to peg-interferon plus ribavirin. HCV directly associates with IR independent of the visceral fat area in non-obese and non-diabetic patients. HCV is directly associated with IR in a dose-dependent manner, independent of the visceral adipose tissue area.
Factors associated with steatosis in chronic hepatitis C are: viral factor host factors , and drug therapy . The mechanisms underlying the development of parenchymal steatosis in HCV infection are not exactly known.
The first mechanism supposes that HCV core protein may block assembly of Apo-A1-A2 with TAG. This will result in decreased export of TAG bound to apolipoprotein- as VLDL out of hepatocyte, which is corrected by antiviral therapy. Others propose that the core protein induces oxidative stress within the mitochondria that contributes to lipid accumulation. Though the exact mechanism remains elusive, it seems that HCV itself can directly induce steatosis in genotype 3 by the cytopathic effect of high titer of intracytoplasmic negative strand HCV RNA.
The main deleterious effect of IR in chronic hepatitis C is the ability to promote fibrosis progression. High serum glucose levels have been found associated with an increased rate of fibrosis progression, even greater than overweight.
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis C Contagious Mayo Clinic
If I Have Ascites How Can I Best Take Care Of Myself
People with ascites should work with a dietitian to plan a sodium-restricted diet. Check food labels, and avoid high-sodium foods.
You can use several salt substitutes. However, avoid substitutes with potassium, since the medicine you may be taking for ascites can also increase potassium. A dietitian can help you plan a healthy diet and provide recommendations for salt alternatives.
In addition, you should:
- Take your diuretics as prescribed.
- Record your weight every day.
- Stop drinking alcohol, which can cause further liver damage.
- Treat hepatitis B or C if necessary.
Natural History And Reversibility Of Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is frequently viewed as an end stage in the evolution of many types of chronic liver diseases. However, in recent years, clinical reports indicate that on cessation of the injurious process, cirrhosis may reverse, or at least improve, histologically.5159 These reports include patients with established cirrhosis in whom subsequent tissue samples have shown incomplete septal cirrhosis, or apparent absence of fibrosis, after successful treatment. This evolution has been documented in patients with hemochromatosis, autoimmune hepatitis, Wilson’s disease, primary biliary cirrhosis, schistosomiasis, extrahepatic biliary obstruction, alcoholic disease, chronic viral hepatitis B and C, and postjejunal bypass steatohepatitis.
Old extinction lesions predominate in livers where the primary disease has remitted, either spontaneously or after successful treatment.51 Fibrosis is progressively removed from extinction lesions so that broad septa become delicate and delicate septa become incomplete or disappear. Thus, micronodular cirrhosis may remodel to macronodular cirrhosis, incomplete septal cirrhosis, or nearly normal liver . The problem with diagnosing regression of cirrhosis is discussed later.
David Shaw, in, 2007
Also Check: Hepatitis A Is A Virus
How Is Liver Cirrhosis Diagnosed
Diseases of the liver may not show symptoms in the early stages, and can therefore remain undetected for a long time.1 Your doctor may suspect cirrhosis if you have certain symptoms.2 They may perform various tests and examinations to confirm the diagnosis, and then decide the appropriate therapy for you.1
Using Complementary And Alternative Medicines Wisely
In general, you should avoid most herbal and other supplements, which may make liver disease worse. Kava is particularly bad for people who have liver problems.
Limited research has shown that the herbal supplement milk thistle may help protect the liver, but other research has not shown a benefit.footnote 2 Milk thistle will not reverse existing liver damage, and it will not cure infection with the hepatitis B or hepatitis C virus. Milk thistle should not be used by people who have complications from cirrhosis . Talk to your doctor about whether you should try milk thistle .
Read Also: Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Steatosis In Chronic Hepatitis C
In chronic hepatitis C patients, the prevalence of steatosis ranges from 40% to 86% . The majority of patients with steatosis have mild steatosis affecting less than 30% of hepatocytes. Thus, steatosis occurs more frequently in patients with chronic hepatitis C than in the general population of adults in the Western world. Macrovesicular steatosis is found in the periportal region of the liver-different from the centrilobular distribution characteristic of NASH patients. Mild steatosis had been reported in nearly 40% of patients with HCV genotype 4.
Moderate or severe steatosis is significantly less frequent in genotype 4 than 3 chronic hepatitis C patients and similar between genotype 4 and 1. In non-diabetic, overweight patients, moderate or severe steatosis is present in only 10%-15% of genotype 4 or 1 compared with 40% of genotype 3 patients. Thus, hepatic steatosis in genotype 4 is mostly associated with metabolic factors, similar to those in genotype 1.