Recommended Immunizations For Children Ages 11 To 12 Years Old
The immunizations that are recommended at this age are for diseases that teens and young adults are at higher risk for plus one booster dose to strengthen immunity for three diseases. Your childs annual wellness visit or back-to-school checkup is the perfect time to get these vaccines.
An overview of immunizations for kids ages 11 to 12 years old
- Tdap At this age, this immunization is whats commonly referred to as a booster shot because it boosts your childs tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis immunity. While related to the DTaP vaccine kids receive during childhood, this vaccine is formulated for adolescents and adults.
- MenACWY The first of two meningococcal vaccine doses is recommended sometime between 11 years old and 12 years old. This vaccine protects against the most common types of meningococcal bacteria that affect adolescents.
- HPV While in some cases doctors may recommend the human papillomavirus vaccine as early as age 9, this vaccine is routinely recommended to begin between 11 and 12 years old. If the initial vaccination is completed before age 14, just two doses are needed. The second dose should be completed 6 to 12 months after the first dose.
British Columbia Specific Information
Hepatitis B is a virus that attacks the liver. It can cause serious disease, including permanent liver damage , and is also the main cause of liver cancer.
The hepatitis B vaccine provides immunity for at least 10 years and likely for a lifetime when completing the full series. There are currently no recommendations for a healthy person to receive a booster for this vaccine if they have completed the full series.
For more information on hepatitis B and the hepatitis B vaccine, see:
You may also call 8-1-1 to speak to a registered nurse or pharmacist. Our nurses are available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week and our pharmacists are available every night from 5:00 p.m. to 9:00 a.m.
Engerix-B
Recombivax HB
tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis, polio, Haemophilus influenzae type b, and hepatitis B combined vaccine
Infanrix Hexa
What Are The Possible Reactions After The Vaccine
Vaccines are very safe. It is much safer for your child to get the vaccine than to get hepatitis B.
Common reactions to the vaccine may include soreness, swelling or redness where the vaccine was given. Some children may experience fever, fussiness or fatigue.
It is important to stay in the clinic for 15 minutes after getting any vaccine because there is an extremely rare possibility, less than 1 in a million, of a life-threatening allergic reaction called anaphylaxis. This may include hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the throat, tongue or lips. Should this reaction occur, your health care provider is prepared to treat it. Emergency treatment includes administration of epinephrine and transfer by ambulance to the nearest emergency department. If symptoms develop after you leave the clinic, call 9-1-1 or the local emergency number.
It is important to always report serious or unexpected reactions to your health care provider.
Don’t Miss: Can You Die With Hepatitis C
How Safe Is The Hepatitis B Vaccine
The HBV vaccine is very safe. Side effects with this vaccine are uncommon, but may include soreness where the shot was given, and fever. Fever after vaccination is a common side effect for most vaccines, and is due to the immune system mounting a response against the vaccine, which is the desired result of vaccination. This fever is low grade and will resolve on its own. Because of how the vaccine is made, people with severe yeast allergy are not recommended to get HBV vaccine.
Moving To Another Country
If you are moving abroad before your baby is one year old, please let your GP know and dont forget to register your baby with a new family doctor in your new country of residence.
Take your babys Red Book with you and make sure your baby receives all of the doses of hepatitis B vaccines on time and has a blood test at 12 months old.
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis B Cause Meningitis
Hepatitis B Vaccination In Pregnancy
Hepatitis B infection in pregnant women may result in severe disease for the mother and chronic infection for the baby. This is why the hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for pregnant women who are in a high-risk category.
There’s no evidence of any risk from vaccinating pregnant or breastfeeding women against hepatitis B. And, as it’s an inactivated vaccine, the risk to the unborn baby is likely to be negligible .
Your Babys First Shot
Shortly after birth, your baby should receive the first dose of the vaccine to help protect against the following disease:
All babies should get the first shot of hepatitis B vaccine within first 12 hours after birth.
This shot acts as a safety net, reducing the risk of getting the disease from you or family members who may not know they are infected with hepatitis B.
If you have hepatitis B, theres additional medicine that can help protect your newborn against hepatitis B its called hepatitis B immune globin . HBIG gives your babys body extra help to fight the virus as soon as your baby is born.
You May Like: How Soon Do Hepatitis C Symptoms Appear
Table : Routine Childhood Immunization Schedule Infants And Children
- For children at-risk due to underlying medical conditions, refer to Table 4 for additional recommendations for immunization.
- = dose may not be required depending upon age of child or vaccine used or both . mos = months. yrs = years. P/T = provincial and territorial.
- Refer to Timing of vaccine administration and Vaccine administration practices in Part 1 regarding administration of multiple injections.
- Refer to vaccine-specific chapters in Part 4 for additional information.
|
Why Vaccinate Newborns For Hepatitis B
If you’re like many parents, you may wonder why doctors recommend vaccinating all children against hepatitis B. Although vaccinating infants of mothers who are infected with hepatitis B and delaying vaccinating others is one strategy for preventing hepatitis B in newborns, it’s not as effective as universal immunization.
In fact, health experts tried this approach first, immunizing select newborns when the hepatitis B vaccination first came out, and unfortunately, it wasn’t successful. Too many children were still getting sick from hepatitis B.
It wasn’t until after the universal immunization program for the hepatitis B vaccine began that the rate of new hepatitis B infections in children began to drop. That’s why medical professionals recommend vaccinating all newborns against hepatitis B.
In a universal immunization program, all newborns are immunized against the virus, even if their mothers test negative for hepatitis B infections.
Giving this birth dose of the vaccination helps prevent the disease from developing in babies who have mothers who have hepatitis B infections but never knew it. It also prevents a scenario in which the mother has a known hepatitis B infection, but the baby somehow misses the hepatitis B shot. This scenario can occur when a mother fails to report her hepatitis B infection to her doctor, forgets that she has the infection, or gets a false negative on her hepatitis B test.
Don’t Miss: How To Catch Hepatitis C
Babies And Children Can Develop Chronic Hbv
You may be wondering why the recommendations for the HBV vaccine start on the first day of life.
Adults who contract HBV will likely not experience long-term complications from hepatitis B. But the same is not the case for babies. As many as of babies who contract an HBV infection at birth from their mothers become chronically infected with HBV.
Children between the ages of 1 and 5 who get an HBV infection have a 25 percent of people who become chronically infected during childhood will develop liver cancer or cirrhosis. Thats why pediatricians want children to have immunity from HBV from the earliest possible age. Many babies and children exposed to HBV receive post-exposure prophylaxis, which decreases chance of infection.
If youre pregnant, youll most likely have a blood test to see if youre positive for hepatitis B. This allows doctors to find out if theres a chance that you could pass on the virus. These tests are highly sensitive and have a good accuracy rate, but they arent perfect. Additionally, a pregnant person may become infected between the time of the test and giving birth. The first dose of the vaccine given at birth lowers the risk of a newborn baby contracting hepatitis B.
Who Should Get Vaccinated
The US recommends 3 doses of HBV vaccine to ensure full protection. Specific vaccination schedules are recommended by the CDC for babies and children, for preteens and teens, and for adults). For babies, the first dose is typically given at birth, the second at 1-2 months of age, and the third at 6-18 months of age. These shots are part of the normal schedule of vaccines that a childs pediatrician will administer, and that will be administered at the time of birth. Additionally, anyone through 18 years of age who has not started the vaccine series should be vaccinated.In addition to the above recommendations, California state law requires that children who attend childcare or K-12 school have received specific numbers of several vaccines, including hepatitis B vaccine. Many colleges also require evidence of hepatitis B vaccination.
Some adults should also be vaccinated if they do not have a history of vaccination, especially if they are at higher risk of infection. Adults who are unsure of their immune status to HBV should speak to their doctor about getting vaccinated. Because infection can be asymptomatic for so long, some people may be advised to get tested for infection before they are vaccinated especially those who were born in countries where Hepatitis B is endemic.
In brief:
- Students in California
- Healthcare personnel: Healthcare workers have specific immunization recommendations
You May Like: How Is Hepatitis A Caused
Babies And Hepatitis B Vaccination
Pregnant women have a routine blood test for hepatitis B as part of their antenatal care.
Babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B need to be given a dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of their birth, followed by further doses at 4, 8, 12 and 16 weeks of age, plus a final dose when they’re 1 year old.
Babies of mothers identified by the blood test as particularly infectious might also be given an injection of HBIG at birth on top of the hepatitis B vaccination to give them rapid protection against infection.
All babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B should be tested at 1 year of age to check if they’ve become infected with the virus.
Benefits Of The Hepatitis B Vaccine
The main benefit of the vaccine is its effectiveness. The AAP note that if doctors give the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of the babys delivery, it is 75 to 95 percent effective in preventing the passage of hepatitis B from the birth mother to the baby.
If the newborn also receives the medication hepatitis B immune globulin at the correct time and a series of follow-up vaccines, the AAP estimate that the infection rate drops to between 0.7 and 1.1 percent.
For the best possible protection, the baby will need to complete the full series of vaccines.
state that the vaccine is very safe. The full series of the vaccine provides the highest possible level of protection from the infection.
Some people still express concern about the safety of vaccination. The reasons for this worry may vary.
Part of the fear may be due to older research. For example, a 2009 study indicated an association between the Engerix B vaccine, a specific type of hepatitis B vaccine, and an increased risk of damage to the central nervous system later in life.
However, the researchers note that this was the exception, not the rule. They also highlight the need for more studies to validate this finding.
On the whole, their research indicates that hepatitis B vaccination generally does not increase the risk of damage to the CNS.
The majority of research indicates that hepatitis B vaccines are a safe and effective way to prevent the infection.
You May Like: How Do You Get Hepatitis A And B
What Is The Nip Schedule
The National Immunisation Program Schedule is a series of immunisations given at specific times throughout your life. The immunisations range from birth through to adulthood.
All vaccines listed in the NIP Schedule are free. Eligibility for free vaccines under the NIP is linked to eligibility for Medicare benefits.
To get the best possible protection, make sure you have your immunisations on time, every time. The NIP Schedule below shows which vaccines you should get and when.
This schedule card provides recommended vaccines and schedule points under the National Immunisation Program from 1 July 2020 .
General Information About Vaccination Outside The Us
In developing countries, the pentavalent vaccine, a combination 5-in-one vaccine that protects against five diseases, diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, Hib and hepatitis B, may be given to babies more than 6 weeks of age, and can be given up to 1 year of age. The first dose is given at 6 weeks, and the second and third doses are given at 10 and 14 weeks of age. The pentavalent vaccine may be made available free of charge with the support of GAVI, the vaccine alliance. Check the GAVI country hub to see the resources and immunizations that may be available:
For babies born to mothers with hepatitis B, waiting for the first dose of the pentavalent vaccine is too late and will NOT protect the baby from vertical or horizontal transmission of hepatitis B. Babies born to a mother with hepatitis B have a greater than 90% chance of developing chronic hepatitis B if they are not properly treated at birth.
WHO recommends the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth for ALL babies. Plan ahead and inquire about the availability and cost of the monovalent , birth dose of the vaccine, as it is not a GAVI provided immunization. This is particularly important to women who are positive for hepatitis B.
If you are unsure of your hepatitis B status, please be sure your doctor tests you for hepatitis B!
*WHO does not recommend a birth dose of HBIG, which may not be available in all countries. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis B Caused By
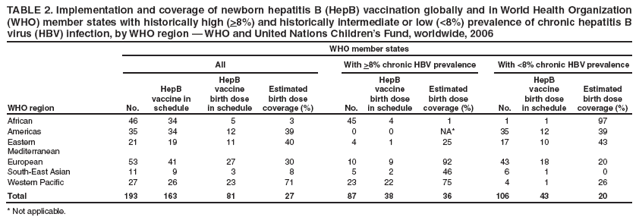
Prevalence Of Chronic Hepatitis B
The prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection varies between and within countries:58-61
- < 0.5% among Caucasians in the United States, northern Europe and Australia
- 15% in Mediterranean countries, parts of eastern Europe, Africa, and Central and South America
- > 10% in many sub-Saharan African, East and Southeast Asian, and Pacific island populations
Regions where 2% of the population is positive to hepatitis B surface antigen are considered to have moderate to high prevalence. In these regions, people mainly acquire the infection perinatally or in early childhood.55
New Zealand Immunisation Schedule
The National Immunisation Schedule is the series of vaccines that are offered free to babies, children, adolescents and adults.
The schedule of vaccines listed below applies from 1 October 2020.
| 1 injection, during the second or third trimester of pregnancy For information about the decision to widen access to pertussis vaccine see the Pharmac website. | |
| 6 weeks | |
|---|---|
| 2 injections given at least 6 months apart for those aged 14 and under3 injections given over 6 months for those aged 15 and older | |
| 45 years | 1 injection for those who have not already received four doses of tetanus vaccine* |
| 65 years |
*From 1 July to 30 September 2020 practices will continue to be supplied with the previously scheduled vaccine brands until these vaccine stocks are depleted.
Links in the table above provide more information about the diseases and the vaccines that prevent them.
You May Like: What Is The Definition Of Hepatitis B
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
The vaccine is given to babies as a series of 3 doses at 2, 4 and 6 months of age. It is usually combined with other childhood vaccines such as diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, and Haemophilus influenzae type b. For more information, see HealthLinkBC File #105 Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis, Hepatitis B, Polio, and Haemophilus influenzae type b Vaccine.
| Hepatitis B Vaccine | Childs Age at Immunization |
|---|---|
| 1st dose | |
| 3rd dose | 6 months |
Some babies are at greater risk of being infected with hepatitis B virus and need to be immunized at birth. For more information, see HealthLinkBC File #25d Protecting Your Baby against Hepatitis B at Birth.
It is important to keep a record of all immunizations received.
Testing Your Baby For Infection
Each year, a very small number of babies may develop infection so your baby will be offered a blood test when they are 1 years old. This is to check that the course of vaccines have prevented them from developing hepatitis B.
There are 2 ways that this may be done and your GP, health visitor or practice nurse will advise you which test your baby will have:
If they do have the infection, they will be referred to a specialist for treatment to reduce their risk of developingserious liver disease.
If a young infant is infected, they are more likely to develop long lasting infection without any signs or symptoms of infection. Even if your baby has no signs or symptoms of infection they should still have the blood test.
Infection can be prevented in 90% of cases if the first dose of vaccine is given at birth and the full course of vaccines is completed on time.
You May Like: What Is Hepatic Luciferase Expression