What Is The Prognosis Of Hepatitis C
Acute fulminant hepatitis C virus infection is rare, but more than 80% of acutely infected individuals develop chronic hepatitis. Most patients chronically infected with hepatitis C virus remain asymptomatic and do not have significant liver disease. The prognosis is guarded for those who have hepatitis C virusrelated complications such as hepatocellular carcinoma and liver failure.
In more than 20% of adults with chronic infection, progression to cirrhosis occurs an average of 20 years after initial infection. Cirrhosis poses a secondary risk of portal hypertension, liver failure, and other complications. Hepatitis C is now the leading reason for liver transplantation in the United States. In 1-5% of patients, most of whom have underlying cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma is diagnosed an average of 30 years after initial hepatitis C virus infection. Annually, hepatitis C virus infection accounts for 8,000-10,000 deaths in the United States.
Definition And Natural History
Cirrhosis is considered to be compensated in the asymptomatic patient with or without gastroesophageal varices. Persons with compensated cirrhosis are not jaundiced and have not yet developed ascites, variceal bleeding, or hepatic encephalopathy. Cirrhosis can remain compensated for many years. The transition from compensated to decompensated cirrhosis occurs at a rate of approximately 5 to 7% per year. The median survival of persons with compensated cirrhosis is approximately 9 to 12 years.
How Common Is Hepatitis C In The United States
In the United States, hepatitis C is the most common chronic viral infection found in blood and spread through contact with blood.14
Researchers estimate that about 2.7 million to 3.9 million people in the United States have chronic hepatitis C.13 Many people who have hepatitis C dont have symptoms and dont know they have this infection.
Since 2006, the number of new hepatitis C infections has been rising, especially among people younger than age 30 who inject heroin or misuse prescription opioids and inject them.15,16
New screening efforts and more effective hepatitis C treatments are helping doctors identify and cure more people with the disease. With more screening and treatment, hepatitis C may become less common in the future. Researchers estimate that hepatitis C could be a rare disease in the United States by 2036.17
Don’t Miss: Natural Treatment For Hepatitis C
What Causes Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus causes hepatitis C. The hepatitis C virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood. Contact can occur by
- sharing drug needles or other drug materials with an infected person
- getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
- being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not kept sterilefree from all viruses and other microorganismsand were used on an infected person before they were used on you
- having contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person
- using an infected persons razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
- being born to a mother with hepatitis C
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
You cant get hepatitis C from
- being coughed or sneezed on by an infected person
- drinking water or eating food
- hugging an infected person
- shaking hands or holding hands with an infected person
- sharing spoons, forks, and other eating utensils
- sitting next to an infected person
A baby cant get hepatitis C from breast milk.18
Who Should Be Tested
Testing for hepatitis A is not routinely recommended.
CDC recommends hepatitis B testing for:
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household and sexual contacts of people with hepatitis B
- People requiring immunosuppressive therapy
- People with end-stage renal disease
- People with hepatitis C
- People with elevated ALT levels
- Pregnant women
- Infants born to HBV-infected mothers
CDC recommends hepatitis C testing for:
- All adults aged 18 years and older
- All pregnant women during each pregnancy
- About 24,900 new infections each year
- About 22,600 new infections in 2018
- Estimated 862,000 people living with hepatitis B
- About 50,300 new infections in 2018
- Estimated 2.4 million people living with hepatitis C
Also Check: How Soon Can You Detect Hepatitis C
Data Collection And Patient Follow
Demographic data and information regarding alcohol consumption, smoking habits, and antiviral treatment history were extracted from the medical records of the patients included in the study. All patients underwent HCV RNA tests and serological testing to determine the presence of HBsAg, anti-HIV, and anti-HCV, alpha-fetoprotein levels, liver biochemical parameters, and blood cell counts prior to starting treatment.
The diagnostic criteria for liver cirrhosis included the presence of portal hypertension manifested as splenomegaly, thrombocytopenia < 100,000/mm3, ascites, varices, or hepatic encephalopathy, and imaging findings consistent with liver cirrhosis.13
Initial treatment strategies for HCC during the study period were surgical resection, radiofrequency ablation , chemoembolization , radiotherapy, and sorafenib. Curative treatment strategies included hepatic resection and RFA. IFN combined with ribavirin was administered for at least 24 weeks as antiviral therapy. SVR was defined as undetectable HCV RNA in the blood at 12 weeks after completion of antiviral treatment.
Follow-up was completed in January 2020. Overall survival was defined as the period from the date of HCC diagnosis to the confirmed death date of patients who died, or the date of the last follow-up for surviving patients.
What The Cdc Recommends
Were you born between 1945 and 1965? If so, then youre a member of the Hepatitis C generation. The CDC recently recommended that all people born between during this time have a 1-time screening test for Hepatitis C. We now have new drugs that can treat and cure Hepatitis C so you should go get tested today.
The life you save may be your own! Please contact your local healthcare provider.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Symptoms Mayo Clinic
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis C
You are more likely to get hepatitis C if you
- Have injected drugs
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you probably will not have symptoms until it causes complications. This can happen decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
Articles On Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a sneaky virus. You may not have any symptoms at all. Most people donât. This is one if the reasons, along with treatability now, that all adults are recommended to get tested. Your doctor could check your liver and see only a little damage. You’re usually not diagnosed until they spot a problem with your liver enzymes after a routine blood test.
Read Also: What Is A Hepatitis B Shot
Hepatitis C And Liver Cancer: What To Know
Several viruses besides HPV have been linked to cancer, includinghepatitis C, which is linked to liver cancer.
If you think HPV is the only virus that causes cancer, think again. Several other viruses have been linked to cancer, including hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is the most common blood-borne infection in the United States. Its also the leading cause of liver cancer.
About 30 percent of people who get exposed to the hepatitis C virus will clear it on their own. The rest will go on to have chronic hepatitis C.
This ongoing infection causes inflammation in the liver. This extended inflammation can cause scarring, called cirrhosis, and can ultimately lead to liver cancer.
Chronic hepatitis C also increases the risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and head and neck cancers.
Unlike hepatitis A and B, there is no vaccine against hepatitis C, and there are few if any symptoms, says Harrys Torres, M.D., associate professor of Infectious Diseases.
Its a silent infection, he says. And its a very clever virus that mutates very fast, so it has been difficult to develop a vaccine.
Knowing the risk factors and getting screened are your best defenses against cancers caused by hepatitis C. Treatment of this virus can reduce your risk of liver cancer by 75%.
Risk factors
About 75% of those infected with hepatitis C in the United States are baby boomers people born between 1945 and 1965.
Other risk factors for hepatitis C infection include:
Meaning Of Hcv Viral Load
The number of HCV RNA international units per milliliter of blood must be measured before treatment and during the course of treatment, to assess response. Before treatment, however, the HCV viral load is not related to the patient’s liver disease severity or HCV prognosis. This is important for patients and providers to understand.
Note: In hepatitis B, unlike hepatitis C, a higher HBV DNA viral load does correlate with increased disease severity and increased likelihood of outcomes such as hepatocellular carcinoma.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis C Be Cured Totally
Treatment Of Hcv In Patients With Compensated Cirrhosis
The major goal of managing patients with HCV and compensated cirrhosis is to treat the HCV infection. Treatment of patients with compensated cirrhosis using newer direct-acting antiviral medications has been associated with sustained virologic response rates of 90% or better. Patients with HCV-related cirrhosis who undergo treatment and achieve a cure have a dramatically decreased 10-year risk of all-cause mortality , liver-related mortality or transplantation , hepatocellular carcinoma , and hepatic decompensation .
Chronic Hepatitis C Prognosis
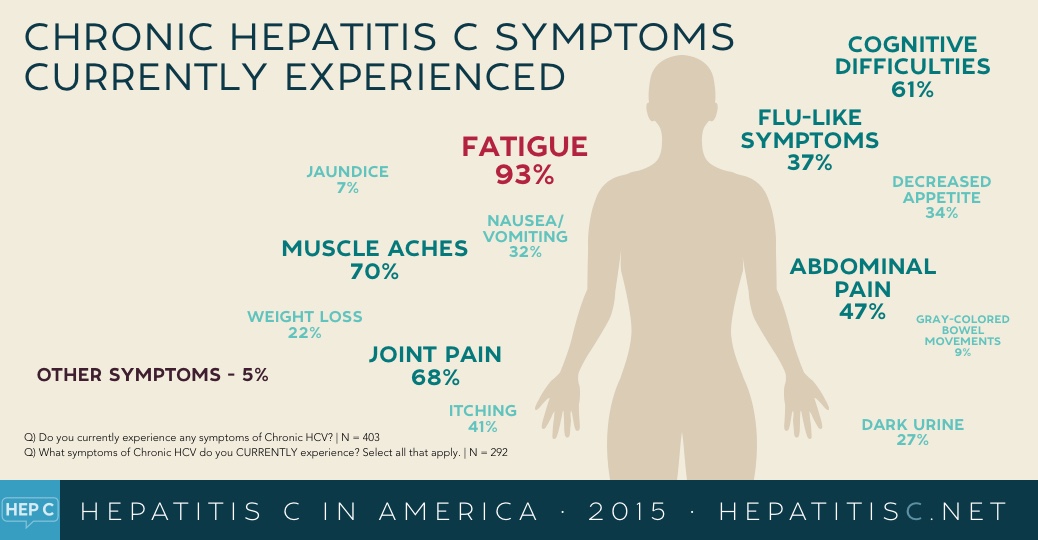
Chronic hepatitis C is a long-term illness that can lead to liver damage, including fibrosis and eventually cirrhosis. In the past, the prognosis for chronic hepatitis C was poor. Treatment involved weekly injections for up to a year. Older hepatitis C drugs were very difficult to tolerate and only cured about half the people taking them. In fact, many people had to stop treatment due to intolerable side effects.
Today, chronic hepatitis C is one of the few chronic diseases doctors can cure. Astounding advances in medication therapy means doctors can now cure more than 95% of people with the virus. Whats more, they can do it with oral medicines over the course of 8 to 12 weeks, for all genotypes of the virus.
Treatment regimens with two antiviral medicines are standard therapy. With some regimens, the cure rate approaches 100%. Cure means you have a sustained viral response lab tests cant detect the virus in your blood six months after stopping medicines.
Left untreated, chronic hepatitis C can progress to cirrhosisor permanent scarring of the liver. Eventually, this can lead to end-stage liver failure when the liver stops working. Up to 20% of people with chronic hepatitis C will develop cirrhosis within 2 to 3 decades. Of those, up to 6% will go on to develop end-stage liver failure. Up to 5% will develop liver cancer.
This risk of progression to cirrhosis is higher if you have the following risk factors:
Read Also: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis B Virus
What If I’m Pregnant And I Have Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be passed from a mother to her child during pregnancy and during delivery. Per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , approximately 6 of every 100 infants born to HCV-infected mothers become infected with the virus. The risk is two to three times greater when the mother has HIV as well.
You and your doctor should discuss and decide if you should receive treatment for hepatitis C during your pregnancy.
Questions For Your Doctor
When you visit the doctor, you may want to ask questions to get the information you need to manage your hepatitis C. If you can, have a family member or friend take notes. You might ask:
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vaccine Dose For Newborns
Tests For The Hepatitis C Virus
If your doctor thinks that you may have hepatitis C, he or she may order:
- A hepatitis C virus test. This is a blood test that looks for antibodies against the hepatitis C virus. It shows whether you have been exposed to the virus.
- A blood test that looks for the genetic material of the hepatitis C virus. This test shows whether you are infected with the virus now.
- A blood test to find out the kind of hepatitis C virus you have. Knowing your genotype will help you and your doctor decide if and how you should be treated.
Cost Of Hepatitis C Medicines
The newer direct-acting antiviral medicines for hepatitis C can be costly. Most government and private health insurance prescription drug plans provide some coverage for these medicines. Talk with your doctor about your health insurance coverage for hepatitis C medicines.
Drug companies, nonprofit organizations, and some states offer programs that can help pay for hepatitis C medicines. If you need help paying for medicines, talk with your doctor. Learn more about financial help for hepatitis C medicines.
You May Like: Royal Canin Feline Hepatic Diet
Treatments For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be treated with medicines that stop the virus multiplying inside the body. These usually need to be taken for several weeks.
Until recently, most people would have taken 2 main medicines called pegylated interferon and ribavirin .
Tablet-only treatments are now available.
These new hepatitis C medicines have been found to make treatment more effective, are easier to tolerate, and have shorter treatment courses.
They include simeprevir, sofosbuvir and daclatasvir.
Using the latest medications, more than 90% of people with hepatitis C may be cured.
But it’s important to be aware that you will not be immune to the infection and should take steps to reduce your risk of becoming infected again.
Tests For Liver Problems
To check how well your liver is working, you may have:
- Liver function tests. These are blood tests that can help your doctor find out if you have liver damage.
- A liver biopsy. The doctor puts a needle in the liver to find out whether the virus has caused scarring or damage to your liver.
- Imaging tests such as a CT scan, an MRI, or an ultrasound to make sure that you don’t have liver cancer.
Also Check: How Is Hepatitis B Virus Transmitted
What Laboratory Tests Diagnose Hepatitis C
Laboratory blood tests will be done to evaluate the patient’s liver function and to look for hepatitis C antibodies . If these tests indicate that the person has hepatitis C, a hepatitis C “viral load” test will be done. This looks for genetic material from the hepatitis C virus and measures the quantity of hepatitis C virus that is circulating in the patient’s blood. This is helpful in determining if treatment is appropriate and to monitor the success of the treatment .
Individuals who had hepatitis C in the past and cleared the virus on their own will have a positive HCV antibody test, but there will be no hepatitis C virus genetic material in the blood. If a person is immunosuppressed due to an immunological condition, cancer chemotherapy, immunotherapy or HIV/AIDS, the test results may be different and need to be evaluated accordingly.
Chronic Phase Of Hepatitis C
After six months 70% to 85% of those infected will have failed to clear the virus spontaneously. After this period the hepatitis C virus enters what is known as the chronic phase. This is when hepatitis C becomes a chronic or long-term infection. The diagnosis is confirmed when over a six month period hepatitis C RNA viral presence is detectable on at least two occasions.
A diagnosis of chronic hepatitis C means the battle between the virus and the immune system that occurs during the acute stage has finally been won by the virus. It is now highly unlikely that the virus can be cleared without treatment.
How the disease then progresses varies significantly from person to person. After many years some people will have minimal liver damage with no scarring while others can progress to cirrhosis within less than ten years. On average it takes about twenty years for significant liver scarring to develop. It is still not known whether chronic hepatitis C infection inevitably leads to cirrhosis. At present it is thought that this is a very likely outcome, although for some people it may take at least 50 years or more. They may well die of other unrelated diseases or conditions before cirrhosis develops. The rate of progression of liver damage cannot be accurately determined by liver enzyme levels, viral load or by genotype.
Liver damage and fibrosis during the chronic stage
Free Radicals and Fibrosis
Recommended Reading: How Can Hepatitis C Be Transmitted
Sharing Toothbrushes Scissors And Razors
There’s a potential risk that hepatitis C may be passed on through sharing items such as toothbrushes, razors and scissors, as they can become contaminated with infected blood.
Equipment used by hairdressers, such as scissors and clippers, can pose a risk if it has been contaminated with infected blood and not been sterilised or cleaned between customers. However, most salons operate to high standards, so this risk is low.
Univariate And Multivariate Analyses
Univariate survival analysis of OS was performed using 10 variables: gender, age, smoking history, alcohol intake, AFP level, HCV-RNA level, antiviral treatment, liver cirrhosis, tumor size, and tumor number. According to the univariate analysis, alcohol intake and AFP > 20 ng/mL were predictors of shorter survival, and SVR after antiviral therapy was a predictor of longer survival. Multivariate analysis confirmed that only SVR after antiviral therapy was an independent predictor of OS for HCC patients with active HCV infection .
|
Table 3 Univariate and Multivariate Analyses Showing Significant Predictive Factors of Mortality in HCC Patients with Active HCV Infection |
Recommended Reading: How Is Hepatitis C Transmitted Cdc