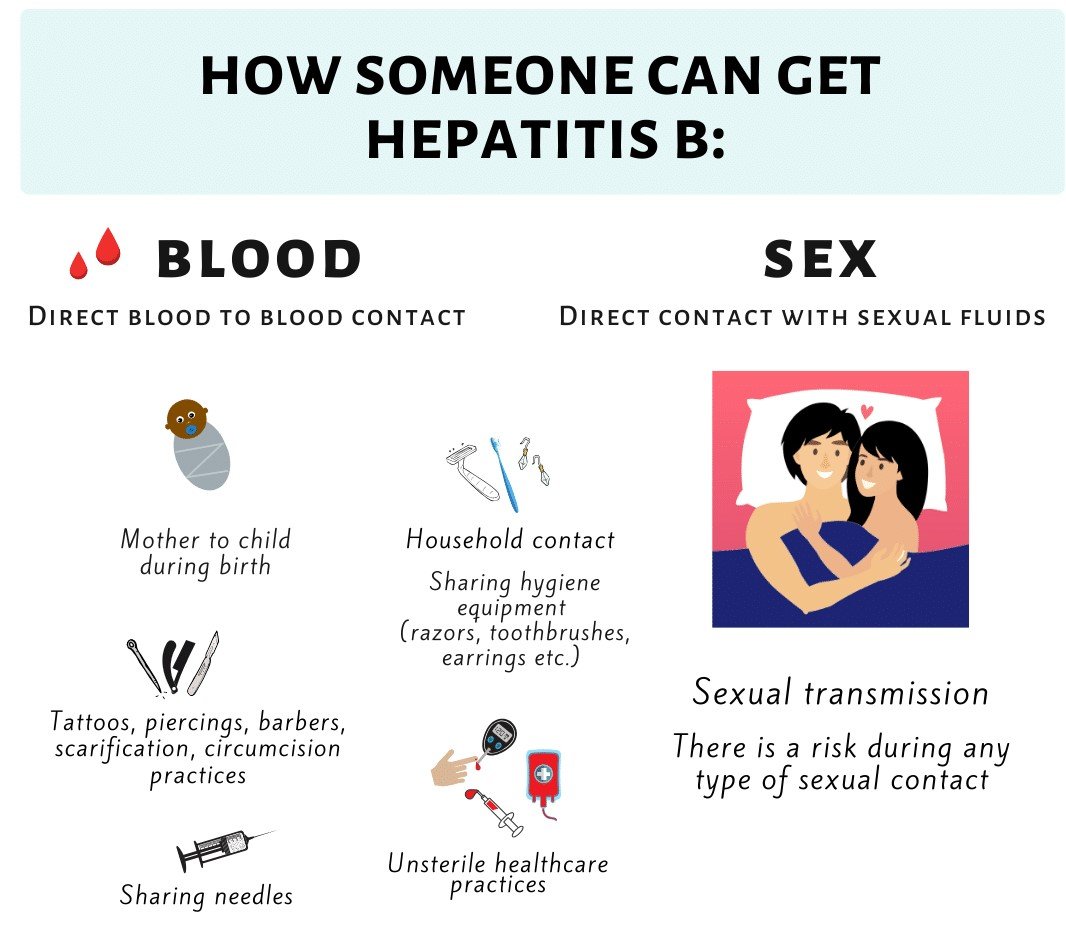
What Causes Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is caused by the hepatitis B virus. It can happen through exposure to infected blood and other bodily fluids in the following situations:
- sharing needles and other injecting drug equipment
- sharing razors, toothbrushes or nail clippers
- tattooing with unsterilised needles and equipment
- close family contact with someone who has hepatitis B
- being born to a mother with hepatitis B
- accidental exposure such as a needle stick injury or being splashed with infected blood or body fluid
- blood transfusion this is now very rare as blood in Australia is screened for hepatitis B
You cannot catch hepatitis B through being coughed or sneezed on by infected people or by consuming contaminated food and drink. You cannot catch the virus from saliva, breast milk or tears.
Who Are Hepatitis B Carriers
Hepatitis B carriers are people who have the hepatitis B virus in their blood, even though they dont feel sick. Between 6% and 10% of those people whove been infected with the virus will become carriers and can infect others without knowing it. There are over 250 million people in the world who are carriers of HBV, with about 10% to 15% of the total located in India. Children are at the highest risk of becoming carriers. About 9 in 10 babies infected at birth become HBV carriers, and about half of children who are infected between birth and age 5 carry the virus. A blood test can tell you if you are a hepatitis B carrier.
Is Hepatitis B Preventable
Chronic hepatitis B infection affects at least 250 million people worldwide, causing over 880,000 deaths annually. It is also the major cause of liver cancer, the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States.
Unlike its cousin hepatitis C, hepatitis B can be prevented with vaccines. If you are accidentally exposed to the virus, there are also drug therapies you can takeâcalled postexposure prophylaxisâto avert the infection.
Also Check: Hepatitis B And C Transmission
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Hepatitis B
Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.
What Are The Treatment Options For Chronic Hep B
For people with acute hep B infection experiencing mild symptoms, doctors often recommend rest, a healthy diet, and fluids to speed up recovery. Severe symptoms may need to be treated in a hospital.
According to the Hepatitis B Foundation, there are currently seven drugs approved by the FDA to treat chronic hep B in the United States. Not everybody needs to take medication, but some people will need to take medication for the rest of their lives.
These drugs fall into one of two categories:
- Antiviral drugs. These drugs help reduce inflammation and liver damage. Theyre usually taken daily in pill form for at least a year.
- Immune modulator drugs. These drugs boost your immune system to help your body fight off the virus. Theyre administered as an injection over 6 to 12 months.
Theres no cure for hep B, acute or chronic, at the moment. However, clinical trials continue to investigate new treatment options.
Don’t Miss: Reactive Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Whats The Prognosis For Hepatitis B
Your doctor will know youâve recovered when you no longer have symptoms and blood tests show:
- Your liver is working normally.
- You have hepatitis B surface antibody.
But some people don’t get rid of the infection. If you have it for more than 6 months, youâre whatâs called a carrier, even if you donât have symptoms. This means you can give the disease to someone else through:
- Unprotected sex
- Contact with your blood or an open sore
- Sharing needles or syringes
Doctors donât know why, but the disease does go away in a small number of carriers. For others, it becomes whatâs known as chronic. That means you have an ongoing liver infection. It can lead to cirrhosis, or hardening of the organ. It scars over and stops working. Some people also get liver cancer.
If youâre a carrier or are infected with hepatitis B, donât donate blood, plasma, body organs, tissue, or sperm. Tell anyone you could infect — whether itâs a sex partner, your doctor, or your dentist — that you have it.
Show Sources
CDC: âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for Health Professionals,â âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for the Public.â
Mayo Clinic: âHepatitis B.â
UpToDate: âHepatitis B virus: Screening and diagnosis.â
CDC.
HealthyPeople.gov: âHepatitis B in Pregnant Women: Screening.â
Annals of Internal Medicine: âScreening for Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Nonpregnant Adolescents and Adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement.â
High Cure Rate For Hepatitis C Prompts Call For Earlier Detection And Testing
Even though it is theoretically possible to contract hep C through contact with blood or blood products, this has become less of a problem. Most people with hepatitis C now receive treatment with an injection rather than a pill, which greatly reduces the chances of them contracting the virus through blood contact. Despite the fact that hep c is currently cured, increased awareness and testing are still required to combat the virus. If treated early, it is possible to prevent long-term health problems.
Read Also: What Is The Definition Of Hepatitis B
How Does The World Health Organization Contribute
When the WHO launched its guidelines for the treatment of hepatitis B in 2015, it was largely based on data from Asian patients. The research team has assessed how the WHO’s treatment criteria perform in Ethiopia. The conclusion is that the WHO guidelines are inappropriate in this part of the world. The consequence of using WHO’s criteria is that treatment will be given to patients with very advanced liver damage. To make a difference, treatment needs to start at an early stage – before patients develop serious complications. The teamâs evaluation of WHO’s guidelines were published in the acclaimed Journal of Hepatology in 2019 , and is a major contribution to the next revision of WHO’s guidelines.
Can Hepatitis B Spread Through Contaminated Water
Breastfeeding, sharing eating utensils, hugging, kissing, holding hands, coughing, and sneezing are all examples of ways to contract hepatitis B. In contrast to some types of hepatitis, the virus is not spread through contaminated food or water.
Hepatitis B: Avoiding Infection
Although these precautions are taken, there is still a chance that you will catch hepatitis B from a person who has the virus. To avoid contracting hepatitis B, avoid contact with people who are infected. If you become infected, protect yourself from spread by washing your hands frequently and avoiding contact with blood and body fluids.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Vaccine Cost Walgreens
Hepatitis B Treatment: What We Know Now And What Remains To Be Researched
Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI
Address Correspondence and Reprint Requests To:
Anna S. Lok, M.D., 1500 East Medical Center Drive, 3912 Taubman Center, SPC 5362, Ann Arbor, MI 48109
Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI
Address Correspondence and Reprint Requests To:
Anna S. Lok, M.D., 1500 East Medical Center Drive, 3912 Taubman Center, SPC 5362, Ann Arbor, MI 48109
Can Hepatitis Be Spread By Sharing Drinks
Kissing, hugging, breastfeeding, sharing eating utensils or drinking glasses, coughing, sneezing, food, water, and casual contact are the only ways to contract Hepatitis B. What are some signs? It is estimated that 30-50% of people aged 5 and up have initial symptoms.
Hepatitis B: Sexual Contact Risks
The chances of being infected with hepatitis B are extremely low, but they are extremely rare.
You May Like: How Does One Contract Hepatitis
Medical Treatment For Hepatitis A B & C
Treatment for hepatitis A, B, or C is based on which type of hepatitis is present in the bloodstream and the severity of the resulting liver damage. Depending on the results of diagnostic tests, our specialists at NYU Langone may recommend antiviral medication to stop the virus from replicating and protect your liver from further damage.
Questions For A Doctor Or Healthcare Professional
A doctor or healthcare professional can give you guidelines on how to best manage your chronic hep B. Together, you can develop a plan that minimizes your chances of complications.
Some questions you may want to ask a doctor include:
- Do I have acute or chronic hep B?
- What do the results of my blood test mean?
- Should I be taking medication?
- What should I do to monitor my disease?
- Are there any clinical trials that Im eligible for?
Also Check: How To Prevent Hepatitis B
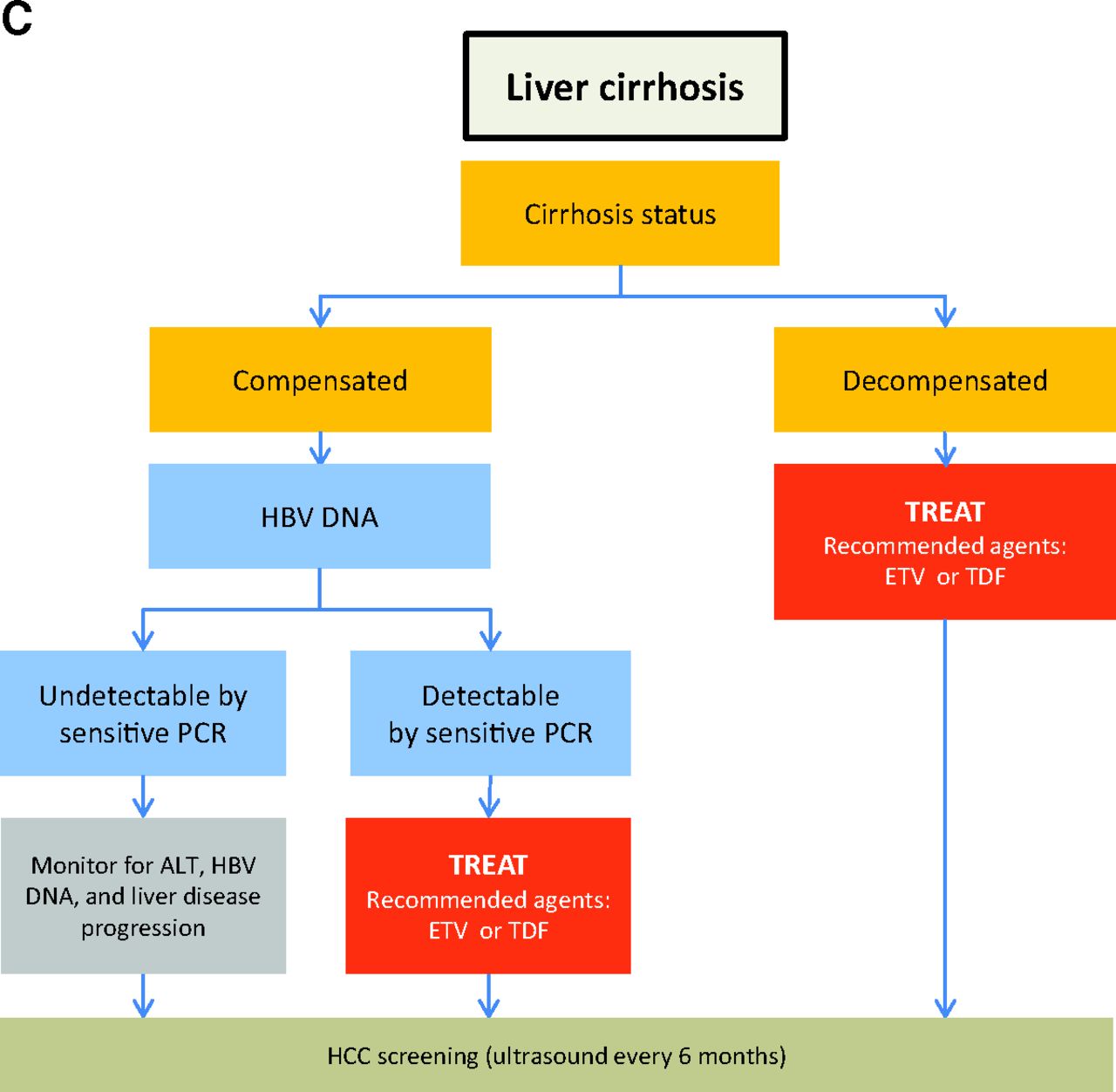
Phases Of Chronic Hbv Infection
The course of chronic HBV infection is characterized by fluctuations in HBV DNA and alanine aminotransferase levels, reflecting variations in the balance between HBV replication and host immune response. Traditionally, three clinical parameters are used to define the four phases of chronic HBV infection .
Phases of chronic HBV infection.3 Traditionally, phases of chronic HBV infection are defined by HBeAg status, serum HBV DNA, and ALT levels. Quantitative HBsAg levels are different in each phase and are generally highest in the immune tolerant phase and lowest in the inactive carrier phase. Although most patients progress from one phase to the next, not all patients go through each phase reversion to an earlier phase can occur. Immune tolerant: HBeAgpositive, high serum HBV DNA but normal ALT levels. Immune clearance/HBeAgpositive chronic hepatitis: HBeAgpositive, high serum HBV DNA, and elevated ALT levels HBeAg seroconversion to antiHBe occurs after varying durations. Inactive carrier: HBeAgnegative, serum HBV DNA low or undetectable. Reactivation/HBeAgnegative chronic hepatitis: HBeAgnegative, elevated levels of HBV DNA and ALT in serum, HBV precore and/or basal core promoter variant often present. Abbreviation: HBsAg, hepatitis B surface antigen.
How You Can Get Hepatitis B
You can get hepatitis B from:
- injecting drugs using shared needles
- being injured by a used needle
- having a tattoo or piercing with unsterilised equipment
- having a blood transfusion in a country that does not check blood for hepatitis B. Blood transfusions in the UK are checked for hepatitis B.
If you’re pregnant and have hepatitis B, you can also pass it onto your baby during pregnancy or birth.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Antibody Screen Result
How Do I Get Hepatitis B Treatment
Usually for adults, hepatitis B goes away on its own and you wont need treatment. Your doctor might tell you to rest, eat well, and get plenty of fluids. You may also get medicines to help with any symptoms you might have but be sure to talk with your doctor or nurse before taking anything.
If you have chronic hepatitis, there are medicines you can take to treat it. Your doctor will tell you about your options and help you get whatever treatment you need.
What Makes Hepatitis B A Serious Illness
Many people with hepatitis B do not know they are infected since they do not look or feel sick, yet they can still spread the virus to others. Acute infection can lead to chronic infection, which can cause cirrhosis , liver cancer, liver failure, and death. During childbirth, a mother may pass hepatitis B to her baby. Newborns infected with hepatitis B have a 90 percent chance of developing chronic hepatitis B. Between 4,000 and 5,000 people die each year in the U.S. from liver disease caused by hepatitis B.
Read Also: Royal Canin Hepatic Dry For Dogs
What Are The Types Of Hepatitis B
There are two types of hepatitis B infection: acute and chronic.
Acute
An acute infection happens at the beginning, when you first get infected with hepatitis B. Many people are able to clear it from their bodies and recover. In fact, this is true of about 4 in 5 adults who are infected.
Chronic
If you are not able to clear the infection within six months or longer, you have chronic hepatitis B. It is chronic hepatitis B that leads to inflammation and the serious, and possibly fatal, illnesses of cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer. Treatment can slow disease progress, reduce the chance of liver cancer and increase your chances of surviving.
What Do I Need To Know About Having Hepatitis B
If you have chronic hepatitis B, getting the right medical care can help you stay healthy. Taking good care of your liver is important. Talk with your doctor before you take any prescription medication, over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, or nutritional supplements to make sure they wont hurt your liver. You should also stay away from alcohol, because drinking can damage your liver.
Recommended Reading: What Happens With Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B During Pregnancy
If a woman with HBV becomes pregnant, they may transmit the virus to their baby. Women should inform the doctor who delivers their baby that they have HBV.
The infant should receive an HBV vaccine and HBIG with 1224 hours of birth. This significantly reduces the risk that they will develop HBV.
The HBV vaccine is safe to receive while pregnant.
People with a high risk of HBV include:
- the infants of mothers with HBV
- the sexual partners of people with HBV
- people who engage in sexual intercourse without contraception and those who have multiple sexual partners
- men who have sex with men
- people who inject illicit drugs
- those who share a household with a person who has a chronic HBV infection
- healthcare and public safety workers who are at risk of occupational exposure to blood or contaminated bodily fluids
- people receiving hemodialysis, which is a type of kidney treatment
- people taking medications that suppress the immune system, such as chemotherapy for cancer
People can prevent HBV infection by:
- wearing appropriate protective equipment when working in healthcare settings or dealing with medical emergencies
- not sharing needles
- following safe sexual practices
- cleaning any blood spills or dried blood with gloved hands using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 10 parts water
A vaccine against HBV has been available since 1982.
People who should receive this vaccine include:
What Treatments Are Available For Chronic Hepatitis B If Medications Dont Work
If you have advanced hepatitis B, you might also become a candidate for a liver transplant. This path does not always result in a cure because the virus continues in your bloodstream after a transplant. To prevent being infected again after your transplant, you may be prescribed hepatitis B immunoglobulin with an antiviral agent.
Recommended Reading: Signs Of Hepatitis C In Men
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
All newborn babies should get vaccinated. You should also get the shot if you:
- Come in contact with infected blood or body fluids of friends or family members
- Use needles to take recreational drugs
- Have sex with more than one person
- Are a health care worker
- Work in a day-care center, school, or jail
Hepatitis C And Pregnancy: What You Need To Know
If you have hepatitis C while pregnant, your baby may be at risk of contracting the disease. There is no cure for hepatitis C, but there are treatments available that can help you manage the disease. It is possible to treat symptoms with counseling and/or medication. If you are infected with hepatitis C, you should be tested and treated as soon as possible to reduce your risk of developing serious health problems.
Also Check: What Are The Signs Of Hepatitis
Who Gets Hepatitis B
One out of 20 people in the United States will get infected with HBV some time during their lives. Anyone can get hepatitis B, but you are at greater risk if you:
- have sex with someone infected with HBV
- have multiple sex partners
- are a man and have sex with men
- have ever been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted disease
- are an injection drug user
- live in the same house with someone who has lifelong HBV infection
- are a health care or public safety worker who has contact with human blood
- are an infant born to an HBV-infected mother
- are a hemodialysis patient
- are an infant/child or immigrant from areas with high rates of infection
What If I Am Pregnant
It’s recommended that all pregnant women have a blood test for hepatitis B in early pregnancy.
If you have hepatitis B and are pregnant, treatments can reduce the risk of transmission of hepatitis B to the baby.
If you have hepatitis B, it is important to protect others from infection.
Important ways to prevent the spread of hepatitis B include:
- vaccination of all your close contacts
- practise safe sex until your sexual contacts are fully vaccinated and immune
- do not donate blood, organs or body tissue
- do not allow your blood to contact another person
- inform healthcare workers
- if your work involves potential for your blood or other body fluid to spread to other people, discuss your situation with your doctor
The hepatitis B vaccine is safe and effective in protecting against hepatitis B infection, providing protection in 95 in 100 vaccinated people.
In Australia, hepatitis B vaccination is part of the standard immunisation schedule for all newborn babies and infants. It’s also recommended for adults who are at high risk of exposure, people who are immunosuppressed or have other liver disease. People in these risk groups should be vaccinated against hepatitis B. Talk to your doctor about your level of risk and whether hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for you.
If you werent vaccinated against hepatitis B as a child, or if youre not sure whether you are vaccinated, talk to your doctor about whether you need a catch-up vaccine.
Read Also: Hiv And Hepatitis Blood Test