What Are The Side Effects Of Prednisone And Azathioprine
Both prednisone and azathioprine have side effects. Because high doses of prednisone are often needed to control autoimmune hepatitis, managing side effects is very important. However, most side effects appear only after a long period of time.
Some possible side effects of prednisone are
- weight gain
- thinning of the bones, a condition called osteoporosis
- thinning of the hair and skin
- diabetes
- cataracts
- glaucoma
Azathioprine can lower white blood cell counts and sometimes causes nausea and poor appetite. Rare side effects are allergic reaction, liver damage, and pancreatitis, which is an inflammation of the pancreas gland with severe stomach pain.
What Is Autoimmune Hepatitis
Hepatitis refers to any of several inflammatory conditions affecting the liver. For example, there are five different types of viral hepatitis: A, B, C, D, and E. Toxins, such as alcohol or various drugs, may also cause hepatitis.
Autoimmune hepatitis is less common, with the National Organization for Rare Disorders reporting about 1 to 2 new cases per 100,000 people each year. Women and people with other autoimmune disorders are much more likely to develop autoimmune hepatitis than men or individuals without any autoimmune conditions.
While the cause is not completely understood by the medical community, suggest that the following three key factors may be at the root of autoimmune hepatitis:
- genetic predisposition
- environmental triggers
- an abnormal response of the bodys natural immune system
As with other autoimmune disorders, autoimmune hepatitis means your bodys immune system attacks healthy cells similar to the way the immune system would try to fight off an infection. In this case, the healthy cells in the liver are under attack. As a result, liver tissue becomes inflamed.
This inflammation can either be acute or chronic. Acute cases dont always require treatment, but in rare, severe situations, it may progress to liver failure.
Incomplete Or Failed Response To Treatment
Some people with autoimmune hepatitis have an incomplete response to treatment, meaning that treatment helps but does not lead to remission. If you have an incomplete response to treatment, you may need to take different medicines to help prevent liver damage.
Some people may fail to respond to treatment, meaning that the inflammation and liver damage of autoimmune hepatitis keep getting worse. Your doctor may recommend additional blood tests and higher doses of medicines. If liver damage leads to complications, you may need treatment for complications.
Also Check: What Is A Hepatic Diet
How Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will look at your health history and give you a physical exam.
Some lab blood tests used to diagnose autoimmune hepatitis include:
- Liver function tests. These check for inflammation or damage to your liver.
- Complete blood count or CBC. Looks at the number and types of cells in your blood.
- Coagulation panel. This test looks at how well the clotting proteins are working.
- Electrolyte panel. Checks to see if you have an electrolyte imbalance.
- Autoimmune antibodies. These are used to see if you have autoimmune hepatitis or another liver disease with similar symptoms.
- Other liver tests. These are done to check for other possible types of liver disease.
You may also have imaging tests such as:
Boost Up Your Glutathione
Glutathione is considered the master anti-oxidant within the body and is produced by every cell in the body where it functions to protect our DNA. Glutathione is our cells security guard that protects the cellular components from outside free radical attack. Longevity scientists now believe that the level of glutathione in our cells has a direct relationship with how long we will live .
Glutathione plays a very important role in establishing immune tolerance . Studies have demonstrated that glutathione enhances the function of T cells and modulates immune activity . In this way, optimizing glutathione levels are extremely important for reducing collateral damage associated with inflammation and autoimmune reactions .
This article goes into more detail on glutathione and its role in reducing inflammation. Hopefully, this article has given you hope and several major action steps to reduce inflammation and heal autoimmune disease.
Don’t Miss: Are There Different Types Of Hepatitis C
S To Heal Autoimmune Disease
With the growth of chronic inflammatory conditions, we need more information on strategies to heal autoimmune disease. We live in a world that puts high demands on our bodies to perform and produce all day long. Many of us sacrifice rest in order to strive towards our goals. We stay up late to work, watch movies, surf the web or spend time with family and friends. When our body gives us signs of fatigue, we hit it with caffeine and energy drinks to keep on going strong.
What is the result? We now have an epidemic of people with adrenal fatigue, hormone imbalances, autoimmunity and chronic inflammatory issues. Autoimmune diseases plague over 250 million people all around the world and many more suffer from a wide-variety of chronic inflammatory conditions . In this article, you will learn strategies you can take to reduce inflammation and heal autoimmune disease.
Is There Anything I Can Do To Help My Liver Heal Itself
No, not directly. However, you can help by giving your liver favourable working conditions, by eating a healthy well-balanced diet, not smoking, and drinking alcohol only in modest amounts or abstaining altogether. Obesity may result in fat deposits in the liver and increases the surgical risk with transplantation. Therefore, if you are overweight, strive for a gradual and sustained weight loss. Introduce exercise into your routine: you can enjoy walking, swimming, gardening, stretching. Please remember that a healthy diet and exercise are important components of any weight-loss regimen.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis A And B Vaccine Schedule For Adults
Autoimmune Hepatitis & Lifestyle Changes
Falk: What kind of changes in lifestyle do patients with autoimmune hepatitis need to do? Or do they need to try to maintain their normal lifestyle as best as possible?
Darling: I think certainly they should try to maintain their normal lifestyle as best as possible. Most patients do feel better once their autoimmune liver disease is under good control. In general, if you decrease inflammation, you usually feel better. We do remind patients that its very important for them to have blood monitoring, so they need to get blood work about every three months, even if theyre on a stable dose of medication. If they already have early cirrhosis, theyre going to need an ultrasound every six months to look for liver cancer which is a risk if you have more advanced scarring in the liver. In general, we want patients to try to maintain a healthy lifestyle and do the things they enjoy doing including working and playing sports.
Falk: What do you tell patients about the fatigue, because that more than likely is the last thing to go away?
Darling: In regards to fatigue, I think I dont necessarily have a great answer for that one. Our patients that are under a lot of stress and are not sleeping, we try to do things that help with getting a good nights rest, especially if theyre stressed about their condition, encouraging some sort of physical activity improves that.
Falk: If you have autoimmune hepatitis, is it okay to drink alcohol?
Who Is At Risk For Autoimmune Hepatitis
About 70 percent of people with autoimmune hepatitis are women, usually between the ages of 15 and 40. Many people with this disease also have other autoimmune diseases, including type 1 diabetes, thyroiditis , ulcerative colitis , vitiligo , or Sjogrens syndrome .
Search for a Clinical Trial
Clinical trials are research studies that test how well new medical approaches work in people. Before an experimental treatment can be tested on human subjects in a clinical trial, it must have shown benefit in laboratory testing or animal research studies. The most promising treatments are then moved into clinical trials, with the goal of identifying new ways to safely and effectively prevent, screen for, diagnose, or treat a disease.
Speak with your doctor about the ongoing progress and results of these trials to get the most up-to-date information on new treatments. Participating in a clinical trial is a great way to contribute to curing, preventing and treating liver disease and its complications.
Start your search here to find clinical trials that need people like you.
Read Also: Can Hepatitis C Turn Into Hiv
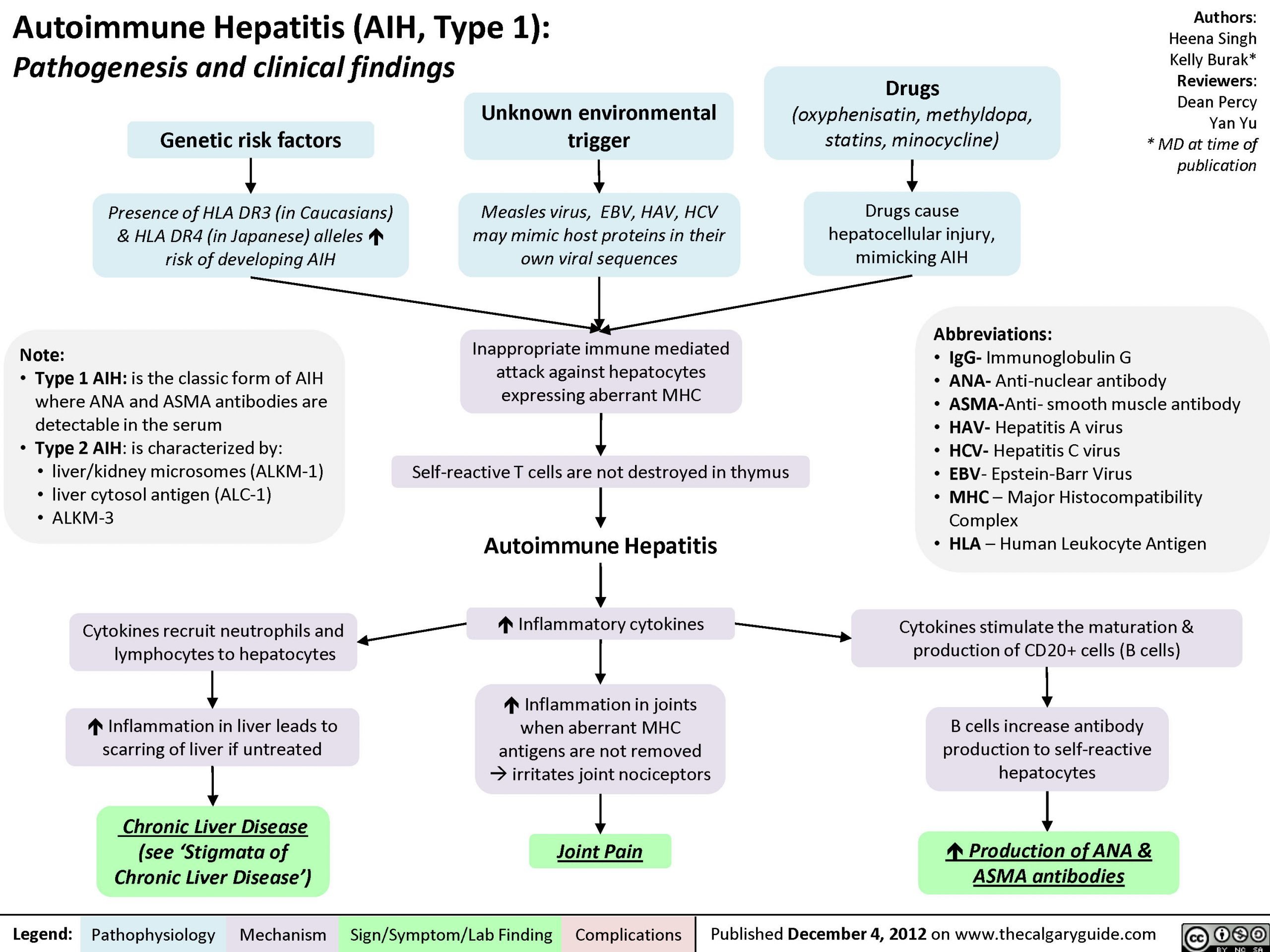
Autoimmune Hepatitis Causes And Risk Factors
Doctors aren’t sure exactly what causes your immune system to turn against your liver. Your genes may have something to do with it, since AIH can run in families.
But genes aren’t the whole story. Something you come into contact with may trigger your genes to set autoimmune hepatitis in motion. This could include:
- Medicines such as statins and hydralazine or antibiotics like nitrofurantoin and minocycline
- Infections such as viral hepatitis, herpes, Epstein-Barr, and measles
Initial Therapy For Adults And Children
The American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases published detailed guidelines regarding the management of autoimmune hepatitis in 2010 and 2019.
The 2010 AASLD guideline delineated absolute and relative indications for immunosuppressive treatment. See Table 2, below.
Table 2. Indications for Treatment of Autoimmune Hepatitis in Adults
|
Absolute Indications |
|
|
Serum aspartate transaminase 10-fold the upper limit of normal |
Symptoms |
|
Serum AST 5-fold the ULN and gamma-globulin level 2-fold the ULN |
Serum AST and/or gamma-globulin less than absolute criteria |
|
Bridging necrosis or multiacinar necrosis on histologic examination |
Note that many patients with cirrhosis and active autoimmune hepatitis respond well to immunosuppression.
The 2010 AASLD guideline also described the following contraindications to treatment :
-
Asymptomatic patients with normal or near normal aspartate aminotransferase and gamma globulin levels
-
Inactive cirrhosis
-
Severe osteoporosis, psychosis, brittle diabetes, or uncontrolled hypertension
-
Severe cytopenias or patients with complete deficiency of thiopurine methyltransferase
In addition, treatment might not be appropriate in patients with decompensated liver disease . Such individuals might be better served by liver transplantation.
The 2010 AASLD guideline also recommended initial treatment strategies for adults as shown in Table 3, below.
Table 3. Treatment Regimens for Adults
Table 4. Treatment Regimens for Children
-
Remission
You May Like: Medicine For Hepatitis C Virus
What Is The Treatment For Autoimmune Hepatitis
Treatment is almost always needed. Early treatment can improve symptoms, reduce the risk of complications, and also greatly improve your outlook . Treatment aims to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system with immunosuppressant medicines:
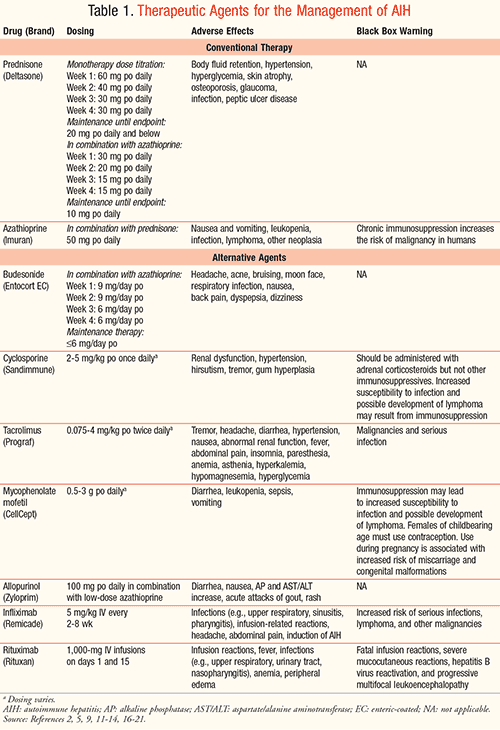
- Steroid medication is the usual first treatment. Steroids are good at reducing inflammation. A high dose is usually needed at first. The dose is then gradually reduced over a few weeks. The aim is to find the lowest dose needed to control the inflammation. The dose needed varies from person to person. See the separate leaflet called Oral Steroids for more detail.
- Azathioprine is an immunosuppressant medicine that works in a different way to steroids. It is usually used in addition to the steroid. A steroid plus azathioprine tends to work better than either alone. Also, the dose of steroid needed is usually less if you also take azathioprine. This means that any side-effects from steroids may be less severe.
Treatment works well in most cases. Usually, the inflammation settles and symptoms improve within a few months of starting treatment. However, it may take a year or more to get the disease totally under control. Azathioprine is usually taken for at least two years.
For some people a liver transplant may be an option – for example:
- In the few people who do not respond to treatment with the medicines mentioned above or
- In people diagnosed in the late stage of the disease with severe ‘scarring’ of the liver or liver failure.
Are Other Treatments For Autoimmune Hepatitis Available
People who do not respond to standard immune therapy or who have severe side effects may benefit from other immunosuppressive agents such as mycophenylate mofetil, cyclosporine, or tacrolimus. People who progress to end-stage liver diseasealso called liver failureor cirrhosis may need a liver transplant. Transplantation has a 1-year survival rate of 90 percent and a 5-year survival rate of 70 to 80 percent.
Read Also: How Long Does Hepatitis B Vaccine Last In The Body
Treatment For Autoimmune Hepatitis
Sometimes, autoimmune hepatitis goes away on its own. But if it does not resolve, prompt treatment is important to limit more serious problems such as cirrhosis and liver failure.
It can take several months of anti-inflammatory medicines before autoimmune hepatitis goes into remission. Some people may require lifelong medication to control the symptoms and prevent a recurrence.
If a liver transplant is necessary, our team works with the Johns Hopkins Comprehensive Transplant Center, known internationally for its innovative procedures and quality patient care.
How Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Treated
The goal of treatment is to stop the bodys attack on itself by suppressing the immune system. This is accomplished with a medicine called prednisone, a type of steroid. Often times, a second drug, azathioprine is also used. Treatment starts with a high dose of prednisone. When symptoms improve, the dosage is lowered and azathioprine may be added. In most cases, autoimmune hepatitis can be controlled but not cured. That is why most patients will need to stay on the medicine for years, and sometimes for life. Unfortunately, long-term use of steroid can cause serious side effects including diabetes, osteoporosis, high blood pressure, glaucoma, weight gain and decreased resistance to infection. Other medications may be needed to control these side effects.
You May Like: How Can A Person Get Hepatitis C
Is There A Cure
Not yet. Since we do not know exactly what causes autoimmune hepatitis, we do not yet have a medical cure for the condition. Steroids and other anti-inflammatory drugs can certainly control the inflammation in the majority of cases. However, in certain patients in whom the inflammation continues or who have not been detected and diagnosed until very late in the course, cirrhosis can occur. Cirrhosis is a condition characterized by increased scar tissue that destroys the normal architecture of the liver.
Even if cirrhosis occurs, patients who have a mild disease without active inflammation generally do well and can live many years or decades without problems. If inflammation continues, the cirrhosis usually worsens, eventually reaching a stage called end-stage liver failure. If this stage has been reached, liver transplantation can be used in some patients to successfully treat the condition.
What Is An Autoimmune Disease
An autoimmune disease causes your immune system to attack healthy cells in your body by mistake. It can affect different parts of your body. There are more than 80 types of autoimmune diseases.
Fortunately, autoimmune hepatitis is treatable with corticosteroids and outcomes are good in patients who seek early treatment.
You May Like: Best Medicine For Hepatitis B
Potential Outcomes Of Immunosuppressant Therapy
The goal of treatment is disease remission. In remission, patients experience the improvement of symptoms, the normalization of abnormal liver chemistries and gamma globulin levels, and the reduction or elimination of inflammatory activity on liver biopsy.
Most patients who embark on a course of immunosuppressant therapy respond well initially. More than 90% of adults started on corticosteroid treatment experience improvements in liver chemistries and gamma globulin levels within 2 weeks.
Remission, if it is to be achieved, typically requires 18-24 months of immunosuppressant therapy. Remission can be achieved in about 65% of patients within 18 months and 80% of patients within 3 years. Once a drug-induced remission is achieved, an attempt should be made to withdraw immunosuppression. However, a sustained remission after total drug withdrawal is seen in 13% of patients at 5 years. Patients who relapse need to restart long-term immunosuppressant therapy in an effort to normalize their biochemical abnormalities and to delay the progression of liver disease. Many such patients are maintained on chronic maintenance therapy with azathioprine.
About 13% of patients experience an incomplete response to treatment, without worsening of their condition. Most incomplete responders need long-term immunosuppression in an attempt to stabilize levels of aspartate transaminase and alanine aminotransferase andby extensionprevent disease progression.
References
S To Reduce Inflammation
Here are the best action steps to get started with on your journey to prevent and/or heal chronic inflammation and autoimmune disease. You should always consult with your physician before stopping or changing medications or taking on new health strategies.
Additionally, you should be working with a functional health practitioner to help guide you through these strategies. This is not an exhaustive list and there are other natural therapeutic strategies that I and functional health practitioners will utilize to help individuals with chronic inflammation and autoimmune disorders.
Recommended Reading: Which Hepatitis Causes Liver Cancer
What Do Researchers Know About What Causes Autoimmune Hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The condition can be triggered by an environmental factor when you are already genetically predisposed to it. The genes HLA DRB1*03 and HLA DRB1*04 have both been linked to an increased risk of autoimmune hepatitis. Autoimmune hepatitis can also be triggered by certain medications or other diseases.
Treatments Available For Autoimmune Hepatitis
Falk: So the reason why you want to see someone earlier in their course, is due to you want to make a correct diagnosis, and if they have an autoimmune disease, youd like to treat them. What kind of treatments are available now?
Darling: We definitely like to see these patients where we can intervene sooner rather than later because it is a reversible process oftentimes, even if the patient has advanced fibrosis or early cirrhosis.
Falk: Scarring of the liver, in other words, and the disease process is no longer inflammation. We use the word cirrhosis or scarring, the liver has scarred like a cut on the skin.
Darling: Right, and when a patient has cirrhosis, we often describe it as bad scarring in the liver. The liver may continue to do its job, but it doesnt have good reserve if it is badly scarred. In regards to treatment for autoimmune hepatitis, steroids or prednisone is a mainstay of treatment. Often it works as a therapeutic and diagnostic therapy.
Falk: In other words, if you get better when youve been given prednisone, you would wonder then if that person had autoimmune hepatitis.
Falk: So there are plenty of options.
Darling: Absolutely. There are a number of different drugs that allow us to lower the dose of prednisone over time. I think this is both a response-driven therapy and a patient-individualized therapy.
Falk: If you start a patient on one of these immunosuppressives, is that a lifelong therapy or can you stop the drug at some point in time?
Don’t Miss: How Can You Catch Hepatitis A