Hepatitis And The Liver
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is important for a range of functions in the body. These include regulating metabolism, making proteins, storing vitamins and iron, removing toxins and producing bile.
If the liver doesnt work properly, it can cause serious illness or sometimes even death.
Hepatitis may be caused by infection, viruses, chemicals, alcohol and other drug use and other factors.
Chronic hepatitis means ongoing inflammation of the liver, irrespective of the underlying cause.
Can You Prevent Hepatitis C Infection
Thereâs no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C. To avoid getting the virus:
- Use a latex condom every time you have sex.
- Don’t share personal items like razors.
- Don’t share needles, syringes, or other equipment when injecting drugs.
- Be careful if you get a tattoo, body piercing, or manicure. The equipment may have someone else’s blood on it.
Find out more on how to prevent hepatitis C.
Can Hepatitis C Be Prevented
There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. But you can help protect yourself from hepatitis C infection by:
- Not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- Wearing gloves if you have to touch another person’s blood or open sores
- Making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools and unopened ink
- Not sharing personal items such toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- Using a latex condom during sex. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Genotype 2 Treatment
Types Of Bloodborne Pathogens:
Human Immunodeficiency Virus :
HIV is a virus that is carried in blood and body fluids and it causes AIDs acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. The virus was first discovered in the early 80s and has since infected millions of people and led to the death of many. The HIV virus attacks the healthy body cells that help in fighting infections also known as CD 4 cells. The virus multiplies as it attacks these cells. As it advances, the body become susceptible to illnesses, a condition referred to as AIDs. An individual is said to have AIDs when their bodys immune system is completely destroyed by the virus. Taking the HIV medicine daily suppresses the virus and prevents its progress. A person is said to have AIDs when their CD 4 count is below 200 CD4 cells per cubic millimeter. The CD 4 cells of a healthy person are between 500 and 1600 per cubic millimeter. In other cases, a person is diagnosed with AIDs when their body is constantly catching opportunistic infections. Without treatment, persons with AIDs have a life expectancy of three years. Taking HIV medicine is life saving even for persons at the late stages of the disease.
Pre-exposure Prophylaxis
Hepatitis:
Hepatitis B :
Hepatitis C :
The symptoms for hepatitis B and C are common, and they include jaundice, fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, diarrhea, abdominal pain, discolored urine and light-colored stool.
Bloodborne pathogens are transmitted during tattooing processes and piercings through:
How Can You Get Hepatitis C

Hepatitis C is a blood-borne disease. The main source of infection is from blood from an infected person.
- Most cases are caused by using contaminated needles or injecting equipment to inject drugs . Even a tiny amount of an infected person’s blood left on a needle is enough to cause spread to others.
- Some people who received blood transfusions or blood prior to 1991 were infected with hepatitis C from some donor blood. Since 1991 all blood and blood products donated in the UK are screened for HCV.
- There is also a risk of contracting hepatitis C from needlestick accidents, or other injuries involving blood spillage from infected people.
- There is a small risk of contracting the virus from sharing toothbrushes, razors and other such items which may be contaminated with infected blood.
- There is even a small risk from inhaling drugs like cocaine, as these can make the inside of your nose bleed. If that happens, tiny spots of blood can fall on to the note you are using and, if that is used by someone else, your blood can travel up their nose and into their bloodstream.
- There is also a small risk from re-used equipment used for tattooing, body piercing, acupuncture, etc.
- There is a small risk that an infected mother can pass on the infection to her baby.
- There is a small risk that an infected person can pass on the virus whilst having sex.
The virus is not passed on during normal social contact, such as holding hands, hugging, or sharing cups or crockery.
You May Like: How To Reverse Hepatic Steatosis
What Laboratory Tests Diagnose Hepatitis C
Laboratory blood tests will be done to evaluate the patient’s liver function and to look for hepatitis C antibodies . If these tests indicate that the person has hepatitis C, a hepatitis C “viral load” test will be done. This looks for genetic material from the hepatitis C virus and measures the quantity of hepatitis C virus that is circulating in the patient’s blood. This is helpful in determining if treatment is appropriate and to monitor the success of the treatment .
Individuals who had hepatitis C in the past and cleared the virus on their own will have a positive HCV antibody test, but there will be no hepatitis C virus genetic material in the blood. If a person is immunosuppressed due to an immunological condition, cancer chemotherapy, immunotherapy or HIV/AIDS, the test results may be different and need to be evaluated accordingly.
Living With Hepatitis C Infection
Many people are living with hepatitis C. If you have hepatitis C, there are several important things that you can do to help yourself and others such as:
- Eat a healthy diet and get plenty of rest.
- To avoid further liver damage:
- Do not drink alcohol.
- Do not take medicine that can cause liver damage .
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis A & B if you are not already immune.
- Do not to pass the infection to anyone else by taking the following precautions, such as:
- Do not share toothbrushes or razors with others.
- Do not to let anyone else come into contact with your blood, urine or feces.
- Use condoms during sexual activity.
- Limit the number of sex partners you have.
- If you use injection drugs, do not share needles or syringes with anyone else.
- It is best to not get tattoos or body piercings.
Although often uncomfortable, you should notify your partner of your hepatitis C prior to having sex. You also must notify all your health care professionals of your infection, so they can take precautions.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatic Cirrhosis Of The Liver
How Is Hepatitis C Spread
Hepatitis C spreads through contact with the blood of someone who has HCV. This contact may be through:
- Sharing drug needles or other drug materials with someone who has HCV. In the United States, this is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.
- Getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on someone who has HCV. This can happen in health care settings.
- Being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not sterilized after being used on someone who has HCV
- Having contact with the blood or open sores of someone who has HCV
- Sharing personal care items that may have come in contact with another person’s blood, such as razors or toothbrushes
- Being born to a mother with HCV
- Having unprotected sex with someone who has HCV
Before 1992, hepatitis C was also commonly spread through blood transfusions and organ transplants. Since then, there has been routine testing of the U.S. blood supply for HCV. It is now very rare for someone to get HCV this way.
How Common Is Hepatitis C
The exact number of people infected is not known. There are around 200,000 people chronically infected with hepatitis C in the UK. Worldwide, over 180 million people are infected. Rates of infection have been relatively stable in recent years, but deaths from hepatitis C have reduced, thought to be because treatment options have become better.
Most cases are in people who inject illegal drugs. It is estimated that up to half of injecting drug users become infected with hepatitis C.
Read Also: How Do You Know You Have Hepatitis B
Does Genotype Predict Response To Daa Therapy Like It Did For Interferon Therapy
Maybe maybe not.
Each of HCVs essential proteins work the same, regardless of genotype. These essential proteins may be structurally different due to small mutations.
Because theyre essential for the HCV life cycle, the structure of their active sites is least likely to change due to random mutation.
Because a proteins active site is relatively consistent between different genotypes, how well a particular DAA agent works is affected by where it binds on the target protein.
The effectiveness of those agents that bind most directly to the proteins active site is least likely to be affected by virus genotype.
All DAA drugs suppress ongoing HCV replication, but they dont eject the virus from its host cell. They also dont remove infected cells. This job is left to the persons immune system.
The variable effectiveness of interferon treatment indicates that the immune system is able to clear cells infected with some genotypes better than those infected by others.
Aside from genotype, there are many variables that can affect the likelihood of treatment success. Some of the more significant ones include:
- amount of HCV virus in your blood
- severity of liver damage before treatment
- the condition of your immune system
- age
- ongoing alcohol misuse
- response to prior therapies
Certain human genes can also predict how well treatment may work. The human gene known as IL28B is one of the strongest predictors of response to PEG/ribavirin treatment in people with HCV genotype 1.
- CC
- CT
- TT
Stages Of Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus affects people in different ways and has several stages:
- Incubation period. This is the time between first exposure to the start of the disease. It can last anywhere from 14 to 80 days, but the average is 45
- Acute hepatitis C. This is a short-term illness that lasts for the first 6 months after the virus enters your body. After that, some people who have it will get rid of, or clear, the virus on their own.
- Chronic hepatitis C. For most people who get hepatitis C — up to 85% — the illness moves into a long-lasting stage . This is called a chronic hepatitis C infection and can lead to serious health problems like liver cancer or cirrhosis.
- Cirrhosis. This disease leads to inflammation that, over time, replaces your healthy liver cells with scar tissue. It usually takes about 20 to 30 years for this to happen, though it can be faster if you drink alcohol or have HIV.
- Liver cancer. Cirrhosis makes liver cancer more likely. Your doctor will make sure you get regular tests because there are usually no symptoms in the early stages.
Learn more about the stages and progression of hepatitis C.
Also Check: What Are The Side Effects Of Hepatitis B
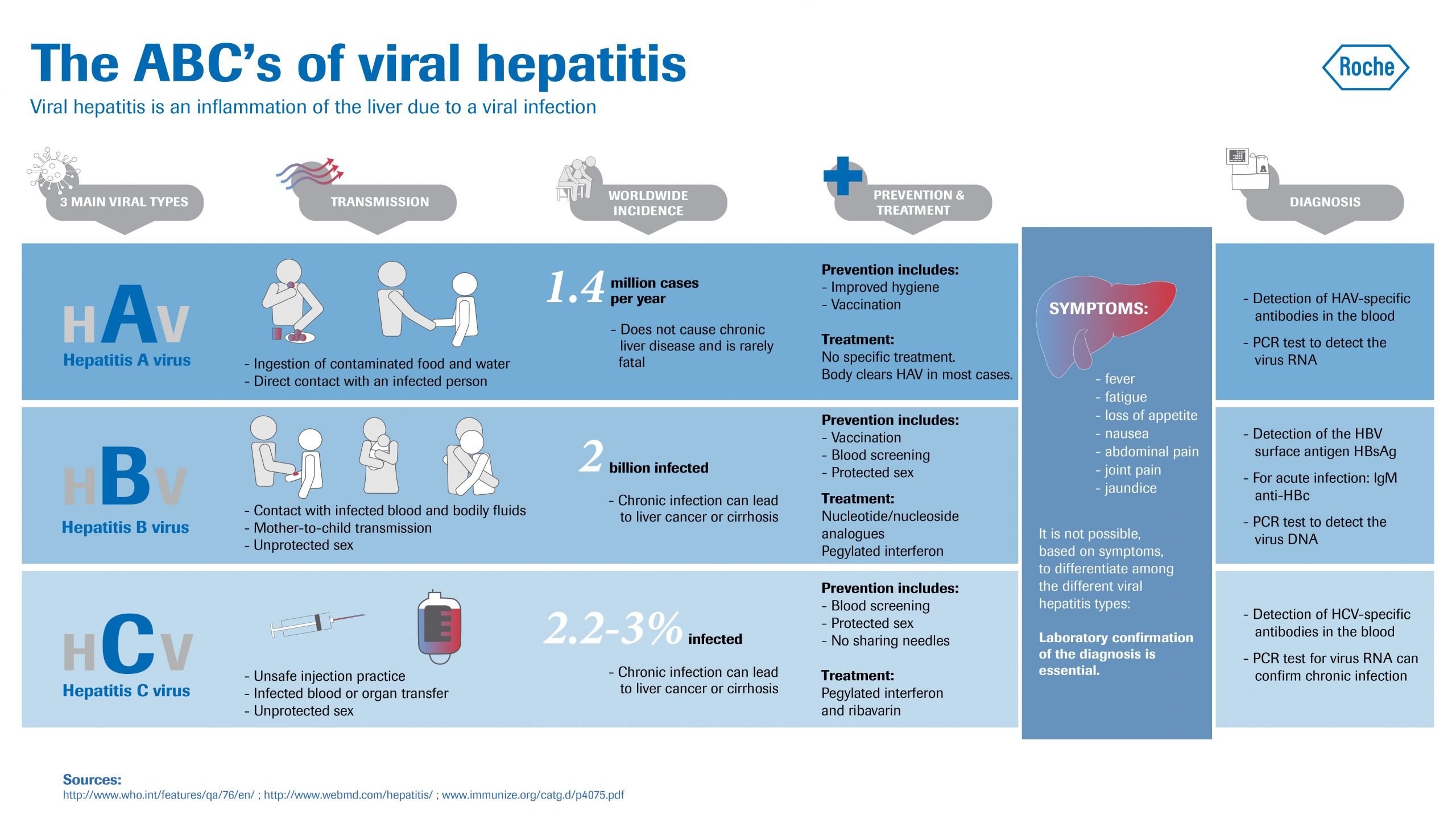
What Are The Symptoms And Signs Of Viral Hepatitis
The period of time between exposure to hepatitis and the onset of the illness is called the incubation period. The incubation period varies depending on the specific hepatitis virus. Hepatitis A virus has an incubation period of about 15 to 45 days Hepatitis B virus from 45 to 160 days, and Hepatitis C virus from about 2 weeks to 6 months.
Many patients infected with HAV, HBV, and HCV have few or no symptoms of illness. For those who do develop symptoms of viral hepatitis, the most common are flu-like symptoms including:
Medical Treatment For Hepatitis A B & C
Treatment for hepatitis A, B, or C is based on which type of hepatitis is present in the bloodstream and the severity of the resulting liver damage. Depending on the results of diagnostic tests, our specialists at NYU Langone may recommend antiviral medication to stop the virus from replicating and protect your liver from further damage.
Also Check: Chronic Hepatitis C Genotype 1a
Which Genotype Do You Have
In the U.S., genotype 1 is the most common. It makes up about 75% of all U.S. cases. The other 25% are mostly genotypes 2 or 3. A few Americans may have genotypes 4, 5, or 6. Genotype 4 is most common in Africa, while genotype 6 is most common in Southeast Asia.
Your doctor can test your blood to find out whether you have hepatitis C and which genotype it is. Most people have one. But some have more than one. Your doctor might call this âmixed infection.â
Youâre more likely to have a mixed infection if you:
- Got blood products like platelets, plasma, red cells, or whole blood many years ago
- Received blood products in a place that doesnât check blood for hep C
- Are on kidney dialysis
- Inject drugs with shared or unsterilized needles
Keep in mind that you might carry the hep C virus even if you donât have symptoms of hepatitis. Once you know your status and genotype, you and your doctor can decide on a treatment plan.
How Do People Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C virus is found in the blood of people with HCV infection. It enters the body through blood-to-blood contact.
Until reliable blood tests for HCV were developed , people usually got hepatitis C from blood products and blood transfusions. Now that blood and blood products are tested for HCV, this is no longer the typical means of infection.
Currently, people usually get hepatitis C by sharing needles for injection drug use. An HCV-infected woman can pass the infection to her baby during birth. It is also possible to get hepatitis C from an infected person through sexual contact, an accidental needlestick with a contaminated needle, or improperly sterilized medical, acupuncture, piercing, or tattooing equipment.
You May Like: Hepatitis C How Is It Contracted
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis C
Treatment for hepatitis C is with antiviral medicines. They can cure the disease in most cases.
If you have acute hepatitis C, your health care provider may wait to see if your infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
If your hepatitis C causes cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Treatments for health problems related to cirrhosis include medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If your hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
How Do You Get Hepatitis A
The main way you get hepatitis A is when you eat or drink something that has the hep A virus in it. A lot of times this happens in a restaurant. If an infected worker there doesn’t wash their hands well after using the bathroom, and then touches food, they could pass the disease to you.
Food or drinks you buy at the supermarket can sometimes cause the disease, too. The ones most likely to get contaminated are:
- Shellfish
- Ice and water
You could catch or spread it if you’re taking care of a baby and you don’t wash your hands after changing their diaper. This can happen, for example, at a day care center.
Another way you can get hep A is when you have sex with someone who has it.
Don’t Miss: Can You Catch Hepatitis C From Kissing
Which Treatment Works For Each Genotype
- All Genotypes: see Epclusa fact sheet
- Genotypes 1 through 4: see Sovaldi, Viekira XR and Technivie, Harvoni, Olysio fact sheets
- Genotypes 1 or 4: see Zepatier fact sheet
- Genotypes 2 or 3: see Sovaldi, Daklinza fact sheets
- Genotype 6: see Harvoni fact sheets
Ribavirin causes birth defects and miscarriage. HCV treatment regimens that include RBV should not be used by pregnant women or by male partners of pregnant women. RBV stays in a persons body for months, so women and their male partners should avoid pregnancy until six months after stopping it .
This fact sheet is current as of December 2016. It is recommended to be read alongside the Adherence and HCV Diagnostics fact sheets. Always check for updated information.
What If I Am Pregnant And I Have Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be passed from a mother to her child during pregnancy and during delivery. Per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , approximately 6 of every 100 infants born to HCV-infected mothers become infected with the virus. The risk is 2-3 times greater when the mother has HIV as well.
You and your doctor should discuss and decide if you should receive treatment for hepatitis C during your pregnancy.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis C And Aids The Same Thing
How Can I Prevent Hepatitis C Infection
Although there is currently no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C, there are things you can do to avoid becoming infected or re-infected and prevent the spread of hepatitis C virus. Hepatitis C is not spread through food or close personal contact such as handshaking, hugging and kissing. Hepatitis C is spread when the blood from an infected person enters the bloodstream of an uninfected person. To avoid this happening:
- do not share needles or other equipment to inject drugs or any other substances
- do not use personal items that may have come in contact with an infected persons blood such as shavers or toothbrushes
- avoid touching blood or open wounds
- avoid sexual practices that might risk blood contact including trauma, during menstruation, or in presence of genital ulcers.