Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis B
Doctors may recommend antiviral medication for people with chronic hepatitis B, which occurs when the virus stays in your body for more than six months.
Antiviral medication prevents the virus from replicating, or creating copies of itself, and may prevent progressive liver damage. Currently available medications can treat hepatitis B with a low risk of serious side effects.
NYU Langone hepatologists and infectious disease specialists prescribe medication when they have determined that without treatment, the hepatitis B virus is very likely to damage the liver over time. People with chronic hepatitis B may need to take antiviral medication for the rest of their lives to prevent liver damage.
There are many different types of antiviral medications available, and your doctor recommends the right type for you based on your symptoms, your overall health, and the results of diagnostic tests. A doctor may take a wait-and-see approach with a person who has a healthy liver and whose blood tests indicate a low viral load, the number of copies of the hepatitis B virus in your bloodstream.
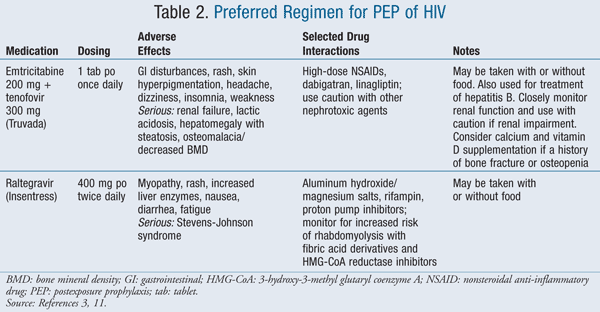
Someone with HIV infection or AIDS may have a weakened immune system and is therefore more likely to develop liver damage. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention strongly recommends that people with HIV infection who are diagnosed with hepatitis B immediately begin treatment with antiviral medication.
Who Should Not Take Tenofovir
Anyone who is allergic to tenofovir shouldn’t take this drug. Also, it’s important to know your HIV status because taking tenofovir can significantly complicate treating HIV. If you have HIV and HBV, do not start therapy for either infection without consulting a physician experienced in treating both infections.
Tenofovir is generally recognized as safe for use during pregnancy, as there is no evidence to suggest it is harmful to a pregnant mother or her fetus.
To Use The Entecavir Oral Solution Follow These Steps:
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis Turn Into Hiv
How Do Doctors Treat The Complications Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
If autoimmune hepatitis leads to cirrhosis, doctors can treat health problems and complications related to cirrhosis with medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If you have cirrhosis, you have a greater chance of developing liver cancer. Your doctor may order an ultrasound or other types of imaging tests to check for liver cancer.
If autoimmune hepatitis causes acute liver failure or cirrhosis with liver cancer or liver failure, you may need a liver transplant.
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infection of your liver. Itâs caused by a virus. There is a vaccine that protects against it. For some people, hepatitis B is mild and lasts a short time. These âacuteâ cases donât always need treatment. But it can become chronic. If that happens, it can cause scarring of the organ, liver failure, and cancer, and it even can be life-threatening.
Itâs spread when people come in contact with the blood, open sores, or body fluids of someone who has the hepatitis B virus.
It’s serious, but if you get the disease as an adult, it shouldnât last a long time. Your body fights it off within a few months, and youâre immune for the rest of your life. That means you can’t get it again. But if you get it at birth, itâ unlikely to go away.
âHepatitisâ means inflammation of the liver. There are other types of hepatitis. Those caused by viruses also include hepatitis A and hepatitis C.
Read Also: How Can You Get Hepatitis A
How Do Doctors Treat Autoimmune Hepatitis
Doctors treat autoimmune hepatitis with medicines that suppress, or decrease the activity of, your immune system, reducing your immune systems attack on your liver. The medicines doctors most often prescribe are corticosteroidsprednisone or prednisolonewith or without another medicine called azathioprine.
Doctors typically start with a relatively high dose of corticosteroids and then gradually lower the dose. Your doctor will try to find the lowest dose that works for you. Your doctor will use blood tests to find out how you are responding to the treatment. A decrease in levels of the liver enzymes alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase shows a response to treatment. ALT and AST falling to normal levels shows a full response. In some cases, a doctor may repeat a liver biopsy to confirm the response to treatment and find out whether the damage has resolved.
Treatment can relieve symptoms and prevent or reverse liver damage in many people with autoimmune hepatitis. Early treatment of autoimmune hepatitis can lower the chances of developing cirrhosis and other complications. A minority of people who have no symptoms or only a mild form of the disease may or may not need medicines.
Do Medicines Used To Treat Autoimmune Hepatitis Have Side Effects
Medicines for autoimmune hepatitis can cause side effects. Your doctor will monitor any side effects and help you manage them while you take these medicines. Your doctor also may adjust the doses or change the medicines you take. You may need to stop taking corticosteroids or azathioprine if you have severe side effects.
Side effects of corticosteroids may include
- changes in how you look, which may include weight gain, a fuller face, acne, or more facial hair
- liver damage
- pancreatitis
Corticosteroids and azathioprine suppress, or decrease the activity of, your immune system, which increases your risk for infections. These medicines can also increase your risk of developing cancers, especially skin cancers.
You May Like: What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B And C
Hepatitis B And Pregnancy
If youâre pregnant, you might pass the virus to your baby at birth. Itâs less likely to happen during your pregnancy.
If your baby gets the virus and isnât treated, they could have long-term liver problems. All newborns with infected mothers should get hepatitis B immune globulin and the vaccine for hepatitis at birth and during their first year of life.
Recommendations For Patients With Hbv/hiv Coinfection
- All patients with chronic HBV should be evaluated to assess the severity of HBV infection . Patients with chronic HBV should also be tested for immunity to hepatitis A virus infection and, if nonimmune, receive the HAV vaccination. In addition, patients with chronic HBV should be advised to abstain from alcohol and counseled on prevention methods that protect against both HBV and HIV transmission.15
- Before ART is initiated, all persons who test positive for hepatitis B surface antigen should be tested for HBV DNA by using a quantitative assay to determine the level of HBV replication , and the test should be repeated every 3 to 6 months to ensure effective HBV suppression. The goal of HBV therapy with nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors is to prevent liver disease complications by sustained suppression of HBV replication.
- Since HBV reactivation has been observed in persons with HBV infection during interferon-free HCV treatment,16,17 persons with HCV/HIV coinfection and active HBV infection should receive ART that includes agents with anti-HBV activity prior to initiating HCV therapy . The diagnosis of HBV reactivation should be considered in persons with current HBV infection who experience elevated liver enzymes during or immediately after HCV therapy.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Viral Load Quantitative
Protease Inhibitor Antiviral Medications
Protease inhibitors work by preventing the spread of infection within the body by stopping viruses from multiplying.
Grazoprevir is a protease inhibitor for hepatitis C genotypes 1 and 4. Its only available in combination with elbasvir and sold as grazoprevir/elbasvir.
The drug combination is sold under the brand name Zepatier.
Emergency Hepatitis B Treatment
See your GP as soon as possible if you think you may have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus.
To help stop you becoming infected, they can give you:
- a dose of the hepatitis B vaccine you’ll also need 2 further doses over the next few months to give you long-term protection
- hepatitis B immunoglobulin a preparation of antibodies that work against the hepatitis B virus and can offer immediate but short-term protection until the vaccine starts to take effect
These are most effective if given within 48 hours after possible exposure to hepatitis B, but you can still have them up to a week after exposure.
Recommended Reading: New Treatment For Hepatitis B
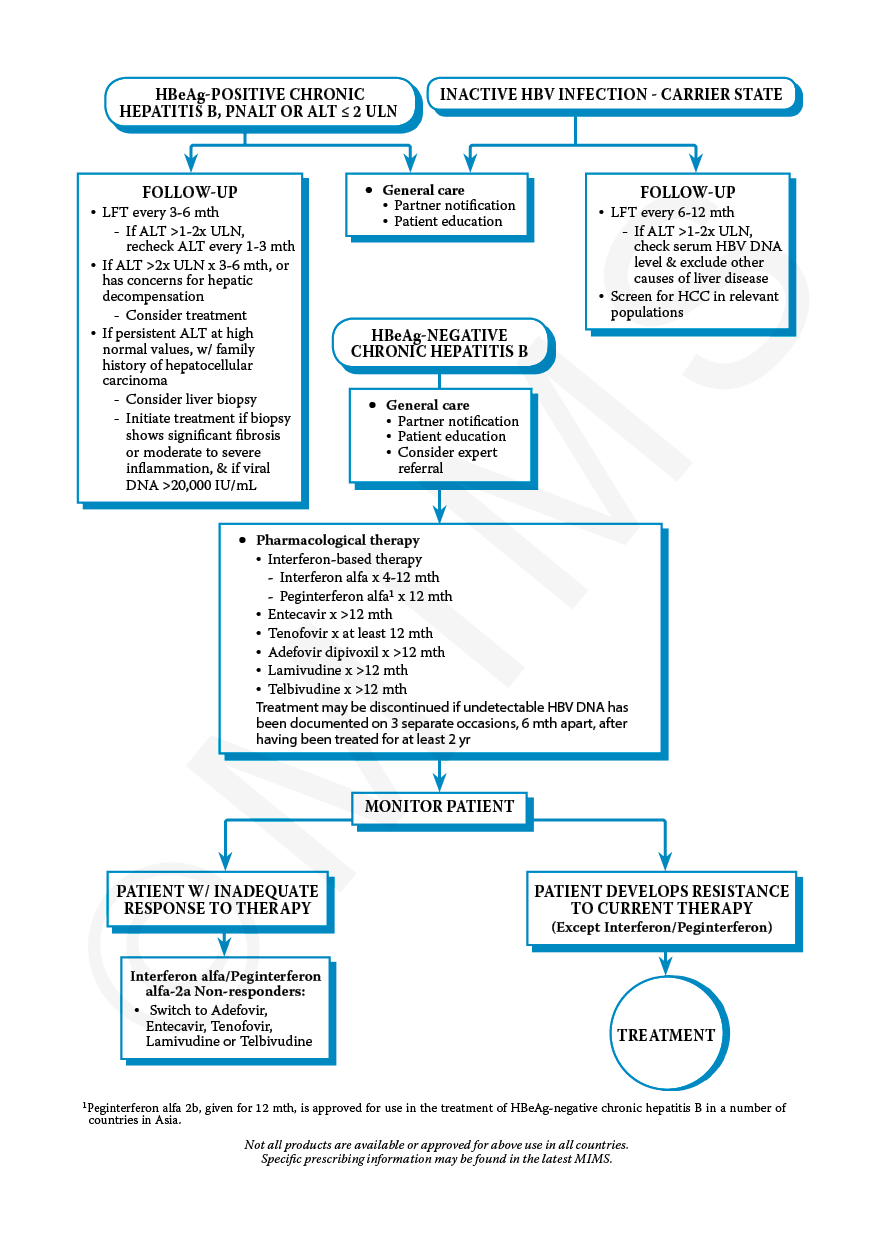
Choosing Oral Antivirals Versus Peginterferon
A primary decision point when choosing an initial therapy in a patient with chronic hepatitis B is whether to use an oral antiviral agent or an interferon-based agent . When an interferon-based agent is used, peginterferon is clearly preferred over interferon, primarily due to more convenient dosing, improved efficacy, and better tolerance. Thus, the following discussion will focus on comparing oral antivirals with peginterferon.
The availability of safe, well-tolerated, highly potent, oral antivirals that have a high genetic barrier to drug resistance, when taken together with the key disadvantages of peginterferon, have made the oral antivirals the preferred treatment for most individuals with chronic HBV infection. The oral antivirals have similar efficacy as peginterferon after 48 to 52 weeks of therapy for persons positive for hepatitis B e Ag and those negative for HBeAg . Long-term follow-up studies have shown that sustained treatment with oral antiviral therapy in persons with chronic HBV markedly reduces the risk of developing cirrhosis, decompensated liver disease, and hepatocellular carcinoma . There are also long-term follow-up studies that suggest interferon or peginterferon treatment for chronic HBV reduces the risk of HCC and improves survival, but these data are less robust than with oral antivirals, especially with peginterferon.
Treating Hepatitis B With Tenofovir
Violetta Shamilova, PharmD, is a board-certified pharmacist and assistant professor at Touro College in New York.
Tenofovir, also called tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, is an antiviral drug for treating chronic hepatitis B in adults and children who are 12 years and older. It is also used, in combination with other drugs, to treat the human immunodeficiency virus or HIV. It’s sold under the brand name Viread by Gilead Sciences, Inc.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Tell If You Have Hepatitis C
Approved Drugs For Adults
There are currently 7 approved drugs in the United States for adults living with chronic hepatitis B infection. These include 5 types of antiviral drugs that are taken as a pill once a day for 1 year or longer. And there are 2 types of immune modulator drugs called interferon that are given as an injection for 6 months to 1 year.
It is important to know that not everyone needs to be treated. A liver specialist should evaluate your health through a physical exam, blood tests, and an imaging study of your liver . Then you can discuss together whether you are a good candidate for treatment since the approved drugs are most effective when there are signs of active liver disease. In addition, talk to your provider about HBV Clinical Trials since there are several new drugs being tested that are available for infected adults.
All adults, however, should be seen regularly by a liver specialist whether they are on treatment or not.
What Is My Risk
Your risk depends of several factors: destination, length of stay, what you do when you are travelling and whether you have direct contact with blood or other body fluids. In certain destinations, your risk may be higher, as some areas have higher numbers of people with chronic hepatitis B in the general population.
The risk increases with certain activities, such as unprotected sex, sharing needles, tattooing and acupuncture.
Aid and health care workers and anyone who receives medical or dental care with unsterilized or contaminated equipment in a country where hepatitis B occurs are also at greater risk.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis B And Hiv The Same Thing
Maoto Suppresses Hepatitis B Virus Production In The Context Of Infection
Next, we examined the relevance of the inhibitory effect of maoto on HBV production in the context of HBV infection using HepG2-NTCP cells and primary human hepatocytes isolated from PXB-mice . HepG2-NTCP cells and PXB-cells were infected with HBV at 2×103 GEq/cell and treated with maoto at the indicated concentrations . The effects of maoto on HBV were evaluated at 6 and 9 days of maoto treatment in HepG2-NTCP cells and at 11 days of the treatment in PXB-cells . As shown in Figure 3B and Figure S1B, maoto did not exhibit any cytotoxicity to HepG2-NTCP cells and PXB-cells. We then found that maoto treatment resulted in dose-dependent suppression of extracellular HBV DNA production without affecting HBeAg expression, similar to the effects in HepAD38.7 cells . The IC50 of the maoto extract to inhibit HBV production was 33.2 ± 5.6 µg/ml in HepG2-NTCP cells and 7.5 ± 5.4 µg/ml in PXB-cells . These results confirmed the relevance of the inhibitory effect of maoto on HBV in the context of HBV infection.
How Is It Transmitted
Hepatitis B is highly infectious, and is spread from one person to another through exposure to infected blood and body fluids . It can be spread through:
- blood transfusions or organ transplantation in countries where blood or blood products have not been properly screened for hepatitis B and other viruses transmitted through blood
- unprotected sex with an infected person
- sharing needles or equipment for injecting drugs
- unsterilized medical/dental equipment and shared/contaminated materials or equipment used for tattooing, body piercing or acupuncture
- sharing toothbrushes or razors
- childbirth
- household contact between family members
Read Also: Hepatitis B What Causes It
Combined Use Of Maoto And Lamivudine Decreases Hepatitis B Virus Replication More Efficiently Than The Individual Use
Considering that maoto suppresses an HBV infection step different from that of lamivudine , i.e., the reverse transcription step, we reasoned that a combined use of 3TC and maoto would suppress HBV replication more effectively. We therefore compared the effect of maoto alone, 3TC alone, and the combined use on HBV replication. Compared to maoto or 3TC alone, the combined use decreased HBV replication more efficiently as expected . These results suggest the potential of maoto for increasing the efficacy of current anti-HBV drugs when used in combination.
Figure 4 Combined use of maoto and 3TC decreases hepatitis B virus replication more efficiently than the individual use. Cells were treated with distilled water , 30 µg/ml maoto alone, 250 nM lamivudine alone, or maoto and 3TC for 9 days with refreshing the medium and drugs every 3 days as shown in Figure 3A. HBV DNA in culture supernatants of the cells after 9 days of maoto treatment was measured by real-time PCR. Values are expressed as the mean percentage + S.E. of three independent experiments. *P< 0.05 **P< 0.01 ****P< 0.001 N.S., no significance.
What Other Information Should I Know
Do not let anyone else take your medication. Ask your pharmacist any questions you have about refilling your prescription.
It is important for you to keep a written list of all of the prescription and nonprescription medicines you are taking, as well as any products such as vitamins, minerals, or other dietary supplements. You should bring this list with you each time you visit a doctor or if you are admitted to a hospital. It is also important information to carry with you in case of emergencies.
Recommended Reading: How Is Hepatitis C Test Done
What Are The Risks For Hepatitis B
Adults with a normal immune system who acquire hepatitis B have approximately a 95% chance of eventually eliminating the virus and making a complete recovery. During the weeks that the body is fighting the virus, the person may be very sick and a few may even die. Patients who do not clear the virus are chronically infected. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that more than one million Americans are chronically infected with HBV.
As discussed above, chronic infection with hepatitis B can cause cirrhosis, liver failure, or even death. Patients with chronic hepatitis B infection are also at risk for liver cancer . Between 15% and 25% of people with chronic infection will die prematurely from complications of hepatitis B. In the United States, chronic HBV infection was listed as the cause of 1,873 deaths in 2013.
Prevention is vital to avoid hepatitis B virus infection. The current recommendation is that all children be vaccinated. Additionally, the following individuals should receive the hepatitis B vaccine:
- adults at high risk ,
- household contacts of infected persons,
- individuals on hemodialysis,
- intravenous drug users, and
- persons with multiple sexual partners.
If a person is exposed to hepatitis B, then hepatitis B immune globulin is sometimes recommended. Hepatitis B immune globulin contains antibodies to the virus which can help reduce the risk of disease.
How do nucleoside/nucleotide analogues work?
Preferred Initial Hbv Therapy
When initiating treatment for chronic HBV, the recommended approach, in most circumstances, is to use a potent oral antiviral that has a high genetic barrier to resistance, typically with long-term administration of the medication. Three oral antivirals are recommended as a preferred option for initial therapy: entecavir, tenofovir alafenamide, or tenofovir DF. For most individuals undergoing treatment for chronic HBV, any one of these three agents can be used. Some special situations, as outlined below, warrant preference of one of these agents over another. Combination therapy, including use of two oral antivirals, one antiviral plus peginterferon, or two antiviral is not recommended for initial treatment.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Viral Rna Genotype Lipa