Drawbacks To Screening For Hepatitis C
A patient’s worry or anxiety while waiting for test results, concerns about insurance coverage of evaluation and treatment, adverse effects of treatment, and complications associated with liver biopsy can limit screening for hepatitis C. However, the accuracy of HCV RNA testing, the availability of medication assistance programs for uninsured patients, and improved treatments with fewer side effects and shorter duration should allay some of the anxiety associated with the screening process.
What Happens During A Hepatitis Panel
A health care professional will take a blood sample from a vein in your arm, using a small needle. After the needle is inserted, a small amount of blood will be collected into a test tube or vial. You may feel a little sting when the needle goes in or out. This usually takes less than five minutes.
You may also be able to use an at-home kit to test for hepatitis. While instructions may vary between brands, your kit will include a device to prick your finger . Youll use this device to collect a drop of blood for testing. For more information on at-home testing for hepatitis, talk to your health care provider.
Harms Of Detection And Early Intervention
The USPSTF found limited evidence on the harms of screening for HCV. Potential harms of screening include anxiety, patient labeling, and feelings of stigmatization.
The USPSTF found adequate evidence on the harms associated with the diagnostic evaluation used to guide treatment decisions . These harms include bleeding, infection, and severe pain in approximately 1% of persons who had a liver biopsy and death in less than 0.2%. However, the use of liver biopsy to guide treatment decisions is declining, and noninvasive tests have sufficient accuracy to diagnose fibrosis and cirrhosis. Thus, the absolute risk to persons who currently receive a diagnosis of HCV infection and subsequent treatment is probably declining.
The USPSTF found adequate evidence that antiviral therapy regimens are associated with a high rate of harms, such as fatigue, headache, influenza-like symptoms, hematologic events, and rash. However, antiviral therapy is given for a defined duration, serious adverse events are uncommon, and adverse events are self-limited and typically resolve after treatment is discontinued. The USPSTF found adequate evidence that these harms of treatment are small.
Recommended Reading: Daa Drugs For Hepatitis C
What To Think About
Under The New Law Do All Patients At
Under the new law, only those patients born between 1945 and 1965 are required to be offered a hepatitis C screening test. Although the new law requires the offer of a test only for those born between 1945 and 1965, CDC recommends hepatitis C testing be offered to all persons at risk for hepatitis C, such as injection drug users, those that received a blood transfusion or organ donation before 1992, persons living with HIV, anyone with abnormal liver tests, health and safety workers who have been exposed to blood on the job and persons on long term dialysis.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Catch Hepatitis B And C
The Cost Of Hepatitis C Treatment
Though all of these drugs have been hailed as major medical breakthroughs, much of the discussion around them has focused on their exorbitant price tags. When sofosbuvir was released, it made news because a 12-week round of treatment came in at a total of $84,000. Harvoni cost even more $94,500 for a 12-week course, though some patients may be cured after only eight weeks, or $63,000. Gileads newer offering, Epclusa, goes for just over $74,000. The gamechanger in the market may be Mavyret, which costs $26,500 for treatment. As of January 2019, there are also of some of these drugs available at lower prices.
There have been many arguments about whether these prices may be justified if they actually do provide a permanent cure. Patients with hep C who are not cured often go on to need far more expensive care. One study estimated that yearly care for an HCV patient without liver damage is approximately $5,800. This goes up to over $27,000 each year for an HCV patient with decompensated cirrhosis of the liver, over $43,000 a year for an HCV patient with liver cancer, and over $93,000 a year for a patient who has had a liver transplant.
In the long term, it is likely cheaper for insurers to pay for treatment with a DAA than to wait and pay for ongoing care once the patient gets sicker. Moreover, curing those who have been diagnosed would also prevent the virus from spreading further, which could in turn keep future costs down.
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a liver disease that results from an HCV infection. The virus passes on through contact with blood from someone who has the infection.
Hepatitis C can be acute or chronic. Chronic hepatitis C can lead to more serious complications, such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
After contracting the infection, nearly 80% of people have no symptoms. Any symptoms typically take
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Virus Dna Quantitative
Enzyme Immunoassays For Detection Of Hepatitis C Antibody
The HCV Ab test is used for initial screening for hepatitis C. The test is performed by enzyme immunoassays , which detect the presence of hepatitis C antibodies in serum. The result of the test is reported as positive or negative. Third-generation EIAs have a sensitivity/specificity of approximately 99%. However, the presence of HCV Ab does not indicate whether the infection is acute, chronic, or resolved. A positive antibody test result should be followed up with an HCV RNA test to confirm that viremia is present.
Other Indications For Measuring Anti
In addition to screening, measuring anti-HCV can be useful in patients with symptoms of chronic liver disease patients who have other viral infections, including chronic fatigue, hepatitis B, HIV, intermittently abnormal ALT, or cirrhosis found on imaging tests or patients undergoing evaluation for organ transplantation.
Don’t Miss: How Is Hepatitis A Spread
Acute Phase Of Hepatitis C
Acute means new or for a short time. This phase lasts for the first six months. When first infected with the virus, most people have no symptoms, or only mild ones. If symptoms do occur, they develop about 7-8 weeks after being exposed to the virus and may include feeling sick , being sick and feeling generally unwell. Some people go yellow. This is due to a build-up of the chemical bilirubin which is made in the liver and spills into the blood in some liver conditions. It is unusual to have severe symptoms.
Following the initial infection:
- In about one quarter to one half of cases the virus is cleared from the body by the immune system within 2-6 months. If this happens then you will have no long-term effects from the virus. Younger people and women are more likely to clear the virus in this way.
- In 5 to 8 out of 10 cases, the virus remains active in the liver and bloodstream long-term. This is called chronic infection with hepatitis C.
We Now Have The Cure For Hepatitis C But Can We Afford It
A long, difficult and costly research effort gives doctors a new cure for hepatitis C
A decades-long search for better treatments for a debilitating liver disorder is finally coming to fruition. Later this year the U.S. Food and Drug Administration is expected to approve a new pill that can cure hepatitis Ca chronic infection that afflicts about 170 million people worldwide and annually kills 350,000 people, including 15,000 in the U.S.faster and with fewer side effects than current remedies.
The breakthrough treatment comes, however, at a price that may place it out of reach for all but the wealthiest or best-insured patients. It will contain two drugs, one of which is already available at $1,000 per dose, or $84,000 for a complete 12-week course. The dual-drug combination will likely cost even more, which has prompted outrage from physicians and patient advocates alike, as well as plans from insurers to ration the combination when it becomes commercially available.
Over the coming months, physicians, patients, economists and insurance companies will no doubt hotly debate whether the treatment is worth the full asking price. There is little doubt, however, that the medications effectiveness is unprecedented and that its development is a significant achievement. A closer look at the complex chemical problems that needed to be solved to develop the cure shows why.
doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0914-32
Also Check: What Do You Do If You Have Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C Is Often Asymptomatic
Offer testing to anyone with a risk factor or clinical indication.
Risk factors:
- shared drug-use equipment, even once
- received personal services , with nonsterile equipment
- exposed to blood during sexual activity
- received blood, blood products, or organ transplant before 1992
- received medical care where non-sterile equipment may have been used
- born, travelled, or lived in a region where hepatitis C is common
- born to a mother with hepatitis C
- diagnosis of HIV or hepatitis B
- clinical clues or symptoms of liver disease
- occupational exposure
Who Else Should Get Tested
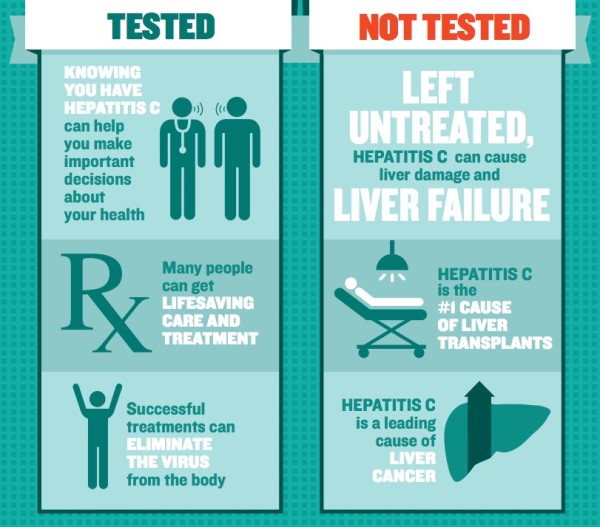
Anyone who has hepatitis C symptoms should speak with a healthcare professional.
The HCV transmits via contact with blood, and it can pass from person to person through:
- sexual intercourse with someone who has the infection
- sharing personal items that may have come into contact with blood, such as razors
- tattooing in conditions that do not meet health and safety standards
- needle prick accidents in healthcare settings
Anyone who may have come into contact with the HCV should speak with a healthcare professional about having a test.
You May Like: Where Do I Get Hepatitis A Vaccine
Cdc Recommendations For Hepatitis C Screening Among Adults In The United States
- Universal hepatitis C screening:
- Hepatitis C screening at least once in a lifetime for all adults aged 18 years and older, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is less than 0.1%*
- Hepatitis C screening for all pregnant women during each pregnancy, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is less than 0.1%*
- Any person who requests hepatitis C testing should receive it, regardless of disclosure of risk, because many persons may be reluctant to disclose stigmatizing risks
Cdc Recommendations For Hcv Screening
On April 10, 2020, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention issued new recommendations for hepatitis C screening among adults in the United States . This new guidance augments prior CDC guidance on HCV screening with two new major recommendations: all adults aged 18 years and older should have HCV screening at least once in their lifetime, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is less than 0.1%, and HCV screening should be performed for all pregnant persons during each pregnancy, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is less than 0.1%. The CDC continues to recommend screening persons for HCV regardless of age if risk factors for acquiring HCV are present, with repeat periodic screening in persons who have ongoing risk for acquiring HCV. These new CDC HCV screening recommendations expand prior guidance that recommended routine HCV screening for all persons born between 1945-1965.
Don’t Miss: How To Check For Hepatitis
Why Test All Your Adult Patients
- New cases of hepatitis C are on the rise, particularly among reproductive age adults. Rates of new HCV infections increased by more than 60% from 2015 to 2019. And in 2019, more than 63% of HCV infections occurred among adults 20-39 years of age.
- Your patients arent aware of their risk. Almost half of people with hepatitis C are unaware of their infection. Testing is the first step to accessing curative treatment. Without treatment, approximately 15-20% of adults with chronic HCV infection will develop progressive liver fibrosis and cirrhosis.
- Hepatitis C can be cured. Over 90 percent of people infected with HCV can be cured with 8-12 weeks of oral therapy. Treatment of hepatitis C is associated with reductions in mortality among persons with chronic hepatitis C.
Where Can A Person Get Tested
A person can have an HCV antibody test at a primary care physicians office, a clinic, or a local laboratory.
Costs vary, depending on whether a person has insurance and which pharmacy they use. Some pharmaceutical companies cover copayments and provide the treatment for free.
Medicare covers testing costs for people:
- with a high risk of hepatitis C
- who had blood infusions before 1992
- who were born between 1945 and 1965
The Department of Veterans Affairs covers most of the associated costs for veterans enrolled in its healthcare program.
The healthcare professional who ordered the test should explain the results in detail, as well as the next steps, if treatment is necessary.
The following table describes several outcomes of an HCV test, according to information from the
| The person once had or currently has the infection. | The person needs a second test to confirm whether they have a current infection. | |
| HCV antibody reactive, HCV RNA detected | This means that the person has the infection. | The doctor will provide counseling and treatment. |
| HCV antibody reactive, HCV RNA undetected | The person does not have the infection. | Usually, there is no need for further action, but the doctor may recommend the second test. |
The second test mentioned above is called a nucleic acid test. It detects a current infection by checking whether there is any of the viruss RNA in the blood.
Don’t Miss: How Did I Get Hepatitis B
Articles On Hepatitis C
If you’ve just been diagnosed with hepatitis C, you may wonder how you got it and worry about passing on the virus to a loved one. If you’ve had the disease for a long time without knowing it, you could dwell on every little incident in the past where you might have accidentally exposed a family member to the disease.
It’s important to remember that hepatitis C isn’t easy to catch. If you take a few precautions, it’s almost impossible to pass on the disease to someone else.
Complications Of Hepatitis C
If the infection is left untreated for many years, some people with hepatitis C will develop scarring of the liver .
Over time, this can cause the liver to stop working properly.
In severe cases, life-threatening problems, such as liver failure, where the liver loses most or all of its functions, or liver cancer, can eventually develop.
Treating hepatitis C as early as possible can help reduce the risk of these problems happening.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis And How Do You Get It
Take An Active Approach To Testing
Testing for HCV: the diagnosis of HCV infection requires 2 tests.
Summary Of Recommendation And Evidence

The USPSTF recommends screening for hepatitis C virus infection in adults aged 18 to 79 years . B recommendation.
See Table 1 for a more detailed summary of the recommendation for clinicians.
Screening for HCV Infection in Adolescents and Adults: Clinical Summary of the USPSTF Recommendation
What does the USPSTF recommend?
Note: For a summary of the evidence systematically reviewed in making this recommendation, the full recommendation statement, and supporting documents, go to .
HCV = hepatitis C virus USPSTF = U.S. Preventive Services Task Force.
Screening for HCV Infection in Adolescents and Adults: Clinical Summary of the USPSTF Recommendation
What does the USPSTF recommend?
Note: For a summary of the evidence systematically reviewed in making this recommendation, the full recommendation statement, and supporting documents, go to .
HCV = hepatitis C virus USPSTF = U.S. Preventive Services Task Force.
Also Check: What Does The Hepatitis B Vaccine Prevent
Home Screening Tests For Hepatitis C
At-home screening tests provide privacy if you prefer not to go to a doctor or clinic for testing. These tests typically look for antibodies to hepatitis C, but they may not always test for active viral infection. Make sure you know what type of test youll be taking before you buy.
Many at-home tests have close to or the same reliability as blood tests received by a medical professional.
If youve recently been exposed to hepatitis C, wait several weeks before testing at home.
When Should I Test For Hep C
Many people dont feel sick when they first get hep C. If you are exposed to hep C, your body will try and fight the virus for 6 months. 1 in 4 people will clear hep C in those first 6 months.
People who dont clear their hep C will have whats called chronic hep C. You can get tested for hep C straight after you think you have been exposed, but you will need to go back for another test after 12 weeks and possibly again at 6 months.
You might be able to access testing and healthcare via your computer or phone.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis C Spread Through Saliva