Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule: Standard Accelerated And Combination
Getting poked with a needle is never fun, but its an extremely important part of protecting yourself and others from infectious diseases! The hepatitis B vaccine is known to be one of the most effective vaccines in the world and very safe too! As a blood-borne disease that typically has no symptoms, hepatitis B can easily be spread by accident simply because people are unaware that they have it! Modes of transmission include mother-to-child during birth, unprotected sex, injection drug use, unsafe medical procedures, and the sharing of personal items that may contain blood remnants, such as body jewelry, razors, and toothbrushes. Although certain precautions can be taken to prevent transmission, the only way to completely protect yourself is to get vaccinated. Once you have been vaccinated, you are protected for life!
There are a few options for receiving the hepatitis B vaccination. In most countries, the vaccine is available through a doctors office or a health clinic. The most common option is the standard three-dose vaccine. This consists of three separate doses of the vaccine given through intramuscular injections. In order for the vaccine to be effective, there must be a minimum amount of time between doses. If the minimum amount of time is not followed, the vaccine will not provide full, long term protection from the infection.
3 Dose Schedule:
2-Dose Schedule :
- 1st shot At any given time
- 2nd shot At least 28 days after the first shot.
Screen For Contraindications And Precautions
- Do not administer Heplisav-B to individuals with a history of severe allergic reaction after a previous dose of any hepatitis B vaccine or to any component of Heplisav-B, including yeast.
- Consult the package insert for precautions, warnings, and contraindications and Hepatitis B Vaccine Safety for additional information and possible side effects.
Emergency Hepatitis B Vaccination
If you have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus and have not been vaccinated before, you should get immediate medical advice, as you may benefit from having the hepatitis B vaccine.
In some situations, you may also need to have an injection of antibodies, called specific hepatitis B immunoglobulin , along with the hepatitis B vaccine.
HBIG should ideally be given within 48 hours, but you can still have it up to a week after exposure.
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis B Virus
People With Other Medical Conditions
People with chronic liver disease and/or hepatitis C are recommended to receive hepatitis B vaccine if they are not immune
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for people with chronic liver disease and/or hepatitis C who are seronegative for hepatitis B. This is because they may have an increased risk of hepatitis B and/or severe liver disease after hepatitis B.11
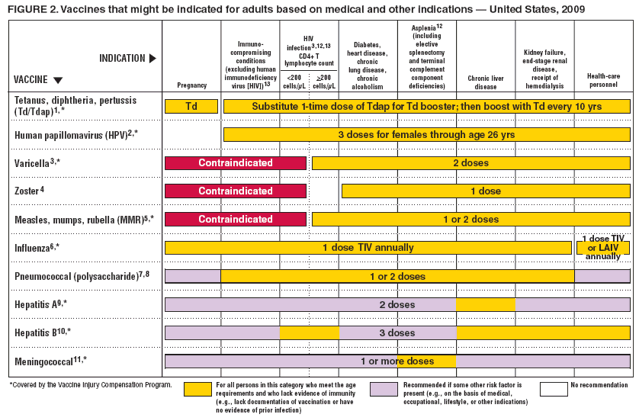
Adult-formulation hepatitis B vaccine should be given in a 3-dose schedule. See Table. Monovalent hepatitis B vaccines for adolescents and adults in Vaccines, dosage and administration.
Levels of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen should be checked after the vaccination course. See Serological testing after hepatitis B vaccination.
The combination hepatitis A-hepatitis B vaccine may be appropriate for people with chronic liver disease and/or hepatitis C if they are not immune to either disease. This is because they have an increased risk of hepatitis B and/or severe liver disease after hepatitis A and B. This is usually given in 3 doses using Twinrix . See Table. Combination hepatitis A-hepatitis B vaccines in Vaccines, dosage and administration.
Low-birthweight and preterm newborns do not respond as well to hepatitis Bcontaining vaccines as full-term infants.12-14
Hepatitis B Vaccine On The Nhs
A hepatitis B-containing vaccine is provided for all babies born in the UK on or after 1 August 2017. This is given as part of the 6-in-1 vaccine.
Hospitals, GP surgeries and sexual health or GUM clinics usually provide the hepatitis B vaccination free of charge for anyone at risk of infection.
GPs are not obliged to provide the hepatitis B vaccine on the NHS if you’re not thought to be at risk.
GPs may charge for the hepatitis B vaccine if you want it as a travel vaccine, or they may refer you to a travel clinic for a private vaccination. The current cost of the vaccine is around £50 a dose.
Read Also: Liver Disease Caused By Hepatitis C
Concurrent Administration Of Vaccines
HB-containing vaccines may be administered concomitantly with other vaccines or with HBIg. Different injection sites and separate needles and syringes must be used for concurrent parenteral injections.
Refer to Timing of Vaccine Administration in Part 1 for additional information about concurrent administration of vaccines.
Serological Testing After Hepatitis B Vaccination
It is recommended that levels of hepatitis B surface antigen in infants born to mothers with chronic hepatitis B are measured 312 months after they complete the infant vaccine course. Do not test the infant before 9 months of age, to avoid detecting anti-HBs
Post-vaccination serological testing is recommended 48 weeks after completing the vaccine course for:
- people at significant occupational risk, such as healthcare workers whose work involves frequent exposure to human tissue, blood or body fluids
- people at risk of severe or complicated hepatitis B, such as people who are immunocompromised and people with pre-existing liver disease not related to hepatitis B
- people who may respond poorly to hepatitis B vaccination, such as haemodialysis patients and people with bleeding disorders who received the vaccine subcutaneously
- close contacts of people who are infected with hepatitis B virus, including sexual partners, household contacts and household-like contacts22
If serological testing 48 weeks after the vaccine course shows levels of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen of < 10 mIU per mL, check the person for acute or chronic hepatitis B virus infection by testing for serological markers, including antibodies to anti-HBs and hepatitis B core antigen.
After the booster dose, check for anti-HBs
A non-responder is a person who:
Recommended Reading: Can You Spread Hepatitis C
New Pneumococcal Vaccine Recommendations For Adults Aged 65 Years Old
PCV13. PCV13 vaccination is no longer routinely recommended for all adults aged 65 years. Instead, shared clinical decision-making for PCV13 use is recommended for persons aged 65 years who do not have an immunocompromising condition, CSF leak, or cochlear implant and who have not previously received PCV13 .
CDC guidance for shared clinical decision-making. When patients and vaccine providers engage in shared clinical decision-making for PCV13 use to determine whether PCV13 is right for the specific individual aged 65 years, considerations may include the individual patients risk for exposure to PCV13 serotypes and the risk for pneumococcal disease for that person as a result of underlying medical conditions .
If a decision to administer PCV13 is made, it should be administered before PPSV23 . The recommended intervals between pneumococcal vaccines remain unchanged for adults without an immunocompromising condition, CSF leak, or cochlear implant . PCV13 and PPSV23 should not be coadministered.
ACIP continues to recommend PCV13 in series with PPSV23 for adults aged 19 years with immunocompromising conditions, CSF leaks, or cochlear implants .
People With Chronic Hepatitis B
The vaccine does not affect people with chronic hepatitis B virus infection there are no therapeutic benefits or associated adverse events. The vaccine is also safe in people who are already immune to hepatitis B through past natural infection, but it offers no additional benefit.
Hepatitis B is an infection caused by hepatitis B virus. It affects the liver.
Also Check: Medicine To Treat Hepatitis C
Babies And Children Can Develop Chronic Hbv
You may be wondering why the recommendations for the HBV vaccine start on the first day of life.
Adults who contract HBV will likely not experience long-term complications from hepatitis B. But the same is not the case for babies. As many as of babies who contract an HBV infection at birth from their mothers become chronically infected with HBV.
Children between the ages of 1 and 5 who get an HBV infection have a 25 percent of people who become chronically infected during childhood will develop liver cancer or cirrhosis. Thats why pediatricians want children to have immunity from HBV from the earliest possible age. Many babies and children exposed to HBV receive post-exposure prophylaxis, which decreases chance of infection.
If youre pregnant, youll most likely have a blood test to see if youre positive for hepatitis B. This allows doctors to find out if theres a chance that you could pass on the virus. These tests are highly sensitive and have a good accuracy rate, but they arent perfect. Additionally, a pregnant person may become infected between the time of the test and giving birth. The first dose of the vaccine given at birth lowers the risk of a newborn baby contracting hepatitis B.
Accelerated Us Children And Adult Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
In some instances, it may be necessary to vaccinate within a short period of time to ensure protection before travel. There are accelerated schedules to provide the highest level of protection over a short period of time. Individuals who need an accelerated schedule must have a booster dose at 1 year to ensure long-term protection. Note that the 2-dose Heplisav-B vaccine will also ensure maximum protection over a 1-month period without the need for a booster dose at 1 year.
4-Dose Vaccine Series for Children and Adults
Engerix-B is a 3-dose vaccine that can be given on an accelerated, four-dose schedule, with 3 shots administered within 2 months, and a booster dose at 1 year to provide maximum long-term protection.
4-Dose Combination Hepatitis A and B Vaccine Series
Twinrix is a 4-dose vaccine that can be given on an accelerated schedule to provide protection against hepatitis A and B. Three doses are administered within 1 month, followed by a booster shot at 1 year. This is a common choice of vaccine for those travelling on short-notice outside the U.S. It is important to complete the booster dose at 1 year, to ensure long-term protection.
2-Dose Vaccine Series
Also Check: Colloidal Silver And Hepatitis C
Interchangeability Of Hepatitis B Vaccines
The Engerix-B and H-B-Vax II vaccines are manufactured by different processes, and the hepatitis B surface antigen content of an equivalent dose of these vaccines is different. Switching vaccine brands is not recommended.
If the brand of vaccine used for previous doses is not known, use another age-appropriate equivalent dose brand. See:
For example, a study in healthy neonates showed comparable high levels of immunogenicity between 2 different mixed regimens that used 2 monovalent hepatitis B vaccines from different manufacturers.33
Indications Dosing And Potential Side Effects

The Twinrix vaccine combines the hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccine into one syringe.
Learn more about this vaccine, including who should be vaccinated, dosing, and potential side effects based on information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and US Food and Drug Administration.
Recommended Reading: How Did You Get Hepatitis B
People Whose Lifestyle Increases Their Risk Of Acquiring Hepatitis A
Serological testing for hepatitis A immunity is not routinely recommended, but may be appropriate for some people
Serological testing for immunity to hepatitis A is not routinely recommended before receiving hepatitis A vaccine.
It is also inappropriate to test people who cannot remember whether they have ever had a hepatitis A vaccine. If a person is recommended for vaccination and has no records of previous vaccination, they should receive a vaccine.
However, certain groups of people should be screened for natural immunity to hepatitis A to avoid unnecessary vaccination:
- people who were born before 1950
- people who spent their early childhood in hepatitis Aendemic areas
- people with an unexplained previous episode of hepatitis or jaundice
People with unexplained jaundice should also be tested for other causes of hepatitis, including hepatitis B.
These people may need to be tested for total hepatitis A antibodies or IgG antibodies against hepatitis A virus. A positive test indicates immunity to hepatitis A. People who are immune do not need hepatitis A vaccination.
To better interpret serological testing results, discuss them with the laboratory that performed the test. Ensure that the laboratory receives the relevant clinical information.
See also Vaccine information and Variations from product information for more details.
International Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
The hepatitis B vaccine is an injection that is generally given in the arm and as a three-dose series. The World Health Organization recommends a 0, 1, and 6-month vaccine schedule, though schedules may vary based on a countrys national immunization program. Completing the hepatitis B vaccine series, preferably beginning at birth, will ensure protection against hepatitis B, hepatitis delta and lower the lifetime risk of liver cancer. Greater than 90% of babies and up to 50% of young children who are not vaccinated and are infected with hepatitis B will have lifelong infection, which makes the birth dose essential to their protection. Please note that the vaccine brand name, manufacturer and associated schedules for adults, children and infants may be unique to different countries, though there is a list of WHO prequalified vaccines.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Infants
The World Health Organization recommends all infants receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth and to complete the vaccine series with additional shots at 1 month and 6 months of age. Beginning the hepatitis B vaccine at birth will ensure protection against hepatitis B for life.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Children and Adults
4-Dose Combination Vaccine Series for Infants
Additional Resource Links:
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Virus Antibody Reactive
Hepatitis B Vaccination In Pregnancy
Hepatitis B infection in pregnant women may result in severe disease for the mother and chronic infection for the baby.
This is why the hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for pregnant women who are in a high-risk category.
There’s no evidence of any risk from vaccinating pregnant or breastfeeding women against hepatitis B.
And, as it’s an inactivated vaccine, the risk to the unborn baby is likely to be negligible .
Does Hepatitis B Go Away
In most cases, hepatitis B goes away on its own. You can relieve your symptoms at home by resting, eating healthy foods, drinking plenty of water, and avoiding alcohol and drugs. Also, find out from your doctor what medicines and herbal products to avoid, because some can make liver damage caused by hepatitis B worse.
Also Check: What Hepatitis Is Sexually Transmitted
Interchangeability And Dosing Schedule
- 2-dose HepB vaccine series only applies when both doses consist of HepB-CpG, administered at least 4 weeks apart.
- Series consisting of a combination of 1 dose of HepB-CpG and a vaccine from a different manufacturer should do the following:
- Adhere to the 3-dose schedule minimum intervals of 4 weeks between dose 1 and 2, 8 weeks between dose 2 and 3, and 16 weeks between dose 1 and 3. However, if HepB-CpG is substituted for dose 2 of HepB-alum, a provider has the option of administering the next dose of HepB-CpG a minimum of 4 weeks from the previous dose for a complete series.
Burden Of Chronic Hepatitis B In Australia
Chronic infection and its sequelae, including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, contribute to most of the hepatitis B disease burden in Australia. The burden from chronic disease has been increasing with the increasing number of immigrants from regions of high hepatitis B prevalence.62
First-generation immigrants from countries of high hepatitis B endemicity usually retain the prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection of the country they are from. Migrants born in Asian, Pacific islands, North African, Middle Eastern and Mediterranean countries have a significantly higher prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection than the Australian-born population.62
Other population groups with higher prevalence of hepatitis B virus infection include:63,64
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people
- people with HIV
- people who injected drugs between 1980 and 1990
- household contacts of someone diagnosed with hepatitis between 1980 and 1990
Notification of chronic hepatitis B virus infection depends on hepatitis B testing and reporting. Many people with chronic hepatitis B virus infection remain undiagnosed. Mathematical modelling suggests that, in Australia in 2015:64
- about 230,000 people were living with hepatitis B virus infection
- about 419 deaths were due to hepatitis B virus infection
Don’t Miss: What Are The Signs Of Hepatitis C
Persons With Inadequate Immunization Records
Evidence of long term protection against HB has only been demonstrated in individuals who have been vaccinated according to a recommended immunization schedule. Independent of their anti-HBs titres, children and adults lacking adequate documentation of immunization should be considered susceptible and started on an immunization schedule appropriate for their age and risk factors. Refer to Immunization of Persons with Inadequate Immunization Records in Part 3 for additional information.
Advisory Committee On Immunization Practices Recommendations

In February 2018, ACIP approved recommendations for Heplisav-B vaccine as an option for previously unvaccinated or incompletely vaccinated persons, including:
- Adults 18 years of age and older who have a specific risk, or lack a risk factor but want protection. See ACIP Recommended Immunization Schedule for Adults for risk factors.
Don’t Miss: Chronic Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma Hcc