Hepatitis C Antibody With Reflex To Pcr
- Hepatitis C Ab w/RFLX PCR
- Lab Code
- Hepatitis C Antibody w/Reflex PCR
- Description
-
The Qualitative detection of Hepatitis C virus IgG and IgM antibodies in human sera by the FDA approved Abbott ARCHITECT Anti-HCV test two-step chemiluminescent immunoassay.
In the first step, sample, assay diluent, and recombinant HCV antigen coated paramagnetic microparticles are combined. Anti-HCV present in the sample binds to the rHCV coated microparticles. In the second step, anti-human IgG/IgM acridinium-labeled conjugate is added, which binds to IgG and IgM anti-HCV. Then pre-trigger and trigger solutions are added to the reaction mixture. The resulting chemiluminescent reaction is measured as relative light units .
The presence or absence of IgG/IgM anti-HCV in the sample is determined by comparing the chemiluminescent signal in the reaction to the cutoff signal determined from an ARCHITECT Anti-HCV calibration. Specimens with signal to cutoff values 1.00 are considered reactive for IgG/IgM anti-HCV. Specimens with S/CO values < 0.79 are considered nonreactive and specimens with S/CO values between 0.80 and 0.99 are Indeterminate.
Reactive anti-HCV will reflex to Hepatitis C RNA, Quantitative for confirmation with an additional charge.
For anti-HCV testing without PCR reflex for REACTIVE results, see Hepatitis C Antibody without PCR reflex on reactive samples .
- Synonyms
Question 9 Why Are Hcv Rna Results Being Reported In Iu/ml What Does Log Iu/ml Mean
HCV RNA results are reported in IU/mL, which is the abbreviation for international units per milliliter. Results are reported in IU/mL to facilitate comparisons between results generated by different test methods. This is important because the various methods used by different laboratories are not standardized against each other. Use of IU/mL reporting units helps to make the comparison of viral load results across different methods more reliable.
HCV RNA results are also reported in log IU/mL, which is the logarithm of IU/mL. Results in this format make it easier to understand whether a change in viral load is clinically meaningful.
Replicating PCR test results using the same specimen can vary analytically by as much as 0.5 log IU/mL thus, only changes greater than 0.5 log IU/mL from one measurement to the next are considered to represent true changes in viral load.8 Reporting the viral load results in log IU/mL units helps the healthcare provider accurately interpret changes in viral load and better assess a patient’s response to antiviral treatment.
Question 8 What Do The Following Hcv Rna Results Mean: < 15 Iu/ml Detected Or < 15 Iu/ml Not Detected
The result < 15 IU/mL, Detected means that HCV RNA is detected, although at a level that is too low to be quantified. This result could indicate current active HCV infection if consistent with other clinical and laboratory data. NOTE: If this test is being performed for HCV diagnosis, then this < 15 IU/mL Detected result should be confirmed using a second sample from the patient.
In contrast, the result < 15 IU/mL, Not Detected means that HCV RNA is not detected and there is no evidence of current active infection.
Quest Diagnostics measures HCV RNA viral load with the Roche cobas® HCV methodology. This is a quantitative real-time PCR assay with a lower limit of quantification of 15 IU/mL the limit of detection is slightly lower, at 10 IU/mL to 13 IU/mL. If the viral load is just at or above this LOD, but less than 15 IU/mL, the assay can determine that HCV RNA is present but cannot provide a reliable quantitative result. In such cases, the qualitative result of < 15 IU/mL, Detected is provided.
Read Also: How Much Is A Hepatitis C Test
Question 6 Is It Possible To Have Hcv Infection And Have A Non
Yes. Among persons with a non-reactive HCV antibody test, who are suspected of having liver disease or are at high risk of acute infection, testing for HCV RNA or follow-up testing for HCV antibody is recommended if high-risk exposure to HCV occurred within the past 6 months. Additionally, testing for HCV RNA can also be considered in persons who are immunocompromised .
Sterilizing Immunity Vs Prevention Of Persistence
The ideal goal of most vaccines is to provide sterilizing immunity that will protect against any infection upon exposure to the pathogen. This can only be achieved by induction of strong NAb responses that would neutralize infectivity. This approach has been very effective when targeting conserved viral surface proteins as is the case in vaccines against hepatitis A, B, and yellow fever. In the context of HCV, sterilizing immunity was not observed in chimpanzee rechallenge or human reinfection studies. Vaccination strategies aiming at inducing high titer bNAbs may indeed achieve sterilizing immunity but this will take time. Hence, it is likely that the first-generation vaccines will focus on achieving milder or blunted infections with lower viral loads and shorter periods of viremia and enhanced rate of viral clearance thus preventing viral persistence and protecting against chronic liver disease.
Recommended Reading: How Did Hepatitis C Start
Standardized Reagents Reagent Repositories And Immunological Methods To Assess Vaccine Efficacy
The advancement of our knowledge of protective immunity requires the availability of standardized reagents for testing as well as immune monitoring protocols. Peptides and a number of other reagents are available through the Biodefense and Emerging Infections Research Resources Repository . Efforts to establish a repository for HCV pseudoparticles were discussed at the 24th International Symposium on HCV and Related Virus. Additional efforts to standardize immune monitoring among different trials should be considered.
Current Hcv Vaccine Strategies
Table 1. Current hepatitis C virus vaccine development strategies.
The second vaccine is based on recombinant HCV gpE1/gpE2. This vaccine was one of the earliest vaccines tested in chimpanzees. Recombinant genotype 1a gpE1/gpE2 vaccination demonstrated effective immunogenicity and protective immunity against homologous or heterologous HCV rechallenge and even sterilizing immunity in some animals . Preclinical evaluation of gpE1/gpE2 adjuvanted with MF59C.1 in human volunteers induced NAbs as well as proliferative CD4 T cell responses against gpE1/gpE2 . This NAb response was cross-reactive and targeted multiple epitopes .
Read Also: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis
How Is A Person Tested For Hepatitis C
A viral-load test is used to check for hepatitis C in the bloodstream. Usually, hepatitis C virus can be found in a persons bloodstream two weeks after he or she becomes infected.
*Except in case of recent risk or in people with a weakened immune system**During the first six months after HCV infection, a person may spontaneously clear the virus if there was a recent risk, repeat viral-load testing to confirm chronic hepatitis C infection
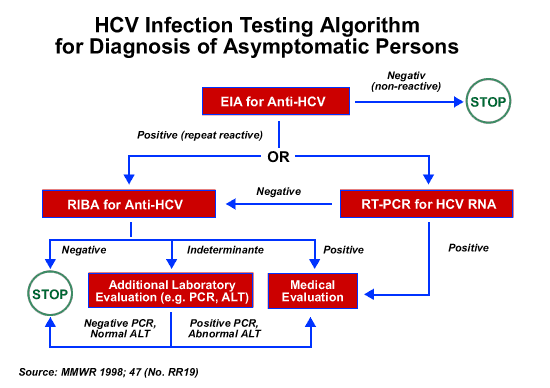
What To Do If The Hcv Antibody Test Is Reactive
If the antibody test is reactive or positive, you need an additional test to see if you currently have hepatitis C. This test is called a nucleic acid test for HCV RNA. Another name used for this test is a PCR test.
If the NAT for HCV RNA is:
- Negative you were infected with hepatitis C virus, but the virus is no longer in your body because you were cured or cleared the virus naturally.
- Positive you now have the virus in your blood.
If you have a reactive antibody test and a positive NAT for HCV RNA, you will need to talk to a doctor about treatment. Treatments are available that can cure most people with hepatitis C in 8 to 12 weeks.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis B Lead To Liver Cancer
Can Hepatitis C Be Treated
Yes, since 2010 enormous progress has been made in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. New therapies called direct-acting antivirals are pills that act on the virus itself to eradicate it from the body, unlike older medicines like interferon injections which work by stimulating an immune response. These new treatments are very effective and can achieve cure rates of over 90%. In most situations now, there is no need for interferon, which was responsible for many of the side effects previously associated with HCV treatment. The new treatment combinations require shorter treatment durations , have reduced side effects and appear to be effective at all stages of the disease.
Because these new therapies are very new, they remain very expensive. As such, drug coverage from both government and private companies may require that your liver disease has progressed to a certain stage before they are willing to cover the cost of these drugs.
Your primary care physician may refer you to a specialist to determine whether you are eligible for treatment. A specialist will help you decide which drug therapy is best for you based on the severity of your liver disease, your virus genotype and whether or not you have been treated in the past.
Evidence Of Protective Immunity Against Hcv Upon Re
Protection against viral persistence upon reinfection in PWIDs was associated with an increase in the magnitude and breadth of HCV-specific T cell responses, and polyfunctional memory T cells that can produce more than one cytokine or effector function . Analysis of the T cell repertoire demonstrated that CD8 T cells expanding upon reinfection were derived from the memory T-cell repertoire with almost no contribution of de novo T cell responses. Furthermore, the T cell repertoire became more focused upon reinfection with selection of T cells of the highest functional avidity .
Protection from viral persistence upon reinfection was also associated with generation of cross-reactive NAbs . These findings re-emphasized the important role of NAbs in mediating protective immunity and as a key component of a successful vaccine against HCV.
Protective immunity upon re-exposure was not absolute as some chimpanzees and humans could still develop chronic infection despite having strong immune responses upon heterologous rechallenge or infection with variant viruses that are not recognized by the pre-existing memory T cells . These observations underscore the importance of inducing broad memory immune responses that target multiple epitopes or variant viruses.
Recommended Reading: How To Cure Hepatitis A
Chronic Hepatitis C Infection
Approximately 25% of those with HCV will spontaneously clear the virus within 6 months. However, in most cases , the infection will become chronic. Chronic hepatitis C is often asymptomatic.
Some individuals with chronic hepatitis C infection experience:
- nausea
- malaise
- abdominal pain
Fluctuating alanine aminotransferase levels are characteristic. In addition, thrombocytopenia may be an indication of cirrhosis. Thrombocytopenia is known to increase with the severity of liver disease.
The late sequelae of chronic hepatitis C infection include:
- liver fibrosis or cirrhosis
- hepatocellular carcinoma
Cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma may develop over a period of 20 to 30 years depending on factors such as sex, age, and level of alcohol consumption. Approximately 1% to 5% of individuals with chronic hepatitis C infection will develop hepatocellular carcinoma.
If cirrhosis develops, individuals may experience:
- ascites
The diagnosis of hepatitis C requires 2 types of tests:
Cohorts For Clinical Trials
One of the difficulties in clinical trials is recruitment of high risk study subjects. Given that the main risk group for HCV infection is PWIDs who also suffer from multiple social, psychological, and marginalization issues, working with this group is challenging . Collaborative efforts with organized cohorts around the world are ongoing and should be maximized in preparation for expanding the current clinical trials or new ones. With the current availability of highly effective DAAs, it is tempting to propose clinical trials of vaccines in healthy volunteers followed by challenge and close monitoring where DAA treatment can be administered at the first sign of viral persistence. This is not a novel approach and has been used in trials for malaria vaccines . Evidently, the ethical implications are not trivial and will have to be considered carefully.
You May Like: How Does Hepatitis Affect The Body
Question 5 How Do You Interpret Hcv Antibody Reactive And Hcv Rna Not
A reactive HCV antibody test result combined with a not-detected HCV RNA result indicates no laboratory evidence of a current active HCV infection no further action is required in most cases.
If distinction between a true positive and a biologic false-positive result for HCV antibody is desired, the CDC suggests that one can consider testing with another HCV antibody assay. If there is concern regarding the handling or storage of the test specimen, obtain a new sample for repeat testing.6
Hcv Core Antigen Testing
The hepatitis C core antigen is a viral protein. Since the core antigen is part of hepatitis C virus, it can usually be found in the bloodstream two weeks after infection.
Since HCV core antigen testing is simpler and less expensive than viral-load testing, some experts suggest using it in resource-limited settings. Core antigen testing can be usedoften with HCV antibody testingto detect acute HCV or to confirm chronic HCV infection. HCV core antigen testing can also be used to measure treatment outcome. Although it does not detect low levels of HCV , usually the hepatitis C viral load is much higher in people who relapse after HCV treatment.
Read Also: Hepatitis C And Liver Damage
Hepatitis C Vaccines Antibodies And T Cells
- 1Centre de Recherche du Centre hospitalier de lUniversité de Montréal , Montréal, QC, Canada
- 2Département de médecine, Faculté de médecine, Université de Montréal, Montréal, QC, Canada
The development of vaccines that protect against persistent hepatitis C virus infection remain a public health priority. The broad use of highly effective direct-acting antivirals is unlikely to achieve HCV elimination without vaccines that can limit viral transmission. Two vaccines targeting either the antibody or the T cell response are currently in preclinical or clinical trials. Next-generation vaccines will likely involve a combination of these two strategies. This review summarizes the state of knowledge about the immune protective role of HCV-specific antibodies and T cells and the current vaccine strategies. In addition, it discusses the potential efficacy of vaccination in DAA-cured individuals. Finally, it summarizes the challenges to vaccine development and the collaborative efforts required to overcome them.
Other Things To Know:
- After a successful course of treatment for hepatitis C, the hepatitis C antibody remains detectable, but the hepatitis C RNA will be undetectable.
- If you plan to donate blood, you will be tested for the hepatitis C antibody and will be turned away even if you do not have an active infection.
- Any patient with a positive test result for the hepatitis C antibody should have additional tests to determine whether or not the virus is still active.
You May Like: Is Hepatitis And Hiv The Same
How Can I Cover Medication Costs
New therapies called direct-acting antivirals are effective and can achieve cures of over 90%. Because these new therapies are very new, they remain very expensive. As such, drug coverage from both government and private companies may require that your liver disease has progressed to a certain stage before they are willing to cover the cost of these drugs.
Talk with your healthcare provider about financial support that may be available.
Below are useful resources when looking for financial assistance:Private health insurance or drug plansIf you have private health insurance or a drug plan at work, you may be able to have the medication paid through your plan. Please consult your private health insurance or drug plan provider to see if your drug is covered.
Publicly funded plansEach provincial and territorial government offers a drug benefit plan for eligible groups. Some are income-based universal programs. Most have specific programs for population groups that may require more enhanced coverage for high drug costs. These groups include seniors, recipients of social assistance, and individuals with diseases or conditions that are associated with high drug costs. For more details, please contact your provincial or territorial health care ministry, or click on the appropriate link below.
Yukon
Available Patient Assistance Programs for Hepatitis C treatment Holkira Pak Maviret
MerckCare Hepatitis C Program 1 872-5773 Zepatier
Tests After The Diagnosis
Once the doctor knows you have hep C, theyâll do tests to find out more about your condition. This will help determine your treatment. They could include:
- Genotype tests to find out which of the six kinds of hepatitis C you have.
- Liver function tests. They measure proteins and enzymes levels, which usually rise 7 to 8 weeks after youâre infected. As your liver gets damaged, enzymes leak into your bloodstream. But you can have normal enzyme levels and still have hepatitis C.
- Tests to check for liver damage. You might get:
- Elastography. Doctors use a special ultrasound machine to feel how stiff your liver is.
- Liver biopsy. The doctor inserts a needle into your liver to take a tiny piece to examine in the lab.
- Imaging tests. These use various methods to take pictures or show images of your insides. They include:
You May Like: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quant
Detection Of Hepatitis C Viral Load
The Real-Time HCV assay was performed to quantify the HCV viral load in all the specimens. The assay had a linear range of 12 IU/mL to 100 million IU/mL . The Limit of Detection of this assay is 12 IU/mL , equivalent to the lower limit of quantitation . The sensitivity for the assay was 12 IU/mL for the 0.5 mL specimen volume and the specificity was 99.5%. HCV viral load1.08 log IU/mL was considered as positive.
Question 1 Where Can I Find The Latest Hcv Management Guidelines
HCV management guidelines are provided by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the Infectious Disease Society of America .1 These organizations publish joint, evidence-based recommendations on the Internet for rapid formulation and dissemination. For more information, visit .
Recommended Reading: Which Hepatitis Is Not Curable
Can I Take The Test At Home
At-home hepatitis C tests are available that allow patients to collect a blood sample at home and mail it to a laboratory for testing. Test samples are collected through pricking a finger with a sharp object, called a lancet, thats included in the test kit.
At-home HCV testing is a form of hepatitis C antibody testing and does not test for hepatitis C RNA or the strains genotype. Testing for hepatitis C at home is not a substitute for testing performed by a health care professional, and positive test results may need to be confirmed by laboratory-based testing.