What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B & C
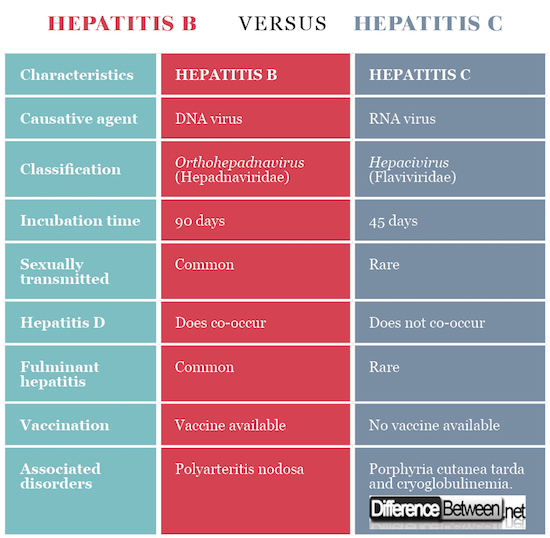
Hepatitis B is caused by coming into contact with bodily fluids of an infected person, where Hepatitis C is transmitted by blood-to-blood contact. Both are viral infections that affect the liver, and it is possible to have both Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C at the same time. Many people with Hepatitis C were born with the condition between 1945 and 1965.
What Is The Difference Between Acute And Chronic Hepatitis B
Acute vs. chronic hepatitis B Your immune system likely can clear acute hepatitis B from your body, and you should recover completely within a few months. Most people who get hepatitis B as adults have an acute infection, but it can lead to chronic infection. Chronic hepatitis B infection lasts six months or longer.
Hepatitis A B And C: Whats The Difference
Hepatitis is often caused by a virus that comes in different strains. The most common strains of hepatitis are hepatitis A, B, and C. They all are contagious, but they differ primarily by the way they are spread.
Table: Differences among hepatitis A, B, and C
Table: Differences among hepatitis A, B, and C
Don’t Miss: How Contagious Is Hepatitis C
What Is The Treatment For Viral Hepatitis
Treatment of acute viral hepatitis and chronic viral hepatitis are different. Treatment of acute viral hepatitis involves resting, relieving symptoms, and maintaining an adequate intake of fluids. Treatment of chronic viral hepatitis involves medications to eradicate the virus and taking measures to prevent further liver damage.
Acute hepatitis
In patients with acute viral hepatitis, the initial treatment consists of relieving the symptoms of nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain . Careful attention should be given to medications or compounds, which can have adverse effects in patients with abnormal liver function . Only those medications that are considered necessary should be administered since the impaired liver is not able to eliminate drugs normally, and drugs may accumulate in the blood and reach toxic levels. Moreover, sedatives and “tranquilizers” are avoided because they may accentuate the effects of liver failure on the brain and cause lethargy and coma. The patient must abstain from drinking alcohol since alcohol is toxic to the liver. It occasionally is necessary to provide intravenous fluids to prevent dehydration caused by vomiting. Patients with severe nausea and/or vomiting may need to be hospitalized for treatment and intravenous fluids.
Chronic hepatitis
Medications for chronic hepatitis C infection include:
- oral daclatasvir
Medications for chronic hepatitis B infection include:
- oral entecavir
- oral tenofovir
Fulminant hepatitis
Which Is More Dangerous Hepatitis B Or C

4.8/5hepatitis Bmorehepatitis Chepatitis Chepatitis B
Similarly, you may ask, which Hepatitis is deadly?
There are 3 main types of hepatitis: hepatitis A, B, and C. Hepatitis C can be more severe and is the most deadly, but even those with acute illness can recover without lasting liver damage. Up to 70% of those chronically infected with hepatitis C develop chronic liver disease, and up to 20% develop cirrhosis.
Similarly, what is the difference between HEP a B and C? The most significant difference between hepatitis B and hepatitis C is that people may get hepatitis B from the bodily fluids of an infected person. Hepatitis C usually only spreads through blood-to-blood contact.
Consequently, which is more dangerous hepatitis A or B?
âHepatitis A virus can cause acute liver disease, but can heal within a few months. It can cause high spiking fevers and is more severe in adults than in children,â says Gulati. âHepatitis B virus has an 85 percent recovery rate, while 15 percent develop cirrhosis or cancer of the liver.â
Is Hepatitis an STD?
Hepatitis B is a serious infection of the liver caused by a virus. The virus is found in blood, semen, vaginal fluids and saliva. Hepatitis B is the only sexually transmitted disease that has a safe and effective vaccine to protect against infection.
Read Also: Is Hepatitis B The Same As Hiv
How Are Hepatitis B And C Diagnosed
Hepatitis B is diagnosed by a series of blood tests. The test may show an ongoing infection or antibodies that indicate that the patient is protected against hepatitis B. In patients who have a positive screening test that suggests the possibility of ongoing infection, further testing is done to determine the levels of the virus in the bloodstream.
Hepatitis C is diagnosed via a blood test called a Hepatitis C Antibody Test. A positive result means that hepatitis C antibodies are present in the blood. But a positive antibody test doesnt necessarily mean a person has hepatitis C. A further blood test is needed to confirm the diagnosis. This second blood test quantifies the amount of the virus or the viral load in the liver and the bloodstream.
How To Protect Yourself Against Hepatitis C
Unfortunately, there is no vaccine available for hepatitis C, but you can protect yourself by avoiding behaviors such as sharing needles and syringes. In addition, the CDC recommends people born between 1945 and 1965 get tested for hepatitis C. Testing is also recommended for people who were treated for blood-clotting problems before 1987 and recipients of blood transfusions or donated organs before 1992.
The UNC Liver Center has a clinic in Chapel Hill that specializes in hepatitis B and C, incorporating the latest clinical trials and most up-to-date therapies. Treatment for hepatitis is also available at our locations in Asheville, High Point, Raleigh and Wilmington. To learn more, call 966-2516.
Michael Fried, MD, is the director of the UNC Liver Center and a professor of medicine at the UNC School of Medicine.
Recommended Reading: How Does A Person Get Hepatitis C
What Is Acute Fulminant Hepatitis
Rarely, individuals with acute infections with HAV and HBV develop severe inflammation, and the liver fails . These patients are extremely ill with the symptoms of acute hepatitis already described and the additional problems of confusion or coma , as well as bruising or bleeding . In fact, up to 80% of people with acute fulminant hepatitis can die within days to weeks therefore, it is fortunate that acute fulminant hepatitis is rare. For example, less than 0.5% of adults with acute infection with HBV will develop acute fulminant hepatitis. This is even less common with HCV alone, although it becomes more frequent when both HBV and HCV are present together.
Hepatitis C And The Hep C Virus
Hepatitis C is a liver infection that can lead to serious liver damage. Its caused by the hepatitis C virus. About 2.4 million people in the U.S. have the disease. But it causes few symptoms, so most of them don’t know. The virus spreads through an infected persons blood or body fluids.
There are many forms of the hepatitis C virus, or HCV. The most common in the U.S. is type 1. None is more serious than any other, but they respond differently to treatment.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Contract Hepatitis C
How Is Viral Hepatitis Diagnosed
Diagnosis of viral hepatitis is based on symptoms and physical findings as well as blood tests for liver enzymes, viral antibodies, and viral genetic materials.
Symptoms and physical findings
Diagnosis of acute viral hepatitis often is easy, but the diagnosis of chronic hepatitis can be difficult. When a patient reports symptoms of fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, darkening of urine, and then develops jaundice, the diagnosis of acute viral hepatitis is likely and can be confirmed by blood tests. On the other hand, patients with chronic hepatitis due to HBV and HCV often have no symptoms or only mild nonspecific symptoms such as chronic fatigue. Typically, these patients do not have jaundice until the liver damage is far advanced. Therefore, these patients can remain undiagnosed for years to decades.
Blood tests
There are three types of blood tests for evaluating patients with hepatitis: liver enzymes, antibodies to the hepatitis viruses, and viral proteins or genetic material .
Liver enzymes: Among the most sensitive and widely used blood tests for evaluating patients with hepatitis are liver enzymes, called aminotransferases. They include aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase . These enzymes normally are contained within liver cells. If the liver is injured , the liver cells spill the enzymes into the blood, raising the enzyme levels in the blood and signaling that the liver is damaged.
Examples of tests for viral antibodies are:
Hepatitis And Liver Transplant
Any form of hepatitis can cause liver damage. If the liver becomes severely damaged, a liver transplant is necessary.
With more than 14,000 Americans on the waiting list for a liver transplant, patients often wait years for a transplant. Living donor transplantation allows a transplant to take place before the disease progresses further.
To reduce time on the transplant waiting list, you can choose to find a living donor. During a living-donor liver transplant, the surgeon takes a small part of the donors healthy liver and transplants it into the recipient. This process is possible because of the livers unique ability to regenerate, or regrow.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis B Vaccine For
How Are Hepatitis B And C Treated
Hepatitis B: Not all patients with chronic hepatitis B infection require treatment. At Yale Medicine, specialists decide on an individual basis whether a patient is an appropriate candidate for treatment. Generally, patients require treatment when their hepatitis B virus level is high, and when laboratory tests demonstrate significant inflammation or injury to the liver.
There are currently seven approved drugs for hepatitis B, two of which are considered to be first-line treatments. These drugs are oral pills taken once daily, and while they’re very effective at suppressing the virus to very low or undetectable levels over the long term, they are not considered curative.
Therefore, the goal of treatment is to control the virus long-term and decrease the risk of hepatitis B related complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Hepatitis C: For the greater part of the last 20 years, treatment of hepatitis C required the use of a chemotherapy-like injection drug called interferon, which has been associated with serious side effects and a low cure rate. Fortunately, advances in hepatitis C treatments within the last three years now allow for the use of oral medications that are significant improvements in terms of safety and effectiveness.
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis A And Hepatitis B
You’ve undoubtedly heard hepatitis A and B mentioned many times before. Whether it was by watching the news, reading a headline, or overhearing a coworker say they had it in the past, it’s an unavoidable topic. But you may not really know what hepatitis A and B are, how dangerous they can be, who’s most at risk, or how you can protect yourself. Let’s look at the specifics so you have the facts to help keep yourself healthy year-round.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Is It Contagious Sexually
How Is Hepatitis Diagnosed
There are several tests that can help with the detection and diagnosis of Hepatitis.
Screening tests to detect if the person is currently infected, had a past infection or has immunity against Hepatitis
- Anti HAV total detects past or present infection with hepatitis A virus or there is immunity against it from e.g. vaccination.
- Hepatitis Bs Antigen detects the protein produced in the presence of the hepatitis B virus in the body. There will be high levels of this protein produced during an acute or chronic infection.
- Hepatitis Bs Antibody detects the antibodies protective against hepatitis. The presence of these antibodies indicates either recovery from a past infection or immunity against it from e.g. vaccination.
- Anti HCV total detects past or present infection with hepatitis C virus or there is immunity against it from e.g. vaccination.
How Do You Treat Hepatitis B
Like hepatitis A, medical treatment for acute hepatitis B is focused on getting plenty of rest and fluids and eating a healthy diet, although sometimes antiviral drugs are recommended for severe cases to help prevent liver failure. Patients with chronic hepatitis B may be given an oral antiviral drug to control the viral infection and minimize liver damage. These drugs are effective, but they rarely cure chronic hepatitis B. Therefore, these medications often have to be taken for life.
Read Also: Hepatitis A Vaccine For Adults
How Is Viral Hepatitis Prevented
Prevention of hepatitis involves measures to avoid exposure to the viruses, using immunoglobulin in the event of exposure, and vaccines. Administration of immunoglobulin is called passive protection because antibodies from patients who have had viral hepatitis are given to the patient. Vaccination is called active protection because killed viruses or non-infectious components of viruses are given to stimulate the body to produce its own antibodies.
Avoidance of exposure to viruses
Prevention of viral hepatitis, like any other illness, is preferable to reliance upon treatment. Taking precautions to prevent exposure to another individual’s blood , semen , and other bodily secretions and waste will help prevent the spread of all of these viruses.
Use of immunoglobulins
Immune serum globulin is human serum that contains antibodies to hepatitis A. ISG can be administered to prevent infection in individuals who have been exposed to hepatitis A. ISG works immediately upon administration, and the duration of protection is several months. ISG usually is given to travelers to regions of the world where there are high rates of hepatitis A infection and to close or household contacts of patients with hepatitis A infection. ISG is safe with few side effects.
Hepatitis A
Individuals at increased risk of acquiring hepatitis A are:
Some local health authorities or private companies may require hepatitis A vaccination for food handlers.
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for:
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis
There are 2 types of Infections from Hepatitis Acute and Chronic.
Acute infections The symptoms in Hepatitis A, B and C are similar and can occur in acute infections. Jaundice , dark coloured urine, pale stools, fever, unexplained prolonged tiredness, poor appetite, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting.
Duration of infection may last for approximately up to 6 months. People with acute infections usually recover completely and will form an immunity to Hepatitis.
Chronic infections symptoms may not be presented at first in people who are infected. However, when symptoms appear, it is often a sign of advanced liver disease.
Duration of infection is usually more than 6 months and in some cases if left untreated, may lead to serious complications such as liver damage, cirrhosis, liver cancer, and even death.
The person who carries the Hepatitis virus is also known as a carrier and can spread the disease to others
Recommended Reading: How Can You Contact Hepatitis C
Do You Need Vaccinations Before Traveling Abroad
The CDC divides travel vaccinations into three categories: 1) routine, 2) recommended, and 3) required. The only vaccine classified as “required” by International Health Regulations is the yellow fever vaccination for travel to certain countries in sub-Saharan Africa and tropical South America.
“Routine” vaccinations are those that are normally administered, usually during childhood, in the United States. These include immunizations against:
- tetanus
What Are The Symptoms And Signs Of Viral Hepatitis
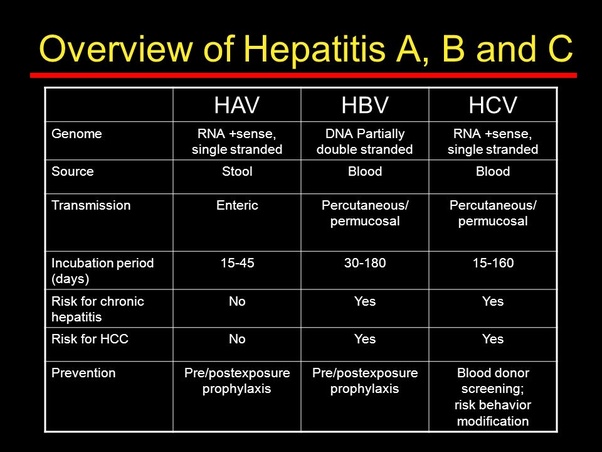
The period of time between exposure to hepatitis and the onset of the illness is called the incubation period. The incubation period varies depending on the specific hepatitis virus. Hepatitis A virus has an incubation period of about 15 to 45 days Hepatitis B virus from 45 to 160 days, and Hepatitis C virus from about 2 weeks to 6 months.
Many patients infected with HAV, HBV, and HCV have few or no symptoms of illness. For those who do develop symptoms of viral hepatitis, the most common are flu-like symptoms including:
Read Also: How Is Hepatitis B And C Transmitted
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause an acute or chronic infection. People with an acute infection usually get better on their own without treatment. Some people with chronic hepatitis B will need treatment.
Thanks to a vaccine, hepatitis B is not very common in the United States. It is more common in certain parts of the world, such as sub-Saharan Africa and parts of Asia.
What Is Hbv Hepatitis C What Are The Differences Between Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis A, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, Ding Gan and so on are all viral hepatitis. Hepatitis B and hepatitis C are the most common ones. In recent years, there are also many patients suffering from hepatitis B and hepatitis C. However, many people do not know much about hepatitis B and hepatitis C, so their importance is not high. So what is hepatitis B and hepatitis C? What is the difference between hepatitis B and hepatitis C? Let’s take a look at this article.
What is hepatitis B and hepatitis C?
What is hepatitis B?
What is hepatitis C
Hepatitis C, referred to as hepatitis C and hepatitis C for short, is a viral hepatitis caused by hepatitis C virus infection. It is mainly transmitted through blood transfusion, acupuncture and drug abuse. Hepatitis C is a global epidemic. According to the statistics of the World Health Organization, the global HCV infection rate is about 3%. It is estimated that about 180 million people are infected with HCV, and there are about 35000 new cases of hepatitis C every year.
Two. The difference between HBV and HCV.
First, the pathogens of the two are different. Hepatitis B virus belongs to DNA virus. In 1960s, it has been found that the level of virus infection is high and easy to detect. Hepatitis C virus belongs to RNA virus. It was found only in 1989. The virus is very small and it is difficult to see its shape under electron microscope. Hepatitis C virus mutates rapidly and has many subtypes.
You May Like: Natural Remedies For Hepatitis C