Hbv Dna Hbv Genotype And Hbv Drug Resistance Assays
Specimen: Serum or plasma
Container: Red-top tube, yellow-top tube , gel-barrier tube, plasma preparation tube, or lavender tube
Collection method: Routine venipuncture
The specimen should be transfused to separate plasma/serum from cells within 6 hours and kept frozen when testing cannot be done promptly.
The tests use PCR amplification, DNA probe hybridization, and sequencing method.
Hepatitis B Core Antibody Test
This test checks whether a person currently has HBV or had it in the past. A positive result means that they have a current or past infection. It can also mean that they are recovering from acute hepatitis B.
Those who receive a positive result should contact a doctor to check the status of their hepatitis B infection.
This product requires finger prick blood collection, and it tests for hepatitis B and hepatitis C.
People can pay a one-time purchase fee or sign up for a subscription plan for regular testing.
Those who purchase this product receive the tools they need for testing. LetsGetChecked recommends that individuals use this test before 10 a.m. It also warns people against having sex if they think they have hepatitis B or C.
Once a person collects their samples, they can mail them to the companys laboratory on the same day.
LetsGetChecked states that its laboratories have a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments certification. This means that it has obtained federal certifications. The company is also part of the College of American Pathologists program.
People should receive their results within 25 days. Additionally, they can contact a LetsGetChecked nurse at any time to discuss their results.
Pros and cons
LetsGetChecked tests come with pros and cons.
Some pros include:
Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Many people with hepatitis B will not experience any symptoms and may fight off the virus without realising they had it.
If symptoms do develop, they tend to happen 2 or 3 months after exposure to the hepatitis B virus.
Symptoms of hepatitis B include:
- flu-like symptoms, including tiredness, a fever, and general aches and pains
- loss of appetite
- tummy pain
- yellowing of the skin and eyes
These symptoms will usually pass within 1 to 3 months , although occasionally the infection can last for 6 months or more .
Recommended Reading: How Hepatitis C Affects The Body
The Treatment Programs Role In The Screening Process
Medical staff members at substance abuse treatment programs might assume the primary role for screening individuals for and explaining the screening process and test results. Opioid treatment programs with medical staff members should screen for and C at intake and periodically as indicated. In programs without onsite medical staff, clients may be referred elsewhere for screening with minimal involvement of the substance abuse treatment program.
Regardless of the type of program, counselors should have a basic understanding of the importance of screening, the screening process, and the meaning of the results. Counselors can encourage clients referred for screening to follow through and complete the screening and evaluation process . Clients might feel anxious about being diagnosed with hepatitis, and they might delay or avoid getting screened.
What Are The Symptoms
During the early stages of infection there may not be any symptoms. If symptoms do develop, this is usually within the first six months after infection. Those who do get symptoms may experience:
- flu-like symptoms, such as high temperature, muscle aches and loss of appetite, feeling tired all the time
- yellowing of the eyes and skin
- abdominal pain
- loss of appetite and weight loss
- sickness and diarrhoea.
Some people clear the virus after this initial stage. However, some people do not clear the virus without treatment and so they will develop a long term infection called chronic hepatitis. This can cause damage to the liver and can lead to liver cancer.
It can take up to 12 weeks for hepatitis B to show up in tests
Also Check: How Much Does Hepatitis C Medicine Cost
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is the most common serious liver infection in the world. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus that attacks and injures the liver. Two billion people have been infected and about 300 million people are living with a chronic hepatitis B infection. Each year up to 1 million people die from hepatitis B despite the fact that it is preventable and treatable.
The hepatitis B virus is transmitted through blood and infected bodily fluids. It can be passed to others through direct contact with blood, unprotected sex, use of illegal drugs, unsterilized or contaminated needles, and from an infected woman to her newborn during pregnancy or childbirth.
Hepatitis B is a silent epidemic because most people do not have symptoms when they are newly infected or chronically infected. Thus, they can unknowingly spread the virus to others and continue the silent spread of hepatitis B. For people who are chronically infected but dont have any symptoms, their liver is still being silently damaged which can develop into serious liver disease such as cirrhosis or liver cancer.
The good news is that hepatitis B is preventable and treatable. There is a simple blood test to diagnose a hepatitis B infection. Testing is the only way to know for sure if you are infected. There is a safe vaccine to prevent hepatitis B. There are effective drug therapies that can manage a chronic hepatitis B infection, and a cure is within sight.
Identifying Patterns Of Risky Behavior
Screening is an opportunity to draw attention to the clients behaviors that put him or her at risk for contracting :
- Ask for the clients perception of his or her risk for having contracted : How likely do you think it is that the test will be positive?
- Listen for and identify behaviors that put the client at risk for contracting , B, and C and HIV, especially unprotected sex and sharing injection drug paraphernalia.
- Assess the clients alcohol consumption.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Blood Test For Hepatitis C
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis B testing is typically prescribed by a doctor and performed in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Taking a hepatitis B test requires a blood sample, which can be collected by a health care professional.
For laboratory-based testing, blood is drawn from a patientâs vein. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Hepatitis B
Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.
Don’t Miss: Interpretation Of Hepatitis A Serologic Test Results
Questions For Your Doctor After At
Its important to talk to your doctor about at-home hepatitis B test results. Questions for your doctor may include:
- What does my at-home hepatitis B test result mean for my health?
- What is my risk of getting hepatitis B?
- Is periodic testing recommended for me?
- What other tests are needed to diagnose or rule out hepatitis B?
- Should I be vaccinated against hepatitis B?
Questions For Your Doctor About Test Results
Patients may find it helpful to ask questions about their hepatitis B test results. Questions that may be helpful include:
- What was my test result?
- Do I have an acute or chronic hepatitis B infection?
- Does the test result suggest that I have immunity for hepatitis B?
- Would I benefit from hepatitis B vaccination?
- Do I need any follow-up tests based on my hepatitis B test results?
Recommended Reading: Royal Canin Hepatic Wet Food
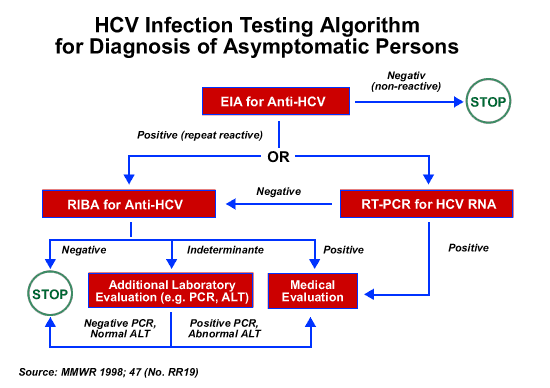
Recommended Tests To Investigate Acute Hbv Infection And The Interpretation Of Results
Acute HBV infection generally presents after an incubation period of six weeks to several months with an onset of nonspecific symptoms that may include fever, malaise, anorexia and nausea, followed by the onset of jaundice, dark urine and pale stools. Approximately 25% to 40% of infected adults will be symptomatic, and most will demonstrate elevations in ALT however, infants, toddlers and immunosuppressed individuals may not manifest signs or symptoms of infection. The management of acute infections is largely supportive unless fulminant hepatitis develops, in which case the patient should be referred to a liver specialist. Because the clinical features of acute hepatitis are very similar for HAV, HBV and HCV, testing for all three agents should be performed when working up an acute case. While the sexual transmission of HCV is rare, varying between zero to six cases per 1000 person-years , HAV that is typically spread by the fecal-oral route poses a clear risk to sexual partners. Figure and Table outline the appropriate serological tests to investigate acute hepatitis.
Hepatitis B Blood Tests
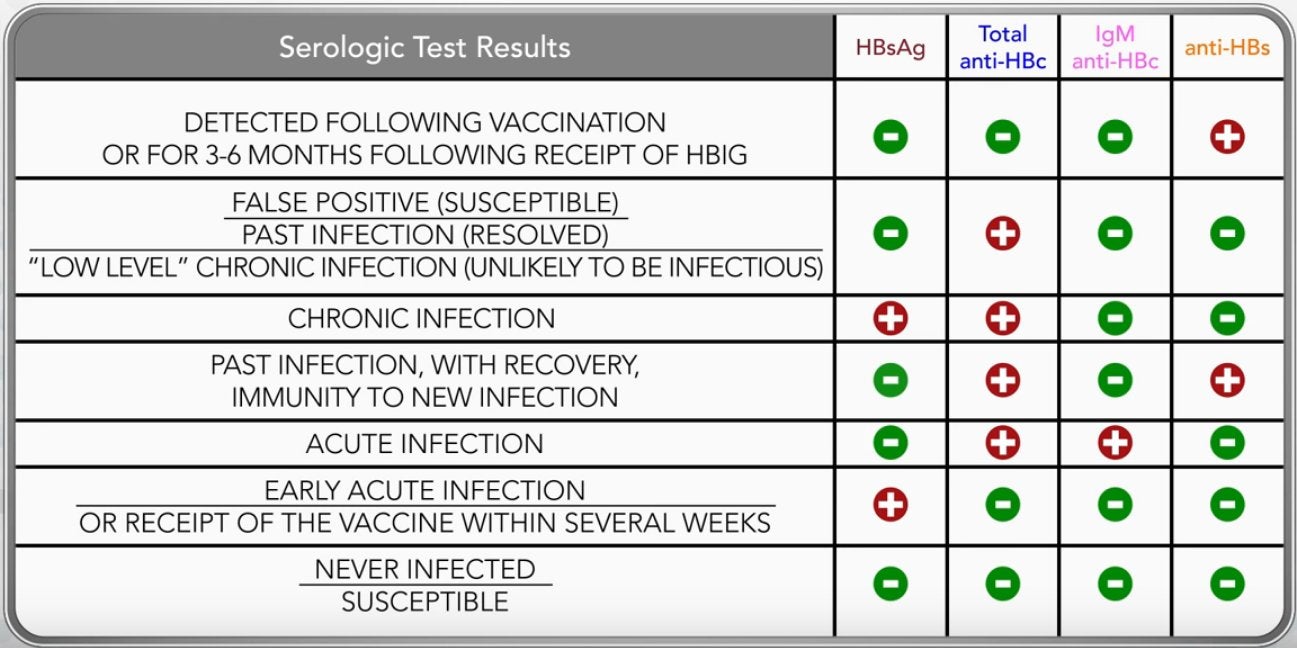
The Hepatitis B Panel of Blood Tests
Only one sample of blood is needed for a hepatitis B blood test, but the Hepatitis B Panel includes three parts. All three test results are needed to fully understand whether a person is infected or not. Below is an explanation of the 3-part Hepatitis B Panel of blood test results.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Hepatitis B And C
Acute Hbv Infection With Recovery
Following acquisition of HBV, the first detectable serologic marker in blood is HBsAg. Detection of HBsAg typically occurs at 4 weeks following infection, with a range of 1 to 9 weeks following infection. Typically, when HBsAg is detectable during acute infection, HBV DNA can also be detected in blood. During early infection, persons may also test positive for HBeAg, which is a marker of infectivity and higher HBV DNA levels. Nearly all persons will test negative for HBsAg and HBV DNA by 15 weeks after the onset of symptoms. With acute HBV infection, IgM anti-HBc is typically detectable at the onset of symptoms and persists for 6 to 9 months following infection. Total anti-HBc, which consists of IgM anti-HBc and IgG anti-HBc, can similarly be detected at the onset of symptoms, but persists indefinitely as a marker of prior infection. During recovery, and after the disappearance of HBsAg, persons who have immunologic control of acute infection will develop antibodies to HBs , which may persist indefinitely or wane over time. It is important to note that following the disappearance of HBsAg and prior to the appearance of anti-HBs, there is a period of time when IgM anti-HBc and total anti-HBc may be the only detectable serologic markers. This period of time is known as the window period.
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if youre contagious. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can spread the virus. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B. This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the .
Read Also: Hepatic Steatosis Treatment Step By Step
Clinical Information Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
Hepatitis B e antigen is a small polypeptide that exists in a free form in the serum of individuals during the early phase of hepatitis B infection, soon after hepatitis B surface antigen becomes detectable. Serum levels of both HBeAg and HBsAg rise rapidly during the period of viral replication. The presence of HBeAg in serum correlates with hepatitis B virus infectivity, the number of infectious virions, and the presence of HBV core antigen in the infected hepatocytes.
During recovery from acute hepatitis B, HBeAg level declines and becomes undetectable in the serum, while hepatitis B e antibody appears and becomes detectable in the serum. Anti-HBe usually remains detectable for many years after recovery from acute HBV infection.
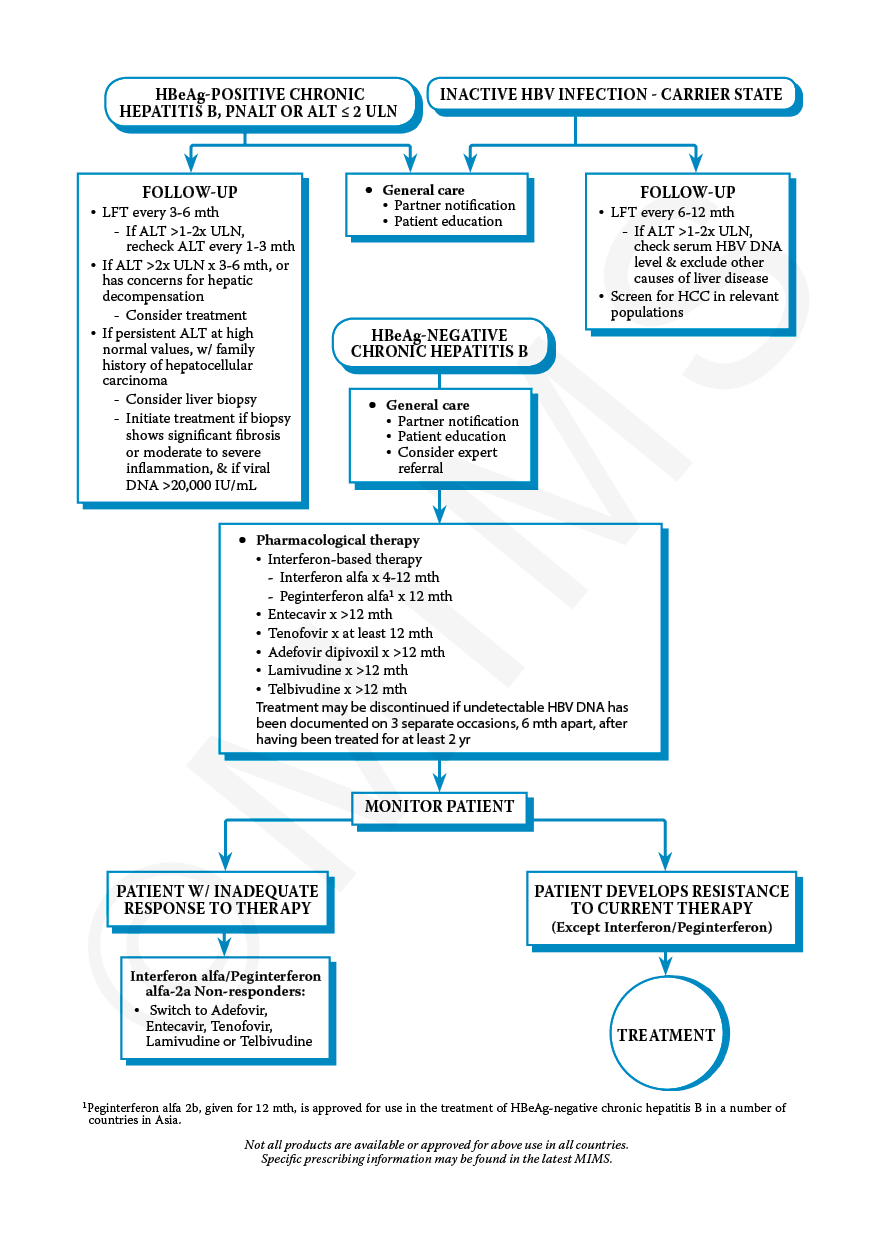
In HBV carriers and patients with chronic hepatitis B, positive HBeAg results usually indicate presence of active HBV replication and high infectivity. A negative HBeAg result indicates very minimal or no HBV replication. Positive anti-HBe results usually indicate inactivity of the virus and low infectivity. Positive anti-HBe results in the presence of detectable HBV DNA in serum also indicate active viral replication in these patients.
Recommended Groups For Routine Hbv Screening
Multiple organizations in the United States recommend performing routine screening for hepatitis B virus infection for persons who are at increased risk of acquiring HBV these organizations include the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force , the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases , and the American College of Physicians The USPSTF recommendation was issued in 2014 as a grade B recommendation, meaning clinicians should offer or provide this service in practice. The following list summarizes the groups considered to be at high risk for HBV infection, in whom screening is recommended by the CDC. Certain indications for screening depend on country level HBV prevalence .
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quant
When Should I Get Hepatitis B Testing
Using hepatitis B tests to screen for HBV is recommended for certain groups that are at an increased risk of infection. Groups that may benefit from hepatitis B screening include:
- Pregnant people
- People born in parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, including Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, South America, and parts of the Middle East
- People who didnât receive a hepatitis B vaccine
- HIV-positive people
- Pain in the joints or abdomen
- Loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- Yellowish skin and eyes
Using hepatitis B testing to assess immunity to HBV may be used before or after vaccination. Pre-vaccination testing is not always needed but may be performed if there is a chance that a patient has previously been infected with HBV or has already been vaccinated. Post-vaccination testing is used in certain groups of people who are at an especially elevated risk for HBV infection, including infants born to mothers with a hepatitis B infection.
Diagnosing Hepatitis A B & C
At NYU Langone, hepatologists, or liver specialists, and infectious disease specialists use blood tests to diagnose hepatitis A, B, and C. These viral infections cause inflammation of the liver.
If the results of a blood test confirm a diagnosis of viral hepatitis, your doctor may recommend imaging tests or a liver biopsy to determine the extent of liver disease.
Don’t Miss: How Soon Do Hepatitis C Symptoms Appear
Can Hepatitis B Be Prevented
The hepatitis B vaccine is one of the best ways to control the disease. It is safe, effective and widely available. More than one billion doses of the vaccine have been administered globally since 1982. The World Health Organization says the vaccine is 98-100% effective in guarding against the virus. Newborns should be vaccinated.
The disease has also been more widely prevented thanks to:
- Widespread global adoption of safe blood-handling practices. WHO says 97% of the blood donated around the world is now screened for HBV and other diseases.
- Safer blood injection practices, using clean needles.
- Safe-sex practices.
You can help prevent hepatitis B infections by:
- Practicing safe sex .
- Never sharing personal care items like toothbrushes or razors.
- Getting tattoos or piercings only at shops that employ safe hygiene practices.
- Not sharing needles to use drugs.
- Asking your healthcare provider for blood tests to determine if you have HBV or if you are immune.
Taking A Hepatitis B Test
Testing for hepatitis B is performed on a sample of blood. A doctor, nurse, or other health care provider can obtain a blood sample using a small needle to draw blood from a vein.
At-home hepatitis B testing requires that users carefully follow instructions provided in the test kit to collect a small sample of blood, package the sample, and mail it to a lab for testing.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Immunity
Igm Class Antibody To Hav
-
If the IgM class antibody to HAV is negative, HAV infection is ruled out in immunocompetent patients .
-
If positive, acute HAV infection is likely. As the anti-HAV-IgM may remain detectable for up to two years after infection in a small subset of patients, the history and clinical presentation must be considered in making an accurate diagnosis .
Hepatitis B And Your Liver
The liver is such an important organ that we can survive only one or two days if it completely shuts down – if the liver fails, your body will fail, too. Fortunately, the liver can function even when up to 80% of it is diseased or removed. This is because it has the amazing ability to regenerate – or create – itself from healthy liver cells that still exist.
If your body were an automobile, your liver would be considered the engine. It does hundreds of vital things to make sure everything runs smoothly:
- Stores vitamins, sugar and iron to help give your body energy
- Controls the production and removal of cholesterol
- Clears your blood of waste products, drugs and other poisonous substances
- Makes clotting factors to stop excessive bleeding after cuts or injuries
- Produces immune factors and removes bacteria from the bloodstream to combat infection
- Releases a substance called “bile” to help digest food and absorb important nutrients
The word hepatitis actually means inflammation of the liver. Thus, hepatitis B refers to inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis B virus. With early detection and appropriate follow-up medical care, people living with a chronic hepatitis B infection can expect to enjoy a long and healthy life.
Recommended Reading: How Did I Get Hepatitis C