Acute Hepatitis B Infection
If you are newly infected with hepatitis B, your infection is considered acute. An acute hepatitis B infection may last up to six months and you may pass the virus to others during this time.
Your doctor will order follow up testing to determine whether you have successfully gotten rid of the virus. Until your health care provider confirms that the blood test shows that there is no more hepatitis B virus in your blood, it is important to protect others from a possible infection.
Hepatitis B can be spread to others through blood and bodily fluids. If your sexual partner and household members are not vaccinated, they should be tested for hepatitis B. If they have not been infected then they should also start the hepatitis B vaccine series. You should use condoms for all sexual activity, wash hands after any potential exposure to blood, and avoid sharing sharp objects such as razors, nail clippers, earrings, and toothbrushes.
Most people experience only mild symptoms or none at all. Symptoms may appear 60-150 days after infection, with the average being 90 days. The majority of acute infections are treated by rest and managing symptoms.
Most common symptoms include:
Rarely, people may experience severe symptoms such as:
- Nausea
- Jaundice
- Bloated stomach
A rare, life-threatening condition called fulminant hepatitis can occur with a new acute infection and requires immediate, urgent medical attention since a person can go into sudden liver failure.
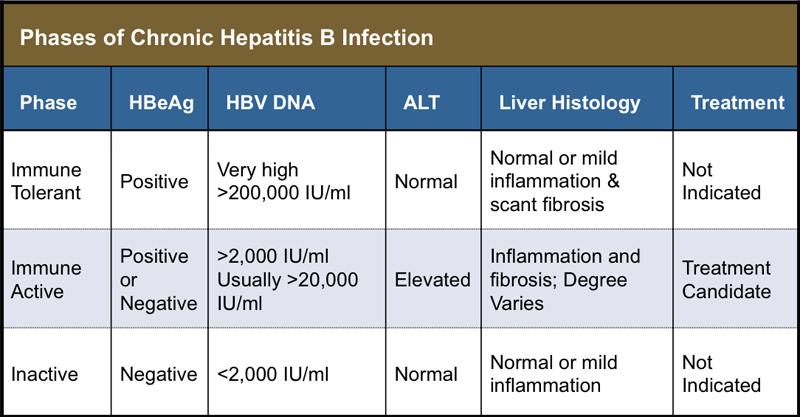
Acute Vs Chronic Hepatitis B
A hepatitis B infection can result in either an acute infection or a chronic infection. When a person is first infected with the hepatitis B virus, it is called an acute infection . Most healthy adults that are infected do not have any symptoms and are able to get rid of the virus without any problems. Some adults are unable to get rid of the virus after six months and they are diagnosed as having a chronic infection. A simple blood test can diagnose an acute or chronic hepatitis B infection.
The risk of developing a chronic hepatitis B infection is directly related to the age at which a person is first exposed to the hepatitis B virus. The younger a person is when they are first infected, the greater the risk of developing a chronic hepatitis B infection:
- More than 90% of infants that are infected will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
- Up to 50% of young children between 1 and 5 years who are infected will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
- 5-10% of healthy adults 19 years and older who are infected will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
The recommendation for hepatitis B vaccination of babies and children is so important because they are at the greatest risk of developing a chronic infection if they are not protected against the hepatitis B virus as soon as possible.
Hiv And Hepatitis C Coinfection
HCV infection is common among people with HIV who also inject drugs. Nearly 75% of people living with HIV who report a history of injection drug use are co-infected with HCV. All people who are diagnosed with HIV are recommended to be tested for HCV at least once. People living with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HCV infection. Fortunately, direct acting antivirals that are used to treat HCV work equally well in people with and without HIV infection. For more information about HIV and HCV coinfection, visit the HIV.govs pages about hepatitis C and HIV coinfection.
Read Also: Is Hiv Transmitted More Easily Than Hepatitis
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis C
Healthcare providers generally treat acute and chronic hepatitis C the same way. The treatment for this infection is called direct-acting antiviral medication. These medications are usually very effective, easy to take, and cause few side effects.
The treatment for hepatitis C takes about eight to 12 weeks. The vast majority of people who take direct-acting antiviral medications have undetected virus levels within six months.
If hepatitis C has progressed to liver failure, treatment may depend on a liver transplant. Thats because you cannot live without a functioning liver.
Talk to your doctor to learn more information about testing guidelines for hepatitis C. All adults should receive at least one hepatitis C test in their lifetime, but if you have certain risk factors, you may need additional testing.
- Sanjai Sinha, MDDr. Sinha specializes in internal medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York.
Terminology Related To Acute Hcv Infection
Clinical reviews and research studies have used numerous terms to refer to acute hepatitis C infection, including acute infection, acute phase infection, very early infection, recent infection, and newly acquired infection. Overall, consensus does not exist regarding the terminology and criteria for defining acute HCV infection. Very early infection typically refers to patients with a positive HCV RNA and documented HCV antibody seroconversion, with this scenario being the most definitive for diagnosing acute HCV infection. Some experts have suggested limiting the multiple possible terms to acute infection and recent infection with the following definitions:
- Acute Infection: estimated duration of infection less than 6 months
- Recent Infection: estimated duration of infection longer than 6 months, but shorter than 2 years.
Also Check: Care Plan For Hepatitis C
Acute Vs Chronic Hepatitis C: Whats The Difference
Without treatment, acute hepatitis C could become chronic.
Without treatment, chronic hepatitis C can cause damage to the liver over time. Scarring on the liver increases the risk of liver cancer and liver failure. Unfortunately, many people do not catch hepatitis C when its in the acute stage when its easier to treat.
What Are The Differences Between Acute Chronic And Resolved Hcv Infection
Acute HCV infection implies a new infection which may or may not resolve . Chronic HCV infection implies that the infection did not resolve and that the liver may suffer permanent damage. Resolved HCV infection means the viral infection has run its course or, if the patient responds to anti-viral treatment, the infection may be cleared by therapy.
Recommended Reading: Labcorp Hepatitis C Viral Load
Can Hepatitis C Be Prevented
There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. But you can help protect yourself from hepatitis C infection by:
- Not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- Wearing gloves if you have to touch another person’s blood or open sores
- Making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools and unopened ink
- Not sharing personal items such toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- Using a latex condom during sex. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
What Is Acute Hepatitis C
Acute hepatitis C refers to an active infection that is typically detected within the first six months. Effective treatments may help get it under control, such as direct-acting antiviral medication. Some people may be able to suppress the infection with their own immune system.
During the acute stage, hepatitis C is less likely to cause long-term damage to the liver. This is important since your liver plays many roles in your health, such as digesting food, removing harmful toxins or poisons from the digestive system, and storing energy.
Not everyone with hepatitis C has symptoms, which is what makes it hard to catch in the early stages. For people who do notice acute hepatitis C symptoms, they may include:
-
Nausea
-
Change in the color of urine or stool
-
Fever
-
Flu-like symptoms
Read Also: Royal Canin Feline Hepatic Diet
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis C
Treatment for hepatitis C is with antiviral medicines. They can cure the disease in most cases.
If you have acute hepatitis C, your health care provider may wait to see if your infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
If your hepatitis C causes cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Treatments for health problems related to cirrhosis include medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If your hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
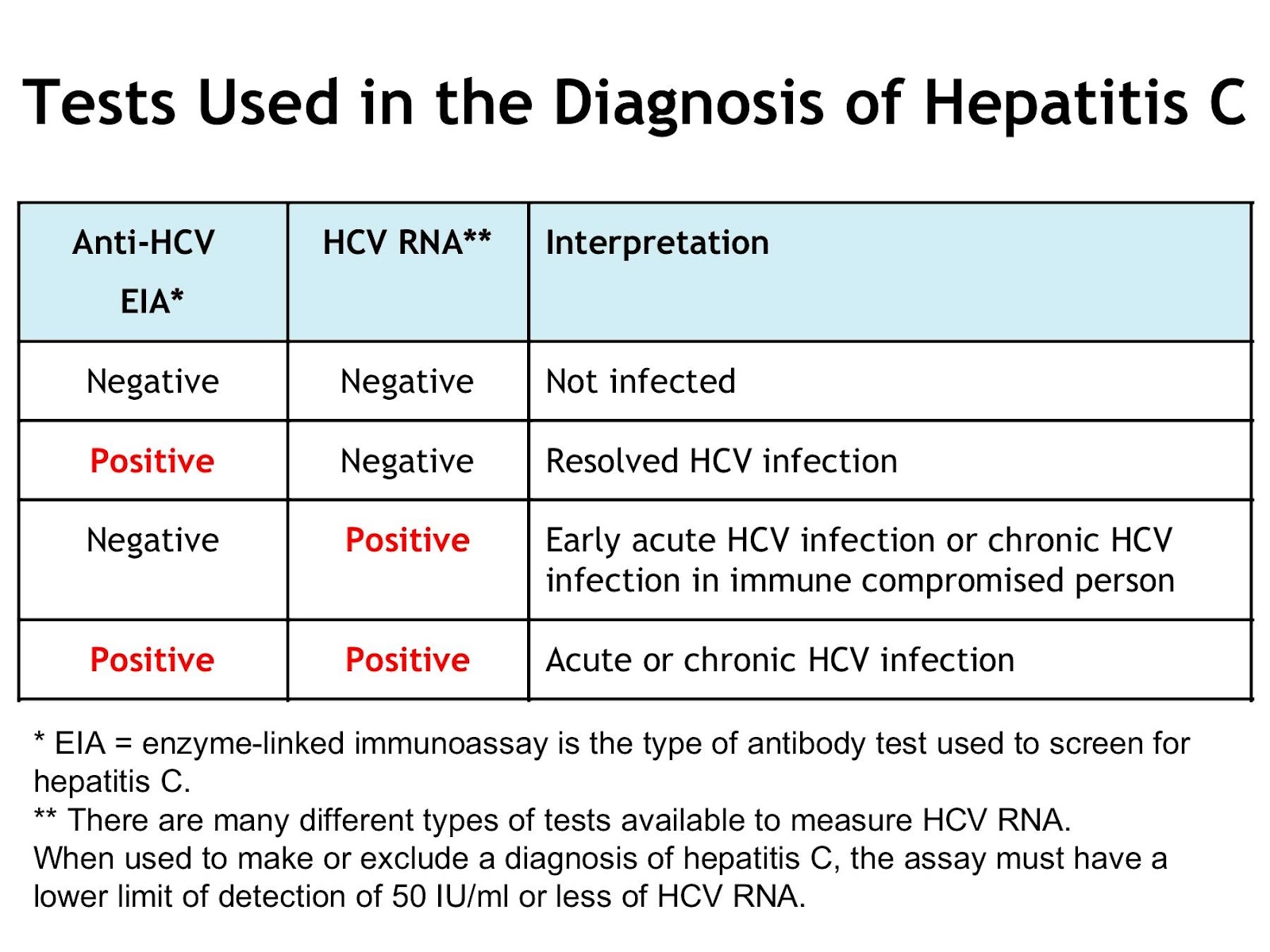
Interpreting Hcv Rna Test Results
It is essential that the provider understands how to interpret HCV RNA test results, especially during the course of HCV treatment.
| Result of HCV RNA Test | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| A quantified viral load — any exact number | Ongoing HCV infection |
| “Detected” | The HCV RNA is detectable but the number of international units is so low that it cannot be quantified accurately. This indicates extremely low level of virus is present. |
| “< 12 IU/mL” or “< 15 IU/mL” or “< 25 IU/mL” All of these are “less than the LLOQ” | HCV RNA is undetectable. No virus is detected at all in the patient’s serum specimen. |
Read Also: How Serious Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C Virus Infection
Steatosis is a hallmark of genotype 3 HCV liver injury. Studies directly comparing genotype-specific injuries are rare, although genotype differences have been studied in the setting of definite hepatic steatosis and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis . Gene expression profiling has identified genotype 3-specific genes SOCS1 and IFITM1, and genotype 1-specific genes CCL3, CCL4, IFNAR, and PRKRIR . Importantly, fibrotic injury did not have a genotype-specific signature . Unique HCV-associated fibrosis signatures have been identified and have led to the correlation of the corresponding proteins of three of these genes inter- inhibitor H1, serpin peptidase inhibitor clade F member 2, and transthyretin being correlated with stages of fibrosis development . Clearly, such proteins may well be useful biomarkers of HCV fibrosis development in the future.
Grzegorz W. Telega, in, 2018
Recommended Reading: What Does Hepatitis Feel Like
Clinical Scenarios That Suggest Acute Hcv Infection
Symptomatic Presentation
Individuals with acute HCV infection can develop significant symptoms and may present with the new onset of jaundice, fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, and malaise. More often, however, these individuals have no obvious symptoms or only have limited symptoms, such as slight malaise.
History of a Recent HCV Exposure but Without Symptoms
Since acute HCV is usually asymptomatic, clinicians should test person for HCV if they suspect a new exposure to HCV could have taken place, regardless of clinical symptoms. The most common exposures include recent injection drug use that involved needle sharing, a needlestick injury, and sexual contact with a partner who has known HCV infection. For persons with acute or recent HCV acquisition, HCV testing soon after the exposure can make the diagnosis of a new infection and distinguish acute from chronic infection. Recent injection drug use with shared needles or equipment would be considered the highest risk exposure, especially if the needle-sharing partner is known to have HCV. Although the exact risk of acquiring HCV through sexual contact is controversial, sexual transmission appears to be highest among men who have sex with men, particularly if this involves persons with HIV who have engaged in physically traumatic or rough sex.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer
Effective Treatments Are Available For Hepatitis C
New medication to treat for HCV have been approved in recent years. These treatments are much better than the previously available treatment because they have few side effects and do not need to be injected. There are several direct-acting antiviral HCV treatments that cure more than 95% of people who take them in 8 to 12 weeks. HCV treatment dramatically reduces deaths among people with HCV infection, and people who are cured of HCV are much less likely to develop cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Take Action! CDCs National Prevention Information Network Service Locator helps consumers locate hepatitis B and hepatitis C prevention, care, and treatment services.
I’m A Health Care Worker Who Was Recently Exposed To Hcv Is There Post
No. Immune globulin is not recommended for postexposure prophylaxis against HCV, and prophylactic antiviral therapy is also not recommended. However, following exposure, a health care worker should be tested for HCV antibody right away and at 6 months so that early HCV infection can be identified. Several studies suggest that interferon treatment begun early in the course of HCV infection is associated with a higher rate of cure however, further studies are needed to confirm this. There is no hepatitis C vaccine.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Symptoms Of Having Hepatitis C
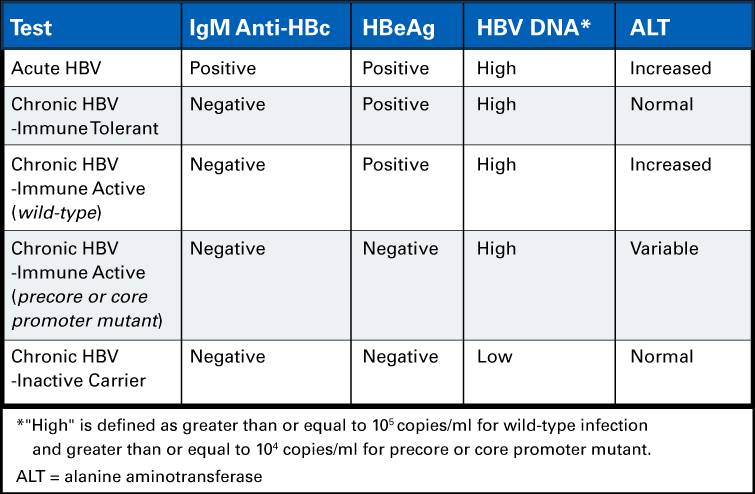
Laboratory Studies For Evaluation Of Initial Infection
The key laboratory studies utilized in the evaluation of possible acute hepatitis C are HCV RNA, anti-HCV, and alanine aminotransferase . Patients who become infected with hepatitis C virus typically develop abnormal laboratory findings in the following order: detectable HCV RNA, followed by elevation in ALT, and then anti-HCV . Patients who develop a clinical illness with acute HCV infection usually have onset of symptoms well after the onset of viremia, but soon after or concomitant with increases in ALT levels.
HCV RNA
Antibodies to HCV
Antibodies to HCV typically become detectable at about 50 to 60 days after infection the detection of HCV-specific antibodies significantly lags behind detectable HCV RNA levels. After 12 weeks, more than 90% of patients will have a positive HCV antibody test. The time period from initial infection until seroconversion is often referred to as the serologic window period . The use of only an HCV antibody test to diagnose acute HCV is not reliable, since only approximately 50 to 70% of patients have detectable HCV antibodies at the onset of symptoms. Further, a positive HCV antibody test does not differentiate acute from chronic HCV infection.
Hepatitis C Core Antigen
Dont Miss: How Can Someone Contract Hepatitis C
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a form of Hepatitis which is transmitted through the exposure to blood and blood products contaminated with the particular virus.
The most common methods of Hepatitis C transmission includes,
- Blood and blood product transfusion
- Contamination with infected injections during invasive medical procedures
- Unprotected sexual intercourse
- Intravenous drug users
Patients with Hepatitis C, in general, will suffer from fever, fatigability, weakness, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, joint pains and signs of jaundice .
Diagnosed as either acute or chronic Hepatitis C with relevant clinical signs and serological investigations, this condition is mainly treated with Antiviral medicines, which is known to be effective in 90% of affected individuals.
Don’t Miss: What Can Hepatitis C Do To You
Can Hepatitis C Be Cured
Yes, you are considered cured if the hepatitis C virus is not detected when measured with a blood test three months after youve completed treatment. This is called a sustained virologic response and data suggest that you will stay virus free indefinitely. And with newer drugs coming to market, cure rates of up to 90% have been seen in patients with hepatitis C.
Even more important sustained virologic response has been associated with lower rates of liver cancer, cirrhosis and all-cause mortality. This means that getting rid of hepatitis C allows individuals to live longer lives.
Cdc Case Definition For Acute Hcv
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has established criteria for the 2020 case definition of acute Hepatitis C. This definition utilizes clinical criteria, laboratory criteria for diagnosis, criteria to distinguish a new case from an existing case, and a case classification . The following summarizes the 2020 CDC Case Definition for Acute HCV.
Don’t Miss: Royal Canin Hepatic Wet Dog Food
What Is Chronic Hepatitis C
Chronic hepatitis C is an infection that lasts more than 6 months. This means that you havent been able to suppress the infection to undetectable levels by medication or your immune system. Many people who have chronic hepatitis C likely were not diagnosed with the infection when it was in the acute stage.
When To Seek Medical Advice
See your GP if you persistently have any of the later symptoms listed, or if they keep returning. They may recommend having a blood test that can check for hepatitis C.
Read more about diagnosing hepatitis C
None of these symptoms mean you definitely have hepatitis C, but it’s important to get them checked out.
You should also speak to your GP about getting tested if there’s a risk you’re infected, even if you don’t have any symptoms. This particularly includes people who inject drugs or have done so in the past.
Read about the causes of hepatitis C for more information about who’s at risk of having the infection.
Page last reviewed: 27 October 2021 Next review due: 27 October 2024
Don’t Miss: Hep Forte Hepatic Lipotropic Nutritional Support
Recommended Testing For Diagnosing Acute Hcv Infection
RECOMMENDED RATING HCV antibody and HCV RNA testing are recommended when acute HCV infection is suspected due to exposure, clinical presentation, or elevated aminotransferase levels . I, C
Recommendations for HCV testing are also found in the Testing and Linkage to Care section.
Diagnosis of acute HCV infection enables estimation of annual incidence rates and transmission patterns, thereby facilitating implementation and assessment of prevention programs. At the individual level, a diagnosis of acute infection expedites linkage to care, counseling regarding high-risk behavior, and timely interventions to reduce virus transmission and liver disease progression . Some persons involved in high-risk behaviors practice serosorting, defined as using HCV antibody serostatus to determine whether to engage in high-risk behaviors with certain individuals . Thus, undiagnosed acutely infected persons may be at greater risk of transmitting HCV to their presumably seronegative contacts than would be expected by chance.
The best laboratory evidence to support a diagnosis of acute HCV infection is a positive HCV RNA test in the setting of a negative HCV antibody test , or a positive HCV antibody test after a prior negative HCV antibody test . There are rare instances in which these approaches may be misleading, such as in immunosuppressed individuals with impaired antibody production .
Discrete Exposure
Also Check:
Criteria To Distinguish A New Case From An Existing Case
All jurisdictions are encouraged to track negative HCV viral detection tests to document both spontaneous clearance of infection or sustained viral response to HCV treatment. Cases that have evidence of having cleared the infection at time of initial report or are considered false positive should not be reported to CDC.
Acute cases determined via anti-HCV test conversion do not need to have a positive HCV viral detection test reported to be considered confirmed acute cases.
A new probable acute case may be reclassified as confirmed acute if a positive HCV viral detection test is reported in the same reporting year .
Collection of risk history data is recommended for probable and confirmed acute HCV cases. Timing of risk history data to collect ranges from 2 weeks to 12 months prior to symptom onset or diagnosis. The time frame to employ depends on the method of classification .
If evidence indicating resolution of infection is received after a confirmed acute case has been reported to CDC, the case report does not need to be modified as it was a confirmed case at the time of initial report. However, negative HCV viral detection test results received on confirmed acute case, subsequent to an initial positive result, should be appended to case reports, as feasible, and considered for the purpose of data analysis by each jurisdiction.
You May Like: Antibody Titer Test For Hepatitis B