Incidence Rates Of Hcc In The Etv And Tdf Groups
Figure 3 shows the cumulative incidence rate of HCC. Like LC-related complications, the cumulative incidence and annual incidence of HCC were analyzed only in the ETV and TDF groups due to the short duration of TAF treatment. Annual incidence rate of HCC was 0.552 per 100-person years in the ETV group and 0.299 per 100-person years in the TDF group. This difference between groups was not significant .
Fig. 3.
Cumulative incidence rates of hepatocellular carcinoma. ETV, entecavir TDF, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate.
HCC occurred in 10 of the 163 ETV-treated patients , 3 of the 154 TDF-treated patients , and no TAF-treated patient during the follow-up period. However, these differences among groups were not statistically significant .
Who Should Not Take Tenofovir
Anyone who is allergic to tenofovir shouldn’t take this drug. Also, it’s important to know your HIV status because taking tenofovir can significantly complicate treating HIV. If you have HIV and HBV, do not start therapy for either infection without consulting a physician experienced in treating both infections.
Tenofovir is generally recognized as safe for use during pregnancy, as there is no evidence to suggest it is harmful to a pregnant mother or her fetus.
What Are The Differences Between Tdf And Taf
December 22, 2019 | Firm News,Mass Torts
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is an antiretroviral medication approved in 2001 to prevent and treat HIV, and in 2008 to treat chronic hepatitis B. Tenofovir alafenamide is a new and improved formulation of tenofovir, approved in 2015. Although TDF is the most commonly prescribed ARV, it presents several safety concerns.
You May Like: Is There Any Treatment For Hepatitis B
Treating Hepatitis B With Tenofovir
Violetta Shamilova, PharmD, is a board-licensed pharmacist. She is an assistant professor at the Touro College School of Health Sciences, and has worked at CVS pharmacy for five years. She completed the certified APhA Delivering Medication Therapy Management Services course.
Tenofovir, also called tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, is an antiviral drug for treating chronic hepatitis B in adults and children who are 12 years and older. It is also used, in combination with other drugs, to treat the human immunodeficiency virus or HIV. It’s sold under the brand name Viread by Gilead Sciences, Inc.
Safety And Efficacy Of Etv And Tdf At 48 Weeks
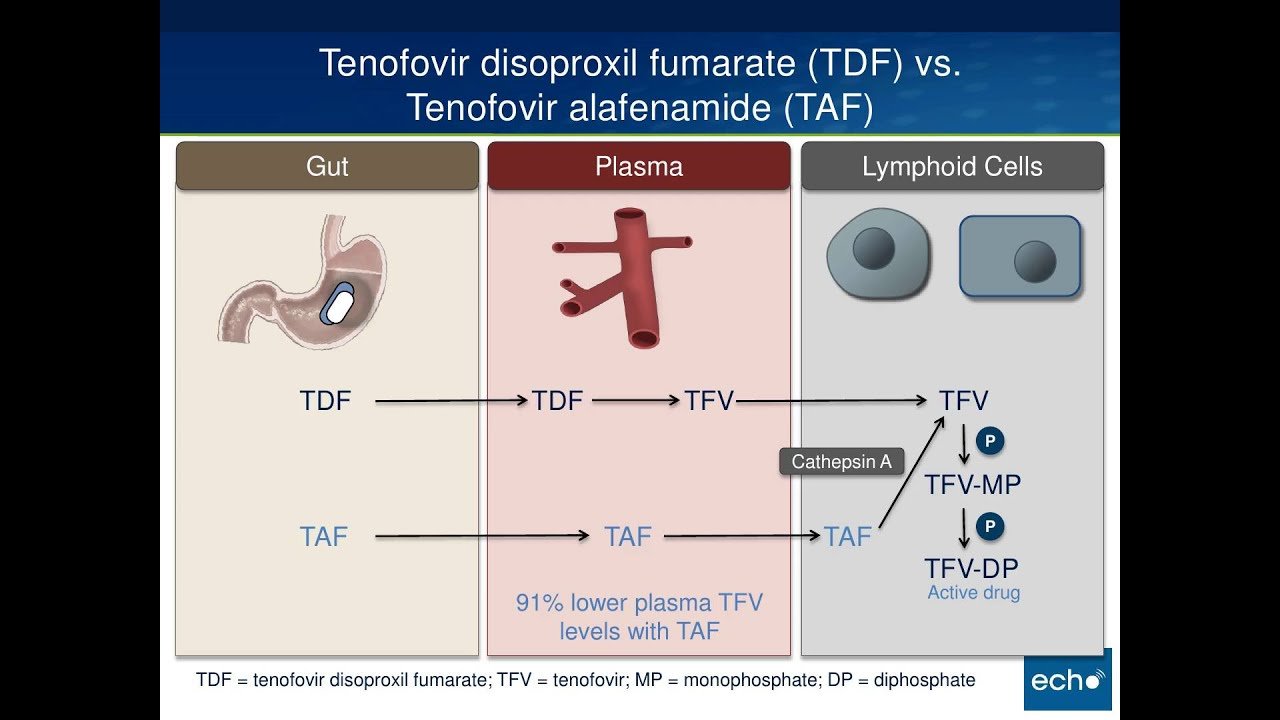
At 48 weeks after ETV or TDF administration, cholesterol increased by 6 mg/dL in the ETV group and decreased by 10 mg/dL in the TDF group . However, there were no significant differences in changes in ALP, eGFR, or LC complications between these 2 groups . Differences in HBeAg seroconversion, CVR, and ALT normalization were not significantly different between the ETV and TDF groups, indicating that these 2 drugs had similar efficacy .
Table 3.
Safety and efficacy of ETV and TDF at 48 weeks
Read Also: Hepatitis B Viral Load Quantitative
Population And Baseline Characteristics
A total of 701 patients with CHB who were treated with ETV, TDF, or TAF were identified . We excluded 338 patients who were treated with antiviral agents for < 48 weeks , had their prescription changed or stopped taking the drug , had incomplete electronic medical records , had low-level viremia at baseline , or were diagnosed with CKD . A total of 363 patients were therefore enrolled in the study. Baseline characteristics and laboratory characteristics of these patients are shown in Table 1.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of the ETV, TDF, and TAF treatment groups
Fig. 1.
Flowchart of participant enrollment. CHB, chronic hepatitis B ETV, entecavir TDF, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate TAF, tenofovir alafenamide CKD, chronic kidney disease.
Median age of patients was 51 years and 66.4% of patients were male. There were some differences among the 3 groups. Median duration of treatment with ETV, TDF, and TAF was 75.0 months , 43.0 months , and 13.0 months , respectively . There were also significant differences in the number of patients previously treated with NAs. The proportion of NA naive patients was 93.3, 73.4, and 78.2% in the ETV, TDF, and TAF groups, respectively .
Safety And Efficacy Of Etv And Taf At 48 Weeks
Table 4 shows the results of laboratory parameters used to assess the safety of ETV and TAF. There were no differences between these 2 groups in cholesterol, ALP, or creatinine levels, or the incidence of LC complications. In terms of efficacy, there were no differences in HBeAg seroconversion, CVR, or ALT normalization between the 2 groups .
Table 4.
Safety and efficacy of ETV and TAF at 48 weeks
Don’t Miss: Interferon Treatment For Hepatitis C
Treatment Of Chronic Hbv Infection With Nucleoside Analogs In Asia: Current Challenges
All three NAs with high barrier against HBV resistance, ETV, TDF, and TAF, recommended by the key guidelines, have been clinically proven to be effective and safe for the treatment of chronic HBV infection and HBV-related cirrhosis. A systematic review and meta-analysis of 20 studies comparing the efficacy of ETV versus TDF in chronic HBV patients reported a significant difference in viral suppression and improvement of liver function, in favor of TDF in the short term at 3 months. This difference, however, did not persist in the long term and in patients with HBV-related cirrhosis . Both ETV and TDF have been clinically proven to be effective in the long term for the treatment of patients with chronic HBV infection, including those who relapsed after PegIFN therapy . Further, ETV has also been found to be effective in patients with chronic kidney disease, including those on hemodialysis, without affecting the renal function . There is also an abundance of literature supporting the efficacy of safety of TAF for the treatment of HBV-infected patients, which will be discussed in detail, in the following sections.
Limitations of Entecavir
In addition to LAM-refractory patients, ETV resistance has also been found to develop in LAM-exposed patients, with no prior LAM resistance, thus highlighting the need for close monitoring of patients treated with ETV, irrespective of the presence or absence of LAM resistance .
Limitations of TDF
Patients Treated With Tdf Are Older With More Liver Fibrosis Compared To The Untreated Group At Baseline
We compared baseline characteristics for individuals treated with TDF vs. non-treated . There was no significant difference in the length of follow-up between the two groups . Treated patients were significantly older than those untreated , and more were male . As expected, based on stratification for treatment using national guidelines , patients treated with TDF were more likely to have raised ALT , higher HBV DNA VL , and higher elastography scores at baseline. However, there was no difference in baseline renal function, based either on eGFR, urea or creatinine.
Read Also: What Are The Early Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Safety And Efficacy Of Taf And Tdf At 48 Weeks
Cholesterol decreased by 10 mg/dL in the TDF group and increased by 5.50 mg/dL in TAF group from baseline, which showed a significant difference between the 2 groups . Table 5 shows the efficacy of TAF and TDF in CHB patients at 48 weeks. There were no differences between the 2 groups in HBeAg seroconversion, CVR, or ALT normalization .
Table 5.
Safety and efficacy of TAF and TDF at 48 weeks
Across Multiple Studies Vemlidy Demonstrated Powerful Antiviral Efficacy With No Known Resistance1
Pivotal trials 108 & 110 design
The efficacy and safety of VEMLIDY 25 mg once daily in the treatment of CHB in adults with compensated liver disease were evaluated in 2 randomized, double-blind, active-controlled, noninferiority trials: Trial 108 and Trial 110 .1,2,4,a
The primary efficacy endpoint for both trials was the proportion of patients with plasma HBV DNA levels below 29 IU/mL at Week 48. Additional efficacy endpoints evaluated at Week 48, Week 96, and Week 144 for both studies include the proportion of patients with HBV DNA < 29 IU/mL, alanine aminotransferase normalization, and hepatitis B surface antigen loss and seroconversion. Hepatitis B envelope antigen loss and seroconversion were also assessed in Trial 110.1,2,4,6 In the original protocol, patients were randomized to VEMLIDY or TDF 300 mg once daily in the double-blind phase for 96 weeks, followed by an open-label VEMLIDY phase through Week 144.6 The original protocol was amended to extend the double-blind phase from 96 weeks to 144 weeks, followed by an open-label phase through Week 384.7 However, before implementation of the amendment protocol, 540 patients entered the open-label phase at Week 96 .b At Week 144, all 1,137 remaining HBeAg and HBeAg+ patients entered the open-label VEMLIDY phase for an extension trial that is still ongoing.8
aKey inclusion criteria: HBV DNA > 20,000 IU/mL ALT > 60 U/L for men and > 38 U/L for women .3,4
Read Also: Hepatitis C Symptoms Mayo Clinic
Rationale And Methodology For Development Of The Current Expert Opinion
Considering the challenges pertaining to the high prevalence, morbidity and mortality of HBV infection, and low rates of treatment with antiviral agents in Asia, along with limitations of ETV and TDF and advantages of TAF over other antiviral agents, a panel of 28 expert hepatologists from Asia convened, reviewed the literature, and developed the current expert opinion-based review article for the use of TAF in the resource-constrained settings in Asia. The recommendations proposed in this article are based on the existing clinical evidences and the expert opinion shared by the panel.
Study Design And Participants
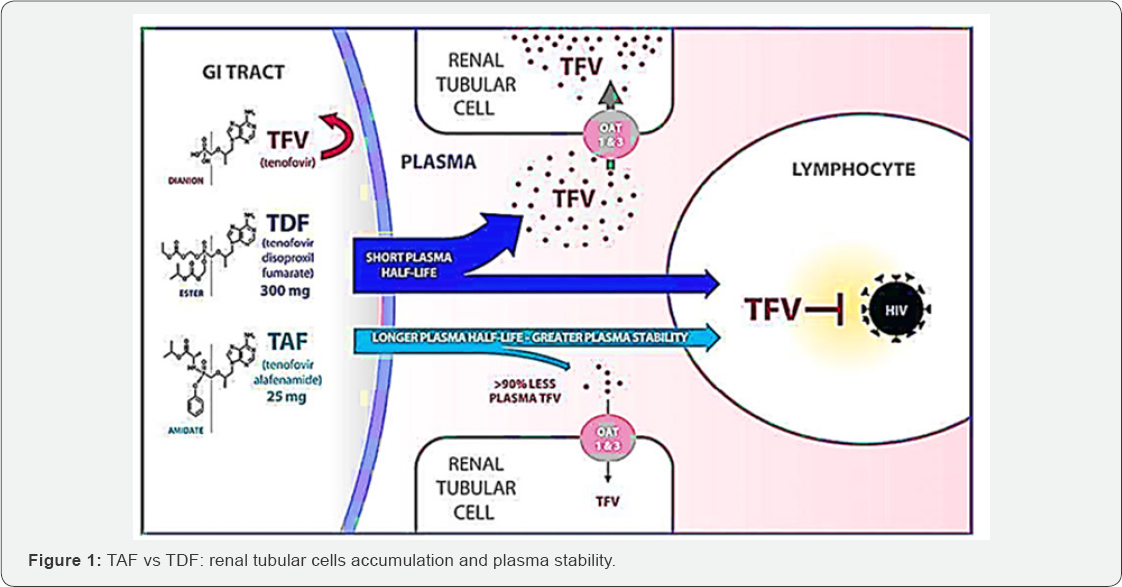
From January 2019 to December 2019, consecutive HBV-related ACLF patients treated with TAF, TDF or ETV monotherapy in the First Affiliated Teaching Hospital of Xian Jiaotong University, the biggest general hospital in northwest China under the direct administration of the Chinese Ministry of Health, were recruited in this study. The inclusion criteria were: age 1870years Hepatitis B surface antigen positive6months ACLF was diagnosed according to the diagnostic criteria recommended by the Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver . Patients were excluded if they had any of the following conditions: concomitant hepatitis A, C, D, E virus, or other hepadnaviruses infections malignancies, such as hepatocellular carcinoma with one or more additional known primary or secondary causes of liver disease, other than hepatitis B.
During hospitalization, antiviral therapy with TAF, TDF or ETV was started immediately when HBV-DNA was tested positive. Adverse side effects were carefully monitored during the study period. All patients were given standard medical treatment, including absolute bed rest, supportive care, energy supplements and vitamins. Therapeutic plasma exchange or double plasma molecular absorption system were administered for patients at doctors discreet decision.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis B Antibody
Tenofovir Alafenamide Effective Against Hepatitis B Reactivation
Serum HBV DNA significantly decreased from week 0-24 in patients treated with entecavir.
Both tenofovir alafenamide and entecavir are safe and effective at treating hepatitis B virus reactivation.
A team, led by Kento Inada, Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Musashino Red Cross Hospital, examined the efficacy and safety of TAF for hepatitis B virus reactivation.
Incidence Of Significant Renal Impairment In The Etv Tdf And Taf Groups At 48 Weeks
We defined significant renal impairment as more than 30% reduction in eGFR at endpoint compared to baseline. 4.3% of patients in the ETV group, 2.6% in the TDF group, and 0% in the TAF group had an eGFR reduction of more than 30%. These differences in significant renal impairment were not statistically significant .
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Surf Ab Quant 3.1
Demographic And Clinical Baseline Characteristics Of The Study Population
We screened 125 ACLF patients during this period, and 88 HBV-related ACLF people were identified. The following patients were excluded:1 patient was treated with lamivudine, 4 patients with combination treatment of two antiviral agents, 10 received 1.0mg entecavir daily and 3 died within 2days after admission. Finally, gender and age matched 10 patients with TAF, 10 with TDF and 20 with ETV treatment were enrolled . They were prospectively followed-up regularly till death or end of the study.
Fig. 1
Patient disposition during the study. ACLF, acute-on-chronic liver failure LAM, lamivudine ETV, entecavir TDF, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate TAF, tenofovir alafenamide
The primary baseline demographics and disease characteristics were summarized in Table . There were no significant differences among three groups in the baseline characteristics of age, gender, serum ALT, AST, WBC, PLT, albumin, urea, creatinine, sodium, eGFR, HBV DNA viral load, CTP score, MELD score, and complications.
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of the study population
Medications Subjected To Litigation
Gilead is facing litigation for the following types of TDF medications:
- Truvada: the original TDF medication.
- Viread: also goes by the name Tenofovir DF and is used to treat Hepatitis B and HIV.
- Atripla: also goes by the name Efavirenz. It is not used for prevention, but only as HIV treatment.
- Complera: also goes by the name Rilpivirine. It is not for prevention, but only as HIV treatment.
- Stribild: also goes by the names Elvitegravir, Cobicistat, and Emtricitabine. It is not for prevention, but only as HIV treatment.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C How Is It Contracted
Weeks Treatment Of Tenofovir Alafenamide Vs Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate For Hepatitis B Virus Infection
- Kosh AgarwalCorrespondenceCorresponding authors. Addresses: Kings College Hospital, London, United Kingdom , or The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong .
- Toronto Western Hospital, Toronto, ON, CanadaErasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, The Netherlands
- Henry L.Y. ChanCorrespondenceCorresponding authors. Addresses: Kings College Hospital, London, United Kingdom , or The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong .
- TAF is a new prodrug of tenofovir developed to treat patients with chronic HBV.
- A lower dose of TAF can be used because it delivers tenofovir more efficiently to hepatocytes than TDF.
- At week 48, TAF had non-inferior efficacy to TDF with improved renal and bone safety.
- Efficacy and safety results at week 96 confirm the 48-week results in both studies.
Treatment Of Chronic Hbv Infection: Current Guideline Recommendations
Currently, two main strategies are available for the treatment of chronic HBV infection: Pegylated interferon- and nucleoside analogs . The high variability of response and unfavorable safety profile limit the use of PegIFN . Treatment of chronic HBV-infected patients with NAs may be a preferred option to PegIFN to achieve safe, sustained, and potent antiviral suppression . Among NAs, while lamivudine , adefovir dipivoxil , and telbivudine represent a class of NAs with a low barrier against HBV resistance, entecavir , tenofovir disoproxil fumarate , and tenofovir alafenamide may be classified as NAs with a high barrier against HBV resistance .
The 2017 guidelines from the European Association for the Study of the Liver recommend ETV, TDF, or TAF as the preferred first-line monotherapy options for the management of all adults with chronic HBV infection. Additionally, EASL recommends the following guidelines for treatment for HBV infection:
Also Check: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis C Virus
Emtricitabine And Tenofovir Alafenamide Vs Emtricitabine And Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate For Hiv Pre
- The Fenway Institute, Fenway Health, Boston, MA, USADepartment of Medicine, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- Peter L AndersonAffiliationsDepartment of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Colorado, Aurora, CO, USA
- Moupali DasCorrespondenceCorrespondence to: Dr Moupali Das, Department of HIV and Emerging Viral Infections Clinical Research, Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA 94404, USA
- Amanda ClarkeAffiliations
- C Bradley HareAffiliations
What Is Tdf And How Does It Work
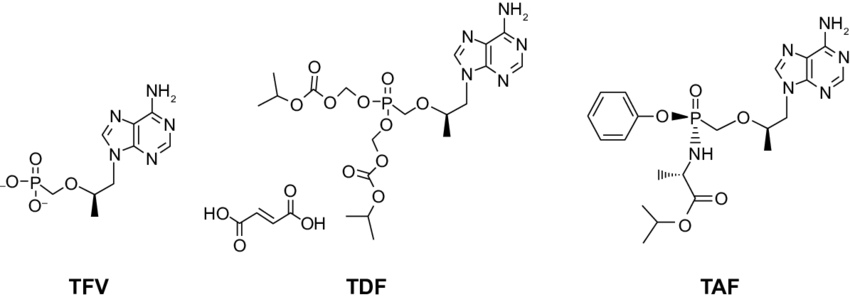
TDF, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, is a drug used to help individuals treat, and prevent or reduce the chances of contracting HIV. When used as a preventative method, doctors refer to it as pre-exposure prophylaxis or PrEP. It is also used as treatment for hepatitis B infections. The drug works by blocking the pathways that viruses use to spread infection. HIV, for example, attacks the immune cells that help your body fight infections. Therefore, TDF can possibly prevent that from occurring or slow the spread of the disease, if the medication is already in the bloodstream. TDF is marketed under the names Truvada, Atripla, Complera, Stribild, and Viread by a manufacturer named Gilead Sciences.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Dose For Newborns
Comparison Of Lc Complications Between The Etv And Tdf Groups
Cumulative incidence of LC-related complication requiring hospitalization is shown in Figure 2. Because the median duration of treatment in the TAF-treated group was 13.0 months, cumulative incidence, and annual incidence were analyzed only in the ETV and TDF groups. Annual incidence rate of LC-related complication was 0.601 per 100-person years in the ETV group and 0.299 per 100-person years in the TDF group, which was not a significant difference .
Fig. 2.
Cumulative incidence rates of complications associated with liver cirrhosis. ETV, entecavir TDF, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate.
During the follow-up period, 11 patients in the ETV group needed hospitalization due to LC-related complications 3 due to varices, 3 due to variceal bleeding, 3 due to ascites, 1 due to spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, and 1 due to hepatic encephalopathy. Three patients in the TDF group were hospitalized due to complications: 2 with variceal bleeding and 1 with hepatic encephalopathy.
Data Collection And Definition
Data were collected from electronic medical records at the Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong and included clinical information, and laboratory data. Medical history, such as LC, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, history of taking lipid-lowering agents, tuberculosis, malignancy, chemotherapy, and immunosuppressive therapy was included in the demographic data. Patients underwent routine blood chemistry test and virological assessments, including hemoglobin, platelets, international normalized ratio of prothrombin time, liver function tests, serum HBV-DNA level, and status of HBeAg every 36 months. According to our outpatient protocol, patients were also followed up every 612 months with ultrasonography and serum alpha-fetoprotein level to screen for HCC.
We calculated eGFR using the modification of diet in renal disease GFR equation as 186 × 1.154 × 0.203 × 1.212 × 0.742 . HBV DNA was measured by a quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay, and CVR was defined as an HBV DNA level below 20 IU/mL. Diagnosis of LC was clinically defined taking into account platelet count, serum albumin level, prothrombin time, international normalized ratio, and radiological image findings included splenomegaly and liver surface nodularity. Endoscopic findings such as esophageal or gastric varices were considered in the diagnosis of LC.
You May Like: How Can Someone Contract Hepatitis C