Hepatitis B Vaccine And Surface Antibody Titer Faqs
PLEASE NOTE: This is program specific some programs require 3 Hepatitis B vaccines AND a positive Hepatitis B Surface Antibody titer while others will accept 3 vaccines OR a titer. Please read the information in your CastleBranch account carefully so that you know exactly what you need to meet your programs requirements. If you have any questions, please email and a team member will respond.
Why Choose Us For Your Hepatitis B Titer
- Since 2002, we have a proven track record of offering excellent customer service, affordable pricing with no hidden fees, and our enduring commitment to protect your personal information.
- No doctor’s order? Our national physician network provides the required doctor’s order for the lab. Insurance is not needed to order lab testing nor will your insurance company be billed.
- We are partnered with two of the largest CLIA certified labs in the US, to offer you the latest lab testing technology with prompt and accurate results.
- With over 3,600 lab locations to choose from and same day collection, we make lab testing quick and convenient. No appointment is needed. Find your local lab with our location finder.
- We offer an extensive and detailed test menu. Ordering can be done online or over the phone. Not finding a test? Simply give us a call.
Prevalence Of Hbv Infection
Data from 5655 children were analyzed. Five children had positive HBsAg test results. All 5 children had negative HBsAb titers and each of their mothers was a confirmed HBV carrier. HBV infection had previously been confirmed in 2 of the 5 children , but was newly identified in the other 3. Of the 3 newly confirmed cases, one patient was lost to follow-up, one had advanced disease and was attending on-going follow-up evaluations, and one patient, confirmed to be in the replication phase with immune clearance, had been receiving treatment for 1 year. Of these children, 2 were in the 1-year-old group, while the other children were in the 2-year-old, 3-year-old, and 9-year-old groups.
You May Like: Hepatic Steatosis Treatment Step By Step
Question 1 What Is The Clinical Indication For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quantitation
Hepatitis B surface antibody quantitation is used to determine hepatitis B immune status, ie, to determine if the patient has developed immunity against the hepatitis B virus. Such immunity may develop following exposure to the hepatitis B virus or its vaccine.
Patients at higher risk of exposure to the virus include:
- Infants born to infected mothers
- Sex partners of infected persons
- People with more than 1 sex partner in the last 6 months
- People with a history of sexually transmitted infection
- Men who have sex with men
- Injection drug users
- Household contacts of an infected person
- Healthcare and safety workers who have contact with blood and body fluids
- People who have lived or traveled in an area in which hepatitis B is common
- People who live or work in a prison
Testing is not recommended routinely following vaccination. It is advised only for people whose subsequent clinical management depends on knowledge of their immune status. These people include:
- Chronic hemodialysis patients
- Immunocompromised people, including those with HIV infection, hematopoietic stem-cell transplant recipients, and people receiving chemotherapy
- Infants born to women who test positive for the hepatitis B surface antigen
- Sex partners of people who test positive for the hepatitis B surface antigen
- Healthcare and public safety workers who have contact with blood or body fluids
Characteristics Of The Patient Group
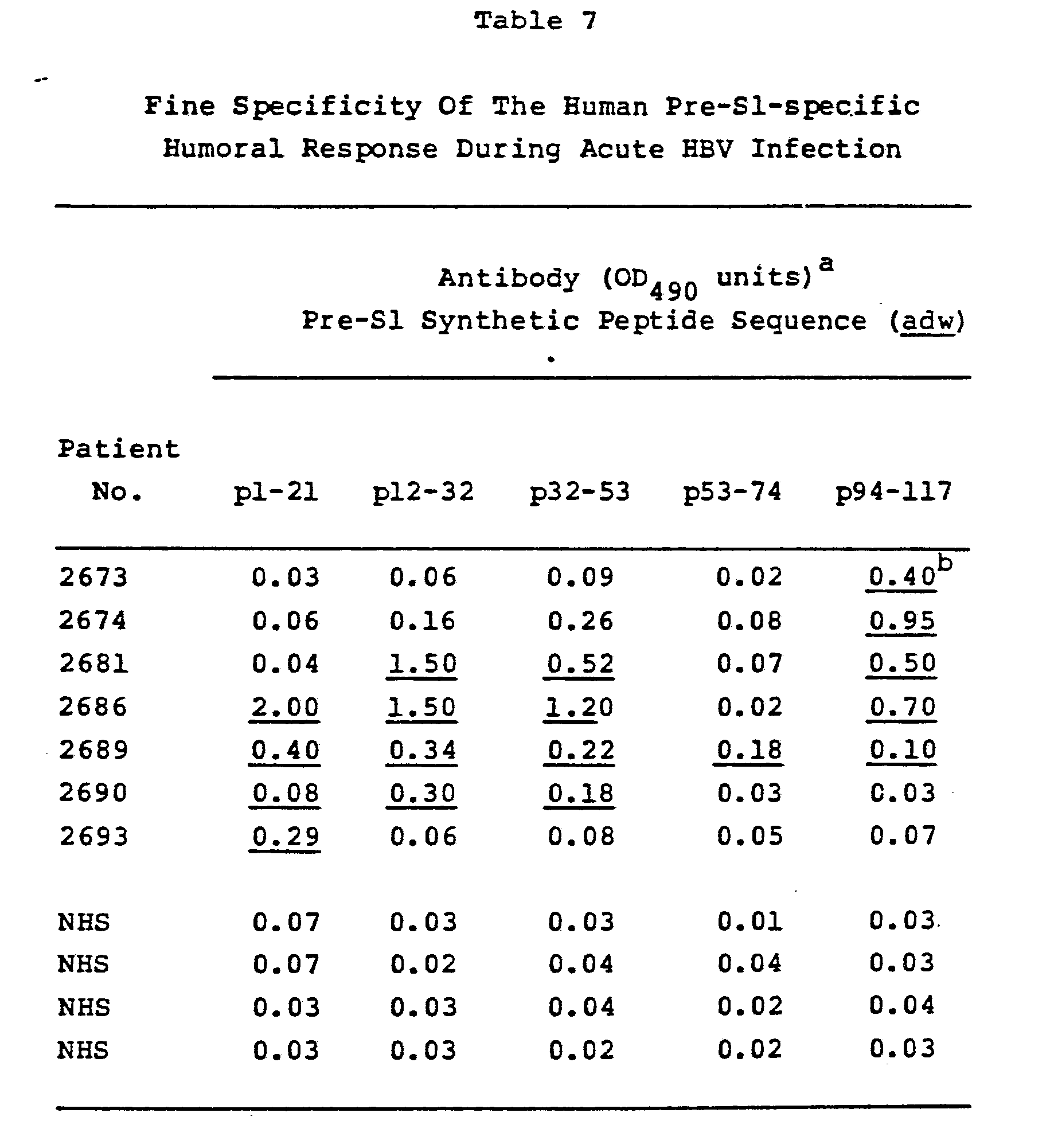
Of the 5650 confirmed HBsAg-negative children , 1909 had positive HBsAb titers, 2262 had weakly positive titers, and 1479 had negative titers . Among the boys, 1063 had positive HBsAb titers, 1189 had weakly positive titers, and 761 had negative titers. The corresponding figures among the girls were 846 , 1073 , and 718 , respectively.
Table 1 Characteristics of the children according to hepatitis B antibody titer
The overall mean age of participants was 48.2 months. The mean ages of children with positive, weakly positive, and negative HBsAb titers were 25.1 months, 46.4 months, and 80.71 months, respectively. Older age was significantly associated with having a negative HBsAb titer . A cross-tabulation analysis demonstrated a slight male preponderance in the antibody-positive group and a slight female preponderance in the antibody-negative group this difference was statistically significant . The differences between the groups in terms of mean age and aspartate aminotransferase level were also statistically significant . However, in the case of AST, the higher the age, the lower the average tended to be, but the result was derived. When we calculated the average of AST/ALT for those < 5 years old and those 5 years old, only AST was significantly higher in those < 5 years of age . Since positive group is younger, AST seems to have come out more meaningfully higher.
Read Also: Causes Of Hepatitis B And C
When Should I Get Hepatitis B Testing
Using hepatitis B tests to screen for HBV is recommended for certain groups that are at an increased risk of infection. Groups that may benefit from hepatitis B screening include:
- Pregnant people
- People born in parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, including Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, South America, and parts of the Middle East
- People who didnât receive a hepatitis B vaccine
- HIV-positive people
- Pain in the joints or abdomen
- Loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- Yellowish skin and eyes
Using hepatitis B testing to assess immunity to HBV may be used before or after vaccination. Pre-vaccination testing is not always needed but may be performed if there is a chance that a patient has previously been infected with HBV or has already been vaccinated. Post-vaccination testing is used in certain groups of people who are at an especially elevated risk for HBV infection, including infants born to mothers with a hepatitis B infection.
How Much Does The Test Cost
The cost of hepatitis B testing depends on the tests that are performed, where the test is conducted, and a patientâs health insurance coverage. When testing is ordered by a doctor, patients with health insurance may find it helpful to discuss the cost of testing with their health insurance company as they may be responsible for testing costs as well as other out-of-pocket costs such as copays and deductibles.
For patients without health insurance or for whom insurance doesnât cover the cost of testing, it may be helpful to discuss the cost of hepatitis B testing with a doctor or hospital administrator.
The cost of at-home hepatitis B testing starts around $45. At-home test kits may also test for additional types of viral hepatitis in the same sample. The cost of test panels that look for more than one type of viral hepatitis start around $80.
Don’t Miss: Signs You Have Hepatitis B
What Is The Normal Range For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are measured in blood samples in milli-International Units/milliliter mIU/mL). The ranges for hepatitis B surface antibodies are:
- Anti-HBs greater than 10-12 mIU/mL: Protected against hepatitis B virus infection, either from vaccination or successful recovery from a previous HBV infection.
- Anti-HBs less than 5 mIU/mL: Negative for HBV infection, but susceptible and hence requires vaccination.
- Anti-HBs from 5-12 mIU/mL: Inconclusive results and the test should be repeated.
However, there is no standardization of these values so it is advisable to check the manufacturers values it is the reason values are mainly reported as positive or negative.
Negative But Other Hepatitis Tests Are Positive
Your HBsAb test may be negative even when other hepatitis B tests are positive, showing active or chronic infection. Further testing is necessary, especially for the hepatitis B surface antigen , which shows that the virus itself is circulating in your bloodstream and that you have an active or chronic infection.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Catch Hepatitis B
What Does The Test Measure
Hepatitis B testing looks for antigens, antibodies, or the genetic material of the hepatitis B virus. HBV antigens are substances from the virus that cause a patientâs body to produce an immune response. Antibodies are substances made by the immune system in response to the hepatitis B virus.
Initial tests for hepatitis B measure antibodies and antigens related to HBV including:
If a patient is diagnosed with hepatitis B based on these initial tests, additional hepatitis B testing may be used to monitor the disease, guide treatment, and determine if a person can spread hepatitis B to others. These additional tests may include:
- Hepatitis B e antigen : Hepatitis B e antigen is a protein from the hepatitis B virus found in some patients who are positive for hepatitis B surface antigen. Measuring this antigen can help doctors understand infectivity, which describes a personâs ability to spread HBV to others.
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Blood Test
This test is used to determine the status of a persons immunity to the Hepatitis B virus . Immunity is determined by screening for antibodies which provide protection against infection. The results of this test are quantitative.
Hepatitis B is a viral infection of the liver spread through contact with contaminated bodily fluids including blood. Transmission can occur through various types of exposure including sexual contact. It is possible for a pregnant woman to spread the infection to her infant during childbirth. More than half of Hep B infections display no symptoms. When symptoms do occur, the most common are loss of appetite, fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, jaundice, and dark colored urine. Chronic Hepatitis B infections may lead to the development of Cirrhosis or Liver Cancer.
A person can have immunity to Hepatitis B for several reasons.
1.) They have been vaccinated for Hep B. Vaccinations do not always provide permanent immunity. It is possible for a person to have been vaccinated and lose their immunity over time.
2.) They have been infected with Hep B, recovered, and now have a natural immunity. Because Hepatitis B does not always display symptoms, it is possible for a person to have been exposed and not be aware of it.
A person who wishes to screen for a current Hepatitis B infection may want to order the Hep B Surface Antigen test.
The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody test typically sees results in 1 business day.
Detection Period:
Recommended Reading: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis B Virus
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis B testing is typically prescribed by a doctor and performed in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Taking a hepatitis B test requires a blood sample, which can be collected by a health care professional.
For laboratory-based testing, blood is drawn from a patientâs vein. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
The Immunological Effect Of Booster Vaccination In Non
To confirm the efficacy of booster HBV vaccination in non-responders and low-responders, we evaluated 33 subjects at 1 year after booster vaccination and 10 subjects at 2 years after booster vaccination. Although the anti-HBs titer increased significantly after booster vaccination, this response was not sustained .
Serial changes in the anti-HB titers of subjects who received a booster vaccination. The vertical axis shows the change in anti-HB titer over time. The horizontal axis shows the indicated time points at which the anti-HB titer was measured at 1 year and 2 years after vaccination. Statistical significance was evaluated using the Friedman test. P values of < 0.05 were considered to indicate statistical significance. n.s.: not significant
Recommended Reading: What Does Non Reactive Hepatitis B Mean
Transmission Symptoms And Treatment
How is HBV transmitted?
HBV is transmitted through activities that involve percutaneous or mucosal contact with infectious blood or body fluids , including
- sex with an infected partner
- injection-drug use that involves sharing needles, syringes, or drug-preparation equipment
- birth to an infected mother
- contact with blood from or open sores on an infected person
- exposures to needle sticks or sharp instruments and
- sharing certain items with an infected person that can break the skin or mucous membranes , potentially resulting in exposure to blood.
How long does HBV survive outside the body?
HBV can survive outside the body and remains infectious for at least 7 days .
What should be used to clean environmental surfaces potentially contaminated with HBV?
Any blood spills should be disinfected using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 10 parts of water. Gloves should be worn when cleaning up any blood spills.
Who is at risk for HBV infection?
The following populations are at increased risk for becoming infected with HBV:
- Infants born to infected mothers
- Sex partners of infected people
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household contacts or sexual partners of known people with chronic HBV infection
- Health-care and public-safety workers at risk for occupational exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- Hemodialysis patients
Who should be screened for HBV?
CDC recommends that the following people be screened for HBV :
- fever,
Does Hepatitis B Show Up In Routine Blood Tests
Routine blood tests do not detect hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B tests are specifically done if blood tests show abnormal liver function results, or if a person experiences symptoms or falls into the high-risk category for HBV infection.
A panel of HBV-specific blood tests are required to detect HBV infection.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis Turn Into Hiv
Can I Take The Test At Home
Samples for hepatitis B testing can be collected at home. At-home hepatitis B testing requires a patient to collect a blood sample, typically from a fingerstick using a very small needle provided in the test kit. Once a blood sample is collected, it is prepared according to the instructions contained in the test kit and mailed to a laboratory for testing.
Because there are numerous types of tests for HBV, it is important to look closely at the specific components of any at-home test kit. Many at-home test kits only look for hepatitis B surface antigen .
About The Hepatitis B Immunity Test
-
What this test is for
The kit tests for hepatitis B antibodies to see whether you are immune. Please note that this is not a test kit for a current hepatitis B infection. The result will tell you whether you have immunity to hepatitis B.
Unsure if you should be purchasing hepatitis B vaccines or an immunity test? Our clinicians can advise you.
-
When to take the test
The test should be done at least 4 weeks after completing a course of hepatitis B injections or at least 4 weeks after a booster injection.
-
How to take the test
You will need to produce a blood sample using a small finger prick device, contained in the kit. You will only need to produce a small amount of blood and it shouldn’t hurt. Full instructions come with the test kit.
You should send your blood sample back to our partner laboratory in the pre-paid envelope provided.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B How Do You Get It
What Is A Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test
Hepatitis B surface antibody test is part of a panel of blood tests to diagnose HBV infection. Hepatitis B surface antibody test determines the presence and quantity of anti-HBs in the blood serum, which can indicate protection from HBV infection.
Hepatitis B disease affects the liver and commonly spreads through body fluids such as blood, semen, and vaginal secretions.
Frequency Analysis Changes In Hbsab Titer With Age
There was a statistically significant difference in the average HBsAb titer between boys and girls , with boys having higher titers than girls. However, this difference was no longer observed when further stratified by age . The positive rate was highest in children < 2 years old, the weakly positive rate was greatest in children aged 24 years old, and the negative rate was highest in children > 5 years. Positive ratios were observed in at least 50% of children up to 16 months of age. Thereafter, < 50% of children demonstrated HBsAb titer positivity .
Table 2 Comparison of the hepatitis B antibody titer according to age and sexFig. 1
Distribution of hepatitis B surface antibody titer group by age group The positive rate was highest in the 0-year-old and 1-year-old age groups and the weakly positive rate was highest in the 2-year-old to 4-year-old age groups the negative rate was highest thereafter. In the most recent 24 months, antibody titer was categorized by month. Positive ratios were observed in at least 50% of children up to 16 months, and in less than 50% thereafter
Fig. 2
Recommended Reading: The Cost Of Hepatitis C Treatment
When And How To Perform Post
Which test to use: If testing is needed following vaccination, use quantitated HBsAb only
- Post-vaccination testing is needed for certain groups who are at especially high risk for HBV infection
- The purpose of post-vaccination testing is to confirm if patients have achieved adequate immune response as measured by hepatitis B surface antibody
- Perform testing 1-2 months after final dose of the HBV vaccine series
- Persons with HBsAb concentrations of > 10 mIU/ml are considered immune
- Post-vaccination testing is recommended for some patients:
- Infants born to HBsAg+ women
- Infants born to women whose HBSAg status remains unknown
- Health care personnel and public safety workers at risk for blood or body fluid exposure
- Hemodialysis patients
- Other immunocompromised persons such as hematopoietic stem-cell transplant patients or persons receiving chemotherapy
- Sex partners of HBSAg+ persons
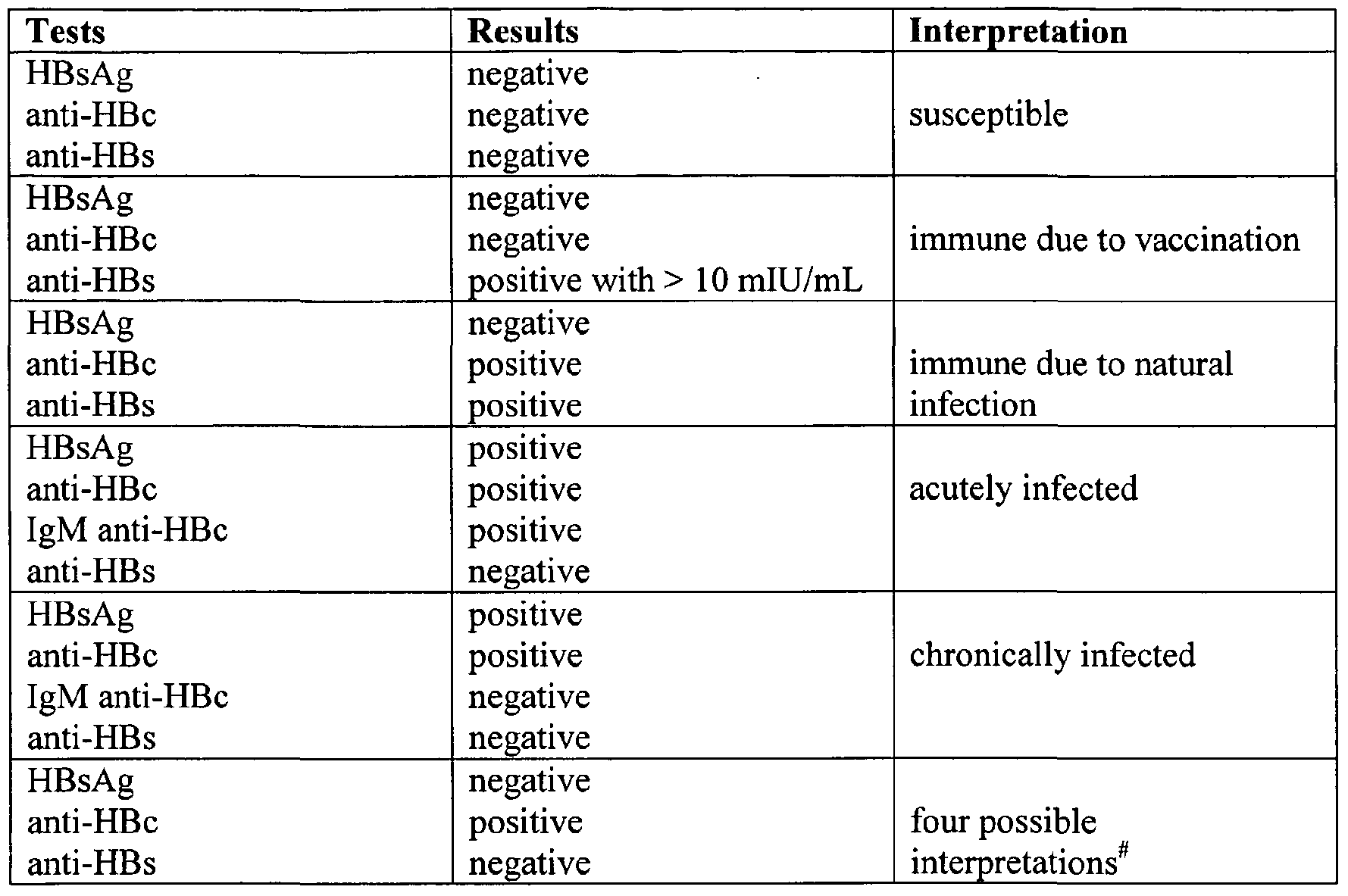
What Is The Purpose Of A Hepatitis B Test
Hepatitis B test is performed to detect, classify, and treat hepatitis B virus infection.
Hepatitis B blood tests involve the measurement of several HBV-specific antigens and antibodies. In addition, HBV blood tests also include liver enzymes and liver function tests to assess and monitor the condition of the liver and provide appropriate treatment.
The HBV specific tests include the following:
- HBsAg: HBsAg is an antigen found on the surface of hepatitis B virus. HBsAg may be detected in the blood any time after 1 week post-exposure to HB virus, but usually appears after 4 weeks.
- Anti-HBs: Anti-HBs are antibodies produced by the bodys immune system to fight HBsAg. Anti-HBs from a prior infection or vaccination provides immunity against further infection.
- Hepatitis B core antigen : HBcAg is an antigen found in the core layer which covers the hepatitis B viral DNA.
- Hepatitis B core antibody : Anti-HBc is the antibody that fights HBcAg. Anti-HBc is the first detectable antibody after HBV infection. There are two kinds of Anti-HBc:
- Immunoglobulin M hepatitis B core antibody : IgM anti-HBc indicates acute or reactivated recent infection within the previous 6 months.
- Immunoglobulin G hepatitis B core antibody : IgG anti-HBc may indicate previous or chronic infection. Once present, IgG anti-HBc persists for a lifetime.
Read Also: Vaccine Available For Hepatitis B