Prognosis Of Persons Diagnosed With Hcc
The overall prognosis for persons diagnosed with HCC in the United States has improved in the past 15 years, but it remains poor, with an overall 5-year survival of approximately 20%. In general, persons who have HCC detected after the onset of symptoms have an even worse prognosis, with an overall 5-year relative survival less than 10%. Symptoms associated with HCC may include abdominal pain, anorexia, early satiety, weight loss, obstructive jaundice, fever, watery diarrhea, and bone pain . In contrast, detection of very early-stage HCC can be cured with an excellent long-term prognosis. Unfortunately, the vast majority of individuals diagnosed with HCC have cancer that is advanced beyond the stage where surgical cure with surgical resection or locoregional ablative therapy is an option.
Stages Of Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus affects people in different ways and has several stages:
- Incubation period. This is the time between first exposure to the start of the disease. It can last anywhere from 14 to 80 days, but the average is 45
- Acute hepatitis C. This is a short-term illness that lasts for the first 6 months after the virus enters your body. After that, some people who have it will get rid of, or clear, the virus on their own.
- Chronic hepatitis C. For most people who get hepatitis C — up to 85% — the illness moves into a long-lasting stage . This is called a chronic hepatitis C infection and can lead to serious health problems like liver cancer or cirrhosis.
- Cirrhosis. This disease leads to inflammation that, over time, replaces your healthy liver cells with scar tissue. It usually takes about 20 to 30 years for this to happen, though it can be faster if you drink alcohol or have HIV.
- Liver cancer. Cirrhosis makes liver cancer more likely. Your doctor will make sure you get regular tests because there are usually no symptoms in the early stages.
Learn more about the stages and progression of hepatitis C.
Evidence Supporting Hcc Screening In Chronic Hepatitis B
The most well-known clinical study to support HCC screening is a cluster-randomized, controlled trial conducted in China that assessed the impact of HCC screening on HCC-related mortality. This study enrolled 18,816 HBV individuals with chronic HBV aged 35 to 59 from 300 factories, businesses and schools in urban Shanghai. Half of these 300 units were randomized to screening using serum alfa-fetoprotein , with cutoff value 20 ng/mL, and ultrasound every 6 months the other arm underwent usual care without screening and were not actively followed. The screening group had only a 58% compliance with screening, but notably had HCC diagnosed at an earlier stage and this group had a lower HCC-related 5-year mortality rate compared with the control group . This study, however, had some methodologic limitations, conferring a high risk for bias. A number of observational cohort studies have since suggested a survival benefit with screening but the quality of this evidence is limited by selection, lead time and length-time biases. There are also several observational trials and reviews involving patients with cirrhosis that have shown surveillance for HCC was associated with earlier-stage tumor detection and improved survival. Despite the suboptimal quality of evidence supporting HCC screening, it is currently the standard of practice and it is unlikely that a rigorously conducted randomized study would take place given the widespread acceptance of screening at this time.
Recommended Reading: What Does Hepatitis C Mean
Do You Need Vaccinations Before Traveling Abroad
The CDC divides travel vaccinations into three categories: 1) routine, 2) recommended, and 3) required. The only vaccine classified as “required” by International Health Regulations is the yellow fever vaccination for travel to certain countries in sub-Saharan Africa and tropical South America.
“Routine” vaccinations are those that are normally administered, usually during childhood, in the United States. These include immunizations against:
- tetanus
Viral Hepatitis Definition And Overview
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Many illnesses and conditions can cause inflammation of the liver, for example, drugs, alcohol, chemicals, and autoimmune diseases. Many viruses, for example, the virus causing mononucleosis and the cytomegalovirus, can inflame the liver. Most viruses, however, do not attack primarily the liver the liver is just one of several organs that the viruses affect. When most doctors speak of viral hepatitis, they are using the definition that means hepatitis caused by a few specific viruses that primarily attack the liver and are responsible for about half of all human hepatitis. There are several hepatitis viruses they have been named types A, B, C, D, E, F , and G. As our knowledge of hepatitis viruses grows, it is likely that this alphabetical list will become longer. The most common hepatitis viruses are types A, B, and C. Reference to the hepatitis viruses often occurs in an abbreviated form The focus of this article is on these viruses that cause the majority of human viral hepatitis.
Hepatitis viruses replicate primarily in the liver cells. This can cause the liver to be unable to perform its functions. The following is a list of major functions of the liver:
Also Check: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Positive
Multivariable And Univariate Cox Regression Models Predicting Hcc Within The Two Years Follow
Table 2 presents an overview of the patients biochemical, clinical, and demographic features with and without HCC.
Table 2 Biochemical, demographic, and clinical characteristics of patients without and with HCC during the follow-up period.
There was no significant difference in total cholesterol, hemoglobin, sex, age, WBCs, serum triglyceride, GGT, INR, serum bilirubin, serum creatinine, CTP classification, MELD score, and eGFR between the two groups . Univariate Cox regression analysis showed that BMI, HOMA-IR, AFP, and AGEs levels are statistically significant between the two groups in Table 3.
Table 3 Cox regression analysis models to predict the development of HCC in the studied patients.
The multivariable Cox regression analysis model outcomes were reassessed after adjusting multiple confounders, applying the formerly described variables at baseline associated with the development of HCC during the two-year follow-up period. This test showed that the only parameters independently related to the development of HCC are AFP and AGEs .
Using the ROC curve, at a cutoff value of > 79.6 ng/ml, AGEs had 100% sensitivity, 96.4% specificity, 0.999 AUC, 100% negative predictive value, 72.2% positive predictive value, and P< 0.001 for prediction of HCC, as presented in Figure 4.
Figure 4 The receiver operating characteristic curve of AGEs in predicting HCC in patients with cirrhosis.
About Hepatitis C Online
Hepatitis C Online is a free educational website from the University of Washington National Hepatitis Training Center. This project is funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention .
This site addresses the diagnosis, monitoring, and management of hepatitis C virus infection.
Free CME credit and CNE/CE contact hours are offered throughout this site. Pharmacology CE for advanced practice nurses is also available for many activities.
Read Also: How To Manage Hepatitis C
Monitoring Of Treatment Efficacy
HCV RNA level was assessed at baseline, at the end of therapy , and 12 weeks after finishing therapy using the Roche COBAS Taq Man HCV assay version 2.0 . Relapse is defined as detectable HCV RNA level during follow-up in a patient with a previously undetected level at the end of the therapy, and virological failure is referred to as nonresponse where HCV RNA levels are still detected at the end of the therapy. The primary virological response was the accomplishment of SVR12, described as the concentration in serum lower than 15 I.U./mL .
The levels of AGEs were measured at the starting point and 12 weeks after finishing therapy.
Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B: A Special Population
- Patients with chronic hepatitis B are at risk of liver cancer even in the absence of cirrhosis
- Ultrasound surveillance is advised every 6 months in the following populations :
- Patients with cirrhosis
- African decent over 20 years of age
- ALL males over 40 years of age
- Asian females over 50 years of age
- In cases of family history of HCC in persons with chronic hepatitis B, surveillance should start 10 years before the age at which the first-degree relative developed HCC
- Persons at a high risk for HCC who live in areas where ultrasound is not readily available, screen with AFP every 6 months
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis C Screening Test
Implementation Of Hcc Screening
In the United States, several potential barriers exist for effective HCC screening in persons with chronic HCV infection have been identified, including unknown fibrosis stage of the individual, lack of clinician awareness of HCC screening guidelines, scheduling logistics, and cost of surveillance. Since current guidelines for persons with chronic HCV recommend HCC screening only for those with cirrhosis or advanced fibrosis, clinicians must first accurately identify which individuals meet these criteria. In one study of the implementation of HCC screening in the VA system that was conducted between 1998 and 2005, investigators identified 126,670 persons with HCV infection and 10.1% of these individuals had cirrhosis among those with cirrhosis , routine HCC surveillance occurred in 12.0%, inconsistent surveillance in 58.5%, and no surveillance in 29.5%. A contemporary assessment of HCC screening practice in the DAA era has not yet been done, but it would clearly need to account for the growing population of individuals who have cleared their HCV yet still have cirrhosis and who are aging with their liver disease.
Indications For Liver Resection
Indicators for liver resection were determined by assessing the liver functional reserve according to Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Japan . Briefly, liver resection was contraindicated in patients who had refractory ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, or both . Patients with up to three lesions were candidates for liver resection.
In order to assess the existence of esophageal varices, gastrointestinal endoscopy was performed preoperatively for all candidates considered eligible for liver resection. Patients with F3 varices or F2 varices or blue varices positive for red color signs were treated prophylactically using esophageal variceal ligation .
Read Also: How Do I Get Hepatitis
Limited Data For Hcc Surveillance With Hcv Infection
There has been significant controversy about whether the findings of the trial conducted in China can be extrapolated to individuals with chronic HCV infection and serve as the basis to recommend HCC screening in persons with HCV infection. To date, there have been no published randomized, controlled trials that have evaluated HCC screening specifically in persons with chronic HCV infection and cirrhosis. This is likely to remain the case given the established role of HCC surveillance in routine clinical care in persons with cirrhosis. There have been a number of small observational studies of varying quality done in mixed populations, but these studies did not separate persons with chronic HCV infection from those with chronic HBV infection.
Progression Of Liver Fibrosis

In the setting of persistent hepatitis C viremia, the rate of progression of liver fibrosis varies widely. There have been extensive studies focusing on the natural course of disease progression from chronic hepatitis C to cirrhosis, HCC, and death. The liver biopsy is the gold standard for the grading and staging of chronic hepatitis C. The activity of liver disease or grade, is gauged by the number of mononuclear inflammatory cells present in and around the portal areas, and by the number of dead or dying hepatocytes. The structural liver damage, also known as fibrosis or stage, is variable in chronic HCV infection. Fibrosis implies possible progression to cirrhosis. In mild cases, fibrosis is limited to the portal and periportal areas. More advanced changes are defined by fibrosis that extends from one portal area to another, also known as “bridging fibrosis.â
Table 2
| Coinfection with HIV or HBV |
| Comorbid disease |
Read Also: Different Types Of Hepatitis C
Life Expectancy Among Patients With Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection And Cirrhosis
Patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection and advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis who attained sustained virological response had survival comparable with that of the general population, whereas patients who did not attain SVR had reduced survival, according to a study in the November 12 issue of JAMA.
Almost three million people in the United States are chronically infected with the hepatitis C virus . The life expectancy of patients with chronic HCV infection is reduced compared with the general population, largely attributable to the development of cirrhosis, liver failure and cancer. Studies have shown that the risk of all-cause death is lower among patients with chronic HCV infection and advanced hepatic fibrosis if sustained virological response is attained, but comparisons have been limited to those without SVR, according to background information in the article.
In total, 530 patients were followed for a median of 8.4 years follow-up was complete in 454 patients , 192 of whom attained SVR. Thirteen patients with SVR died, resulting in a cumulative 10-year overall survival of 91.1 percent, which did not differ significantly from the age- and sex-matched general population. In contrast, 100 patients without SVR died. The cumulative 10-year survival was 74.0 percent, which was significantly lower compared with the matched general population.
Explore further
Treatment Of Chronic Hepatitis C Infection
For clinicians treating chronic hepatitis C infection. Material covered includes recommendations for treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced persons with chronic HCV infection genotypes 1-6, based on the Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and Infectious Diseases Society of America HCV Guidance.
Track your progress and receive CE credit
Read Also: How Do You Catch Hepatitis
Populations For Which There Is No Guidance
- HCC is increasingly being reported in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis without cirrhosis the pathogenesis of HCC in this population may be different than in the population with viral hepatitis there are currently no recommendations for surveillance in this population
- Several studies have reported that patients with cirrhosis who have achieved sustained viralogic response after direct-acting antiviral therapy for hepatitis C may experience decreased risk of HCC and/or regression of fibrosis the natural history of cancer risk and regression of fibrosis in this population is still being studied therefore, patients with stage 3 or 4 fibrosis at the time of initiation of DAA therapy should continue HCC surveillance until more data are available
Rationale For Hcc Screening
The rationale for HCC screening of asymptomatic patients is that this practice may detect tumors at an early stage when potentially curative treatment, either surgical or locoregional, can be offered. Early detection with HCC is particularly important, given the very poor prognosis associated with advanced or metastatic HCC.
Also Check: Hepatitis A Vs B Vs C
Can You Prevent Hepatitis C Infection
Thereâs no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C. To avoid getting the virus:
- Use a latex condom every time you have sex.
- Don’t share personal items like razors.
- Don’t share needles, syringes, or other equipment when injecting drugs.
- Be careful if you get a tattoo, body piercing, or manicure. The equipment may have someone else’s blood on it.
Find out more on how to prevent hepatitis C.
Inclusion And Exclusion Criteria
Patients who underwent initial liver resection for HCC, but were positive for HBsAg were excluded from the study. Patients who were negative for HBsAg and HBcAb but positive for HBsAb, and those who were positive for HCV antibody but negative for HCV-RNA were also excluded. In addition, patients whose HBsAb or HBcAb status had not been determined were also excluded.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Hepatitis C Screening
Relationship Between Hcv Chronic Infection And Hcc
In 2015, the WHO estimated that viral hepatitis accounted for 1.34 million deaths. These deaths resulted from chronic liver disease and primary liver cancer . Each year, the number of deaths related to viral hepatitis has been growing and is represented by the increase in mortality related to viral hepatitis by 22% since 2000.
Around 75% of people exposed to HCV infection will not be able to eradicate the virus – 60%-70% of them will develop chronic liver diseases and of the remainder, 5%-20% will develop cirrhosis over a period of 20-30 years and 1%-5% will die from cirrhosis or HCC.
Globally, the estimated annual percentage change in liver cancer due to age-standardized HCV incidence rate has increased 0.57 between 1990 and 2016. This pattern is heterogeneous across regions and countries. This rate was also higher in low- and middle-income countries than in high-income countries.
In 2016, the percentage contribution of HCV to absolute liver cancer incidence in Tropical, Southern, Central and Andean Latin America were 37.4%, 47.9%, 34.2% and 13.6%, respectively. Deaths due to HCC related to HCV infection had the highest incidence in the Dominican Republic at 3.27 per 100, 000 people, followed by Chile with 3.22, Cuba with 2.96, Argentina with 2.84, and Mexico with 2.68 .
*2015 year-end estimate is a model output projection based on historic data. HCV: hepatitis C virus
Jaundice And Immune Response
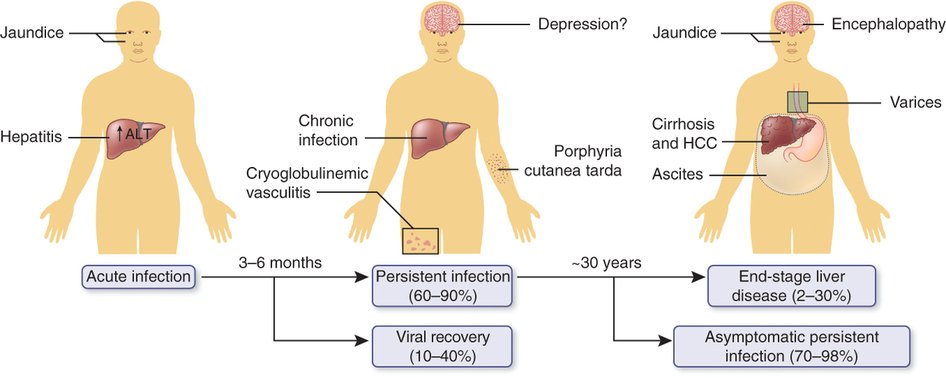
The rate of chronic HCV infection is lower in patients who develop jaundice or symptoms during the acute onset of HCV infection as compared to those who are anicteric. In a prospective study of 142 HCV-infected subjects with a history of illicit drug use, subjects with viral clearance were more likely to have symptoms of jaundice . Furthermore, the long-term follow-up study of women infected with contaminated Rh immune globulin in Germany exhibited a rate of chronicity in 43% of those with history of jaundice, as compared to 60% among those who remained anicteric . Many have speculated that the jaundice may be associated with a more robust immune Th1 lymphocyte and cytokine response to the HCV. The competency of the immune response plays a significant role in the development of chronic hepatitis C, as well as the progression of liver fibrosis. The rates of chronic HCV infection developing in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection and CD4 < 200, have been higher than in patients without HIV infection.
Read Also: What Is The Best Medication For Hepatitis B