How Is Hepatitis A Treated
Unlike other types of viral hepatitis, hepatitis A rarely causes long-term liver damage and doesn’t become a long-term illness. There isnt a specific treatment for hepatitis A, and most people will recover fully within one to two months. Usually, symptoms are managed at home with plenty of rest and painkillers and/or medication to help with itchiness, nausea or vomiting may be prescribed.
Occasionally hepatitis A can last longer and, in rare cases, it can be life-threatening if it causes the liver to stop working properly .
Whether youve got symptoms or not, dont prepare food for others or have sex until a healthcare professional tells you that youre no longer infectious.
Once youve recovered from hepatitis A youre immune this means you cant get it again. But you can get other types of hepatitis.
How Do You Get It
HAV can be present in the stool and blood of someone with the virus. Its mainly transmitted through the fecal-oral route, which involves ingesting virus thats present in the stool of someone with hepatitis A.
There are several ways you can get hepatitis A:
- having close person-to-person contact with someone who has hepatitis A, such as:
- taking care of someone whos currently sick
- having sex with someone who has the virus
Data Collection Laboratory Procedures
Data were collected by professional nurses and laboratory technologists including socio-demography, clinical, anthropometric, and laboratory measurements. First, the data collectors were trained in the aim of the study by the principal investigators. The data collection procedure was carried out under the supervision of the principal investigator.
You May Like: What Is A Hepatitis Panel
Factors That Affect Treatment Success
A number of factors can help predict how well hepatitis C treatment is likely to work for you.
Before starting treatment, it is important to have a test to see what genotype of hepatitis C you have. This determines which DAAs will work and predicts treatment response. Some DAAs are ‘pangenotypic’ or active against all genotypes.
There are at least six major hepatitis C genotypes. Genotype 1 is the most common type in the UK, Europe and the US. It has two subtypes, 1a and 1b. Genotype 1 was hard to treat with interferon-based therapy, but it can be successfully treated with all approved DAAs. However, genotype 1a is harder to treat than 1b.
effectiveness
How well something works . See also ‘efficacy’.
Hepatitis C genotype 2 is less common worldwide. It responded best to interferon-based treatment, but is susceptible to fewer DAAs than genotype 1. Genotype 3 is the most common type in the Indian sub-continent and south-east Asia, but it is also found in the UK. Genotype 3 has been the hardest to treat with DAAs, but newer pangenotypic drugs are highly effective against it.
Genotype 4 is the most common type of hepatitis C in the Middle East and North Africa, but it has also been seen in hepatitis C outbreaks in the UK and Europe. Genotype 4 generally responds to the same DAAs as genotype 1. Genotype 5 and 6 are less common and less well studied.
Learning Objective Performance Indicators
- Explain the impact of HIV on coinfection with HCV
- Discuss sustained virologic response outcomes demonstrated in key studies using direct-acting antiviral agents to treat HCV in persons with HIV coinfection
- Differentiate HCV treatment duration for HCV monoinfection versus HCV-HIV coinfection
- Summarize recommendations for monitoring persons with HCV-HIV coinfection after initiating antiretroviral therapy
- Highlight drug interactions from the perspective of direct-acting antivirals and antiretroviral medication classes
Read Also: Antiviral Drugs For Hepatitis A
Diagnosing Hepatitis C In People Living With Hiv
Everyone with HIV should be tested to see if they also have hepatitis C. A blood test for antibodies to hepatitis C is used to see whether you have been exposed to the virus. You might be given a PCR test to confirm infection.
In people living with HIV, the diagnosis of hepatitis C can be more difficult, as the infection may not show up on their antibody tests.
If you think you may be at risk of hepatitis C infection, you should have regular tests to see if you have been infected with the virus.
Future Prospects For Hbv
Are we progressing to a similar situation for HBV where categorization and treatment decisions are more simple, rapid and clear cut? Or to a situation where treatment is advocated for all?
Assessments of immune responsiveness and exhaustion have allowed classification and monitoring to be revisited, and data on outcomes in those previously defined as immune tolerant have directed a re-appraisal of patient categorization. For example, studies have demonstrated that the previously labeled immune-tolerant phenotype is actually associated with immune activation and increased expression of immune check point inhibitors such as PD-1 . These factors, and a general better understanding of outcomes, have allowed a reassessment of classification of patients with HBV infection.
Table 2 Current EASL Guidelines
This delay in progression of promising agents to general use also means that we remain in a situation where not all patients meet criteria for treatment. If we develop an agent, or combination, that has a significant impact on ccc-DNA, then it is possible that we move to a situation in HBV analogous to that currently in HIV and HCVtreatment for all and not dependent on sub-classification.
Also Check: Where To Get A Hepatitis B Shot
Should People With Hiv Get Tested For Hbv
CDC recommends that all people with HIV get tested for HBV. Testing can detect HBV even when a person has no symptoms of the infection.
There are several HBV blood tests. Results of different tests show different things. For example, a positive hepatitis B surface antigen test result shows that a person has acute or chronic HBV and can spread the virus to others.
How To Prevent Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a liver infection caused by a virus . It can be serious and theres no cure, but the good news is its easy to prevent. You can protect yourself by getting the hepatitis B vaccine and having safer sex. If you have oral, anal, and vaginal sex, use condoms and dental dams to help stop the spread of hepatitis B and other STDs.
Read Also: Is Hepatitis C An Std
Hcv Treatment Data In Persons With Hiv Coinfection
Multiple HCV treatment studies using direct-acting antiviral -based therapy have demonstrated sustained virologic response rates in individuals with HIV-HCV coinfection that are comparable to those with HCV monoinfection , providing convincing evidence that persons with HIV-HCV coinfection should no longer be considered as a treatment-refractory population. In these trials, most participants did not have cirrhosis and most had CD4 counts well above 200 cells/mm3. Subsequently, however, a variety of observational cohort studies with heterogeneous cohorts of persons with HIV-HCV coinfection, including those with more advanced liver disease and lower CD4 cell counts, showed comparable HCV SVR rates in persons with HIV-HCV coinfection compared with those who have HCV monoinfection. The following provides a summary of key clinical trials involving DAA treatment of HCV infection in persons with HIV coinfection.
Initial Evaluation And Treatment Recommendations For Patients With Hepatitis C Virus/hiv Coinfections
Prior to initiating ART, screen patients with HIV infection for HCV using sensitive immunoassays licensed for the detection of antibody to HCV in blood to confirm the presence of chronic infection, persons who are HCV seropositive should be tested for HCV ribonucleic acid using a qualitative or quantitative assay.
Advise patients with HCV/HIV to avoid alcohol and receive HAV and HBV vaccines, if screened negative via serology.
Drug-induced liver injury following ART is more common in HIV/HCV coinfection eradication of HCV infection may decrease the likelihood of antiretrovirus-associated DILI.
It is important to monitor alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase levels at 1 month and then every 3 months after the initiation of ART.
ART should be started in persons co-infected with HCV and HIV in accordance with the recommendations for initiating ART in treatment-naive patients. ART should be started at least 4-6 weeks before hepatitis C treatment is initiated.
The objective of HCV antiviral treatment is to cure the HCV infection, reflected by a sustained virologic response. Although patients with HIV and HCV coinfection traditionally had lower response rates to HCV treatment with older regimen of ribavirin and peginterferon compared to individuals without HIV infection, patients with coinfection appear to have comparable sustained virologic response rates with all oral, direct-acting antiviral combination therapy.
You May Like: What Organ Does Hepatitis B Affect
Who Should Be Vaccinated
Children
- All children aged 1223 months
- All children and adolescents 218 years of age who have not previously received hepatitis A vaccine
People at increased risk for hepatitis A
- International travelers
- Men who have sex with men
- People who use or inject drugs
- People with occupational risk for exposure
- People who anticipate close personal contact with an international adoptee
- People experiencing homelessness
People at increased risk for severe disease from hepatitis A infection
- People with chronic liver disease, including hepatitis B and hepatitis C
- People with HIV
Other people recommended for vaccination
- Pregnant women at risk for hepatitis A or risk for severe outcome from hepatitis A infection
Any person who requests vaccination
There is no vaccine available for hepatitis C.
Risks Of Hepatitis C And Hiv Coinfection
The CDC reports that HIV coinfection can accelerate the course of hepatitis C, including the rapid progression of chronic liver disease from hepatitis C to cirrhosis, a form of permanent liver damage. This is particularly true in people with advanced immunodeficiency .
In addition, coinfected individuals with cirrhosis progress more rapidly to end-stage liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma than those with hepatitis C alone. Both of these liver conditions can be life threatening. In fact, according to the CDC, liver disease much of which is caused by hepatitis B or hepatitis C is a leading non-AIDS cause of death in people with HIV.
Hepatitis C has also been associated with an increased risk for conditions such as vasculitis , kidney disease, and the skin condition porphyria cutanea tarda.
Untreated, patients with HIV and hepatitis C coinfection have a worse prognosis in terms of liver disease progression and outcomes, Sherman says.
Don’t Miss: Hepatomegaly With Diffuse Hepatic Steatosis
How Is It Treated
Hepatitis A is treated using supportive methods. These can include things like rest, fluids, and healthy foods. Medications can also help to ease some symptoms like fever, aches, and pains.
Theres a vaccine available to protect against infection with HAV. This is typically recommended for children as well as for people at an increased risk for contracting the virus.
Also, receiving a single dose of the hepatitis A vaccine may prevent you from becoming ill if youve been exposed to HAV. For it to be effective, the vaccine needs to be given of exposure.
Is Hepatitis A The Same As Hepatitis B
One might believe that hepatitis A and B are basically the same thing. However, many are unfamiliar with what hepatitis is and does. Learn more about hepatitis, such as the various types and the difference between them by reading further. When you overhear the term hepatitis, it just means one thing: inflammation of your liver. There are several ways that you can develop this health condition. Alcohol and certain medications are some of these causes. It is typically proliferated through viruses of different types these have been named A, B, C, D, and E. To make everything easier for you, here are well-defined differences between the notable hepatitis viruses, hepatitis A and hepatitis B .
Read Also: How Can I Get Hepatitis C
How Do You Test For Hepatitis A
If youve been in contact with someone who has had hepatitis A, are at risk of getting hepatitis A, or if you start to have symptoms its a good idea to talk to a healthcare professional. A simple blood test will show whether you have the virus.
If you test positive, they may also do another type of blood test to check if your liver is working properly. You should also be tested for other STIs.
Its important that you tell people you live with or have close contact with, and your recent sexual partner/s so they can also get tested. Many people who have hepatitis A dont notice anything wrong, and by telling those youre in close contact with you can help to stop the virus being passed on.
Hepatitis C Treatment Guidelines
Guidelines issued by WHO in April 2016 recommend four preferred regimens, each including the drug sofosbuvir, in order to simplify treatment decisions for hepatitis C.36 Depending on the regimen, treatment may last 12 or 24 weeks.
When these guidelines were issued, the choice of drug regimen was dependent on which of the six genotypes the patient had. Different genotypes, each with its own genetic composition of the virus, are more common in different parts of the world. Each patient therefore required genotype testing before treatment could be provided.
In July 2018, WHO updated these treatment guidelines to reflect certain key developments. It recommended that the use of DAA regimens for all people with chronic hepatitis C infection, rather than reserving DAA treatment for people with more advanced disease as had previously been done. In part, this is linked to the continued substantial reduction in , which has enabled treatment to be rolled out rapidly in a number of low- and middle-income countries. In addition, as several new pangenotypic DAA medicines have now been approved, the need for genotyping to guide treatment decisions has been reduced.37
Read Also: What Are The Signs Of Hepatitis C
Why Does Heroin Use Create Special Risk For Contracting Hiv/aids And Hepatitis B And C
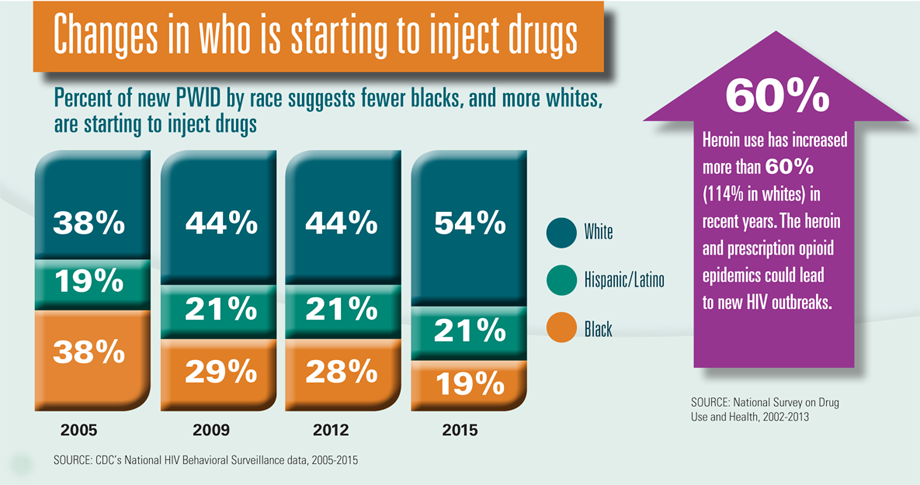
Heroin use increases the risk of being exposed to HIV, viral hepatitis, and other infectious agents through contact with infected blood or body fluids that results from the sharing of syringes and injection paraphernalia that have been used by infected individuals or through unprotected sexual contact with an infected person. Snorting or smoking does not eliminate the risk of infectious disease like hepatitis and HIV/AIDS because people under the influence of drugs still engage in risky sexual and other behaviors that can expose them to these diseases.
People who inject drugs are the highest-risk group for acquiring hepatitis C infection and continue to drive the escalating HCV epidemic: Each PWID infected with HCV is likely to infect 20 other people.21 Of the 30,500 new HCV infections occurring in the United States in 2014, most cases occurred among PWID.22
Hepatitis B infection in PWIDs was reported to be as high as 25 percent in the United States in 2014,22 which is particularly disheartening since an effective vaccine that protects against HBV infection is available. There is currently no vaccine available to protect against HCV infection.
Hiv And Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Coinfection
Hepatitis B and hepatitis C are liver infections caused by a virus. Because these infections can be spread in the same ways as HIV, people with HIV in the United States are often also affected by chronic viral hepatitis.
Viral hepatitis progresses faster and causes more liver-related health problems among people with HIV than among those who do not have HIV. Liver disease, much of which is related to HBV or HCV, is a major cause of non-AIDS-related deaths among people with HIV.
Given the risks of hepatitis B or hepatitis C coinfection to the health of people living with HIV, it is important to understand these risks, take steps to prevent infection, know your status, and, if necessary, get medical care from someone who is experienced in treating people who are coinfected with HIV and HBV, or HIV and HCV.
You May Like: How Long Is The Hepatitis B Vaccine Good For
Treatment Of Hepatitis C Virus With Coexisting Hiv Infection
Increased rates of cirrhosis in patients with hepatitis C virus are attributable to various factors, including older age, alcoholism, male sex, and HIV infection higher rates of progression to cirrhosis are seen in patients with HCV/HIV.
HCV infection in patients with HIV infection can have significant consequences, including liver disease progression, liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, increased rates of end-stage liver disease, and shortened lifespan after hepatic decompensation.
Genotype 1 accounts for approximately 75% of hepatitis C infections in the United States.
The Silent Epidemic Killing More People Than Hiv Malaria Or Tb
Nuru was prepared for the worst when she went to get screened for HIV eight years ago. After caring for her mother in Uganda, who died as a result of the virus, Nuru moved to the United Kingdom to study, and decided to take her health into her own hands. I was ready to be told I had HIV, she says. I felt, Thats okay. Ive looked up to my mother.
What she didnt expect was to be diagnosed with a different viral infection altogether: hepatitis B. The way the health worker delivered it to me, it was like, Its worse than HIV. I was confused, I was suicidal, says Nuru . I just didnt understand what it was because no one ever talks about hep B they talk about HIV. Thats well researched, its well talked about, well documented. Its all over the television. But hep B is not.
The hepatitis B virus , which spreads through blood and bodily fluids and invades liver cells, is thought to kill just under 1 million people every year around the world, mostly from cancer or scarring of the liver. HBV is less likely to be fatal than HIV, and many people who carry the virus dont have symptoms. But because more than 250 million people live with chronic HBV infections, more than 7 times the number with HIV, its global death toll now rivals that of the more-feared virus.
Source: Global Health Estimates 2016
Source: WHO Hepatitis B dashboard
Read Also: Is Hepatitis B Virus A Std