Is The Hepatitis D Vaccine Available
No vaccine is available for hepatitis D. A vaccine for hepatitis B is available, which can, in turn, be helpful in preventing hepatitis D also.
Hepatitis D is a serious condition that can result in serious life-threatening complications. Hepatitis D infection is also termed Delta virus infection. If you are diagnosed with hepatitis D, make healthy choices, and eat a proper healthy diet to protect your liver from further damage. Inform your dentist before taking any dental treatments to avoid the spread of the infection and also avoid coming in close contact with other healthy people to avoid its spread. Chronic hepatitis B can lead to chronic liver infection and can lead to end-stage liver disease and associated complications like accelerated fibrosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and liver decompensation.
Query:Hello doctor,Two years back, after a routine blood test I was diagnosed with fatty liver due to raised liver enzymes ALT 53 ALP 66 and GGT188. I later underwent a liver scan and the conclusion was Child A Cirrhosis-possibly secondary to NASH. Advised to lose weight with no medication prescribed. Y… Read Full »
Most Popular Articles
How Is Hepatitis A Diagnosed
Some people have only a few symptoms and no signs of jaundice. Without visible signs of jaundice, its hard to diagnose any form of hepatitis through a physical examination. When symptoms are minimal, hepatitis A can remain undiagnosed.
After you discuss your symptoms with your doctor, they may order a blood test to check for the presence of a viral or bacterial infection. A blood test will reveal the presence of the hepatitis A virus.
Complications due to a lack of diagnosis are rare.
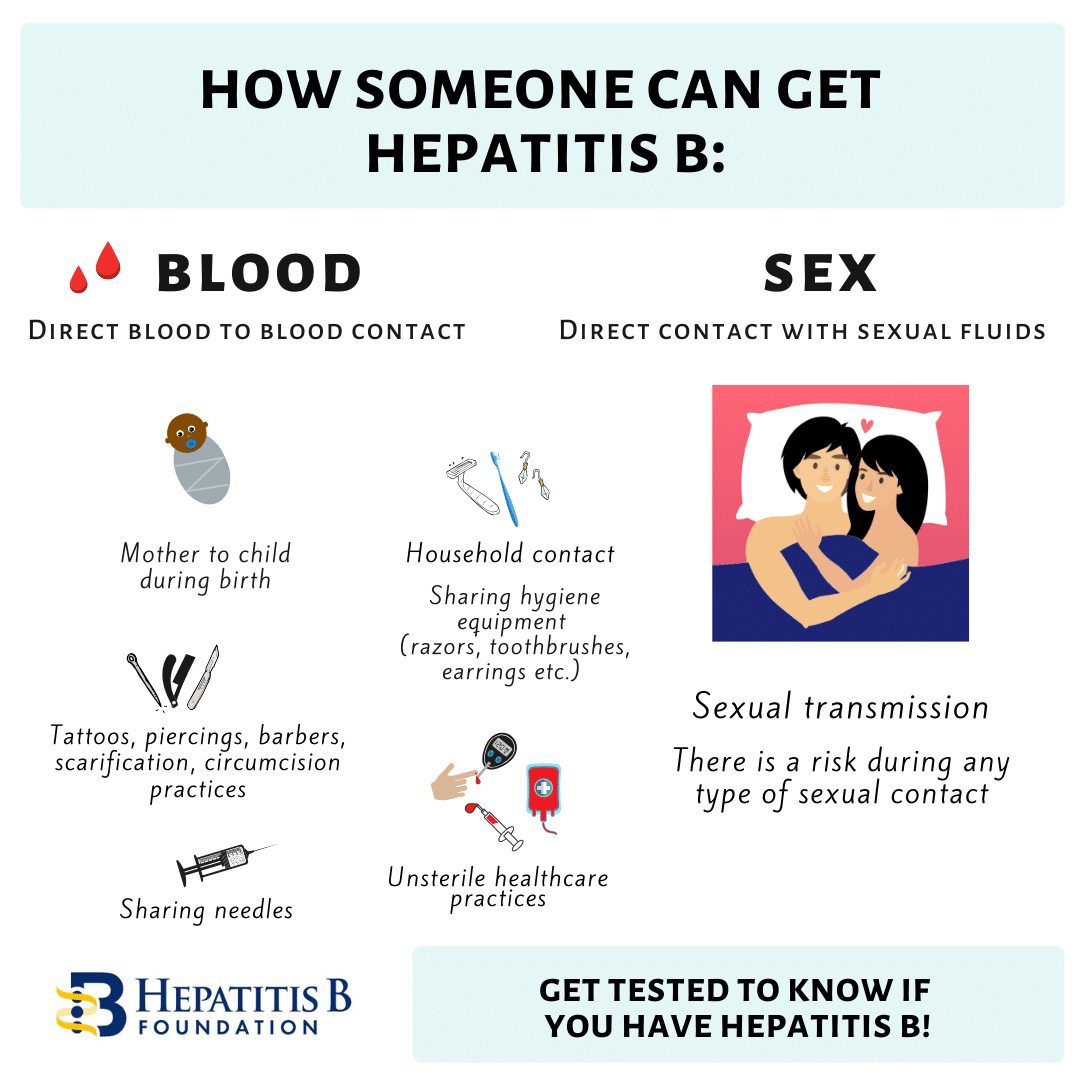
How You Can Get Hepatitis B
You can get hepatitis B from:
- injecting drugs using shared needles
- being injured by a used needle
- having a tattoo or piercing with unsterilised equipment
- having a blood transfusion in a country that does not check blood for hepatitis B. Blood transfusions in the UK are checked for hepatitis B.
If you’re pregnant and have hepatitis B, you can also pass it onto your baby during pregnancy or birth.
You May Like: Immunoglobulin Injection For Hepatitis B
Where Is The Hepatitis B Virus Found And How Is It Transmitted
Blood is the major source of the hepatitis B virus in the workplace. It can also be found in other tissues and body fluids, but in much lower concentrations. The risk of transmission varies according to the specific source. The virus can survive outside the body for at least 7 days and still be able to cause infection.
Who Is At Risk Of Getting Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is usually spread from person to person, making it highly contagious. But certain factors can increase your risk of contracting it, including:
- living in an area where hepatitis A is common, including most countries with low sanitation standards or a lack of safe water
- injecting or using illegal drugs
- living in the same household as someone whos hepatitis A-positive
- having sexual activity with someone whos hepatitis A-positive
- being HIV-positive
World Health Organization reports that more than 90 percent of children living in countries with low sanitation standards will have had a hepatitis A infection by age 10.
In past decades, people with clotting disorders like hemophilia were at higher risk of contracting hepatitis A via transfusion therapy, though these cases are extremely rare today.
Read Also: How To Catch Hepatitis C
How Is The Diagnosis Made For Hepatitis D
The following diagnostic methods are used:
1. Blood Test:
-
IgM antibody to hepatitis A virus .
-
Hepatitis B surface antigen .
-
Serologic testing.
-
IgM antibody to IgM anti-HBc, which is hepatitis B core, antibody-HCV , and HCV RNA PCR, that is, hepatitis C RNA PCR.
-
HDV – High levels of anti-HDV immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin M are confirmed by the detection of HDV RNA serum.
2. Elastography: A special ultrasound used to measure the stiffness of the liver.
3. Liver Biopsy: A needle is used to remove a small piece of tissue from the liver, and it is sent to the laboratory. The tissue is examined under a microscope to look for signs of any type of damage and disease to the liver.
Treatment: Chronic Hepatitis C
The latest drug to be approved by the FDA is glecaprevir and pibrentasvir . This medication offers a shorter treatment cycle of 8 weeks for adult patients with all types of HCV who donât have cirrhosis and who have not been previously treated. The length of treatment is longer for those who are in a different disease stage. The prescribed dosage for this medicine is 3 tablets daily.
There are several other combination drugs available, as well as some single drugs that may be used in combination. Your doctor will choose the right one for you depending on the type of hepatitis C you have, how well your liver is functioning and any other medical problems you may have. Also be sure to discuss your insurance coverage since these medications are expensive.
Also Check: Where Does Hepatitis Come From
Hiv And Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Coinfection
Hepatitis B and hepatitis C are liver infections caused by a virus. Because these infections can be spread in the same ways as HIV, people with HIV in the United States are often also affected by chronic viral hepatitis.
Viral hepatitis progresses faster and causes more liver-related health problems among people with HIV than among those who do not have HIV. Liver disease, much of which is related to HBV or HCV, is a major cause of non-AIDS-related deaths among people with HIV.
Given the risks of hepatitis B or hepatitis C coinfection to the health of people living with HIV, it is important to understand these risks, take steps to prevent infection, know your status, and, if necessary, get medical care from someone who is experienced in treating people who are coinfected with HIV and HBV, or HIV and HCV.
Can You Be A Blood Or Organ Donor
People with hepatitis C cant currently donate blood. The American Red Cross eligibility guidelines prohibit people who have ever tested positive for hepatitis C from donating blood, even if the infection never caused symptoms.
According to the Department of Health and Human Services , information on organ donation, those with underlying medical conditions shouldnt rule themselves out as organ donors. This reflects new guidelines for organ donation announced by the HHS.
People with HCV are now able to be organ donors. This is because advances in testing and medical technology can help the transplant team determine which organs or tissues can be safely used for transplantation.
Also Check: What Can Hepatitis C Do To You
The A B Cs Of Hepatitis
Hepatitis A
The hepatitis A virus causes acute inflammation of the liver that almost always gets better on its own, although it can be more serious if you get it when you are older or if you already have liver disease. It is easily spread from person to person, in food and water, and can infect many people at once. For example, if a food handler at a restaurant is infected with hepatitis A, those who eat food prepared by that handler may be infected. Hepatitis A can be prevented by getting vaccinated.
Hepatitis B
The hepatitis B virus can be both acute and chronic and is spread through blood or other body fluids in various ways. Hepatitis B is very common in Asia and Africa and those who were born or lived in these areas should be checked for hepatitis B. Like hepatitis A, a vaccine is available to prevent HBV infection as long as you have not been previously exposed. Although chronic HBV cannot be cured, there are oral medications available to treat and control the virus.
Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus is almost always chronic and spreads mostly by direct blood to blood contact. Although hepatitis A and B can be prevented by vaccination, hepatitis C cannot. However, there are currently oral medications available that are able to cure Hepatitis C in 95% of all cases regardless of prior treatment history.
Hepatitis B: What Happens
Many adults who get hepatitis B have mild symptoms for a short time and then get better on their own. But some people are not able to clear the virus from the body, which causes a long-term infection. Nearly 90% of infants who get the virus will carry it for life. Over time, hepatitis B can lead to serious problems, such as liver damage, liver failure, and liver cancer.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Side Effects Of Hepatitis
Enteric Routes: Transmission Of Hepatitis A And Hepatitis E
The Hepatitis A and hepatitis E viruses are both transmitted by enteric, that is digestive or by fecal, routes. This is also known as the fecal-oral route. To be exposed to these viruses, you must ingest fecal matter that is infected with the virus. While there are several ways in which this fecal-oral route can be established, poor hygiene and poor sanitary conditions in some countries lead to higher rates of infection of these viruses.
As a result, some areas of the world, like India, Bangladesh, and Central and South America, are particularly prone to the hepatitis E virus. About one-third of people in the United States have been exposed to the hepatitis A virus.
It is believed that the hepatitis F virus may also be spread by enteric routes.
Knowing Your Risk For Chronic Hepatitis C
Because chronic hepatitis may have no symptoms, it is important to know your risk for chronic hepatitis C virus . Risk factors include:
- Those who had a transfusion of blood or blood products before 1992 .
- Those born between the years of 1945-1965.
- Those who have or are experimenting with intravenous drugs.
- Those who have snorted or are snorting cocaine.
- Those who have gotten tattoos with a non-sterile needle.
- Those who have had unprotected multiple sexual partners.
- Those with HIV.
- Children born to mothers with HCV infection.
Although these are the most common ways to acquire Hepatitis C, there are other risk factors that can lead to infection. Thus, in 2020 the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention updated its screening guidelines to recommend all adults 18 years or older get screened at least once in their lifetime for HCV.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does Hepatitis C Live Outside The Body
How Many People Have Hepatitis C
During 2013-2016 it was estimated that about two and half million people were chronically infected with HCV in the United States. The actual number may be as low as 2.0 million or as high as 2.8 million.Globally, hepatitis C is a common blood-borne infection with an estimated 71 million people chronically infected according to the World Health Organization .
How Can Hepatitis D Be Prevented
-
Avoiding hepatitis B infection is the only way to prevent hepatitis D infection. All methods to prevent hepatitis B infection will lead to prevention and reduce the risk of getting hepatitis D.
-
Getting vaccinated: Vaccination is bliss vaccination of hepatitis B is available. All children should be vaccinated. Adults with a high risk of infection are recommended for vaccination. This vaccination is usually an episode of three consecutive injections over six months.
-
Be cautious during tattooing and piercing, inquire about the sterilization of the equipment, and make sure they use sterile needles. Go to a trustworthy place.
-
Stop using drugs, and avoid injectable recreational drugs like heroin and cocaine. Use sterile needles each time in case you are not able to avoid drugs and never share the needle with other people.
-
Always practice safe sex, and use protection such as condoms. Never have unprotected sex with someone who has been infected by any type of hepatitis or any STDs .
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Cvs Cost
How To Prevent Hepatitis C
There is currently no vaccine for hepatitis C. Avoiding contact with infected blood is the only way to prevent the condition.
The most common way for people to contract hepatitis C is by injecting street drugs. Because of this, the best way to prevent hepatitis C is to avoid injecting.
Treatments can help many people quit. People in the U.S. can call the National Helpline for help with finding treatments.
If a person finds it difficult to stop, they can reduce the risk of contracting hepatitis C by never sharing drug equipment, ensuring a clean, hygienic environment, and always using new equipment, including syringes, ties, alcohol swabs, cottons, and cookers.
People who may come into contact with infected blood, such as healthcare workers and caretakers, should always wash the hands thoroughly with soap and water after any contact, or suspected contact, with blood. They should also wear gloves when touching another persons blood or open wounds.
People can also reduce their risk by making sure that any tattoo artist or body piercer they visit uses fresh, sterile needles and unopened ink.
The risk of contracting hepatitis C through sexual contact is low. Using barrier protection, such as condoms, reduces the risk of most sexually transmitted infections.
People who have hepatitis C can reduce the risk of transmitting it to others by:
There are many misconceptions about how hepatitis C spreads. People cannot transmit or contract the virus through:
What Laboratory Tests Are Available For Hepatitis B
Tests are available to detect the types of antigens used to identify the hepatitis B virus. The tests determine if the virus is present in the body tissue or blood. The amount of each type of antigen present indicates how advanced the disease is and how infective the individual has become.
Other tests are available to detect the body’s reaction to the viral infection or the body’s reaction to vaccination against the virus. These tests work by measuring the number of antibodies present in the blood.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis B Shot
What Is Hepatitis
Hepatitis refers to inflammation of the liver. Inflammation is a tissues reaction to irritation or injury which generally results in swelling and can cause pain.
There are many causes of hepatitis. Viral hepatitis is caused by a virus and can either be acute or chronic . Viral hepatitis can be spread from person to person. Some types of viral hepatitis can be spread through sexual contact.
There are five known hepatitis viruses which are categorized by the letters A through E.
Several viruses are known to cause hepatitis. Common forms of viral hepatitis include:
Healthcare providers might not be able to identify the virus causing hepatitis as one of these. Other viruses, such as CMV, EBV, and HSV can also cause hepatitis.
Most people recover from hepatitis, and the disease is often preventable. However, it is still considered a serious health risk because it can:
- Destroy liver tissue.
- Being transferred from mother to unborn child.
- Being in contact with an infected person’s body fluids.
An infected mother has a high chance of giving hepatitis B to her child during or after birth. All pregnant women should be tested for hepatitis B. Within 12 hours of birth, infants born to mothers with hepatitis B need to receive treatment with hepatitis B antibody and hepatitis B vaccine. This can prevent transmission of hepatitis B from mother to the baby.
A person can get hepatitis C from:
You can get hepatitis D from:
How Common Is It
In 2006, the Public Health Agency of Canada reported the incidence of HBV as 2.0 cases for every 100,000 or about 650 cases reported annually in Canada. In the year 2013, the incident rate was 0.5 per 100,000 . Incidence of the disease varies from region to region but has been declining due to increasing use of the vaccine and universal immunization programs.
Recommended Reading: What Does Hepatitis C Antibody Mean
How Are Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Spread From Person To Person
Like HIV, the hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses spread:
- From mother to child: Pregnant women can pass these infections to their infants. HIV-HCV coinfection increases the risk of passing on hepatitis C to the baby.
- Sexually: Both viruses can also be transmitted sexually, but HBV is much more likely than HCV to be transmitted sexually. Sexual transmission of HCV is most likely to happen among gay and bisexual men who are living with HIV.
Is There Any Way To Prevent Hepatitis A
The No. 1 way to avoid getting hepatitis A is by getting the hepatitis A vaccine. This vaccine is given in a series of two injections, 6 to 12 months apart.
If youre traveling to a country where hepatitis A transmission is more common, get your vaccination at least 2 weeks before traveling. It usually takes 2 weeks after the first injection for your body to start building immunity to hepatitis A. If youre not traveling for at least a year, its best to get both injections before leaving.
Check your destination on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention site to see if you should get a hepatitis A vaccination.
To limit your chance of contracting hepatitis A, you should also:
- thoroughly wash your hands with soap and warm water before eating or drinking, and after using the restroom
- drink bottled water rather than local water in developing countries, or in countries where theres a high risk of contracting hepatitis A
- dine at established, reputable restaurants, rather than from street vendors
- avoid eating peeled or raw fruit and vegetables in an area with low sanitation or hygienic standards
Recommended Reading: Sign And Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis A Vaccine And International Travel
Who should get the hepatitis A vaccine before traveling internationally?
All unvaccinated people, along with those who have never had hepatitis A, should be vaccinated before traveling to countries where hepatitis A is common. Travelers to urban areas, resorts, and luxury hotels in countries where hepatitis A is common are still at risk. International travelers have been infected, even though they regularly washed their hands and were careful about what they drank and ate. Those who are too young or cant get vaccinated because of a previous, life-threatening reaction to the hepatitis A vaccine or vaccine component should receive immune globulin. Travelers to other countries where hepatitis A does not commonly occur are not recommended to receive hepatitis A vaccine before travel.
How soon before travel should I get the hepatitis A vaccine?
You should get the first dose of hepatitis A vaccine as soon as you plan international travel to a country where hepatitis A is common. The vaccine will provide some protection even if you get vaccinated closer to departure. For older adults , people who are immunocompromised, and people with chronic liver disease or other chronic medical conditions the health-care provider may consider, based on several factors, giving an injection of immune globulin at the same time in different limbs.
What should I do if I am traveling internationally but cannot receive hepatitis A vaccine?