Treatment Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is treated with antiviral medications that aim to clear the virus from your body.
New all-tablet treatments have greatly improved the outcomes for people with hepatitis C. These treatments can cure more than 95% of individuals with chronic hepatitis C. There are several new tablets that are used in combination to treat all hepatitis C strains . They are effective for people with no liver damage and those who have more advanced liver damage or cirrhosis.
These new tablet medications are available and subsidised on the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme, and can be prescribed by specialists, general practitioners and specialised nurse practitioners.
There are no restrictions on accessing treatment it is available for all adults with a Medicare card. People under 18 are able to access treatment and it is recommended they are referred to a pediatrician experienced in the treatment of hepatitis C.
For more information on the new medications for the treatment of hepatitis C, see our video: Hepatitis C Cure what it means for Victorians.
If your doctor does not know about the new treatments, you can call the LiverLine on for information, and to find a GP who can help you.
Talk with your doctor about treatment options and the potential for interactions with other medications, herbal preparations and other drugs. If you take prescribed medication this will be managed so you can access treatment.
In general, if you have hepatitis C you will feel better if you:
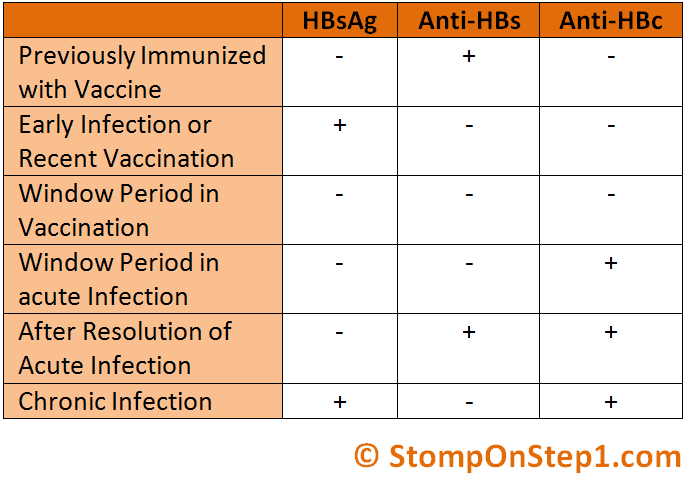
Negative But Other Hepatitis Tests Are Positive
Your HBsAb test may be negative even when other hepatitis B tests are positive, showing active or chronic infection. Further testing is necessary, especially for the hepatitis B surface antigen , which shows that the virus itself is circulating in your bloodstream and that you have an active or chronic infection.
Recommended Reading: How Much Is A Hepatitis C Test
What Is A False Positive
A false-positive result means that a test indicated that you have a disease or condition when you actually dont.
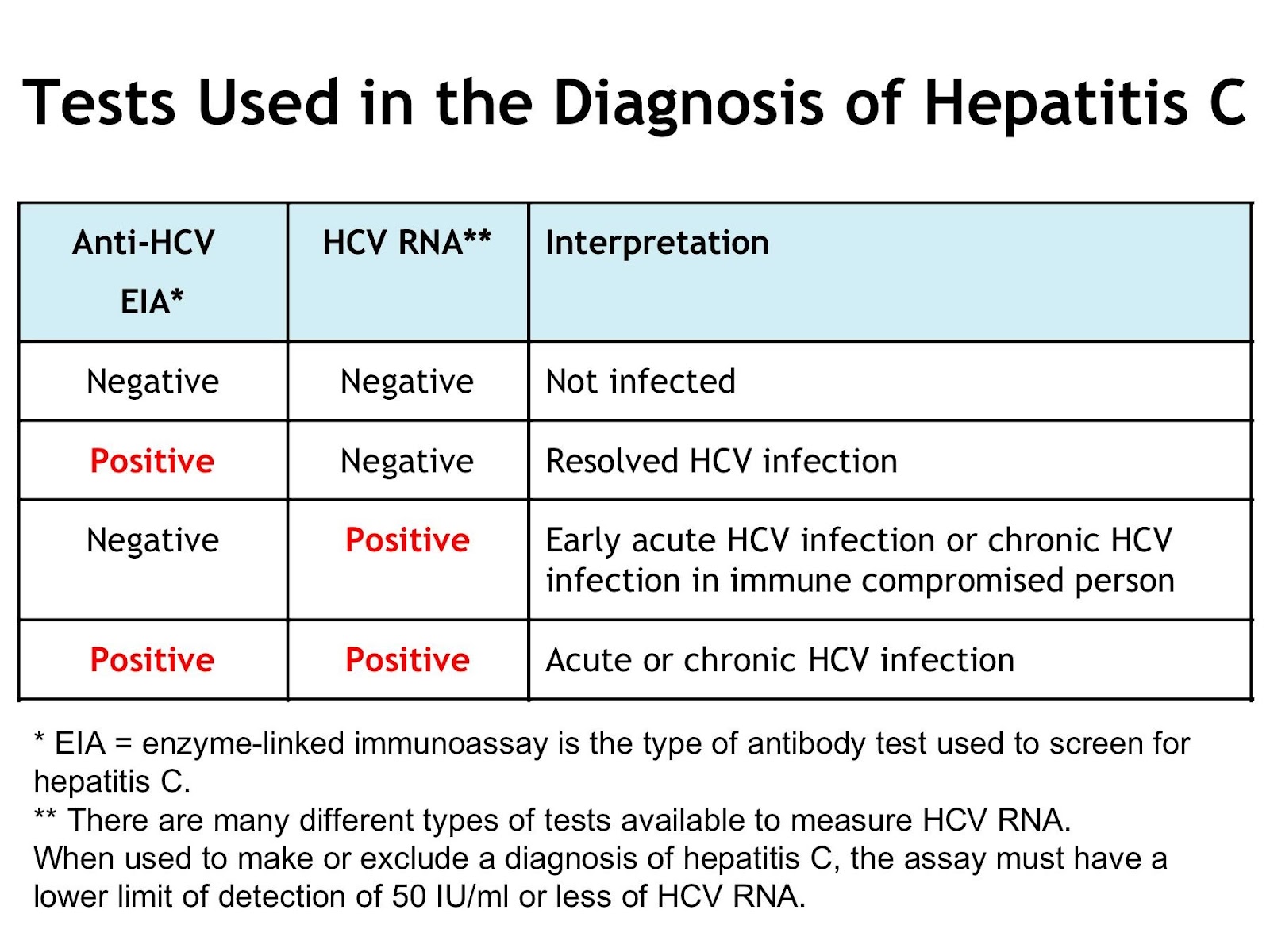
There are two blood tests used to diagnose hepatitis C. The antibody test, also called the anti-HCV test, tests for HCV antibodies that the body has produced in response to the infection.
One drawback is that the anti-HCV test cant differentiate between an active infection versus a chronic or previously acquired infection.
A positive anti-HCV test doesnt necessarily mean that you have hepatitis C. Antibodies picked up by the test may have been triggered by an infection other than HCV, leading to a positive result.
This phenomenon is known as cross-reactivity, and it often results in a false positive. The results may be verified through a second blood test.
The hepatitis C viral load test, also called an RNA test, will show whether you have chronic hepatitis C or a false positive.
2017 report , 22 percent of 479 subjects received a false-positive anti-HCV test.
According to a 2020 report, the rate of false-positive test results among 1,814 reactive serum samples was 10 percent.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Vaccine Schedule For Adults
Blood Transfusion Issues And Donor Counseling
Guidelines for donor notification for donors positive for transfusion transmissible infections are outlined in An Action Plan for Blood Safety by National AIDS Control Organization 2004. A blood donor is offered an option to know his TTI status at the time of registration for blood donation after due counseling and give consent for the same.
Notifying donors regarding a single positive screening test is fraught with the risk of causing undue anxiety and stress to a donor. If a screening test is positive, the blood unit should be immediately discarded. Presently there are no guidelines regarding confirming the test results before informing the donor. In case of samples with low S/CO and grey zone samples, a retesting of the donor samples using a different assay would be imperative before notifying the donor. There are clear cut guidelines regarding donor notification and referral for HIV positive blood donors with integrated counseling and testing centers available for the same. Donors who are positive for viral hepatitis markers have to be counseled by blood bank staff. An algorithm for donor counseling for HCV positive donors is outlined in .
Algorithm for donor counseling for HCV positive donors
Also Check: Can A Hepatitis B Carrier Get Vaccinated
Rna Or Viral Load Test
If you test positively for hepatitis C antibodies, you will need to get a RNA or viral load test. The RNA test is a blood test that checks to see if hepatitis C is active in your body.
- Negative
- If your RNA test result is negative, you do not have hepatitis C.
- Positive
- If your RNA test result is positive, you may have chronic hepatitis C. Talk to your doctor right away about a treatment plan.
You May Like: How To Test For Hepatitis C At Home
Explanation Of Test Results:
If this test result is positive, it means your body was exposed to the hepatitis C virus and made antibodies . However, it does not tell you whether you are still infected with hepatitis C. If the antibody test result is positive, you should be tested for hepatitis C RNA , which determines whether you are chronically infected. The lab will perform this RNA test automatically if your hepatitis C antibody test is positive.
If the antibody test result is negative, it means you have not been infected with the hepatitis C virus, and further testing for hepatitis C usually is not needed.
What Is A Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test
Hepatitis B surface antibody test is part of a panel of blood tests to diagnose HBV infection. Hepatitis B surface antibody test determines the presence and quantity of anti-HBs in the blood serum, which can indicate protection from HBV infection.
Hepatitis B disease affects the liver and commonly spreads through body fluids such as blood, semen, and vaginal secretions.
Recommended Reading: Genotype 4 Hepatitis C Treatment
How Is Hepatitis Spread
The hepatitis C virus is usually spread when someone comes into contact with blood from an infected person. This can happen through:
Sharing drug-injection equipment Today, most people become infected with hepatitis C by sharing needles, syringes, or any equipment used to prepare and inject drugs.
Birth Approximately 6% of infants born to infected mothers will get hepatitis C.
Healthcare exposures Although uncommon, people can become infected when healthcare professionals do not follow the proper steps needed to prevent the spread of bloodborne infections.
Sex with an infected person While uncommon, hepatitis C can spread during sex, though it has been reported more often among men who have sex with men.
Unregulated tattoos or body piercings Hepatitis C can spread when getting tattoos or body piercings in unlicensed facilities, informal settings, or with non-sterile instruments.
Sharing personal items People can get infected from sharing glucose monitors, razors, nail clippers, toothbrushes, and other items that may have come into contact with infected blood, even in amounts too small to see.
Blood transfusions and organ transplants Before widespread screening of the blood supply in 1992, hepatitis C was also spread through blood transfusions and organ transplants.
Question 3 How Is The Quantitative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test Performed
An immunometric technique is used. The anti-HBs binds to HBsAg ad and ay subtypes, which are coated on the test wells. Binding of a horseradish peroxidase-labeled HBsAg conjugate to the anti-HBs completes the sandwich formation. Unbound materials are then washed away. In the next step, the horseradish peroxidase catalyzes oxidation of a luminogenic substrate, producing light. Light signals are detected and quantified. Intensity of the light is proportional to the amount of anti-HBs present in the patient sample. The result is standardized to an international unit system and reported as milliinternational units per milliliter .
Also Check: Treatment For Hepatitis C Medications
What Are The Recommendations For Follow
Anti-viral agents or immune globulin should not be used for postexposure prophylaxis.
For the source, baseline testing for anti-HCV.
For the person exposed to an HCV-positive source, baseline and follow-up testing including baseline testing for anti-HCV and ALT activity and follow-up testing for anti-HCV and ALT activity.
Dont Miss: How Dangerous Is Hepatitis C
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Surface Antibody And Antigen
An antigen is a substance that induces antibody production. Hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
Don’t Miss: Who Needs Hepatitis C Screening
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. Its transmitted through contact with blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not transmitted through sharing utensils or kissing. Its also not transmitted through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding.
Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure. Symptoms can last for several weeks.
But even without symptoms, you can still transmit the infection to others. The virus can live outside the body and remains infectious for at least
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious condition. Its associated with many serious complications, some of which can be life threatening.
But there are many treatment options available and multiple ways you can prevent infection, including getting vaccinated.
If you suspect you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a doctor to prevent infection and determine the best course of treatment for you.
Recommended Reading: How To Know If I Have Hepatitis C
Limitations Of Screening For Hepatitis C
Barriers to screening for hepatitis C include limited access to healthcare, inadequate health insurance coverage, individuals’ decreasing recall of past risky behaviors, lack of knowledge of hepatitis C prevalence, natural history, and available tests and treatments for hepatitis C at the provider level.29–32 Moreover, nearly 42% of primary care physicians reported being unfamiliar with the CDC guidelines in a survey of community-based physicians.33
Don’t Miss: How Soon Can You Detect Hepatitis C
What Does A Negative Hcv Antibody Test Result Mean
A negative antibody test result usually means that the person has not been infected with hepatitis C .
The body needs at least two months to make antibodies. People with weakened immune systems are not always able to produce antibodies. This might happen in people with autoimmune disorders , HIV-positive people with a CD4 cell count below < 200 cells/mm3, and people taking immunosuppressants.
What Do The Results Mean
There are two results from a hepatitis C antibody test.
- A non-reactive or negative test result means that the person does not have the virus. The exception is if someone has come into contact with the virus recently, such as through contaminated blood. If this is the case, they will need to have another test.
- A reactive or positive test result means that the person has had the virus at some point but does not mean that they still have it. Further tests will be needed to check whether the virus is still active in the body and if treatment will be required.
Once diagnosed with hepatitis C, a person will need to undergo a series of different tests to see how the virus has affected their body.
These tests will check for any liver damage, identify how well the liver is working, and help a healthcare professional to decide on treatment.
Hepatitis C is treated with medication known as an antiviral. It gets this name because it aims to clear the virus out of the body.
Another aim of the medication is to slow down damage to the liver. It may also reduce the chance of a person getting liver cancer or developing serious liver scarring, known as cirrhosis.
A person with hepatitis C will require regular testing during treatment to see how well the medication is working. Keeping healthy, getting enough sleep, and avoiding drugs and alcohol can help treatment to work.
Recommended Reading: When Should You Get Hepatitis A Vaccine
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Core Antibody And Surface Antibody
The basic blood test for hepatitis B consists of three screening tests: a hepatitis B surface antigen test, which determines whether a person currently has the infection a hepatitis B core antibody test, which determines whether a person has ever been infected and a hepatitis B surface antibody test, which determines.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are measured in blood samples in milli-International Units/milliliter mIU/mL). The ranges for hepatitis B surface antibodies are:
- Anti-HBs greater than 10-12 mIU/mL: Protected against hepatitis B virus infection, either from vaccination or successful recovery from a previous HBV infection.
- Anti-HBs less than 5 mIU/mL: Negative for HBV infection, but susceptible and hence requires vaccination.
- Anti-HBs from 5-12 mIU/mL: Inconclusive results and the test should be repeated.
However, there is no standardization of these values so it is advisable to check the manufacturers values it is the reason values are mainly reported as positive or negative.
Other Things To Know:
- After a successful course of treatment for hepatitis C, the hepatitis C antibody remains detectable, but the hepatitis C RNA will be undetectable.
- If you plan to donate blood, you will be tested for the hepatitis C antibody and will be turned away even if you do not have an active infection.
- Any patient with a positive test result for the hepatitis C antibody should have additional tests to determine whether or not the virus is still active.
Recommended Reading: How Does One Catch Hepatitis B
Hepatitis C Can Be Prevented
Although there is no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C, there are ways to reduce the risk of becoming infected.
- Avoid sharing or reusing needles, syringes, or any other equipment used to prepare and inject drugs, steroids, hormones, or other substances.
- Do not use personal items that may have come into contact with an infected persons blood, even in amounts too small to see, such as glucose monitors, razors, nail clippers, or toothbrushes.
- Do not get tattoos or body piercings from an unlicensed facility or in an informal setting.
Is Vitamin C Good For Hepatitis B Patient
Based on the conducted randomized clinical trials, convincing evidence that beta-carotene, vitamin A, vitamin C, and vitamin E or their combinations are beneficial for the treatment of alcoholic, autoimmune, hepatitis B or hepatitis C virus liver diseases or liver cirrhosis could not be found, contrary to in vitro.
You May Like: How Do You Know If You Have Alcoholic Hepatitis
Hep C Antibodies Do Not Prevent Re
What does it mean, in any real terms? Well, in terms of my status as being cured, it means nothing at all, because we do believe, as a fact, that antibodies for hep C offer no protection and so have no real value. It is interesting to me, and that is only because of my interest in the science of why and how things work, and there is some science that points to diminished antibody presence over time, and is it the same with all treatments? We dont know, and no need to be concerned, unless you too have a mildly science and nerdy side like me.
How Often Do I Need A Viral Load Test
Understanding the specifics of your viral load is important at the time of diagnosis. Once you begin treatment, follow-up testing will let your doctor know if the current treatment is effective.
Other than that, theres no need for repeat testing. This is because the viral load doesnt provide information about your symptoms or whether your liver is functioning properly. Other liver tests, such as a biopsy, can provide that information.
Certain groups are more vulnerable to contracting HCV. Among them are:
- people on dialysis
- children born to HCV-positive mothers
- anyone who may have had contact with the blood of someone with hepatitis C
The most common methods of HCV transmission are:
- sharing needles and syringes used for injecting drugs
- a mother with hepatitis C transferring HCV to her child during childbirth
Occasionally HCV is transmitted through:
- having sex with someone who has hepatitis C
- getting a tattoo in a place that doesnt have good infection control
- sharing personal care items, such as a razor or toothbrush, with someone who has hepatitis C
Hepatitis C cant be transmitted through:
- coughing or sneezing
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Cvs Cost
Using Elisa And Hcv Rna Tests Together:
- Negative ELISA = No hepatitis C antibodies found in blood. You are probably not infected with HCV.
- Positive ELISA = You may have HCV infection. However, it is possible this is a false-positive. More testing is required.
- Negative HCV RNA = No active HCV infection.
- Positive HCV RNA = Active HCV infection.
What Is The Difference Between Relapse And Nonresponse
The goal of treating chronic hepatitis C is to completely clear the virus. This means that your viral load is zero or so low that the virus cant be detected with standard blood tests.
Without treatment, the hepatitis C virus in liver cells constantly makes copies of itself, and the virus ends up not just in liver cells but also in the bloodstream. Treatment is intended to completely stop reproduction of the virus so that it doesnt continue to enter the bloodstream or cause any more injury to liver cells.
Successful treatment results in a sustained virological response. This means the virus becomes completely undetectable before the treatment is finished, and it remains undetectable for 6 months after treatment is stopped.
A relapse means the viral load drops to an undetectable level before treatment is completed, but becomes detectable again within 6 months after treatment is stopped. Even if the virus returns at a level that is lower than it was before treatment, a relapse is still considered to have occurred. A relapse can be determined if the viral load starts to rise during treatment, or at any time after the virus becomes undetectable.
A nonresponse means the viral load never drops significantly and the virus remains detectable throughout the course of treatment.
Dont Miss: What Does It Mean If You Have Hepatitis C Antibodies
Don’t Miss: How To Read Hepatitis B Test Results