What Causes Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C occurs as the result of percutaneous transmission of the hepatitis C virus through infectious blood. Percutaneous means the infected blood must be absorbed through the skin and enter the bloodstream of another person in other words, blood-to-blood. Hepatitis C is approximately seven times more infectious than HIV.
Hepatitis C is most commonly transmitted in the following manner:
- Intravenous drug use Currently, the most common means of Hepatitis C transmission in the United States. The rate of infection is rising with the explosive increase in the misuse of opioids and heroin.
- Blood and Blood Product Transfusions
- Organ Transplants
- Household Contact
- Medical Procedures
Hepatitis C is not transmitted by casual contact like hugging or kissing, nor is it transmitted through breast milk , food, water or sharing food or water with an infected person.
How Do You Get Hepatitis B
The virus that causes hepatitis B lives in blood, semen, and other fluids in your body. You usually get it by having sex with someone who’s infected.
You also can get it if you:
- Have direct contact with infected blood or the body fluids of someone who’s got the disease, for instance by using the same razor or toothbrush as someone who has hepatitis B, or touching the open sores of somebody who’s infected.
- If you’re pregnant and you’ve got hepatitis B, you could give the disease to your unborn child. If you deliver a baby who’s got it, they need to get treatment in the first 12 hours after birth.
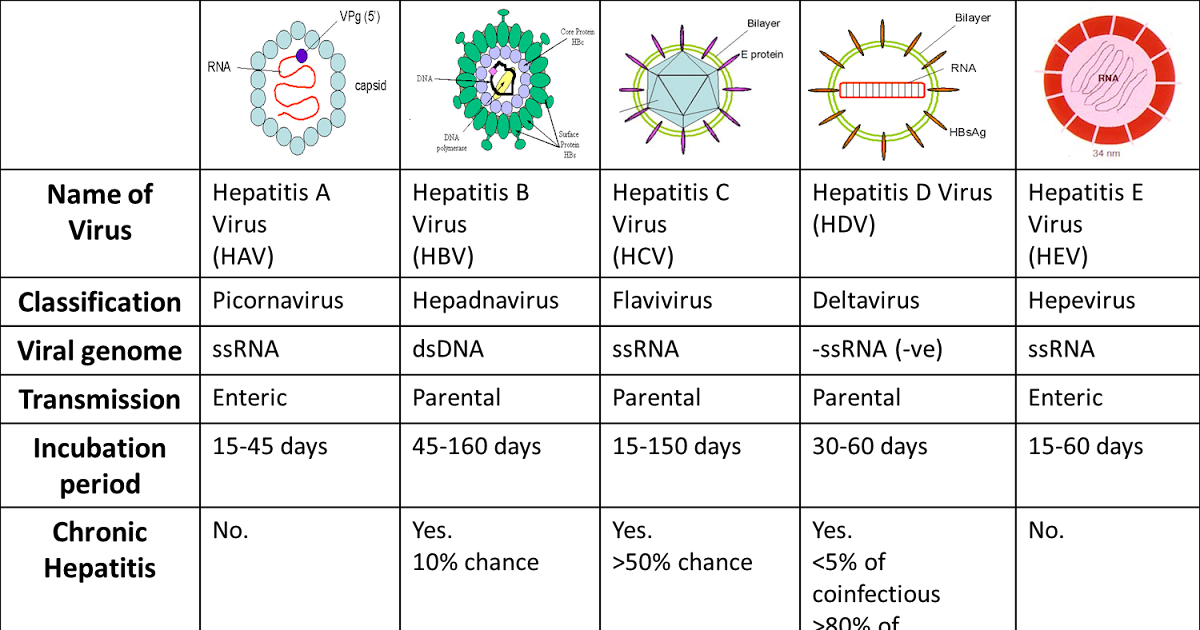
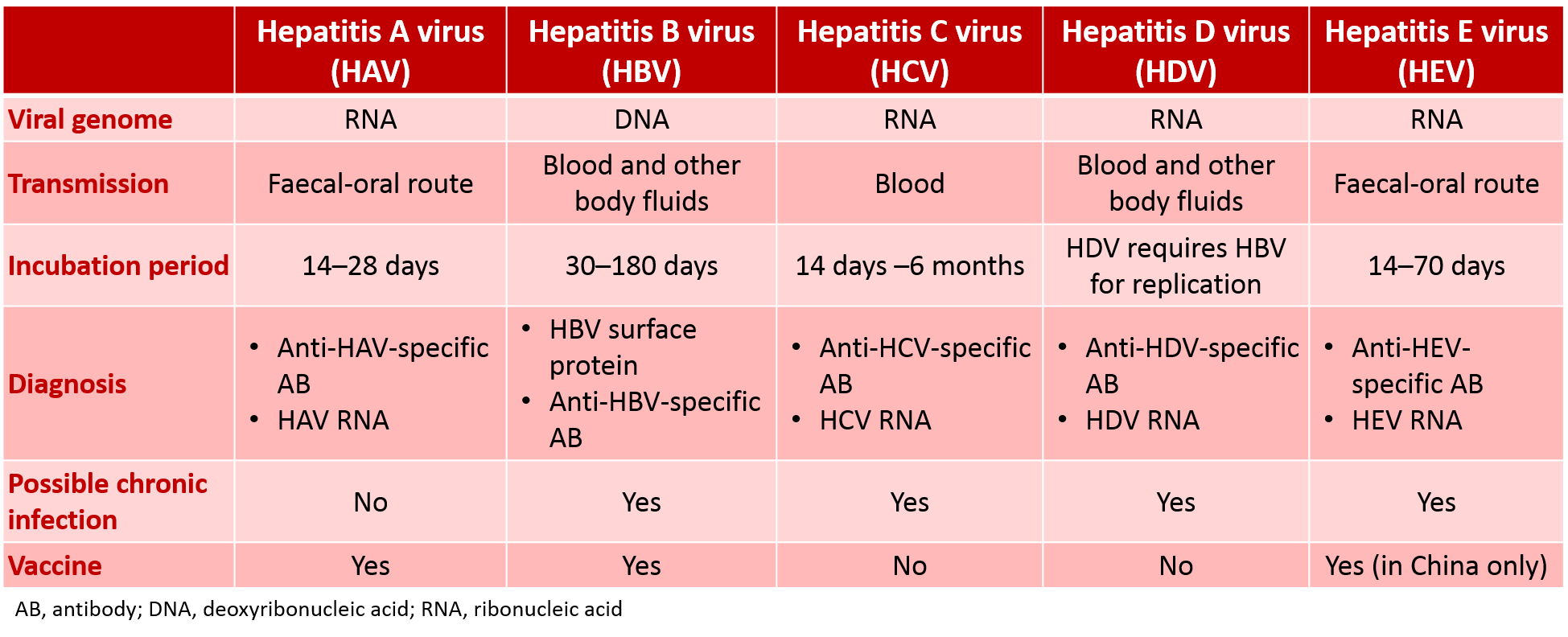
Types Of Viral Hepatitis In Summary
- Hepatitis A: It is one of the most common hepatitis. It is caused by type A virus, and occurs in the feces of the infected person.Generally, it is transmitted through direct contact with the contagious person, their secretions or blood, and contaminated food. Although it usually does not last more than two months, it usually appears between two weeks and 40 days after infection. There is a vaccine for this disease.
- Hepatitis B: It is a hepatitis that is caused by infection with the B virus. It can be transmitted through the blood, through the contact of the mother with the fetus, or through sexual contact. It is certainly common in people who exchange syringes, so that it can also be transmitted through wounds made with already infected objects. Its incubation period may reach half a year, and it may evolve to cirrhosis or liver cancer. There is a vaccine for this disease.
- Hepatitis C: It is one of the most severe hepatitis, and it has a greater chance of becoming chronic. It is produced by virus C, and is transmitted by contact with infected blood, genitals, mouth, transfusions and from mother to fetus at the time of delivery. At the moment there is no vaccine for this disease.
- Hepatitis D: It is caused by the virus D. It is transmitted along with hepatitis B, which causes greater chronicity. It makes hepatitis B much more destructive.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis C Turn Into Hiv
How Long Does It Last
Hepatitis A can last from a few weeks to several months.
Hepatitis B can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious, life-long condition. More than 90% of unimmunized infants who get infected develop a chronic infection, but 6%10% of older children and adults who get infected develop chronic hepatitis B.
Hepatitis C can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious, life-long infection. Most people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop chronic hepatitis C.
What Is The Treatment For Viral Hepatitis
Treatment of acute viral hepatitis and chronic viral hepatitis are different. Treatment of acute viral hepatitis involves resting, relieving symptoms, and maintaining an adequate intake of fluids. Treatment of chronic viral hepatitis involves medications to eradicate the virus and taking measures to prevent further liver damage.
Acute hepatitis
In patients with acute viral hepatitis, the initial treatment consists of relieving the symptoms of nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain . Careful attention should be given to medications or compounds, which can have adverse effects in patients with abnormal liver function . Only those medications that are considered necessary should be administered since the impaired liver is not able to eliminate drugs normally, and drugs may accumulate in the blood and reach toxic levels. Moreover, sedatives and “tranquilizers” are avoided because they may accentuate the effects of liver failure on the brain and cause lethargy and coma. The patient must abstain from drinking alcohol since alcohol is toxic to the liver. It occasionally is necessary to provide intravenous fluids to prevent dehydration caused by vomiting. Patients with severe nausea and/or vomiting may need to be hospitalized for treatment and intravenous fluids.
Chronic hepatitis
Medications for chronic hepatitis C infection include:
- oral daclatasvir
Medications for chronic hepatitis B infection include:
- oral entecavir
- oral tenofovir
Fulminant hepatitis
Also Check: How Does One Get Hepatitis B And C
What Is The Long Term Prognosis For Hepatitis C
The future looks promising for those with Hepatitis C. Fortunately, scientific advances and intense research and development have led to the development of many oral antiviral drugs. In addition, research shows that combining specific supplements such as milk thistle shows promise in assisting the liver of patients with Hepatitis C.
The odds of living well with Hepatitis C rather than dying from Hepatitis C are very good. By maintaining a positive attitude, working closely with ones physician after diagnosis, getting support from as many areas as possible , and making positive lifestyle changes, Hepatitis C doesnt have to be the death sentence it was once believed to be.
Effective Treatments Are Available For Hepatitis C
New medication to treat for HCV have been approved in recent years. These treatments are much better than the previously available treatment because they have few side effects and do not need to be injected. There are several direct-acting antiviral HCV treatments that cure more than 95% of people who take them in 8 to 12 weeks. HCV treatment dramatically reduces deaths among people with HCV infection, and people who are cured of HCV are much less likely to develop cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Take Action! CDCs National Prevention Information Network Service Locator helps consumers locate hepatitis B and hepatitis C prevention, care, and treatment services.
You May Like: Genotype 2a Hepatitis C Virus
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
There are two types of Hepatitis C acute and chronic . Individuals with acute Hepatitis C usually do not manifest symptoms and the small percentage that do will experience symptoms similar to the other cases of acute hepatitis, including flu-like symptoms, joint aches or mild skin rash. Individuals that are particularly likely to experience a severe course of Hepatitis C are those individuals that already have Hepatitis B and become infected with acute Hepatitis C.
Other symptoms which may be experienced by individuals with acute Hepatitis C are:
- Loss of appetite
- Grey colored stool
- Jaundice
As is the case for acute Hepatitis C, most people who have chronic Hepatitis C do not experience symptoms in the early stages or even in the advanced stages of the disease. Therefore, it is not uncommon to find out, by surprise, that one has the virus when donating blood or during a routine blood examination. It is possible to have Hepatitis C for many years and not know it which is the reason why the disease has been referred to as a silent killer.
If symptoms do occur, they will most likely exhibit as:
- Pain and tenderness in the area of the liver
- Fever
- Jaundice
- Fatigue
In those persons who do develop symptoms, the average time period from exposure to symptom onset is 412 weeks .
Viral Hepatitis Definition And Overview
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Many illnesses and conditions can cause inflammation of the liver, for example, drugs, alcohol, chemicals, and autoimmune diseases. Many viruses, for example, the virus causing mononucleosis and the cytomegalovirus, can inflame the liver. Most viruses, however, do not attack primarily the liver the liver is just one of several organs that the viruses affect. When most doctors speak of viral hepatitis, they are using the definition that means hepatitis caused by a few specific viruses that primarily attack the liver and are responsible for about half of all human hepatitis. There are several hepatitis viruses they have been named types A, B, C, D, E, F , and G. As our knowledge of hepatitis viruses grows, it is likely that this alphabetical list will become longer. The most common hepatitis viruses are types A, B, and C. Reference to the hepatitis viruses often occurs in an abbreviated form The focus of this article is on these viruses that cause the majority of human viral hepatitis.
Hepatitis viruses replicate primarily in the liver cells. This can cause the liver to be unable to perform its functions. The following is a list of major functions of the liver:
Also Check: How Do You Cure Hepatitis A
How Is Viral Hepatitis Diagnosed
Diagnosis of viral hepatitis is based on symptoms and physical findings as well as blood tests for liver enzymes, viral antibodies, and viral genetic materials.
Symptoms and physical findings
Diagnosis of acute viral hepatitis often is easy, but the diagnosis of chronic hepatitis can be difficult. When a patient reports symptoms of fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, darkening of urine, and then develops jaundice, the diagnosis of acute viral hepatitis is likely and can be confirmed by blood tests. On the other hand, patients with chronic hepatitis due to HBV and HCV often have no symptoms or only mild nonspecific symptoms such as chronic fatigue. Typically, these patients do not have jaundice until the liver damage is far advanced. Therefore, these patients can remain undiagnosed for years to decades.
Blood tests
There are three types of blood tests for evaluating patients with hepatitis: liver enzymes, antibodies to the hepatitis viruses, and viral proteins or genetic material .
Liver enzymes: Among the most sensitive and widely used blood tests for evaluating patients with hepatitis are liver enzymes, called aminotransferases. They include aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase . These enzymes normally are contained within liver cells. If the liver is injured , the liver cells spill the enzymes into the blood, raising the enzyme levels in the blood and signaling that the liver is damaged.
Examples of tests for viral antibodies are:
Do You Need Vaccinations Before Traveling Abroad
The CDC divides travel vaccinations into three categories: 1) routine, 2) recommended, and 3) required. The only vaccine classified as “required” by International Health Regulations is the yellow fever vaccination for travel to certain countries in sub-Saharan Africa and tropical South America.
“Routine” vaccinations are those that are normally administered, usually during childhood, in the United States. These include immunizations against:
- tetanus
You May Like: Hepatitis C Is It Curable
How Is Hepatitis C Transmitted
Because HCV is primarily spread through contact with infected blood, people who inject drugs are at increased risk for HCV infection. HCV can also be transmitted from an infected mother to child at the time of birth, from unregulated tattoos or body piercings, and from sharing personal items that may be contaminated with infected blood, even in amounts too small to see. Much less often, HCV transmission occurs through sexual contact with an HCV-infected partner, especially among people with multiple sex partners and men who have sex with men. Currently in the United States, health care related transmission of HCV is rare, but people can become infected from accidental needle sticks and from breaches in infection control practices in health care facilities.
Clinical Relevance Of Hcv Genotypes
Although the impact of HCV heterogeneity and genotypes on the day-to-day clinical management of chronic HCV infection has not been established, its role as an epidemiologic marker has been clearly shown. Furthermore, the sensitivity and specificity of serologic and virologic assays for the detection of HCV may be influenced by the heterogeneity of HCV. However, the exact role of genotypes in the progression of liver disease, the outcome of HCV infection, and the response to interferon therapy are much less well understood than their role as an epidemiologic marker. The study of these issues has been hampered by the long natural history of HCV infection and the lack of information about the exact time of exposure to the infection. The following subsections in this section specifically address these issues on the basis of the information available.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C And Treatment Options
Stages Of Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus affects people in different ways and has several stages:
- Incubation period. This is the time between first exposure to the start of the disease. It can last anywhere from 14 to 80 days, but the average is 45
- Acute hepatitis C. This is a short-term illness that lasts for the first 6 months after the virus enters your body. After that, some people who have it will get rid of, or clear, the virus on their own.
- Chronic hepatitis C. For most people who get hepatitis C — up to 85% — the illness moves into a long-lasting stage . This is called a chronic hepatitis C infection and can lead to serious health problems like liver cancer or cirrhosis.
- Cirrhosis. This disease leads to inflammation that, over time, replaces your healthy liver cells with scar tissue. It usually takes about 20 to 30 years for this to happen, though it can be faster if you drink alcohol or have HIV.
- Liver cancer. Cirrhosis makes liver cancer more likely. Your doctor will make sure you get regular tests because there are usually no symptoms in the early stages.
Learn more about the stages and progression of hepatitis C.
Hiv And Hepatitis C Coinfection
HCV infection is common among people with HIV who also inject drugs. Nearly 75% of people living with HIV who report a history of injection drug use are co-infected with HCV. All people who are diagnosed with HIV are recommended to be tested for HCV at least once. People living with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HCV infection. Fortunately, direct acting antivirals that are used to treat HCV work equally well in people with and without HIV infection. For more information about HIV and HCV coinfection, visit the HIV.govs pages about hepatitis C and HIV coinfection.
Recommended Reading: Glomerulonephritis Due To Infectious Hepatitis
Can Hepatitis C Be Prevented
There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. But you can help protect yourself from hepatitis C infection by:
- Not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- Wearing gloves if you have to touch another person’s blood or open sores
- Making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools and unopened ink
- Not sharing personal items such toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- Using a latex condom during sex. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
The 5 Types Of Hepatitis
Viral hepatitis can be caused by five varieties of the hepatitis virus. According to the international classification, each virus is named after a letter of the alphabet: A, B, C, D, and E.
Below, discover what happens when someone becomes infected with any of these viruses.
1. Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is the mildest of this group of viral infections. Its transmitted through the fecal-oral route. In other words, an infected person expels it through their feces, contaminates food or water that another person eats or drinks, and the virus finds a new host.
Hepatitis A patients suffer from gastroenteritis symptoms with liver involvement. Thus, fever, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and vomiting appear.
As the liver is inflamed, the bile stagnates and doesnt circulate. As a result, the skin turns yellowish . This occurs because bilirubin impregnates the skin and mucous membranes, which is why the whites of the eyes also turn yellow. Excess bilirubin is eliminated through the urine, which also becomes darker.
The usual symptoms last about 15 days. Although the disease can last for a month or more, this isnt common. Patients tend to recover without any major problems and, if there was no dehydration, they wont suffer from any lasting effects.
The most dangerous symptom is fluid loss, especially in young children. Due to how fast it spreads, extreme precautionary measures should be taken when there are outbreaks in closed populations, such as schools.
2. Hepatitis B
3. Hepatitis C
Don’t Miss: Does Hepatitis C Have A Cure
Hepatitis C Testing And Diagnosis
Doctors will start by checking your blood for:
Anti-HCV antibodies: These are proteins your body makes when it finds the hep C virus in your blood. They usually show up about 12 weeks after infection.
It usually takes a few days to a week to get results, though a rapid test is available in some places.
The results can be:
- Nonreactive, or negative:
- That may mean you donât have hep C.
- If youâve been exposed in the last 6 months, youâll need to be retested.
If your antibody test is positive, youâll get this test:
HCV RNA: It measures the number of viral RNA particles in your blood. They usually show up 1-2 weeks after youâre infected.
- The results can be:
- Negative: You donât have hep C.
- Positive: You currently have hep C.
You might also get:
Liver function tests: They measure proteins and enzyme levels, which usually rise 7 to 8 weeks after youâre infected. As your liver gets damaged, enzymes leak into your bloodstream. But you can have normal enzyme levels and still have hepatitis C. Learn the reasons why you should get tested for hepatitis C.