Infants Born To Mothers Who Have Hepatitis B: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
Protecting Your Baby
Infants born to women with hepatitis B must receive accurate doses of hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin to ensure complete protection. In order to protect these infants, medications should be given immediately after birth in the delivery room or within the first 12-24 hours of life*.
* See Testing and Treatment During Pregnancy section for details. Please note that testing of all pregnant women for hepatitis B is a global recommendation.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Infants
The World Health Organization recommends that infants born to hepatitis B positive mothers receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth, and ideally a dose of hepatitis B immunoglobulin . These shots must be followed by the additional vaccine doses given on the recommended schedule. In the U.S., infants should follow a 1 month and 6-month schedule for the additional two doses.
4-Dose Combination Vaccine Series for Infants
Who Should Not Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Generally seen as a safe vaccine, there are some circumstances in which doctors advise against receiving the HBV vaccine. You shouldnt have the hepatitis B vaccine if:
- youve had a serious allergic reaction to a previous dose of the hepatitis B vaccine
- you have a history of hypersensitivity to yeast or to any other vaccine components
- youre experiencing a moderate or severe acute illness
If youre currently experiencing an illness, you should postpone receiving the vaccine until your condition has improved.
What Should I Tell My Health Care Provider Before Receiving A Hepatitis B Vaccine
Before receiving a hepatitis B vaccine, tell your health care provider:
Ask your health care provider about possible side effects from getting a hepatitis B vaccine. Your health care provider will tell you what to do if you have side effects.
Also Check: Human Hepatic Stellate Cell Line
Approaches By Virus Life Cycle Stage
consist of a and sometimes a few stored in a capsule made of , and sometimes covered with a layer . Viruses cannot reproduce on their own and instead propagate by subjugating a host cell to produce copies of themselves, thus producing the next generation.
Researchers working on such “” strategies for developing antivirals have tried to attack viruses at every stage of their life cycles. Some species of mushrooms have been found to contain multiple antiviral chemicals with similar synergistic effects.Compounds isolated from fruiting bodies and filtrates of various mushrooms have broad-spectrum antiviral activities, but successful production and availability of such compounds as frontline antiviral is a long way away. Viral life cycles vary in their precise details depending on the type of virus, but they all share a general pattern:
Before cell entry
This stage of viral replication can be inhibited in two ways:
Uncoating inhibitor
Inhibitors of uncoating have also been investigated.
During Viral Synthesis
Reverse transcription
Transcription
The Hepatitis B Vaccine
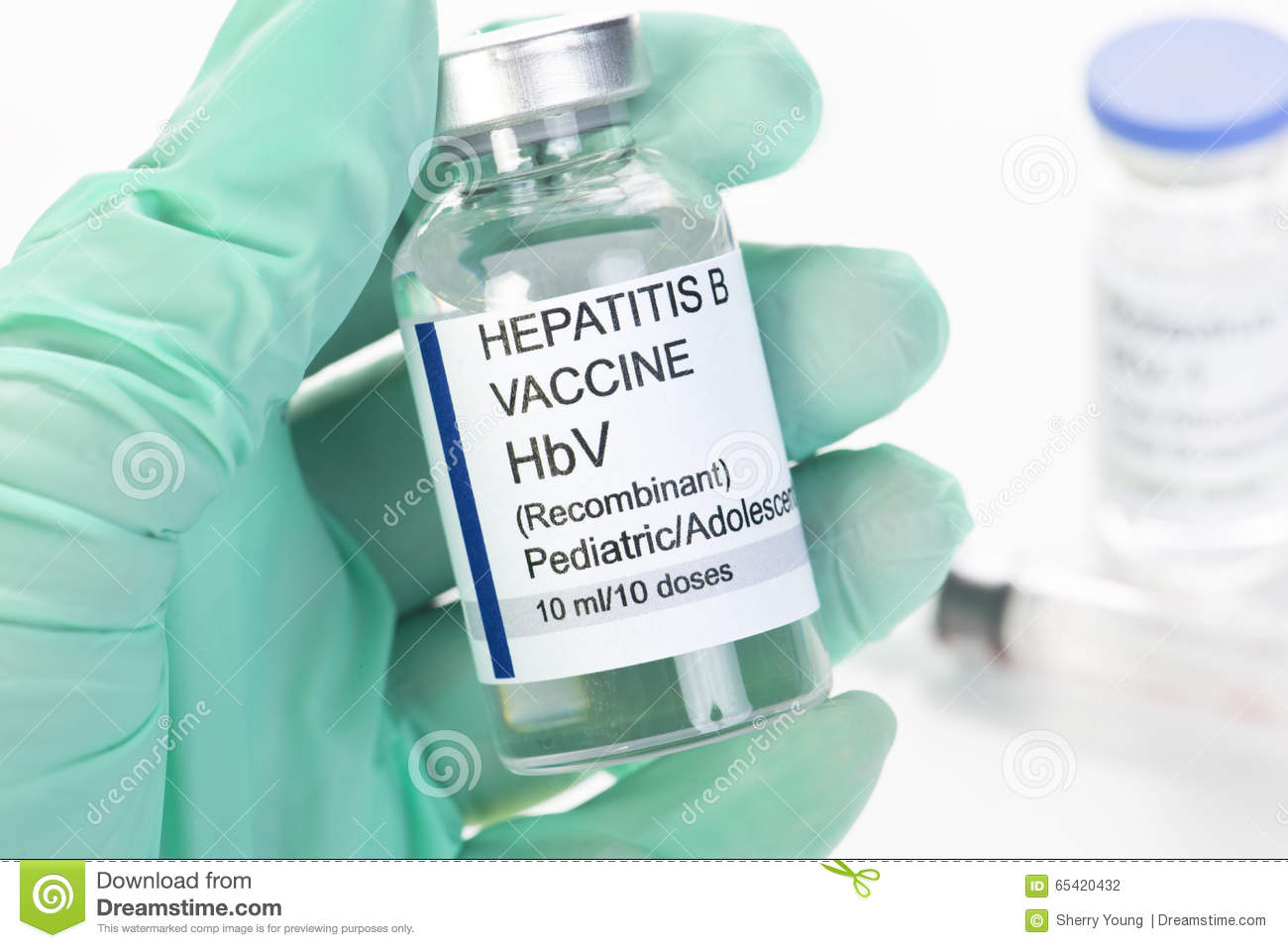
The hepatitis B vaccine sometimes known by the trade name Recombivax HB is used to prevent this infection. The vaccine is provided in three doses.
The first dose can be taken on a date you choose. The second dose must be taken one month later. The third and final dose must be taken six months after the first dose.
Adolescents 11 to 15 years old may follow a two-dose regimen.
Don’t Miss: How Did You Get Hepatitis C
Why Should I Vaccinate My Newborn Child If I Know That I Am Not Infected With Hepatitis B Virus
Before the hepatitis B vaccine, every year in the United States about 18,000 children were infected with hepatitis B virus by the time they were 10 years old. This statistic is especially important because people are much more likely to develop liver cancer or cirrhosis if they are infected early in life, rather than later in life .
About 9,000 of the 18,000 children infected in the first 10 years of life caught the virus from their mother during birth. However, many young children didn’t catch the disease from their mother. They caught it from either another family member or someone else who came in contact with the child. Because hepatitis B can be transmitted by relatively casual contact with items contaminated with blood of an infected person, and because many people who are infected with hepatitis B virus don’t know that they have it, it is virtually impossible to be “careful enough” to avoid this infection.
For these reasons, all young children are recommended to receive the hepatitis B vaccine. The best time to receive the first dose is right after birth. This will ensure that the child will be protected as early as possible from catching hepatitis B from people who dont know that they are infected with the virus.
Listen to Dr. Offit explain why newborns get the hepatitis B vaccine by watching this short video, part of the series Talking About Vaccines with Dr. Paul Offit.
Site Of Injection For Vaccination And Antibody Response
Hepatitis B vaccination should be given in the upper arm or the anterolateral aspect of the thigh and not in the buttock. There are over 100 reports of unexpectedly low antibody seroconversion rates after hepatitis B vaccination using injection into the buttock. In one center in the USA a low antibody response was noted in 54% of healthy adult health-care personnel. Many studies have since shown that the antibody response rate is significantly higher in centers using deltoid injection than centers using the buttock. On the basis of antibody tests after vaccination, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in the USA recommended that the arm be used as the site for hepatitis B vaccination in adults, as has the Department of Health in the UK.
These observations have important public health implications, well illustrated by the estimate that about 20% of the 60 000 people immunized against HBV in the buttock in the USA by March 1985 had failed to attain a minimum level of antibody of 10 IU/l and were therefore not protected.
Hepatitis B surface antibody titers should be measured in all people who have been immunized against HBV by injection in the buttock, and when this is not possible a complete course of three injections of vaccine should be administered into the deltoid muscle or the anterolateral aspect of the thigh, the only acceptable sites for HBV immunization.
Dean A. Blumberg, in, 2012
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Flu Like Symptoms
Persons With Inadequate Immunization Records
Evidence of long term protection against HB has only been demonstrated in individuals who have been vaccinated according to a recommended immunization schedule. Independent of their anti-HBs titres, children and adults lacking adequate documentation of immunization should be considered susceptible and started on an immunization schedule appropriate for their age and risk factors. Refer to Immunization of Persons with Inadequate Immunization Records in Part 3 for additional information.
What Are Side Effects Of Inactivated Viral Vaccines
Side effects of inactivated viral vaccines may include the following:
- Injection site reactions include:
Information contained herein is not intended to cover all possible side effects, precautions, warnings, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or adverse effects. Check with your doctor or pharmacist to make sure these drugs do not cause any harm when you take them along with other medicines. Never stop taking your medication and never change your dose or frequency without consulting your doctor.
Read Also: How To Reduce Hepatitis B Viral Load Naturally
Treatment Options For Antiviral Resistant Pathogens
If a virus is not fully wiped out during a regimen of antivirals, treatment creates a bottleneck in the viral population that selects for resistance, and there is a chance that a resistant strain may repopulate the host. Viral treatment mechanisms must therefore account for the selection of resistant viruses.
The most commonly used method for treating resistant viruses is combination therapy, which uses multiple antivirals in one treatment regimen. This is thought to decrease the likelihood that one mutation could cause antiviral resistance, as the antivirals in the cocktail target different stages of the viral life cycle. This is frequently used in retroviruses like HIV, but a number of studies have demonstrated its effectiveness against influenza A, as well. Viruses can also be screened for resistance to drugs before treatment is started. This minimizes exposure to unnecessary antivirals and ensures that an effective medication is being used. This may improve patient outcomes and could help detect new resistance mutations during routine scanning for known mutants. However, this has not been consistently implemented in treatment facilities at this time.
Despite their successes, in the United States there exists plenty of stigma surrounding vaccines that cause people to be incompletely vaccinated. These “gaps” in vaccination result in unnecessary infection, death, and costs. There are two major reasons for incomplete vaccination:
Concurrent Administration Of Vaccines
HB-containing vaccines may be administered concomitantly with other vaccines or with HBIg. Different injection sites and separate needles and syringes must be used for concurrent parenteral injections.
Refer to Timing of Vaccine Administration in Part 1 for additional information about concurrent administration of vaccines.
Also Check: How Can I Get Hepatitis
Emergency Hepatitis B Vaccination
If you have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus and have not been vaccinated before, you should get immediate medical advice, as you may benefit from having the hepatitis B vaccine.
In some situations, you may also need to have an injection of antibodies, called specific hepatitis B immunoglobulin , along with the hepatitis B vaccine.
HBIG should ideally be given within 48 hours, but you can still have it up to a week after exposure.
Who Should Get The Hbv Vaccine
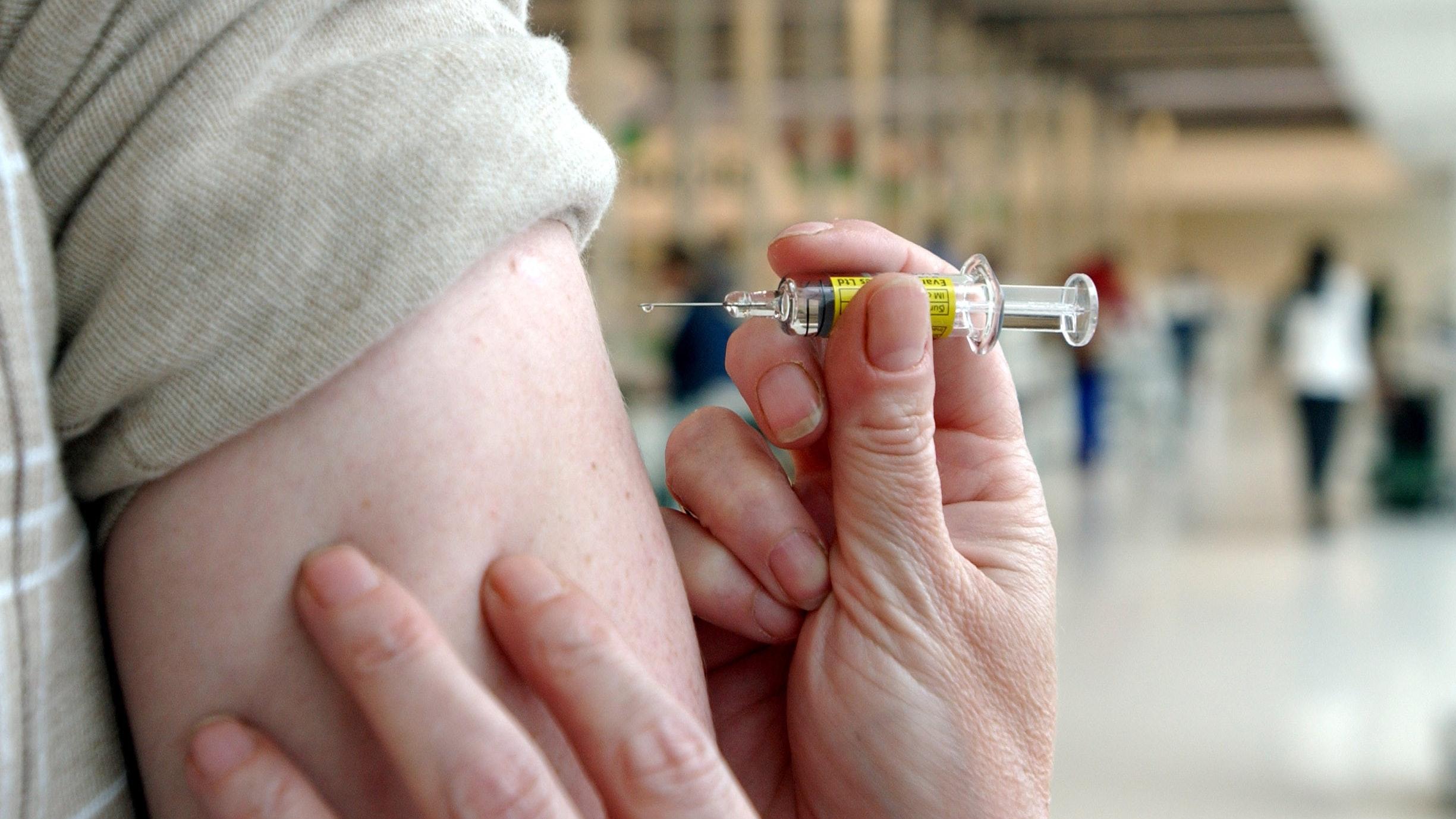
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that children should get their first hepatitis B vaccine at birth and complete the doses by 6 to 18 months of age. However, the HBV vaccine is still recommended for all children if they havent already gotten it, from infanthood up to 19 years old. Most U.S. states require a hepatitis B vaccine for school admittance, however.
Its also recommended for adults at an increased risk of catching the HBV infection, or anyone who fears they have or will be exposed to it in the near future.
The HBV vaccine is even safe to administer to pregnant women.
Recommended Reading: Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Hepatic
What Is Hepatitis B Virus
Hepatitis B virus attacks the liver. Hepatitis B virus infections are known as the “silent epidemic” because many infected people don’t experience symptoms until decades later when they develop hepatitis , cirrhosis , or cancer of the liver . Every year in the United States about 22,000 new hepatitis B infections occur and about 2,000 people die from their infections.
Important Information About Vaccine And Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin Shot Administration
Where available, the hepatitis B birth-dose and HBIG should be administered within 24 hours of birth in order to prevent the transmission of hepatitis B from mother to child. It is very important that the shots be given in opposite limbs, to ensure the highest effectiveness. Please see chart above for more information.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Core Antibody Positive
How Can I Contract Hepatitis B
You can contract hepatitis B by coming into contact with the bodily fluids of an infected person.
Resort activities that may put you at risk for hepatitis B include:
Getting a manicure, pedicure, tattoo, piercing, or acupuncture with improperly sterilized tools
Having sexual contact with an infected partner
Giving first aid to, or receiving it from, an infected person
Receiving a medical or dental procedure with contaminated equipment
Sharing personal grooming items with an infected person
How Do Inactivated Viral Vaccines Work
Inactivated viralvaccines are sterile biologic products that provide immunity against viral infections. Inactivated viral vaccines work by stimulating the bodys immune system to produce antibodies against specific types of viruses, and protect a person from becoming infected when exposed to these viruses.
In the case of SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus that causes respiratory illness and has led to the COVID-19 pandemic, vaccines do not entirely prevent infection but protect vaccinated individuals from serious illness and hospitalization from the disease.
Inactivated viral vaccines contain particles of proteins or genetic material from viruses. Inactivated viral vaccines may also contain substances that preserve and stabilize the vaccine, and enhance immune response. Some viral vaccines are delivered in inactivated harmless viruses such as human adenovirus.
Inactivated viral vaccines may be made from:
- Surface proteins of the viruses enable the virus to hold on to a human cell, enter inside and replicate.
- Modified RNA particles from the virus can enter host cells and induce the production of viral antigen, which stimulates an immune response from the body.
- Recombined DNA material from multiple strains and subtypes of viruses, killed to eliminate disease-causing capability.
Currently, inactivated viral vaccines approved by the FDA protect against viral infectious diseases that include:
- Coronavirus disease , caused by SARS-Cov-2 virus
Adults
Don’t Miss: How Do People Contract Hepatitis C
Complications Of Hepatitis B In Infants And Children
Mothers who are infected with hepatitis B can pass the virus to their children either through the womb or at the time of birth. Hepatitis B virus can also be spread through exposure of broken skin or mucous membranes to the blood or other body fluids of an infected person.
If newborn babies are quickly immunised with 2 vaccines, they can be protected from getting hepatitis B.
Many people who are infected with hepatitis B have no symptoms. Babies and children who are infected with hepatitis B are less likely than adults to have symptoms of infection, but are more likely to develop chronic hepatitis B.
A child who contracts chronic hepatitis B has an increased risk of developing liver disease and cancer later in life. A small proportion of adults who become infected with the hepatitis B virus develop a long-term hepatitis B infection.
Before Taking This Medicine
Hepatitis A and B vaccine will not protect you against infection with hepatitis C or E, or other viruses that affect the liver. It will also not protect you from hepatitis A or B if you are already infected with the virus, even if you do not yet show symptoms.
You should not receive this vaccine if you are allergic to yeast or neomycin, or if you have ever had a life-threatening allergic reaction to any vaccine containing hepatitis A or hepatitis B.
Before receiving this vaccine, tell the doctor if you have:
-
an allergy to latex rubber or
-
a weak immune system caused by disease, bone marrow transplant, or by using certain medicines or receiving cancer treatments.
You can still receive a vaccine if you have a minor cold. In the case of a more severe illness with a fever or any type of infection, wait until you get better before receiving this vaccine.
FDA pregnancy category C. Tell your doctor if you are pregnant. It is not known whether hepatitis A and B vaccine will harm an unborn baby. However, not vaccinating the mother could be harmful to the baby if the mother becomes infected with a disease that this vaccine could prevent. Your doctor will decide whether you should receive this vaccine, especially if you have a high risk of infection with hepatitis.
If you are pregnant, your name may be listed on a pregnancy registry. This is to track the outcome of the pregnancy and to evaluate any effects of this vaccine on the baby.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis B Caused By
What Are Warnings And Precautions For Hepatitis B Vaccine
Warnings
This medication contains the hepatitis b vaccine. Do not take Engerix B or Recombivax HB if you are allergic to the hepatitis b vaccine or any ingredients contained in this drug.
Keep out of reach of children. In case of overdose, get medical help or contact a Poison Control Center immediately.
Contraindications
How Is A Hepatitis B Vaccine Given
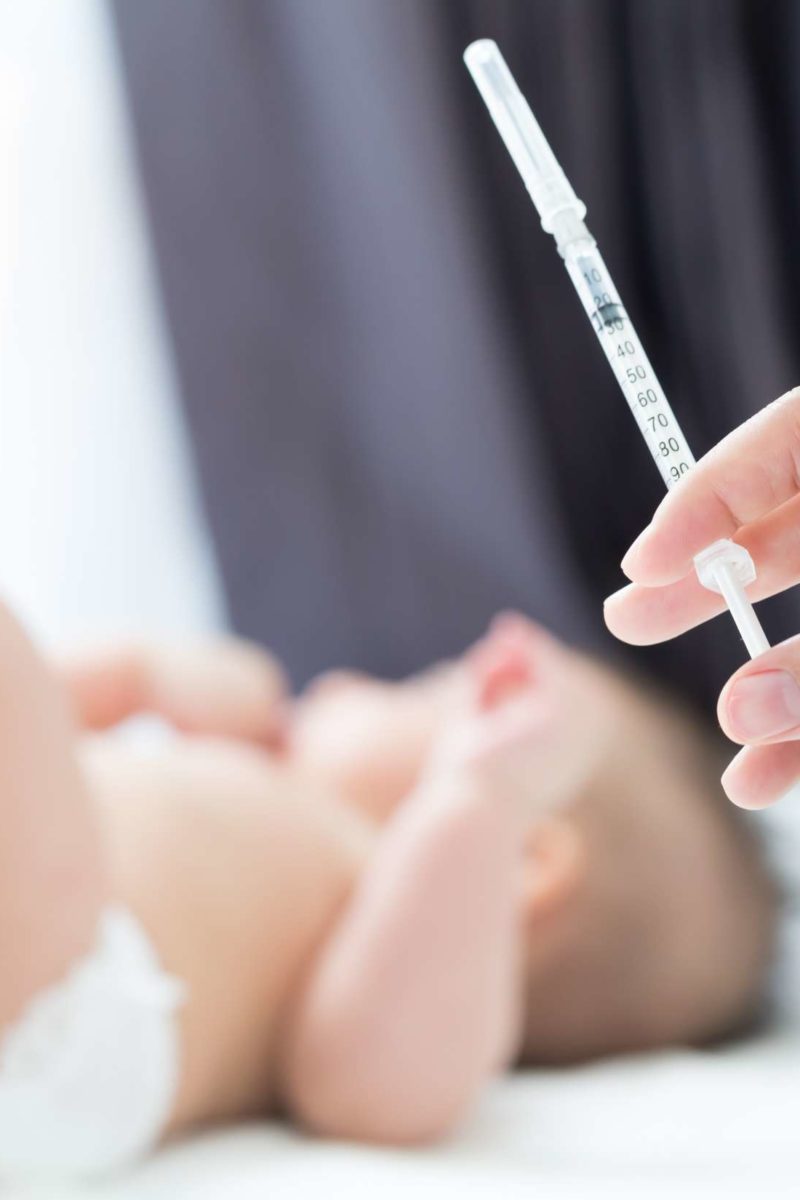
A health care provider gives the hepatitis B vaccine. The vaccine is given as a shot injected into a muscle, usually in the arm for adults and children older than 1 year and in the thigh for infants and children younger than 1 year. Vaccination with a hepatitis B vaccine is usually given as a series of injections over a period of time, depending on the specific brand of the vaccine. Read any printed information that your health care provider gives you about the hepatitis B vaccine.
Also Check: Medicine That Cures Hepatitis C
How Hepatitis Is Spread
Hepatitis A: About 20,000 people in the U.S. contract hepatitis A each year. The hepatitis A virus is found in the stool of the infected person. It is spread through contaminated food or water or by certain types of sexual contact.
Children who get hepatitis A often don’t have symptoms, so they can have the virus and not know it. However, they can still spread it easily. Fortunately, children are now routinely vaccinated against hepatitis A.
Most people who get hepatitis A recover completely within two weeks to six months and don’t have any liver damage. In rare cases, hepatitis A can cause liver failure and even death in older adults or people with underlying liver disease.
Hepatitis B: Every year, about 40,000 people in the U.S. become infected with hepatitis B. Acute hepatitis lasts from a few weeks to several months. Many infected people are able to clear the virus and remain virus-free after the acute stage. However, for others, the virus remains in the body, and they develop chronic hepatitis B infection, which is a serious, lifelong condition. About 1.2 million people in the U.S. have chronic hepatitis B. Of these, 15% to 25% will develop more serious health problems, such as liver damage, cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer, and some people die as a result of hepatitis B-related disease.
Hepatitis B cannot be spread by contaminated water, food, cooking, or eating utensils, or by breastfeeding, coughing, sneezing, or close contact such as kissing and hugging.