Ifn In Hbeagnegative Chb
The therapeutic effects of IFN are secondary to its antiviral, antiproliferative and immunomodulatory properties. High pretreatment ALT and lower levels of serum HBV DNA are the most important predictors of response to IFN. IFN is usually given subcutaneously in a dose of either 5 million units daily or 10 million units three times weekly for 12months. Several published studies have reported using IFN for HBeAgnegative CHB. Manesis and Hadziyannis, in a retrospective study, found that IFN induced longterm biochemical and virological remission in about 18% of naive or retreated patients with HBeAgnegative CHB. Sustained responders showed considerable histological improvement and a high rate of HBsAg loss .
In four different randomised controlled trials,,, which included 86 patients receiving therapy with IFN and 84 untreated patients with HBeAgnegative CHB, a 3890% endoftreatment response was seen in the treated group compared with 037% in the untreated group. The sustained rate 12months after discontinuation of treatment was 1047% in the treated group compared with 0% in the untreated group.
IFN treatment markedly improves the necroinflammatory activity and reduces the rate of progression of fibrosis, mainly in patients with sustained response.,
Hbsag Levels Measurement And Evaluation Of Treatment Response
Serum samples were serially collected from each patient when rescue treatment with LMV-ADV combination was initiated and every 3 months thereafter all samples were frozen and stored at -80.
HBsAg levels in the stored samples were measured at baseline, 6 months, and annually from 1 year to 5 years after treatment, using a chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay . HBsAg was quantified at a 1:500 dilution according to the manufacturer’s instruction. To bring HBsAg levels within the measurable range, samples with above and below this range required a lower and higher dilution, respectively.
HBV DNA levels were also measured by using real-time polymerase chain reaction . Alanine aminotransferase , bilirubin, hepatitis B ‘e’ antigen and antibody to HBeAg were measured.
Virological response was defined as undetectable HBV DNA by real-time PCR, and LMV-resistance was detected using restriction fragment mass polymorphism method, as described previously.
Relationship Of Symptoms And Spontaneous Clearance
Overall, when combining data from multiple historical studies, approximately 25 to 35% of person with acute HCV infection have spontaneous clearance of HCV. The rates of spontaneous clearance are significantly lower in persons who are Black and in those individuals who have HIV coinfection. In contrast, rates of spontaneous clear are higher in females and in persons who acquired HCV in childhood. It has also been demonstrated that patients who present with symptomatic acute HCV infection and jaundice have higher rates of spontaneous clearance of HCV, in the range of 35 to 50%. The presence of jaundice is believed to reflect hepatic inflammation caused by a more robust initial immune response against HCV.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Symptoms And Causes
Definitions Of Acute Hcv Infection
Most commonly, acute hepatitis C virus infection is defined as the 6-month time period following acquisition of hepatitis C virus. The definition of acute hepatitis C is irrespective to whether the patient has clinical signs or symptoms of acute hepatitis. The rationale for choosing 6 months as the time period to define acute infection is based on evidence that most individuals who spontaneously clear HCV will do so by 6 months.
Terms And Abbreviations Used In This Publication
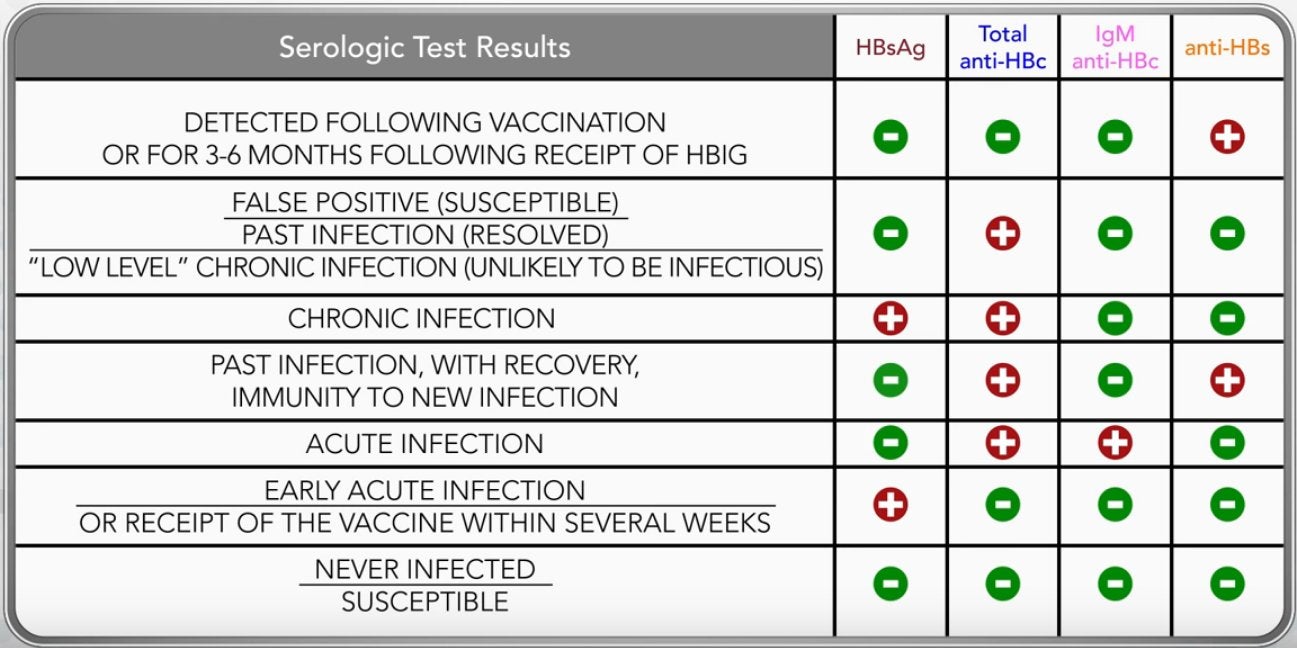
Acute hepatitis B Newly acquired symptomatic hepatitis B virus infection. Acute hepatitis C Newly acquired symptomatic hepatitis C virus infection. ALT Alanine aminotransferase, previously called SGPT. Anti-HBc Antibody to hepatitis B core antigen. Anti-HBe Antibody to hepatitis B e antigen. Anti-HBs Antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen. Anti-HCV Antibody to hepatitis C virus. Anti-HDV Antibody to hepatitis D virus. AST Aspartate aminotransferase, previously called SGOT. AV Persistent infection with HBV characterized by detection of HBsAg > 6 months after newly acquired infection. Chronic HCV infection Persistent infection with HCV characterized by detection of HCV RNA > 6 months after newly acquired infection. Chronic hepatitis B Liver inflammation in patients with chronic HBV infection characterized by abnormal levels of liver enzymes. Chronic hepatitis C Liver inflammation in patients with chronic HCV infection characterized by abnormal levels of liver enzymes. CNS U.S. Food and Drug Administration. GISA Hepatitis B virus deoxyribonucleic acid. HCV Hepatitis C virus ribonucleic acid. HDV Anti-HBc positive, HBsAg negative, and anti-HBs negative. MRSA National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance system. RIBA Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. SGOT Serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase, now called AST. SGPT Serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase, now called ALT. VISA Vancomycin-resistant enterococci.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Treat Hepatic Encephalopathy
Aurocs Of Hbsag Levels
The AUROCs of HBsAg levels at 6 months, 1 year and 2 years were 0.770, 0.781, and 0.768, respectively . These values did not significantly differ . With a cutoff value of 3.21 Log10 IU/mL for HBsAg at 6 months, the sensitivity and specificity for predicting a VR were estimated to be 45.0% and 100%, respectively, and the Youden index was 0.45. Kaplan-Meier analysis with the log-rank test showed a significance of difference in the VR rate according to this cutoff value .
Kaplan-Meier curves of virological response with respect to HBsAg level 6 months.
Socioeconomic Impact Of Hbeag Seroconversion And The Ability To Discontinue Therapy
Because of the high incidence of morbidity and mortality and the need for prolonged courses of treatment of patients with CHB, the direct and indirect costs of care are significant. In the United States, CHB is estimated to account for an average of $40,000 in costs over 2 years for healthcare services and medication. Furthermore, costs increase with disease severity, with estimated annual costs of $4,000 for a patient with compensated cirrhosis, $22,000 for a patient with decompensated cirrhosis, $19,000 for a patient with HCC, and $89,000 for a liver transplantation . The economic burden of CHB on national healthcare systems is even more pronounced in countries with high endemicity . For example, the estimated cost of medical treatment of chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and HCC in Taiwan was 5.6 billion new Taiwan yen in 2002 . Li and colleagues reported that CHB accounted for about 4% of the national healthcare expenditure in Hong Kong, whereas Yang and colleagues reported that the direct costs of HBV disease comprised 3.2% of the South Korean national healthcare expenditure.
Read Also: How To Remove Hepatitis B Virus From Body
Special Considerations During Immunosuppressive Therapy
As patients with HIV infection live longer, treatment of individuals with HIV infection with immunosuppressive therapy, both in the context of malignancy and rheumatologic/autoimmune diseases is becoming common. HBV reactivation in HIV-negative patients with HBsAg-positive/anti-HBc positive disease receiving immunomodulatory therapy is well described.143,144 Even in patients with HBsAg-negative/anti-HBc positive disease, HBV reactivation occurs in occurs in 8% to 18% and 1.7% of patients receiving anti-cancer145 and rheumatologic disease drugs,146 respectively.
Infection Control Training And Education
Training and education is recommended for both staff members and patients . Training should be appropriate to the cognitive level of the staff member, patient, or family member, and rationales should be provided for appropriate infection control behaviors and techniques to increase compliance. Regulations and recommendations regarding infection control training for health-care workers in general, and dialysis personnel in particular, have been previously published . The following recommendations are intended to highlight and augment the earlier recommendations.
Also Check: Hepatomegaly With Diffuse Hepatic Steatosis
Hbv Primary Care Workgroup
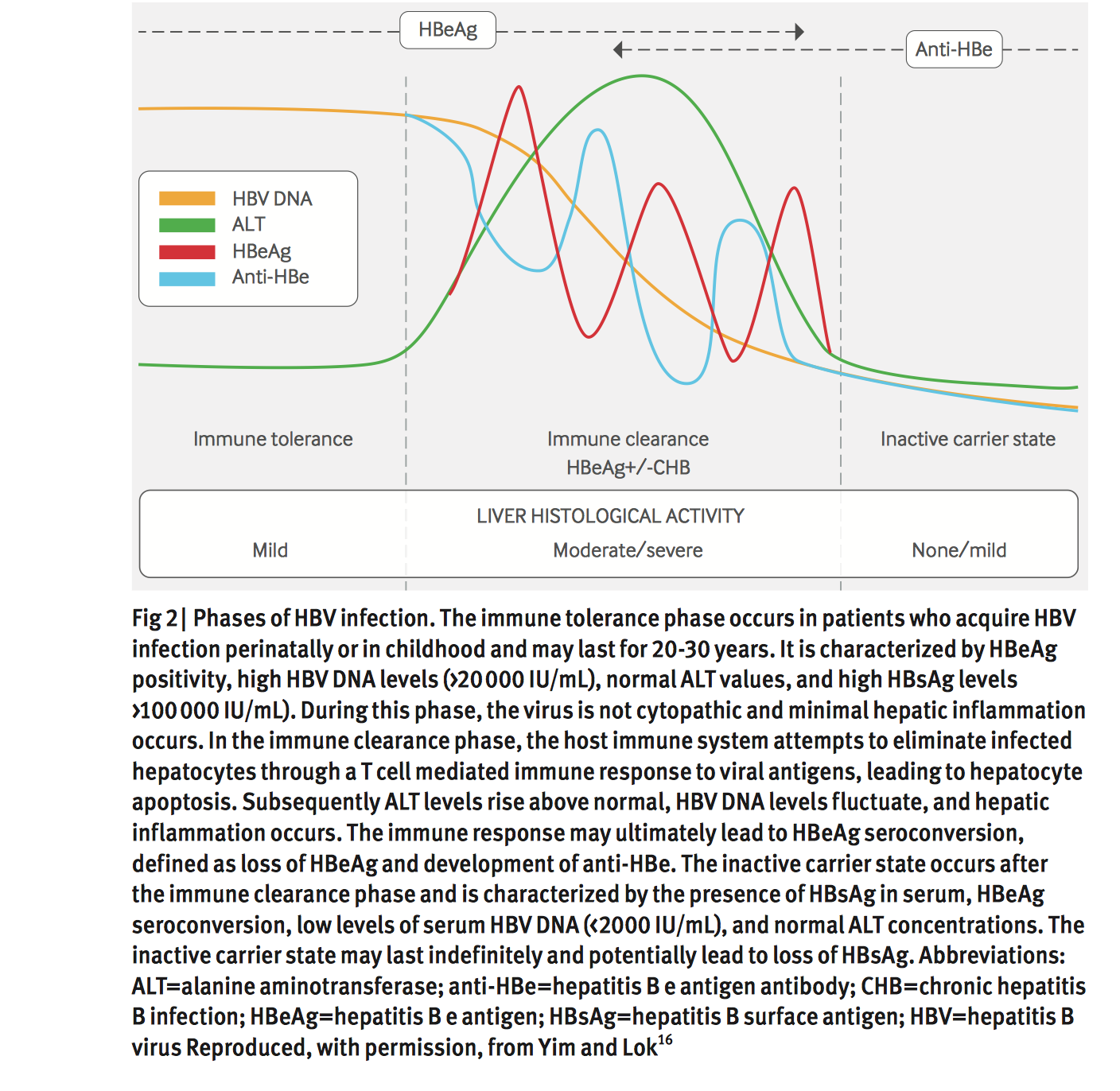
The HBV Primary Care Workgroup includes members in the United States from hepatology, infectious diseases, pharmacy, primary care, and public health. The 2020 HBV Primary Care Workgroup Guidance was first released in early 2020 and is accessible on this web site , with the aim to have regular updated versions posted online. The goal of this document is to provide simplified, up-to-date, and readily accessible HBV management guidance for primary care medical providers. Note, this guidance does not incorporate HBeAg status in the initial decision-making process, but persons positive for HBeAg are recommended to undergo monitoring of HBeAg for evidence of HBeAg seroconversion. The 2020 HBV Primary Care Workgroup Guidance recommends initiating HBV treatment in the following situations.
- : Treatment is recommended but persons should be promptly referred to a hepatologist.
- Cirrhosis: Treatment is recommended for all persons with cirrhosis, regardless of HBV DNA level, ALT level, or HBeAg status.
- Without Cirrhosis: For persons without cirrhosis, treatment is recommended if the HBV DNA level is greater than 2,000 IU/mL and the ALT level is elevated, regardless of HBeAg status. For this purpose, elevated ALT is defined as greater than 25 U/L in females and greater than 35 U/L in males that is persistent for at least 3 to 6 months.
Analysis According To Vr Within 1 Year And 2 Year And Hbeag Status
Thirty nine patients were HBeAg positive and 21 were negative. Twenty nine patients achieved VR within 1 year . HBsAg level at baseline was not significantly different according to VR , but became lower in patients with VR at 6 months and 1 year . HBV DNA level also showed significant differences at 6 months and 1 year , but not at baseline . On subanalysis according to HBeAg status, HBsAg levels at baseline, 6 months and 1 year were not different according to VR or not, in both HBeAg positive and negative patients. HBV DNA levels have become significantly lower in patients with VR at 6 months and at 1 year in HBeAg positive, and at baseline and at 1 year in HBeAg negative group .
Thirty six patients achieved VR within 2 years . HBsAg level was significantly lower in patients with VR at 6 months , 1 year and 2 years . HBV DNA level also significantly lower in patients with VR at 6 months , 1 year and 2 year . Because all of HBeAg negative patients achieved VR, only subanalysis for HBeAg positive patients were performed. HBsAg level was significantly lower in HBeAg positive VR group at 6 months . HBV DNA levels were lower in HBeAg positive VR group at 6 months , 1 year and 2 years .
Recommended Reading: How Long Does Hepatitis C Live Outside The Body
Diagnosed With Chronic Hepatitis B What Does Your Hbv Dna Test Tell You
If you have been diagnosed with chronic hepatitis B, your doctor has probably run several blood tests that show if the infection is harming your liver and identify what stage of infection you are in. Doctors consider all of these results when deciding if you need treatment and how often you should be monitored.
In this blog, well examine how one of the tests the HBV DNA or viral load test can give you a snapshot into your hepatitis B infection and your health. The HBV DNA test is performed on a blood sample using a Polymerase Chain Reaction technique that rapidly generates HBV DNA fragments so they can be measured. Today, viral load is usually measured using international units per milliliter . However, in the past it was measured in copies per milliliter , and in some regions and labs, it is still used.
If you ever need to convert copies into international units, there are about 5.6 copies in one international unit, so 5,000 copies/mL equals about 893 IU/mL. Remember to keep copies of your lab information on file so you can track your status. An Excel spreadsheet works great.
The sensitivity of HBV DNA tests may vary with each lab so its a good idea to use the same lab for your test. Labs usually measure down to less than 200 IU/mL. Below the threshold, the viral load is considered undetectable something everyone with chronic hepatitis B wants to hear.
Special Considerations During Pregnancy
Pregnant women with HIV infection should be screened for HBsAg, and co-infection with HBV may be first diagnosed at this time .148 Those who are both HBsAg and anti-HBs-negative should be offered vaccination against HBV. Treatment of symptomatic acute HBV infection during pregnancy should be supportive, with special attention given to maintaining blood glucose levels and normal clotting status. Risk of pre-term labor and delivery may increase with acute HBV infection. High maternal HBV DNA levels correlate strongly with perinatal HBV transmission, including failures of HBV passive-active immunoprophylaxis.149-152 See HIV/Hepatitis B Virus Coinfection in the Recommendations for the Use of Antiretroviral Drugs in Pregnant Women with HIV Infection and Interventions to Reduce Perinatal HIV Transmission in the United States.
ART including drugs active against both HIV and HBV is recommended for all individuals with HIV/HBV coinfection, including pregnant women . TDF given in combination with 3TC or FTC is the preferred dual-NRTI backbone for pregnant women with chronic HBV infection .153 There are no data on use of TAF in pregnancy, therefore it is not recommended.154 Once HBV therapy with nucleoside analogs and ART is initiated in patients with HIV/HBV coinfection, treatment should be continued indefinitely.
Recommendations for Preventing and Treating Hepatitis B Virus Infection
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quantitative Titer
How Do I Get Hepatitis B Treatment
Usually for adults, hepatitis B goes away on its own and you wont need treatment. Your doctor might tell you to rest, eat well, and get plenty of fluids. You may also get medicines to help with any symptoms you might have but be sure to talk with your doctor or nurse before taking anything.
If you have chronic hepatitis, there are medicines you can take to treat it. Your doctor will tell you about your options and help you get whatever treatment you need.
Alternative Treatment Of Hbv In Patients With Hiv Infection Who Are Not Receiving Art
HBV and HIV co-treatment is essential and recommended.84 There are few options that can be used for treatment of HBV alone in the patient with HIV/HBV coinfection. Directly acting HBV drugs must not be given in the absence of a fully suppressive ART regimen . Only pegylated interferon-alfa-2a monotherapy may be considered for patients with HIV/HBV coinfection who are not receiving ART and who meet criteria for HBV therapy as described in the AASLD 2018 guidelines.100
Some patients with HIV/HBV coinfection also have chronic HCV infection. There is scant information on the treatment of HBV/HCV/HIV coinfection. Because patients with HBV, HCV, and HIV appear to have accelerated progression of liver fibrosis, higher risk of HCC, and increased mortality,101-103 attempts should be made to treat both hepatitis viruses, if feasible. If ART is administered, then anti-HBV therapy must be included as part of the regimen and anti-HCV therapy can be introduced as needed . As HBV reactivation can occur during treatment for HCV with directly active agents in the absence of HBV-active drugs, all patients with HIV/HBV coinfection who will be treated for HCV should be on HBV-active ART at the time of HCV treatment initiation .104-107
Don’t Miss: How Do You Prevent Hepatitis C
Special Considerations With Regard To Starting Art
Preferred Regimen
The Department of Health and Human Services Guidelines for the Use of Antiretroviral Agents in Adults and Adolescents Living with HIV recommend the fixed-dose coformulations of TDF or TAF/emtricitabine or abacavir/lamivudine as nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor regimen backbones for ART-naive patients regardless of CD4 cell count.84 Because both tenofovir and emtricitabine have anti-HBV activity, the tenofovir combinations are also the treatment of choice for patients with HIV/HBV coinfection regardless of CD4 count and HBV DNA level. TDF and TAF are both active against wild-type and lamivudine-resistant HBV strains. Studies in patients with HIV/HBV coinfection have shown, on average, 4 log10 declines in HBV DNA levels.85-90 TDF and TAF have a high genetic barrier for development of resistance mutations .3,91
Chronic administration of lamivudine or emtricitabine as the only active drug against HBV should be avoided because of the high rate of selection of HBV drug-resistance mutations .
Surveillance For Infections And Other Adverse Events
Develop and maintain a separate centralized record-keeping system to record the results of patients’ vaccination status, serologic testing results for viral hepatitis , episodes of bacteremia or loss of the vascular access caused by infection ,* and adverse events . Designate a staff person to promptly review the results of routine testing each time such testing is performed and periodically review recorded episodes of bacteremia or vascular access infections. Specify a procedure for actions required when changes occur in test results or in the frequency of episodes of bacteremias or vascular access loss because of infection. Maintain records for each patient that include the location of the dialysis station and machine number used for each dialysis session and the names of staff members who connect and disconnect the patient to and from a machine.
You May Like: How Do You Get Hepatitis A And B
How Do You Get Hepatitis B
The virus that causes hepatitis B lives in blood, semen, and other fluids in your body. You usually get it by having sex with someone who’s infected.
You also can get it if you:
- Have direct contact with infected blood or the body fluids of someone who’s got the disease, for instance by using the same razor or toothbrush as someone who has hepatitis B, or touching the open sores of somebody who’s infected.
- If you’re pregnant and you’ve got hepatitis B, you could give the disease to your unborn child. If you deliver a baby who’s got it, they need to get treatment in the first 12 hours after birth.
Principle Of Hbv Reactivation During Rituximab Treatment
After HBV infection, HBV-DNA synthesis is initially suppressed by cytokine production from NK and other cells. A subsequent cytotoxic T-cell reaction occurs due to the presence of CD8-positive T lymphocytes. Because hepatitis is triggered by CTLs, a time lag likely exists between the HBV infection and the manifestation of hepatitis. On the other hand, rituximab induces CD4 lymphopenia. In a mouse model, B-cell depletion reduced the number and the fraction of CD4 memory T-cells and impaired immunity against virus infection. A reduction in CD20 Bcells shifted the CD4 effector phenotype to that of enhanced interferon-, interleukin -2, and tumor necrosis factor. Perhaps the depletion of CD20 positive B-cells reduces the production of IL-7 and IL-15, both of which are critical for memory T-cell survival, from monocytes or stromal cells. Furthermore, HBV replication is likely accelerated by the indirect effects of B-cell depletion on immune globulin production. It has been reported that rituximab treatment induces a change in CD8 distribution. This might reduce the number of CD8-positive cells and the subsequent acceleration of HBV replication. Once the number of CD8-positive T-cells recovers, cells are produced that specifically target HBV. However, since memory T-cells are impaired by their reduced numbers, CD8-positive T-cells randomly attack HBV, resulting in severe hepatitis.
Recommended Reading: Help With Hepatitis C Treatment