How Can I Prevent Hepatic Encephalopathy
Proper management and treatment of liver disease is key to lowering the chances of developing hepatic encephalopathy. These steps can lower your risk:
- Avoid alcohol, which damages liver cells.
- Avoid medications that affect the nervous system, such as sleeping pills and antidepressants.
- Eat a nutritious diet, exercise and maintain a healthy weight .
- Take your prescribed medications to treat liver disease.
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
If you or someone you love has hepatic encephalopathy, you may want to ask your doctor:
- How is liver disease affecting my body?
- What can I do to improve liver function or slow liver disease?
- What liver disease treatment will work best for me now?
- What is the best treatment for hepatic encephalopathy?
- How long do I need to take medication for hepatic encephalopathy?
- Are there any medications I should avoid?
- Should I make any dietary changes to support liver function?
- Could I benefit from a liver transplant?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
Remember, hepatic encephalopathy is a serious but treatable condition. Symptoms often resolve with early detection and proper treatment. If you have liver disease, ask your doctor about warning signs of hepatic encephalopathy so you can start treatment promptly. You should also discuss how to best manage liver disease to keep hepatic encephalopathy from occurring or worsening.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 04/16/2020.
References
Common Precipitants Of Hepatic Encephalopathy
Some patients with a history of hepatic encephalopathy may have normal mental status while under treatment. Others have chronic memory impairment in spite of medical management. Both groups of patients are subject to episodes of worsened encephalopathy. Common precipitating factors are as follows:
Renal failure: Renal failure leads to decreased clearance of urea, ammonia, and other nitrogenous compounds.
Gastrointestinal bleeding: The presence of blood in the upper gastrointestinal tract results in increased ammonia and nitrogen absorption from the gut. Bleeding may predispose to kidney hypoperfusion and impaired renal function. Blood transfusions may result in mild hemolysis, with resulting elevated blood ammonia levels.
Infection: Infection may predispose to impaired renal function and to increased tissue catabolism, both of which increase blood ammonia levels.
Constipation: Constipation increases intestinal production and absorption of ammonia.
Medications: Drugs that act upon the central nervous system, such as opiates, benzodiazepines, antidepressants, and antipsychotic agents, may worsen hepatic encephalopathy.
Diuretic therapy: Decreased serum potassium levels and alkalosis may facilitate the conversion of NH4+ to NH3. At the authorâs institution, diuretic-induced hypovolemia is the most common reason for patients with previously well-controlled hepatic encephalopathy to present to the emergency room with worsening mental function.
You May Like: How Long Does Hepatitis A Vaccine Last
What Causes Hepatic Encephalopathy
When you have liver disease, the liver struggles to filter natural toxins out of the body. Toxins, such as ammonia, accumulate in the blood. Toxins in the bloodstream can travel to the brain and temporarily affect brain function.
People with chronic liver disease are at risk for hepatic encephalopathy. Something usually triggers the condition, such as:
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of He
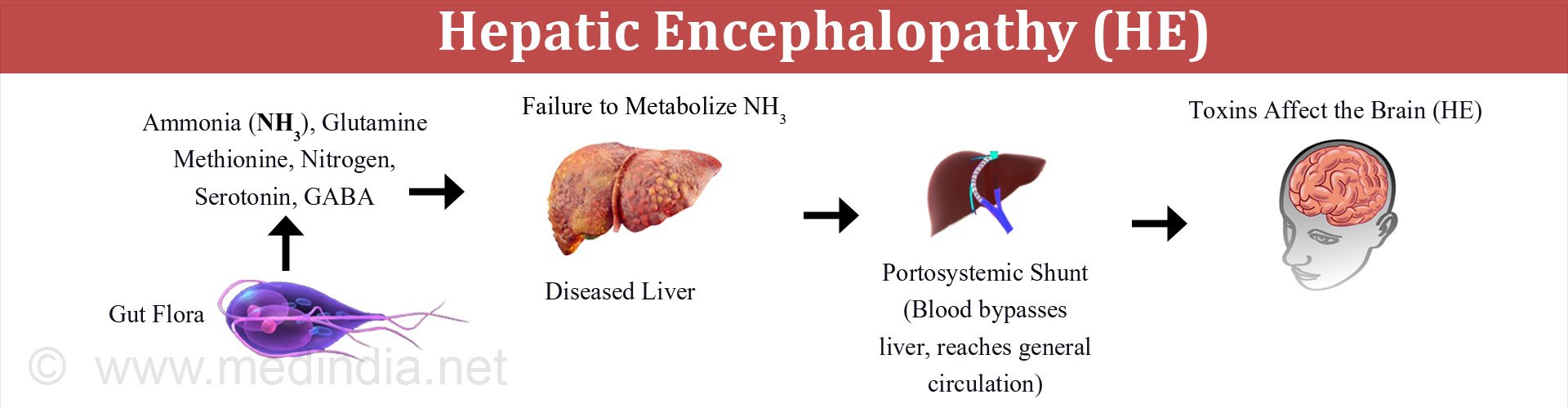
At first, you may have only mild symptoms. Over time, you may develop more severe symptoms:
- Mood changes, a short attention span, and drowsiness
- Confusion and forgetfulness
- Changes in sleeping habits and difficulty with speaking or writing
- A musty, sweet odor to your breath
- Flapping motion of your hands when your arms are outstretched
- Sleepiness and decreased awareness
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis B And Hiv The Same
When Should You Contact The Doctor
You should see your doctor in the following cases:
- If you have liver disease and have signs and symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy, such as impaired thinking, mood changes, trouble sleeping, and hands trembling.
- If you have liver disease and suffer from constipation, the lack of bowel movements can lead to a buildup of toxins in your body.
Treatments To Improve Sleep Disturbances
Sleep disturbances are more common in patients with cirrhosis than in control subjects. Whether or not this relates to hepatic encephalopathy is unclear. A trial compared the histamine H1 blocker hydroxyzine with placebo in patients with cirrhosis and minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Sleep efficiency and the patients’ subjective quality of sleep improved in patients receiving hydroxyzine at bedtime. However, there was no accompanying improvement in cognition, as measured by neurophysiologic tests. The authors urged caution when prescribing hydroxyzine, on account of the risk of worsening encephalopathy in some patients.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Side Effects Of Hepatitis B
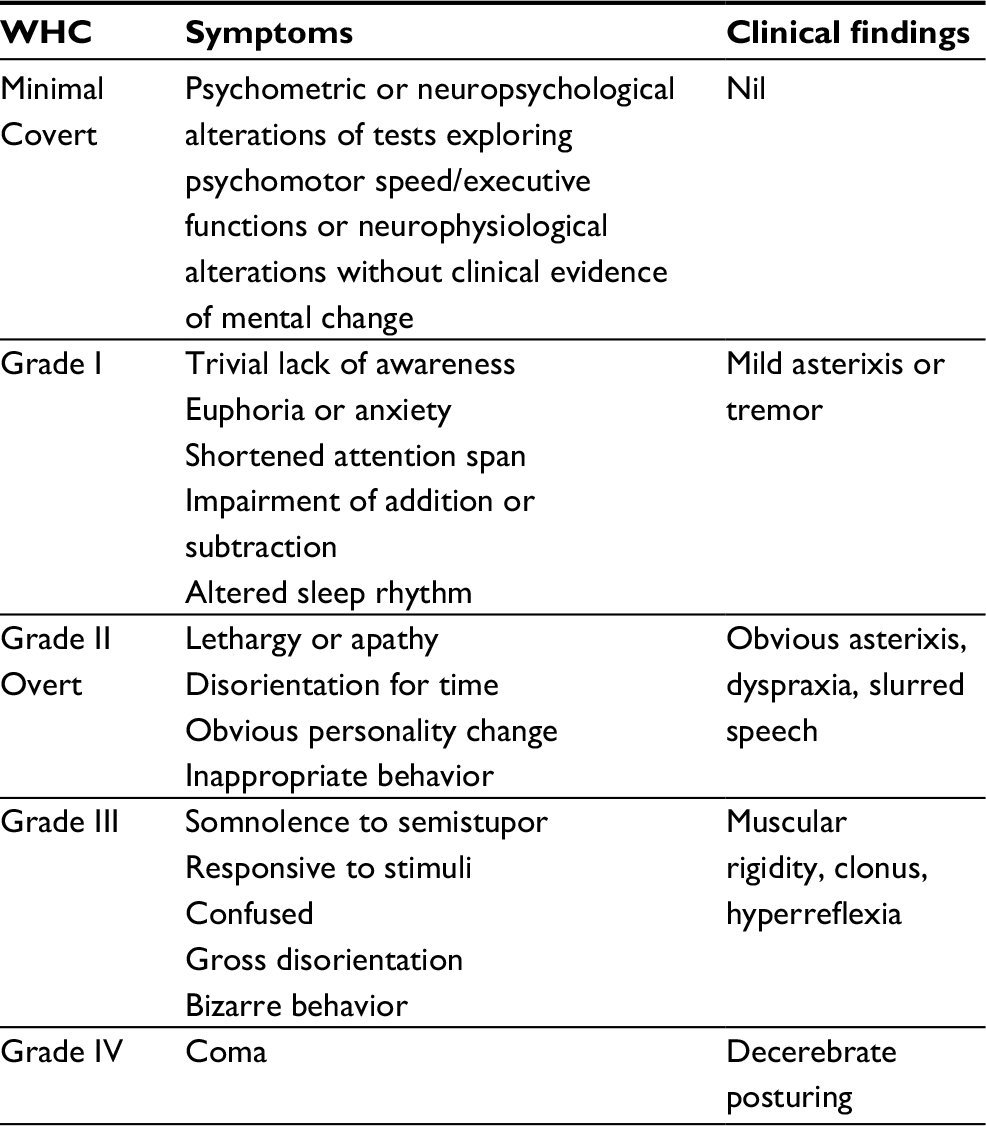
Clinical Features Of Hepatic Encephalopathy
Two broad categories of hepatic encephalopathy are covert and overt hepatic encephalopathy. CHE is particularly associated with poor outcomes.
Grading of the symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy is performed according to the so-called West Haven classification system, as follows :
-
Grade 0 – Minimal hepatic encephalopathy lack of detectable changes in personality or behavior minimal changes in memory, concentration, intellectual function, and coordination asterixis is absent.
-
Grade 1 – Trivial lack of awareness shortened attention span impaired addition or subtraction hypersomnia, insomnia, or inversion of sleep pattern euphoria, depression, or irritability mild confusion slowing of ability to perform mental tasks
-
Grade 2 – Lethargy or apathy disorientation inappropriate behavior slurred speech obvious asterixis drowsiness, lethargy, gross deficits in ability to perform mental tasks, obvious personality changes, inappropriate behavior, and intermittent disorientation, usually regarding time
-
Grade 3 – Somnolent but can be aroused unable to perform mental tasks disorientation about time and place marked confusion amnesia occasional fits of rage present but incomprehensible speech
-
Grade 4 – Coma with or without response to painful stimuli
In terms of the physical examination finding of asterixis, it must be emphasized that the flapping tremor of the extremities is also observed in patients with uremia, pulmonary insufficiency, and barbiturate toxicity.
Treatment Of Hepatic Coma
Log in to MyKarger to check if you already have access to this content.
Buy a Karger Article Bundle and profit from a discount!
If you would like to redeem your KAB credit, please log in.
Save over 20%
- Rent for 48h to view
- Buy Cloud Access for unlimited viewing via different devices
- Synchronizing in the ReadCube Cloud
- Printing and saving restrictions apply
USD 8.50
- Access to all articles of the subscribed year guaranteed for 5 years
- Unlimited re-access via Subscriber Login or MyKarger
- Unrestricted printing, no saving restrictions for personal use
The final prices may differ from the prices shown due to specifics of VAT rules.
Read Also: How Much Is Hepatitis A Vaccine
Could I Have It
HE often starts slowly, and at first, you may not be aware you have it. The stages of HE span from mild to severe and involve numerous symptoms. It is important for you and your family to become familiar with the signs and symptoms of HE so you can tell your doctor right away if you think you may have it. Prompt diagnosis is essential in order that your doctor can initiate the treatment of HE.
If you have been diagnosed with a chronic liver disease, you could have HE if you are experiencing the following symptoms:
- Trouble sleeping at night
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms listed above, please talk with your healthcare provider.
Treatment Of Precipitating Causes
The most important aspect of HE management is prompt recognition and treatment of precipitating factors rather than assuming a deterioration of hepatocellular function. Fessel and colleagues demonstrated that HE is caused by reversible factors in over 80% of patients. These common reversible factors include constipation, infection, hypokalemia, gastrointestinal bleeding, increased protein intake, sedatives, and tranquilizers. Thus, identifying and correcting the reversible precipitating factors can be beneficial in treating most episodes of HE.
Recommended Reading: Can You Donate Blood If You Had Hepatitis A
How Is He Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will examine you and do a neurological exam. A neurologic exam can show healthcare providers how well your brain works after an injury or illness. Healthcare providers will check how your pupils react to light. They may check your memory and how easily you wake up. Your hand grasp and balance may also be tested. You may also need blood and urine tests to look for infection or test liver function. Healthcare providers may also use the tests to get information about your overall health.
Altered Level Of Consciousness
| , |
An altered level of consciousness is any measure of other than normal. Level of consciousness is a measurement of a person’s arousability and responsiveness to from the environment. A mildly depressed level of or may be classed as someone in this state can be aroused with little difficulty. People who are have a more depressed level of consciousness and cannot be fully aroused. Those who are not able to be aroused from a sleep-like state are said to be . is the inability to make any purposeful response. Scales such as the have been designed to measure the level of consciousness.
An altered level of consciousness can result from a variety of factors, including alterations in the chemical environment of the brain , insufficient or in the brain, and excessive . Prolonged unconsciousness is understood to be a sign of a . A deficit in the level of consciousness suggests that both of the or the have been injured. A decreased level of consciousness correlates to increased and . Thus it is a valuable measure of a patient’s medical and neurological status. In fact, some sources consider level of consciousness to be one of the .
Read Also: Hepatitis C Dna Or Rna
Taking Care Of Yourself
The best thing you can do to keep your HE under control is stick with the treatment plan that your doctor suggests.
Since you already have a lot of medical stuff to do because of your long-term liver disease, it might seem like your new treatment is a big nuisance. But it’s really important. Don’t skip any doses of medicines, and make sure you follow your doctor’s diet advice. Ask your friends and family to help you stay on track.
If you play by the rules, you’ll get results. Your symptoms can improve and sometimes go away.
What Are The Treatment Options For Hepatic Encephalopathy
Treatment options for hepatic encephalopathy depend on the severity and underlying cause of the condition.
Youll likely need to eat less protein if eating too much protein caused the condition. Since protein is necessary for your body to function properly, a dietician or doctor can create a diet thatll allow you to get enough protein without making your symptoms worse. High-protein foods to avoid include:
- poultry
- eggs
- fish
Medications can also help slow the rate at which your blood absorbs toxins. Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics and lactulose , a synthetic sugar. These medications can draw ammonia, created by intestinal bacteria from your blood, into your colon. Your body will then remove the blood from your colon.
In severe cases that cause difficulty breathing, a ventilator or oxygen mask may be necessary.
Some people with the condition may be eligible to receive a liver transplant.
People with chronic hepatic encephalopathy have better recovery rates than those with the acute version of the condition. The rate of recovery increases if you receive treatment before the condition gets worse.
Hepatic encephalopathy and its symptoms can be reversible with proper treatment.
Also Check: How To Treat Viral Hepatitis
Why Does Liver Disease/failure Lead To Brain Dysfunction
Unhealthy liver, unhealthy brain.The liver is an important organ which is responsible for a lot of essential tasks in life. Everything that is consumed passes down into the intestines where the food and drink are metabolized into various molecules which are passed into the bloodstream and sent to the liver.
Not only does the liver filter out the bad from the good from what is sent from the intestines, it also plays an important role in producing blood clotting factors and helping to control glucose levels in the blood. When your liver is severely damaged, it can no longer remove these toxic molecules or produce the vital elements. In addition, the sick liver releases toxic molecules. A combination of all these factors affects the brain from properly functioning, causing HE.
What factors cause HE?
Brain edema
Brain edema, an accumulation of water which leads to swelling of the brain, is commonly associated with HE. In acute liver failure, brain edema contributes to an increase in pressure in the skull which can be fatal. In cirrhosis, even though an increase in pressure within the skull is not observed, brain edema is still present. An accumulation of water in the brain is primarily due to swelling of the astrocytes . Astrocytes work very closely with neurons to help maintain normal brain function. However, swollen astrocytes lead to dysfunction in neurons and therefore brain function is impaired.
The following triggers can cause or worsen HE:
What Is The Prognosis For People With Hepatic Encephalopathy
People with hepatic encephalopathy can slow, stop or reverse the disease by sticking to their prescribed treatment plan. People who have chronic liver disease may need to keep treating hepatic encephalopathy to stop symptoms from getting worse or coming back.
Its important to see a doctor right away when you first notice signs of hepatic encephalopathy. Untreated hepatic encephalopathy can get worse and increase your risk of serious complications, such as coma.
People who develop end-stage liver disease may need to consider a liver transplant. Youll undergo testing to see if you can withstand such a major procedure. A new liver often gets rid of hepatic encephalopathy.
You May Like: Where Can I Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine For Free
What Is Hepatic Encephalopathy Treatment
Hepatic encephalopathy is a syndrome that is observable among patients that have cirrhosis. Hepatic encephalopathy falls under the spectrum of neuropsychiatric problems among individuals suffering from liver dysfunction, without including brain disease. Liver function examinations check for elevated enzyme levels. A raise in enzymes suggests stress on the liver or alternatively liver damage. Inform your doctor in case you suffer from liver disease or kidney disease. The symptoms you are encountering together with your medical background can oftentimes be adequate to detect hepatic encephalopathy. But is Hepatic encephalopathy treatment possible?
Using treatment, this syndrome is usually reversible. In fact, full recovery is a possibility, especially if it was induced by a correctable cause. Then again, men and women with a chronic liver condition are susceptible to upcoming attacks of encephalopathy. Several require prolonged treatment. The prevalence of encephalopathy serious enough to result in hospitalization associates with survival possibility of 42% during one year of follow-ups, and at 23% for three years. Roughly 30% of sufferers suffering from the final stage of liver disease suffer from significant encephalopathy, drawing near to coma. Continue reading to learn more about hepatic encephalopathy treatment which is crucial to aid you if you have this syndrome specifically.
Management Of Hepatic Encephalopathy
G. Wright
1University College London Institute of Hepatology, The Royal Free Hospital, Pond Street, London NW3 2PF, UK
2Department of Gastroenterology, King Georges Hospital, Barley Lane, Goodmayes, Ilford, Essex IG3 8YB, UK
Abstract
Hepatic encephalopathy , the neuropsychiatric presentation of liver disease, is associated with high morbidity and mortality. Reduction of plasma ammonia remains the central therapeutic strategy, but there is a need for newer novel therapies. We discuss current evidence supporting the use of interventions for both the general management of chronic HE and that necessary for more acute and advanced disease.
1. Introduction
There are a plethora of therapeutic approaches to targeting varying severities of hepatic encephalopathy , the neuropsychiatric presentations of liver disease. There is a need for newer therapies for patients with advanced HE and worsening acute liver injury. Reduction of plasma ammonia remains the central strategy although novel strategies may be beneficial. We discuss current evidence supporting the use of therapeutic interventions for both the general management of chronic HE and that necessary for more acute and advanced disease.
2. General Management of Chronic Encephalopathy
| HE grade: I-II |
| Antiepileptic drugs |
| N-acetylcysteine |
2.1. Ammonia-Lowering Strategies
2.1.1. Dietary Protein Supplementation
2.1.2. Branched-Chain Amino Acids
2.1.3. Glycaemic Control
2.1.4. Vitamins and Nutrients
3. Probiotics
4. Purgatives
You May Like: How Can You Get Hepatitis A
What Is Hepatic Encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy is an often-temporary neurological disorder due to chronic, severe liver disease. A diseased liver struggles to filter toxins from the bloodstream. These toxins build up in the body and travel to the brain. Toxicity affects brain function and causes cognitive impairment.
People with hepatic encephalopathy may seem confused or have difficulty processing their thoughts. Treatments can remove the toxins and reverse the problem. As liver disease progresses, the condition may worsen and become less treatable. Hepatic encephalopathy is also known as portosystemic encephalopathy .
Symptoms Of Hepatic Encephalopathy

Symptoms are those of impaired brain function, especially reduced alertness and confusion. In the earliest stages, subtle changes appear in logical thinking, personality, and behavior. The person’s mood may change, and judgment may be impaired. Normal sleep patterns may be disturbed. People may become depressed, anxious, or irritable. They may have trouble concentrating.
At any stage of encephalopathy, the person’s breath may have a musty sweet odor.
As the disorder progresses, people cannot hold their hands steady when they stretch out their arms, resulting in a crude flapping motion of the hands . Their muscles may jerk involuntarily or after people are exposed to a sudden noise, light, a movement, or another stimulus. This jerking is called myoclonus Myoclonus Myoclonus refers to quick, lightning-like jerks of a muscle or a group of muscles. Myoclonus may occur normally … read more . Also, people usually become drowsy and confused, and movements and speech become sluggish. Disorientation is common. Less often, people with encephalopathy become agitated and excited. Eventually, as liver function continues to deteriorate, they may lose consciousness and lapse into a coma. Coma often leads to death, despite treatment.
You May Like: How Can A Person Get Hepatitis C