Alcoholism & Hepatitis C
What happens if you are an alcoholic and you contract hepatitis C?
Significant liver damage can be expected, even leading to cirrhosis.
It is of the utmost importance that you stop drinking forever.
If you are HCV positive, just three or more drinks a day or more increases your risk of cirrhosis, according to a JAMA study.
Need more reasons to stop drinking? Continued alcohol use may also interfere with your ability to consistently adhere to a medication regimen that can tackle HCV infection. In fact, you may not be prescribed HCV treatment if you continue to drink.
What Is The Prognosis For Patients Who Have Alcoholic Hepatitis
If the patient who has alcoholic hepatitis gives up drinking alcohol completely, the liver may improve, and the long-term prognosis is good if there is no underlying scar in the liver. However, if the patient continues to drink excessively, the liver will continue to get worse and possibly develop cirrhosis, a serious condition that may ultimately lead to liver failure over time. Other health problems may also develop, including infections and malnutrition.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 06/21/2018.
References
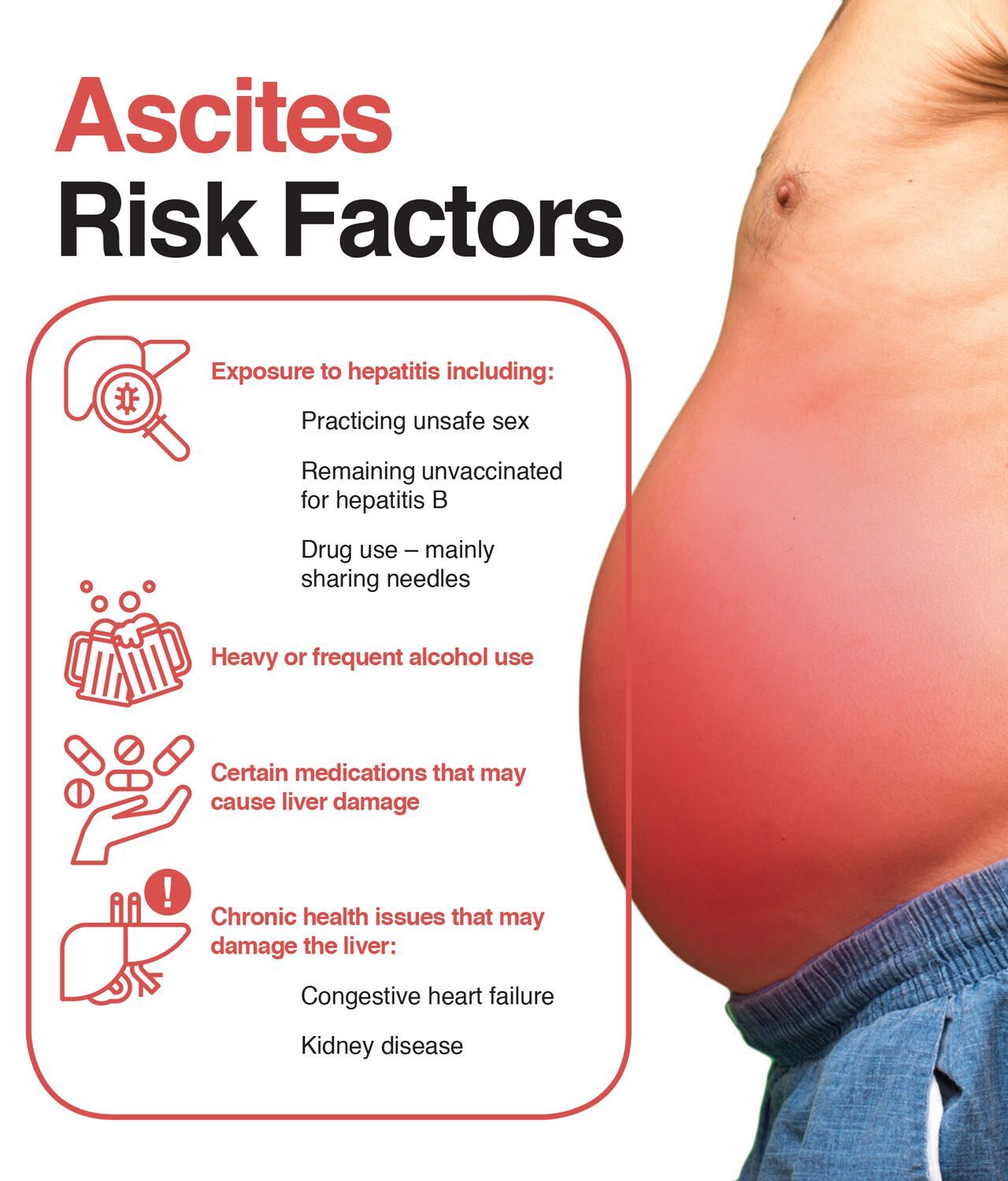
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis
Individuals who share needles and practice unprotected sex increase their likelihood of contracting hepatitis. The main risk factor for alcoholic hepatitis is protracted alcohol abuse. Gender, weight, ethnicity, and certain genetic factors may affect the extent to which acute or chronic hepatitis develops in some people. Furthermore, some forms of hepatitis are transmitted genetically, through contaminated food, sharing silverware, or injury. So, it is difficult to completely reduce the risk of all forms of hepatitis. However, living a purposeful life enhanced by exercise and a healthy diet can reduce the risk for illness.
Don’t Miss: Does Hepatitis C Have A Cure
How Can You Prevent Alcoholic Hepatitis
The best way to prevent alcoholic hepatitis is to avoid alcohol or drink only in moderation. Moderate drinking is defined as less than two drinks per day for men and less than one drink per day for women.
You can also reduce your risk by taking steps to protect yourself from hepatitis B and hepatitis C. The bloodborne viruses that cause these conditions can be transmitted in several ways, including shared needles or razors and through body fluids during sex. Currently, vaccines are available for hepatitis B, but not for hepatitis C.
Your healthcare team may also recommend certain lifestyle changes based on your specific symptoms and health needs.
For example:
Its Ok To Ask For Help With Alcohol And Hepatitis
If your hepatitis was the result of behavior linked to an addiction or if you need to stop drinking in order to treat hepatitis but are having trouble doing so, you may want to consider looking into rehab options. Treatments may include:
- Alcoholics Anonymous or other 12-step support groups
- Inpatient therapy
- Outpatient or residential treatment
Most rehab facilities are very familiar with the relationship between alcohol and hepatitis and will be both understanding and helpful. If youre suffering from an addiction to alcohol and want to begin your recovery, contact a treatment provider now.
Recommended Reading: What Is Diffuse Hepatic Steatosis
Should I Be Screened For Hepatitis C
Doctors usually recommend one-time screening of all adults ages 18 to 79 for hepatitis C. Screening is testing for a disease in people who have no symptoms. Doctors use blood tests to screen for hepatitis C. Many people who have hepatitis C dont have symptoms and dont know they have hepatitis C. Screening tests can help doctors diagnose and treat hepatitis C before it causes serious health problems.
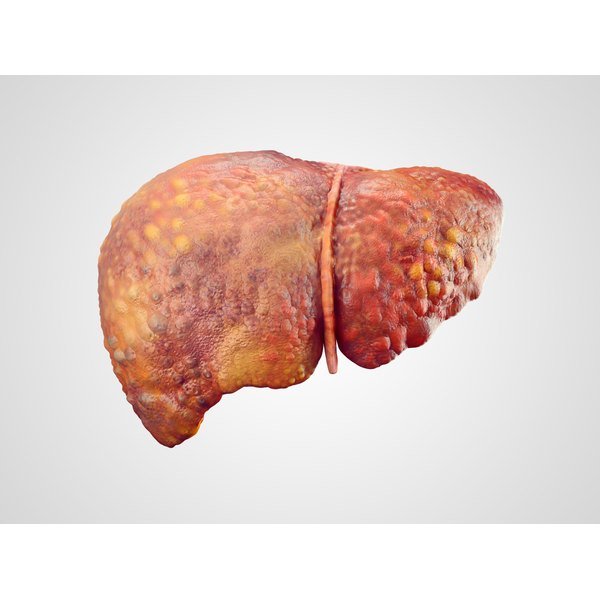
Stage : Alcoholic Cirrhosis
Stiff and swollen at this stage, the liver has suffered extensive damage. Similarly, its functioning can be severely compromised. Alcoholic cirrhosis is considered to be irreversible.
Symptoms include:
Your healthcare professional can diagnose alcoholic cirrhosis with a physical exam, blood tests and imaging techniques.
A biopsy is the definitive method for diagnosing cirrhosis, however.
Once again, its vital that you stop drinking alcohol to minimize further damage. The survival rate for those with severe cirrhosis is 50 percent at two years and only 35% within five years. Cirrhosis is the ninth leading cause of death in the U.S.
Alcohol related cirrhosis puts you at a much risker risk for liver cancer.
Similarly, if you have hepatitis B or C and are a heavy drinker, your risk for cirrhosis increases substantially.
These stages are not necessarily linear or absolute. Someone can have evidence of two or three at once, especially if they have been abusing alcohol for a long time.
The good news is that there are treatments available for cirrhosis. They include dialysis, lifestyle changes, nutritional therapy, and, if all else fails, a liver transplant.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Antigens And Antibodies
Treatment Options For Alcoholic Hepatitis
Alcohol use both causes and worsens alcoholic hepatitis, so a diagnosis of alcoholic hepatitis means you may want to consider stopping drinking gradually. Quitting drinking can help reduce symptoms and prevent further damage to your liver.
In the early stages of the condition, avoiding alcohol may even help reverse liver damage. Once more significant damage has occurred, the changes to your liver may become permanent.
Even if the damage is too severe to reverse, quitting drinking could prevent further harm to your liver.
Alcoholic hepatitis can lead to severe and lasting liver damage, which can, in turn, cause serious health complications. In some cases, these complications can be life threatening.
Can You Get Hepatitis C From Alcohol Addiction
Research has shown a link between alcohol addiction and hepatitis C . While alcohol addiction may not directly cause HCV, it can make you more susceptible to the infection.
In one study, actively drinking alcoholics were more likely to have hepatitis C, despite not using drugs intravenously or having other known risk factors.
Alcohol can also lead to liver inflammation, which studies have found to be associated with hepatitis C antibodies. Again, this is without any other known infection risk factors.
And, if you have hepatitis C, alcohol can make it worse and speed its progression.
Read Also: Hepatitis A Ab Total Reactive
Reduced Effectiveness Of Peginterferon
While the drug peginterferon is used much less in modern HCV therapy, it is still common in cases where there has been previously failed treatment and/or a diagnosis of advanced liver disease. Ironically, it is often patients with a history of alcohol abuse who require peginterferon-based therapy.
Alcohol interferes with the efficacy of peginterferon, resulting in a 300% risk of viral rebound after completion of therapy. Surprisingly, the risk of failure was seen to be the same between both light and heavy drinkers when compared to non-drinkers with HCV.
How Is It Diagnosed
- Medical history. Your doctor may ask about your medical past to see if thereâs reason to believe you may have alcohol-related liver problems.
- Questionnaire. Theyâll ask you questions to determine if your drinking has become a problem.
- Blood tests. These will check your liver enzymes. Abnormally high levels are a sign of liver damage.
- Liver biopsy. Your doctor may request one in addition to blood tests.
Also Check: Food To Cure Hepatitis B
Stage : Alcoholic Hepatitis
At this stage, the liver becomes inflamed and experiences degenerative changes. Significant, permanent scarring and lever cell damage and death can occur.
Common clinical signs of alcoholic hepatitis include:
- Abdominal tenderness/pain
- Swollen, painful liver
Alcoholic hepatitis can be diagnosed using blood tests, electrolyte tests and liver function studies as well as an abdominal ultrasound, CT scan, MRI and/or a liver biopsy.
Unfortunately, there are no medications available to treat alcoholic hepatitis. The symptoms can be addressed, however.
It is imperative to stop alcohol consumption so that your liver can recover as much as possible. Even though scarring is permanent, your liver will, over time, repair some of the damage.
If heavy drinking continues, 40 percent of alcoholic hepatitis cases will develop into cirrhosis.
If you have alcoholic hepatitis, it would be wise to be vaccinated against the viral forms of hepatitis . Contracting them can lead to even more damage to your liver.
Hopefully, alcoholic hepatitis can be caught early. If it does progress, severe alcoholic hepatitis carries a 50 percent death rate.
Other Factors Influencing Ald Development
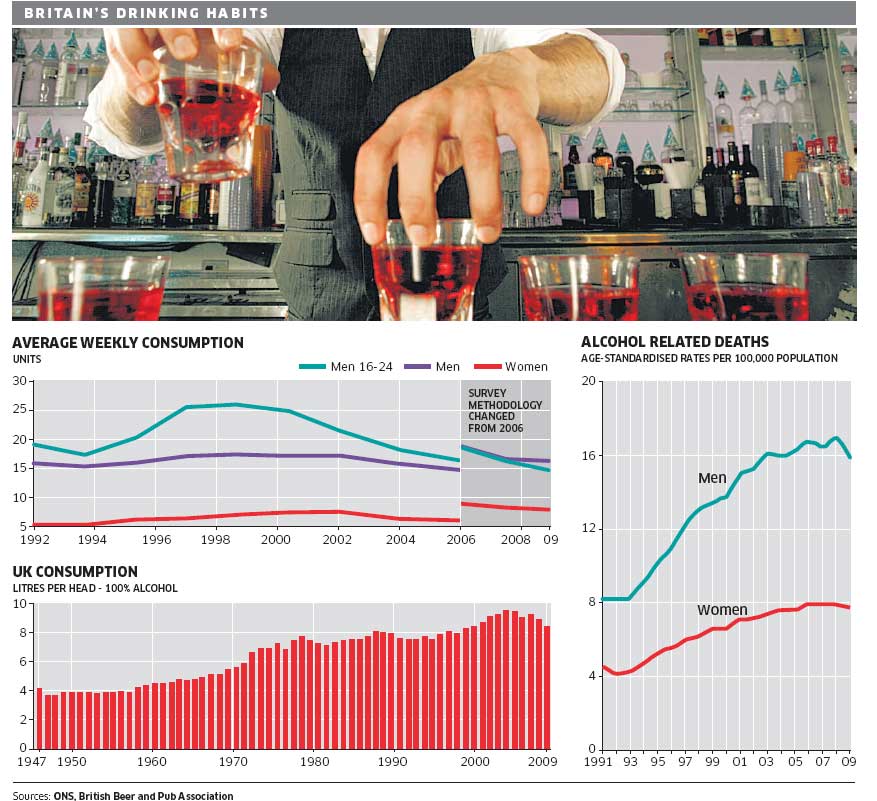
Other factors besides alcohol also may influence ALD development, including demographic and biological factors such as ethnic and racial background, gender, age, education, income, employment, and a family history of drinking problems.
Women are at higher risk than men for developing cirrhosis. This higher risk may be the result of differences in the way alcohol is absorbed and broken down. When a woman drinks, the alcohol in her bloodstream reaches a higher level than a mans even if both are drinking the same amount. The chemicals involved in breaking down alcohol also differ between men and women.
For example, womens stomachs may contain less of a key enzyme needed for the initial breakdown of alcohol. This means that a woman breaks down alcohol at a slower rate, exposing her liver to higher blood alcohol concentrations for longer periods of time-a situation that is potentially toxic to the liver. Differences in how a womans body breaks down and removes alcohol also may be linked to how much and how often she drinks, the fact that estrogen is present in her body, and even her liver size.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Core Ab Total
Risk Factors For Alcohol Related Liver Disease
Not everyone who drinks heavily develops ALD. While the amount of alcohol and the length of time as a heavy drinker are the key risk factors, additional forces impact the outcome. They are:
- Obesity/Overweight: Carrying extra weight increases the risk of liver disease because fat builds up in the liver. The fat cells secrete acids which cause a reaction that destroys healthy cells in the liver, leading to scarring. Add alcohol to the mix and the combined effect adds additional liver damage.
- Malnutrition: Often people who drink heavily, eat poorly. They also may have trouble absorbing nutrients because alcohols toxic byproducts make it difficult to break down food. The lack of nutrients contributes to liver cell damage.
- Genetic component: How a body metabolizes alcohol is influenced by genetics. If certain enzymes are missing, that can affect the risk of developing ALD.
- Demographic influencers: Rates of alcohol cirrhosis are higher in African-American and Hispanic males than they are in Caucasian males. Women are more susceptible than men to the impact of alcohol because they become more impaired than men after drinking equal amounts.
- Having viral hepatitis, especially hepatitis C: Adding alcohol to a liver already taxed by hepatitis increases the risk of developing liver disease, as well as liver cancer.
What Causes Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus causes hepatitis C. The hepatitis C virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood. Contact can occur by
- sharing drug needles or other drug materials with an infected person
- getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
- being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not kept sterilefree from all viruses and other microorganismsand were used on an infected person before they were used on you
- having contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person
- using an infected persons razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
- being born to a mother with hepatitis C
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
You cant get hepatitis C from
- being coughed or sneezed on by an infected person
- drinking water or eating food
- hugging an infected person
- shaking hands or holding hands with an infected person
- sharing spoons, forks, and other eating utensils
- sitting next to an infected person
A baby cant get hepatitis C from breast milk.18
Read Also: Itchy Back And Hepatitis C
How Can Alcohol Use Cause Hepatitis
Every food and drink you consume passes through your liver for processing. Your liver helps metabolize nutrients and filters out toxins. When alcohol goes to your liver for processing, it acts as a toxin. It offers no nutritional value and instead breaks down into poisonous chemicals.
Chronic heavy alcohol use can overload your liver with fat and toxins to process. When your liver can no longer keep up, these toxins and fat build up and begin to injure your liver. The injury produces an inflammatory response. This is your bodys way of attempting to heal and ward off further injury.
Like a fever, inflammation is supposed to be a temporary intervention. But when the assault is constant, the inflammation becomes constant. In your liver, this means swelling with fluid. If the swelling is severe and persistent, over time it will damage the tissues, causing cell death.
What Is The Difference: Alcohol
Cirrhosis is late-stage liver disease. Its what happens when chronic inflammation does cumulative damage to your liver over time. As cells in the inflamed tissues die, they’re gradually replaced with scar tissue. When a significant portion of your liver tissue has become scar tissue, that’s cirrhosis. In Western societies, alcohol-induced hepatitis causes 50% of cirrhosis cases.
Cirrhosis will eventually stop your liver from working properly. As scar tissue replaces healthy tissue in your liver, it blocks the flow of blood and slows your livers ability to process nutrients and filter toxins. This leads to many complications, including malnutrition, blood toxicity, liver failure and death. In the West, alcohol-induced liver disease causes 80% of liver toxicity deaths.
Don’t Miss: Causes And Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis C
People more likely to get hepatitis C are those who
- have injected drugs
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- have hemophilia and received clotting factor before 1987
- have been on kidney dialysis
- have been in contact with blood or infected needles at work
- have had tattoos or body piercings
- have worked or lived in a prison
- were born to a mother with hepatitis C
- are infected with HIV
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have or had sex with men
In the United States, injecting drugs is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.13
What Effect Does Alcohol Have On Patients With Hep C
How alcohol worsens HCV and speeds up progression of liver disease is not completely understood. We do know that alcohol acts in several ways to worsen the impact that the virus has on the body. Specifically, excessive alcohol consumption1 :
- Increases HCV replication
- Increases the rate of HCV mutations, increasing the chances for resistant HCV quasispecies
- Has a general negative effect on the health of the body
In one laboratory study, HCV replication or reproduction was increased three-fold in HCV cells that were treated with alcohol. Other studies have looked at how alcohol affects immunity on a cellular level. Alcohol and HCV both decrease the function of specific types of immune system cells involved in protecting liver and other cells. In studies conducted in animals, alcohol consumption resulted in an impaired immune response to HCV.1
Not only does alcohol affect how the body responds to HCV, it also affect how well antiviral medications work against the virus. Alcohol inhibits the effects of antiviral medications, including interferon.1
Alcohol increases the ability of HCV to mutate into quasi species. An increase in the number of HCV quasi species is associated with increased resistance to treatment and poor responses to interferon-based therapy.1
Also Check: Glomerulonephritis Due To Infectious Hepatitis
When To Speak With A Doctor
Anyone who suspects they may have a liver condition should speak with a doctor as soon as possible. The sooner a healthcare professional diagnoses liver conditions, such as HCV and alcoholic hepatitis, the earlier treatment can begin. This may reduce the risk of permanent liver damage and complications.
Individuals can also speak with a doctor or a support organization if they find it difficult to reduce their alcohol consumption.
Seeking help for addiction may seem daunting or even scary, but several organizations can provide support. If you believe that you or someone close to you is struggling with addiction, you can contact the following organizations for immediate help and advice:
Alcohol And Hepatitis C
If youve been diagnosed with hepatitis C, your doctor has probably advised you to give up alcoholic beverages. For some people, this can be one of the most difficult lifestyle adjustments to make. But its also one of the most important.
Several studies have shown that among people with hepatitis C, regular drinkers have higher levels of virus than nondrinkers, according to a report in the journal Hepatology. Studies also show that when people infected with the hepatitis C virus stop drinking alcohol, levels of the virus decrease.
Researchers have found that alcohol causes the hepatitis C virus to multiply in the liver by increasing the activity of a protein that triggers the virus to make new copies of itself. These new copies speed the progress of the infection and raise the risk of liver damage.
Protecting your liver
There are other compelling reasons not to drink alcoholic beverages if you have hepatitis: One of the livers jobs is to process alcohol. Too much alcohol can poison liver cells and cause a form of the disease called alcoholic hepatitis. If people continue to drink excessively, the condition can lead to permanent liver damage, or cirrhosis.
If youve been diagnosed with hepatitis C, drinking alcohol adds to the strain on the liver, increasing the risk of damage to cells. That raises the danger of cirrhosis and liver cancer. If your liver has already been damaged by the virus, drinking can make things even worse.
How to get help
Recommended Reading: Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection
How Do I Remove Hepatitis A From My Drinking Water
To kill or inactivate Hepatitis A, bring your water to a rolling boil for one minute Water should then be allowed to cool, stored in a clean sanitized container with a tight cover, and refrigerated.
Because of the small size of the virus, using a point-of-use filter will not remove it from water. You may also disinfect your well adequate chlorination kills the Hepatitis A virus. Contact your local health department for recommended procedures. Remember to have your well water tested regularly, at least once a year, after disinfection to make sure that the problem does not recur.
Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination websites privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance on other federal or private website.