Treatment Options For Hepatitis B
People living with chronic hepatitis B infection should expect to live a long and healthy life. There are decisions people can make to protect their livers such as seeing a liver specialist or health care provider regularly, avoiding alcohol and tobacco, and eating healthy foods. There are also approved drugs for both adults and children that control the hepatitis B virus, which helps reduce the risk of developing more serious liver disease, but there is still no complete cure.
Current treatments for hepatitis B fall into two general categories:
- Immune modulator Drugs These are interferon-type drugs that boost the immune system to help get rid of the hepatitis B virus. They are given as a shot over 6 months to 1 year.
- Antiviral Drugs These are drugs that stop or slow down the hepatitis B virus from reproducing, which reduces the inflammation and damage of your liver. These are taken as a pill once a day for at least 1 year and usually longer.
It is important to know that not everyone with chronic hepatitis B infection needs to be treated. This can be difficult to accept when first diagnosed because taking a drug to get rid of the virus seems like the first step to getting better. Current treatments, however, are generally found to be most effective in those who show signs of active liver disease .
Hepatitis B Drug Watch
Visit the HBF Drug Watch for a complete list of the approved treatments for hepatitis B and promising new drugs in development.
What Do I Need To Know About Having Hepatitis B
If you have chronic hepatitis B, getting the right medical care can help you stay healthy. Taking good care of your liver is important. Talk with your doctor before you take any prescription medication, over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, or nutritional supplements to make sure they wont hurt your liver. You should also stay away from alcohol, because drinking can damage your liver.
How Does Hepatitis B Spread
The hepatitis B virus is known as a blood-borne virus because it is transmitted from one person to another via blood or fluids contaminated with blood. Another important route of transmission is from an infected mother to a newborn child, which occurs during or shortly after birth.
- Direct contact with blood may occur through the use of dirty needles during illicit drug use, inadvertent needle sticks experienced by healthcare workers or contact with blood through other means. Semen, which contains small amounts of blood, and saliva that is contaminated with blood also carry the virus.
- The virus may be transmitted when these fluids come in contact with broken skin or a mucous membrane of an uninfected person.
People who are at an increased risk of being infected with the hepatitis B virus include the following:
In some cases, the source of transmission is never known.
You cannot get hepatitis B from the following activities:
- Having someone sneeze or cough on you
- Hugging someone
Half of all people infected with the hepatitis B virus have no symptoms and may never realize that they have been infected. Adults are more likely to develop symptoms than children. For those who do get sick, symptoms usually develop within 1 to 4 months after exposure to the virus. The initial symptoms are often similar to the flu.
Common symptoms of hepatitis B include:
Other types of acute viral hepatitis such as hepatitis A and hepatitis C have symptoms that are indistinguishable from hepatitis B.
You May Like: Is Hepatitis C An Autoimmune Disease
Complications Of Hepatitis B
A small proportion of people who become infected with the hepatitis B virus develop a long-term hepatitis B infection. They may have the virus in their bloodstream for most of their life without realising they are infected.
People with chronic hepatitis B infection may not notice any health problems until they develop liver problems such as liver disease or liver cancer later in life. Treatment for hepatitis B is essential because it is not possible to be a healthy carrier of the hepatitis B virus. Chronic hepatitis B infection occurs more commonly in some communities, including:
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities.
- In people from parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, such as:
- North-East Asia
- Sub-Saharan Africa.
How Is Acute Hepatitis B Treated

Acute hepatitis B doesnt always require treatment. In most cases, a doctor will recommend monitoring your symptoms and getting regular blood tests to determine whether the virus is still in your body.
While you recover, allow your body to rest and drink plenty of fluids to help your body fight off the infection. You can also take an over-the-counter pain reliever, such as ibuprofen , to help with any abdominal pain you have.
See a doctor if your symptoms are severe or seem to be getting worse. You may need to take a prescription antiviral medication to avoid potential liver damage.
Like acute hepatitis B, chronic hepatitis B may not require medical treatment to avoid permanent liver damage. In some patients, monitoring symptoms and getting regular liver tests is appropriate.
Treatment generally involves antiviral medications, such as:
- peginterferon alfa-2a injections
- antiviral tablets, such as tenofovir or entecavir
Antiviral medications can help to reduce symptoms and prevent liver damage. But they rarely completely get rid of the hepatitis B virus. Instead, the goal of treatment is to have the lowest viral load possible. Viral load refers to the amount of a virus in a blood sample.
Theres no cure for hepatitis B, but the condition is easily preventable by taking a few precautions. Hepatitis B is often spread through sexual contact, shared needles, and accidental needle sticks.
You can reduce your risk of developing hepatitis B or spreading the virus to others by:
You May Like: Hepatitis C Antibody Reactive Means
Advances In New Drugs To For Curing Hepatitis B And Hepatitis D Announced At Ilc 2021
For Immediate Release
Media Release
Advances in new drugs to for curing Hepatitis B and Hepatitis D announced at ILC 2021
Thursday 24 June 2021 Leading hepatology researchers announced important new developments in hepatitis research at the International Liver Congress 2021 today. This includes new data on antivirals to cure Hepatitis B and Hepatitis D and the application of infusion chemotherapy with P-1 inhibitors to treat liver cancer.
Other announcements included a review of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on efforts to eliminate Hepatitis C in the USA and some encouraging data from a trial of a new liver dialysis device to treat acute on chronic liver failure .
Scientists and advocates have long argued that if we are realistically going to eliminate Hepatitis B, then we will need a functional cure, said Philip Newsome, Secretary General of EASL and Professor of Experimental Hepatology and Director of the Centre for Liver Research at the University of Birmingham in the UK. The results from the trial of RNAi therapeutic drug VIR-2218 are an encouraging example that a cure is possible sooner than later with potential real-world implications for the 300 million people living with the disease.
Todays official press conference highlighted five studies covering treatment and cure research for hepatitis and acute on chronic liver failure selected from over 1500 abstracts being presented at ILC 2021.
Impact of COVID-19 on eliminating Hepatitis in the U.S.
Contact:
What Is Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis B is a serious disease caused by a virus. Hepatitis causes inflammation of the liver, vomiting, and jaundice . Hepatitis can lead to liver cancer, cirrhosis, or death.
Hepatitis B is spread through blood or bodily fluids, sexual contact, and by sharing items such as a razor, toothbrush, or IV drug needle with an infected person. Hepatitis B can also be passed to a baby during childbirth when the mother is infected.
The hepatitis B adult vaccine is used to help prevent this disease in adults. The dialysis form of this vaccine is for adults receiving dialysis.
This vaccine helps your body develop immunity to hepatitis B, but it will not treat an active infection you already have.
Vaccination with hepatitis B adult vaccine is recommended for all adults who are at risk of getting hepatitis B. Risk factors include: living with someone infected with hepatitis B virus having more than one sex partner men who have sex with men having sexual contact with infected people having hepatitis C, chronicliver disease, kidney disease, diabetes, HIV or AIDS being on dialysis using intravenous drugs living or working in a facility for developmentally disabled people working in healthcare or public safety and being exposed to blood or body fluids living or working in a correctional facility being a victim of sexual abuse or assault and traveling to areas where hepatitis B is common.
You May Like: How Serious Is Hepatitis C
Treatment For Chronic Hepatitis B
If blood tests show that you still have hepatitis B after 6 months, your doctor may recommend medication to reduce the risk of complications of hepatitis B and regular tests to assess the health of your liver.
Treatment is usually offered if:
- your immune system is unable to control the hepatitis B by itself
- there’s evidence of ongoing liver damage
Hepatitis B medications can help keep the virus under control and stop it damaging your liver, although they will not necessarily cure the infection and some people need lifelong treatment.
The main medicines for chronic hepatitis B include peginterferon alfa 2-a and antiviral medicines.
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
There are three main ways to diagnose HBV infection. They include:
- Blood tests: Tests of the blood serum shows how your bodys immune system is responding to the virus. A blood test can also tell you if you are immune to HBV.
- Abdominal ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to show the size and shape of your liver and how well the blood flows through it.
- Liver biopsy: A small sample of your liver tissue is removed though a tiny incision and sent to a lab for analysis.
The blood test that is used to diagnose hepatitis B is not a test that you get routinely during a medical visit. Often, people whove become infected first learn they have hepatitis B when they go to donate blood. Blood donations are routinely scanned for the infection.
The virus can be detected within 30 to 60 days of infection. About 70% of adults with hepatitis B develop symptoms, which tend to appear an average of 90 days after initial exposure to the virus.
You May Like: Home Remedies For Hepatitis C
Causes Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is spread through contact with blood that contains the hepatitis B virus. If infected blood or body fluids enter another persons bloodstream, that person may become infected.
The time from exposure to the hepatitis B virus to the appearance of the illness is 45 to 180 days.
Risky activities that can cause infection include:
- Sharing unsterile or unclean equipment for injecting drugs.
- Piercing the skin with equipment that is not properly cleaned, disinfected and sterilised.
- Sharing razor blades or toothbrushes.
- Coming into contact with infected blood through open cuts or the mucous membranes of another person.
- Having unprotected sex , especially if there is blood present.
Mothers who have hepatitis B can pass the virus to their babies or children at the time of birth or after birth. If the newborn baby is quickly immunised with 2 vaccines, they can be protected from getting hepatitis B.
All blood and blood products produced for medical purposes in Australia are carefully screened for hepatitis B and other blood-borne viruses. The risk of getting infected with hepatitis B from a blood transfusion is extremely low .
What Is The Outlook For People With Hepatitis B
The outlook for people with HBV is better now than ever before. You are certainly able to live a full life and help yourself stay healthy. You should make sure to have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider who is qualified to treat hepatitis B, possibly a liver doctor.
Make sure you are vaccinated against hepatitis A. Check with your healthcare provider or pharmacist before taking other medications or over-the-counter products, including supplements and natural products. These could interfere with your medication or damage your liver. For instance, taking acetaminophen in large doses may harm your liver.
Follow the usual guidelines for living a healthy life:
- Eat nutritious foods, choosing from a variety of vegetables, fruits and healthy proteins. It is said that cruciferous vegetables are especially good at protecting the liver.
- Exercise regularly.
- Dont smoke and dont drink. Both tobacco and alcohol are bad for your liver.
- Do things that help you cope with stress, like journaling, talking with others, meditating and doing yoga.
- Avoid inhaling toxic fumes.
Read Also: What Are The Effects Of Hepatitis B
Acute Hepatitis B Symptoms
There are three phases of acute hepatitis B infection, and symptoms may differ depending on the stage. Early in the disease, called the prodromal phase, symptoms may include:
- Fever
- Dark urine and light stool color
During the icteric phase:
- Jaundice develops
- Anorexia, nausea and vomiting may worsen
- Irritated skin lesions may develop
- Other symptoms may subside
Diagnosis Of Hepatitis B
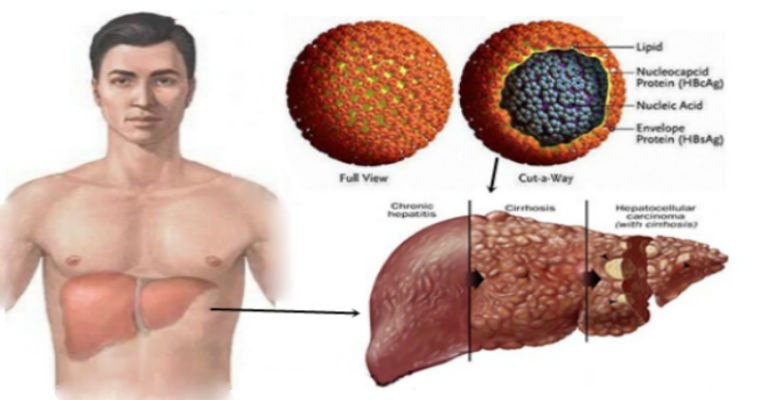
Blood tests are available to determine if you are or have been infected with hepatitis B. It may take 6 months from the time of infection before a blood test can detect antibodies to hepatitis B, so follow-up testing may be required. During this 6-month period, until you know whether you are infected or not, take action to prevent potential infection of other people.
There are also tests that can assess liver damage from hepatitis B. The interpretation of these tests can be complicated and specialist advice is needed, so talk to your doctor.
All pregnant women are tested for hepatitis B. If you are found to have chronic hepatitis B, your doctor can help reduce the risk of transferring the infection to your newborn child.
Also Check: How To Check For Hepatitis C
What Is Involved In A Liver Transplant
A liver transplant is considered necessary when the liver is damaged and cannot function or in some cases of liver cancer. Your liver is very important. It is responsible for many functions related to making sure that your body stays healthy and is able to digest foods.
You may be eligible for a transplant if you have chronic hepatitis B infection or some of the diseases that may result from it, including liver cancer and cirrhosis. You will have to complete testing and be evaluated before being approved for a transplant. It is likely that you will be placed on a waiting list while an appropriate organ is found.
Donated livers come from two types of donors: living and deceased. Because the liver can regenerate, it is possible to use part of a liver for transplant. The remaining sections in both the donor and the receiver will grow into livers of adequate size.
People who get liver transplants must take anti-rejection drugs for the rest of their lives. These drugs make you more susceptible to infection. However, liver transplants have become more successful over time and continue to improve.
Are There Home Remedies For Hepatitis B
The goals of self-care are to relieve symptoms and prevent worsening of the disease.
- Drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration. Broth, sports drinks, gelatin, frozen ice treats , and fruit juices are preferred because they also provide calories.
- Ask your physician before taking any medications, even those that are over-the-counter. Some medications depend on the liver, and liver damage may impair the body’s ability to metabolize these drugs. If you are on prescription medications, check with your physician to see if the doses should be adjusted or if the medication should be temporarily discontinued.
- Avoid drinking alcohol until your healthcare practitioner allows it. Individuals with chronic HBV should avoid alcohol for the rest of their lives.
- Try to eat a diet that provides adequate nutrition. Take it easy. It may take some time for your energy level to return to normal.
- Avoid prolonged, vigorous exercise until symptoms start to improve.
- Avoid any activity that may spread the infection to other people .
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis A And How Do You Get It
If I Am Infected How Can I Prevent Passing On The Virus To Others
If you have a current hepatitis B infection you should:
- Avoid having sex with anyone until they have been fully immunised and checked with a blood test to see that the immunisation has worked.
- Not share any injecting equipment such as needles, syringes, etc.
- Not donate blood or semen or carry a donor card.
- Not share razors, toothbrushes, etc, that may be contaminated with blood.
- Cover any cuts or wounds with a dressing.
- Make sure that, if any of your blood spills on to the floor or other surfaces following an accident, it is cleaned away with bleach.
Treatment Of Acute Hepatitis B
-
General measures
Liver transplantation Liver Transplantation Liver transplantation is the surgical removal of a healthy liver or sometimes a part of a liver from a living person and then its transfer into a person whose liver no longer functions. (See… read more is the most effective treatment for fulminant hepatitis B and is the best hope of survival, particularly for adults.
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis Ca Sexually Transmitted Disease
What Is My Risk
Your risk depends of several factors: destination, length of stay, what you do when you are travelling and whether you have direct contact with blood or other body fluids. In certain destinations, your risk may be higher, as some areas have higher numbers of people with chronic hepatitis B in the general population.
The risk increases with certain activities, such as unprotected sex, sharing needles, tattooing and acupuncture.
Aid and health care workers and anyone who receives medical or dental care with unsterilized or contaminated equipment in a country where hepatitis B occurs are also at greater risk.