What Are The Different Types Of Hepatitis B
In most of the adult cases of hepatitis B , the virus is completely cleared from the body upon treatment. However, the remaining 5% can go on to develop chronic forms of the disease. It has been observed that within 6 months of the treatment, most people not only clear the virus but also become immune to the same. In general, there are 3 distinct types of hepatitis B infections seen:Healthy Chronic Carriers These people carry the virus but dont develop any symptoms. They are not infectious to others but have a higher risk of developing hepatic conditions such as cirrhosis. However, if the immune system in such individuals gets suppressed owing to an infection or treatment via immunosuppressant drugs, there are chances that they may develop hepatitis B infection. Chronic Infectious Carriers They are the contagious carriers of the disease as they have virus replicating in their systems. They show signs of hepatitis such as damaged liver that progresses into liver cirrhosis. Only 5% of the cases can show remission of the virus.Chronic Mutant The chronic mutant form is a result of a mutated strain of the virus that causes permanent alteration to the hepatitis B viruss genetic makeup. Those with it have the risk of being infectious to others and it is observed to be more resistant to treatment than other forms of hepatitis B.
Recommended Reading: What Is Autoimmune Hepatitis C
Hbv Dna Hbv Genotype And Hbv Drug Resistance Assays
Specimen: Serum or plasma
Container: Red-top tube, yellow-top tube , gel-barrier tube, plasma preparation tube, or lavender tube
Collection method: Routine venipuncture
The specimen should be transfused to separate plasma/serum from cells within 6 hours and kept frozen when testing cannot be done promptly.
The tests use PCR amplification, DNA probe hybridization, and sequencing method.
An Interesting Case Of Isolated False
He S. Yang
1Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, New York Presbyterian Hospital, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, USA
2Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, New York Presbyterian Hospital, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, USA
Abstract
1. Introduction
Here, we report a case of a female patient with persistent isolated HBsAg positivity with a lack of symptoms, other serological markers, risk factors, or vaccination to explain the positivity, highly suggestive of a false-positive result requiring thorough investigation to evaluate potential interferences.
2. Case Report
Upon further review of the patients history, no recognized, self-reported risk factors for viral hepatitis including unprotected sex, blood transfusions, tattoos, or intravenous drug abuse were reported. Furthermore, the patient denied personal or family history of liver disease or jaundice. Physical examination did not reveal stigmata of liver disease. Considering the patients low risk for blood-borne infections, it was suspected that the HBsAg and HIV screening results might be false positives due to an unknown interference with the analytical assays.
The patient was retested 3 months after her Mohs surgery. The HBsAg and HIV screening tests remained positive. This study has been approved by the institutional review board of Weill Cornell Medicine.
3. Discussion
Data Availability
Conflicts of Interest
Don’t Miss: How Hepatitis C Is Transmitted Sexually
Hepatitis B Blood Tests
The Hepatitis B Panel of Blood Tests
Only one sample of blood is needed for a hepatitis B blood test, but the Hepatitis B Panel includes three parts. All three test results are needed to fully understand whether a person is infected or not. Below is an explanation of the 3-part Hepatitis B Panel of blood test results.
Question 2 What Is The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
The hepatitis B surface antibody is the antibody that is produced in response to hepatitis B surface antigen , a protein present on the surface of the hepatitis B virus. Anti-HBs appears after convalescence from acute infection and lasts for many years. It can also be produced in response to hepatitis B vaccination.
Other hepatitis B antibodies are not produced in response to vaccination. This is because these antigens are not in the vaccine.
Also Check: What Form Of Hepatitis Is Sexually Transmitted
Recommended Reading: How Would You Know If You Have Hepatitis
Can Hbsag And Hbsab Be Positive
Both in vitro simulation and in vivo animal models demonstrated that HBsAg antigen and HBsAb of the same serotypes could not coexist, but HBsAg antigen and HBsAb of different serotype could coexist. HBsAg/HBsAb double positive hepatitis B virus infection could be due to infection of viruses of different serotypes.
When Is It Ordered
Hepatitis B tests may be ordered when someone has signs and symptoms associated with acute hepatitis to determine if they are due to infection with HBV. Some of these include:
- Fever
- Joint pain
- Jaundice
Hepatitis B tests may be done as follow up when routine tests results such as ALT and/or AST are elevated. Sometimes acute forms of hepatitis may be detected this way since they may cause only mild symptoms that can be confused with the flu. Chronic hepatitis more often has no symptoms and is more commonly detected when routine test results are abnormal.
A test for hepatitis B surface antigen may be used for screening when someone falls into one of the high-risk categories for chronic hepatitis B. Joint guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and American College of Physicians were published in December 2017 and recommend the following groups be tested for HBsAg:
When hepatitis B tests are used to monitor people with chronic hepatitis B infections, they may be performed on a regular basis. Hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B e antigen , often along with HBV DNA, are usually measured about every 6 months to a year since, in some people, HBeAg will go away on their own. In those who are being treated for chronic HBV, HBeAg and HBV DNA tests can be used to determine whether the treatment is successful.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Is It Curable
Understanding Your Test Results
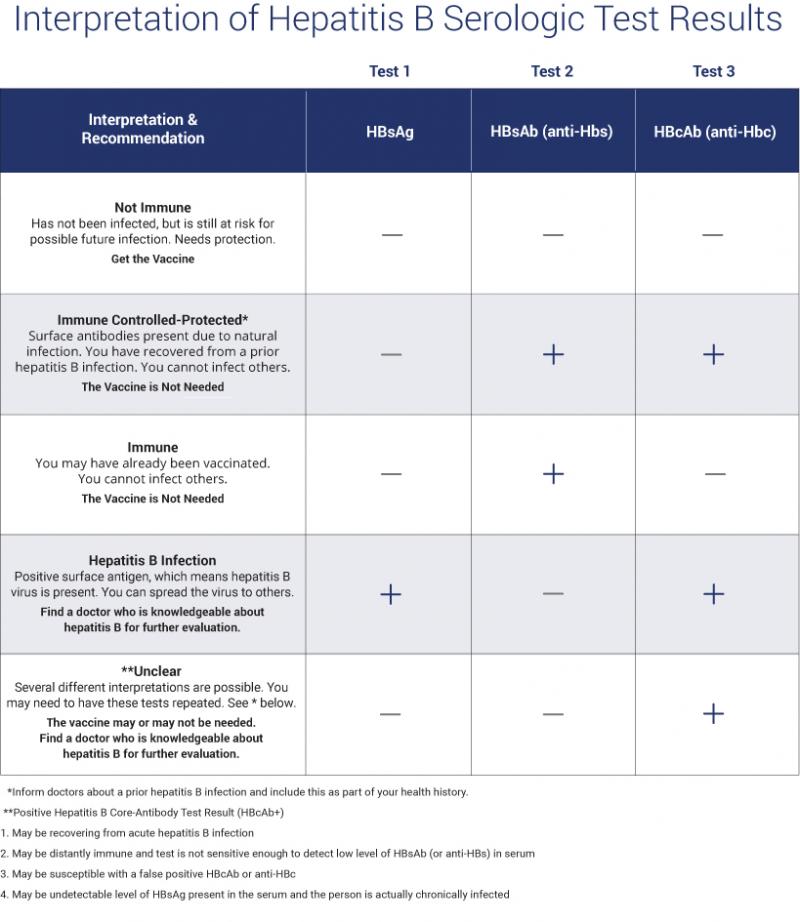
Understanding your hepatitis B blood tests can be confusing. It is important to talk to your health care provider so you understand your test results and your hepatitis B status. Are you infected? Protected? Or at risk? The Hepatitis B Panel of blood tests includes 3 tests and all three results must be known in order to confirm your status.
Below is a chart with the most common explanation of the test results, but unusual test results can occur. Please note that this chart is not intended as medical advice, so be sure to talk to your health care provider for a full explanation and obtain a printed copy of your test results. In some cases, a person could be referred to a liver specialist for further evaluation.
More Detailed Information About Hepatitis B Blood Tests
An acute hepatitis B infection follows a relatively long incubation period – from 60 to 150 days with an average of 90 days. It can take up to six months, however, for a person to get rid of the hepatitis B virus. And it can take up to six months for a hepatitis B blood test to show whether as person has recovered from an acute infection or has become chronically infected .
The following graphic from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention represents the typical course of an acute hepatitis B infection from first exposure to recovery.
According to the CDC, a hepatitis B blood test result varies depending on whether the infection is a new acute infection or a chronic infection.
Hepatitis B Core Antibody Reactive
We are experienced manufacturer. Wining the majority of the crucial certifications of its market for Hepatitis B Core Antibody Reactive, In Vitro Rapid Diagnostic Test, Dengue Ig G Positive, Quickvue Influenza,Dengue Test Igm Positive Means. To acquire a consistent, profitable, and constant growth by getting a competitive advantage, and by continuously increasing the value added to our shareholders and our employee. The product will supply to all over the world, such as Europe, America, Australia,Armenia, Durban,Istanbul, Myanmar.Our products are exported worldwide. Our customers are always satisfied with our reliable quality, customer-oriented services and competitive prices. Our mission is “to continue to earn your loyalty by dedicating our efforts to the constant improvement of our products and services in order to ensure the satisfaction of our end-users, customers, employees, suppliers and the worldwide communities in which we cooperate”.
Recommended Reading: Is There A Shot For Hepatitis C
What Is The Difference Between The Hepatitis B Surface Antigen And The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
The basic blood test for hepatitis B consists of three screening tests: a hepatitis B surface antigen test, which determines whether a person currently has the infection a hepatitis B core antibody test, which determines whether a person has ever been infected and a hepatitis B surface antibody test, which determines
Hepatitis B Vaccine And Surface Antibody Titer Faqs
PLEASE NOTE: This is program specific some programs require 3 Hepatitis B vaccines AND a positive Hepatitis B Surface Antibody titer while others will accept 3 vaccines OR a titer. Please read the information in your CastleBranch account carefully so that you know exactly what you need to meet your programs requirements. If you have any questions, please email and a team member will respond.
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis C A Disease
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is the most common serious liver infection in the world. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus that attacks and injures the liver. Two billion people have been infected and about 300 million people are living with a chronic hepatitis B infection. Each year up to 1 million people die from hepatitis B despite the fact that it is preventable and treatable.
The hepatitis B virus is transmitted through blood and infected bodily fluids. It can be passed to others through direct contact with blood, unprotected sex, use of illegal drugs, unsterilized or contaminated needles, and from an infected woman to her newborn during pregnancy or childbirth.
Hepatitis B is a silent epidemic because most people do not have symptoms when they are newly infected or chronically infected. Thus, they can unknowingly spread the virus to others and continue the silent spread of hepatitis B. For people who are chronically infected but dont have any symptoms, their liver is still being silently damaged which can develop into serious liver disease such as cirrhosis or liver cancer.
The good news is that hepatitis B is preventable and treatable. There is a simple blood test to diagnose a hepatitis B infection. Testing is the only way to know for sure if you are infected. There is a safe vaccine to prevent hepatitis B. There are effective drug therapies that can manage a chronic hepatitis B infection, and a cure is within sight.
Question 5 How Can Quantitative Hbsag Levels Help Distinguish The Different Phases Of Hbv Infection
Quantitative HBsAg results, along with selected immunologic and virologic characteristics, may help differentiate infection phases and inform prognosis and therapeutic decision-making. For example, the HBeAg-negative inactive carrier state may be identified by low HBV DNA and low HBsAg in patients with certain genotypes.2 Low serum HBsAg levels measured 1 year after documented HBeAg seroconversion may predict subsequent HBsAg loss in HBV genotype B or C infection.5 It has been documented that a drop in HBsAg levels in patients who are on NA treatment can predict subsequent HBsAg loss. The observed decrease in HBsAg concentration may help predict HBsAg loss and support the decision to discontinue peg-IFN and/or NA therapy.
Peg-interferon and/or NA treatment may lead to reductions in HBsAg. In general, sustained responders display greater and/or more rapid HBsAg decline than non-responders.1-2,4-6 The quantitative HBsAg level that best predicts sustained virologic response has yet to be well established. However, some experts consider 2 or more measurements of HBsAg below the assayâs lower limit of detection obtained â¥6 months apart to be a potentially useful endpoint for antiviral therapy.9-11
Recommended Reading: What Are Some Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Don’t Miss: What Lab Test For Hepatitis C
What Is The Hepatitis B Virus And What Causes Its Transmission
The Hepatitis B virus consists of five types names as A, B, C, D and E. These viruses target the liver. The spread of hepatitis B infection takes place through contact with contaminated bodily fluids such as blood, seminal fluid and vaginal secretions. While the virus cannot spread through mere touch, sneezing or coughing, HBV can spread to others through the use of contaminated needles, illegal drugs, and unprotected sex. An infected mother can pass on the infection to her unborn baby during pregnancy or childbirth. Most patients complain of symptoms of Hepatitis only several weeks after the infection.
Mutant Viruses And Chronic Infection
Anti-HBe-positive patients in the reactivated phase of the disease are also referred to as the HBeAg-negative viremic group. Genomic analyses has revealed that such patients carry natural mutants of the virus that have either reduced levels or complete abrogation of HBeAg production. These variants are selected at the time of, or soon after, seroconversion, and become dominant during the reactivation phase. The most common precore mutation is the G1896A substitution, which creates a premature stop codon in the precursor protein from which HBeAg is elaborated. This mutation affects the stem of the encapsidation signal, but leads to stronger base pairing with the A1896 change in genotypes with a T at position 1858 of the precore region, such as B, C, D, and E. The double mutation affecting the core promoter region is thought to result in decreased transcription of the precore mRNA, with a knockon effect on HBeAg production, while pgRNA production remains the same or is even upregulated. It is now apparent that additional mutations in this region may contribute to this phenotype.
Geoffrey M. Dusheiko, in, 2003
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Core Antibody Positive Treatment
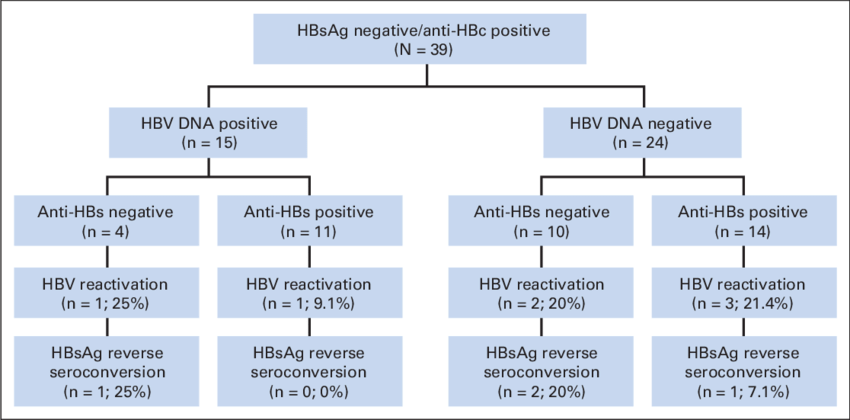
Negative But Other Hepatitis Tests Are Positive
Your HBsAb test may be negative even when other hepatitis B tests are positive, showing active or chronic infection. Further testing is necessary, especially for the hepatitis B surface antigen , which shows that the virus itself is circulating in your bloodstream and that you have an active or chronic infection.
Resolution Of Acute Infection
During resolution of acute infection, IgM anti-HBc is replaced by antibody of the IgG subclass , and anti-HBs develops . Anti-HBs is a protective, neutralizing antibody, and its presence indicates recovery from acute infection and immunity to reinfection. The period when all HBsAg has been neutralized by anti-HBs, and neither HBsAg nor anti-HBs is detectable, is referred to as the window period. During the window period, the only serologic marker of infection is IgM anti-HBc. During resolution, anti-HBe replaces HBeAg. In people with past HBV infection, IgG anti-HBc usually remains detectable for life, but anti-HBs might become undetectable in remote infection.3,109
Howard C. Thomas, Jennifer A. Waters, in, 1998
Also Check: Can Hepatitis C Be Contracted Sexually
When To Get Tested
When you have risk factors for HBV infection or when you have signs and symptoms of hepatitis, such as jaundice or unexplained elevated blood levels of alanine aminotransferase , a liver-associated enzyme when you have a condition that requires chemotherapy or drugs that suppress your immune system when you are being treated for HBV or hepatitis C when it is unclear whether you have immunity and your healthcare practitioner is considering giving you the hepatitis B vaccine
What Does The Test Result Mean
The tests for hepatitis B may be ordered individually but are often ordered in some combination, depending on the reason for testing. Results of the tests are typically evaluated together. Sometimes the meaning of one result depends on the result of another test. However, not all tests are performed for all people.
The table below summarizes possible interpretations of some common patterns of results.
| Initial Tests | |
| None detected or detected at very low level | Chronic infection but low risk of liver damage carrier state |
*Note: There are some types of HBV that do not make e-antigen. In areas where these strains of HBV are common , testing for HBeAg is not very useful. In these cases, a negative HbeAg result does not necessarily mean that the person is not infectious it may be that the person is infected with a strain that does not make the e-antigen.
Monitoring treatment of chronic infection: If the results from initial and follow-up testing indicate that a person has chronic hepatitis B, then the individual may be treated with medication and the effectiveness of that treatment may be monitored using the tests for HBe and HBs antigen and antibody and HBV DNA:
Don’t Miss: What Happens To Your Body When You Have Hepatitis C
Should I Get The Hbv Vaccine
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that adults in high-risk groups get vaccinated. Some of these groups include people:
- In close contact with someone who has hepatitis B
- Who undergo dialysis
- With chronic liver or kidney disease
- With HIV or who seek treatment for other sexually transmitted diseases or drug treatment
- Who travel to countries where hepatitis B is common
- Who are healthcare workers with potential exposure to HBV
Unless there is something in your medical history to the contrary, it is prudent to get the series of vaccinations. Babies, children and adolescents are routinely given the series of shots if you have already been vaccinated, you probably are protected for many years, perhaps for life, and will not usually need to get the vaccine again.
Dont Miss: Hepatitis B And C Can Be Spread By