Reactivation Of Hepatitis B Virus: A Review Of Clinical Guidelines
Department of Medicine, David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA
The Vatche and Tamar Manoukian Division of Digestive Diseases, Department of Medicine, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA
CORRESPONDENCE
Anthony Myint, M.D., Department of Medicine, Olive View UCLA Medical Center, 2B-182, 14445 Olive View Dr., Sylmar, CA 91342. E-mail:
Myron J. Tong M.D., Ph.D.
Department of Medicine, David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA
The Vatche and Tamar Manoukian Division of Digestive Diseases, Department of Medicine, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA
Simon W. Beaven M.D., Ph.D.
Department of Medicine, David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA
The Vatche and Tamar Manoukian Division of Digestive Diseases, Department of Medicine, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA
Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Olive View-UCLA Medical Center, Sylmar, CA
Department of Medicine, David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA
The Vatche and Tamar Manoukian Division of Digestive Diseases, Department of Medicine, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA
CORRESPONDENCE
Anthony Myint, M.D., Department of Medicine, Olive View UCLA Medical Center, 2B-182, 14445 Olive View Dr., Sylmar, CA 91342. E-mail:
Myron J. Tong M.D., Ph.D.
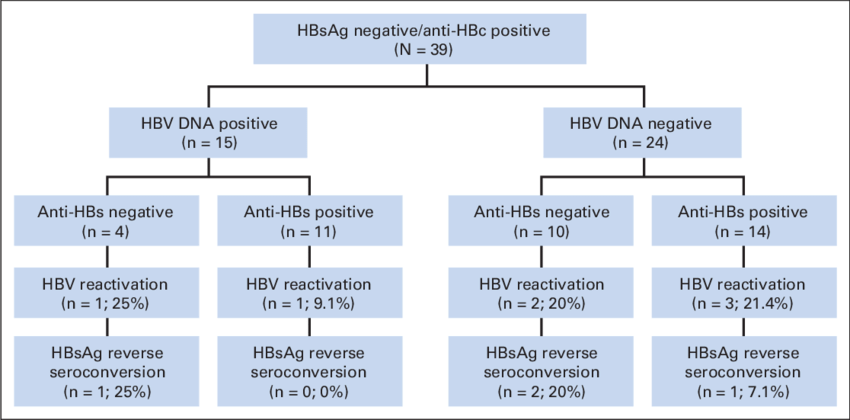
Hbc Antibody Positive/hbs Antigen Negative/hbs Antibody Negative
The HBc antibody positive/HBs antigen negative serotype is further divided into naïve and occult types . However, since HBV reactivation is often observed in HBc antibody positive/HBs antigen negative cases, it may be preferable to divide HBc antibody positive/HBs antigen negative cases based on whether they are positive or negative for HBs antibodies. For HBc antibody positive patients, perhaps HBV reactivation is induced by rituximab. Although Hui et al reported a 3%-25% reactivation rate, prophylactic treatment may be desirable since the mortality is relatively high after reactivation occurs. In 2013, Huang et al conducted a randomized controlled trial to evaluate the effect of the prophylactic administration of entecavir on the frequency of HBV reactivation in HBc antibody positive patients. In their report, unlike in retrospective analyses, the prophylactic administration of entecavir was the most important factor, at least for HBc antibody positive patients. Furthermore, Seto et al recently reported frequent reactivation of HBV in patients with 10 mIU/mL HBs antibody prior to rituximab treatment. In HBc antibody positive patients, prophylactic treatment is necessary, at least for those who are antibody negative prior to rituximab treatment . We believe that the prophylactic administration of a nucleic acid analog is preferable in HBc antibody positive/HBs antigen negative/HBs antibody negative cases.
What Do I Need To Know About Having Hepatitis B
If you have chronic hepatitis B, getting the right medical care can help you stay healthy. Taking good care of your liver is important. Talk with your doctor before you take any prescription medication, over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, or nutritional supplements to make sure they wont hurt your liver. You should also stay away from alcohol, because drinking can damage your liver.
You May Like: Different Types Of Hepatitis C
Phases Of Chronic Hbv
Within module 7 which outlines the natural history of chronic hepatitis B, there is a pictorial diagram. This diagram captures the four phases of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. It illustrates that the natural history and the progression of chronic hepatitis B is complex and non-linear, and varies from person to person. In general, transition from e-antigen positive to e-antigen negative is not always permanent hepatitis B e-antigen may transition back and forth between positive and negative. Active hepatitis, reactivation, and hepatitis flares increase the risk for cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B.
The diagram also illustrates the fluctuation of hepatitis B DNA and alanine aminotransferase levels during various phases of chronic hepatitis B and the impact these levels can have on histological activity and degrees of fibrosis that can occur in the transition between phases.
In the immune tolerant phase, hepatitis B e-antigen is always present, the hepatitis B DNA levels are high and alanine aminotransferase levels are low. There is minimal histological activity and scant fibrosis in the liver.
During the immune-active chronic hepatitis B phase the patient can be either hepatitis B e-antigen-positive or negative. In this phase the levels of hepatitis B DNA and alanine aminotransferase fluctuate. Histology shows active hepatitis and variable degrees of fibrosis, hence, treatment is appropriate.
Risk Of Hbv Perinatal Transmission
The overall rate of transmission of HBV from an HBsAg-positive woman to her neonate during the perinatal period can be as high as 90% in the absence of immunoprophylaxis. The presence of HBeAg and the associated higher HBV DNA levels mediate this risk: mothers with a positive HBeAg test have a perinatal transmission rate of 70 to 90% whereas those with a negative HBeAg test have a rate of transmission less than 10%. Most perinatal transmission of HBV occurs during or shortly before delivery, but can take place less frequently in utero. The exact rate of perinatal HBV transmission among mothers with HIV-HBV coinfection is not well established. Most perinatal transmission of HBV occurs during or shortly before delivery, but can take place less frequently in utero.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Affects What Organs
How Do I Get Hepatitis B Treatment
Usually for adults, hepatitis B goes away on its own and you wont need treatment. Your doctor might tell you to rest, eat well, and get plenty of fluids. You may also get medicines to help with any symptoms you might have but be sure to talk with your doctor or nurse before taking anything.
If you have chronic hepatitis, there are medicines you can take to treat it. Your doctor will tell you about your options and help you get whatever treatment you need.
Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation Following Rituximab Treatment In Rheumatoid Arthritis
Baseline hepatitis B surface antigen positivity is a significant protective factor for reactivation of hepatitis B virus in patients with HBsAg-negative, HBV core antibody -positive rheumatoid arthritis receiving rituximab therapy, according to study results published in the International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases.1
Worldwide, approximately 2 billion people are infected by HBV, and 75% of them inhabit Southeast Asia and the Western Pacific regions.2,3 A considerable number of patients with RA have coexisting HBV infection, and RA is a risk factor for developing rHBV as a result of using immunosuppressive therapies.4-7 RTX is used for treating patients with RA with an inadequate response to anti-tumor necrosis factor -alpha therapy, and rHBV has recently been recognized as a complication of RTX therapy.8-18
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatic Steatosis Of The Liver
What Is This Test
This test looks for antibodies called IgM in your blood. The test is used to find out whether you are actively infected with the hepatitis B virus .
HBV has a central core and a surrounding envelope. Your immune system makes IgM antibodies for the core of HBV during the active stage of infection. Hepatitis B core IgM antibodies begin to appear in your blood several weeks after you are first infected with HBV. People who have had the hepatitis B vaccine will not have the core antibody in their blood.
HBV is 1 of 5 hepatitis viruses. The others are hepatitis A, C, D, and E. Most hepatitis infections are caused by these 5 viruses. HBV is spread through blood, seminal fluid, and vaginal secretions. It can take 60 to 150 days to develop symptoms of hepatitis B after you become infected. The virus causes an infection in the liver. In most cases, this virus clears up on its own within 6 months. But in a small portion of adults and a larger portion of children, the virus does not go away. This is especially true for newborns. This is called having a chronic infection. It may lead to liver cell damage, scarring, cirrhosis, or liver cancer.
Hbv Prevention Measures For Neonates
Infants weighing greater than 2,000 grams who are born to women with HBV infection, regardless of HBV treatment status during pregnancy, should receive one dose of hepatitis B immune globulin and the first dose of the HBV vaccine series within 12 hours of birth. The second and third doses of vaccine should be administered at 1 and 6 months of age, respectively. Management of infants weighing less than 2,000 grams is the same except that the initial vaccine dose should not be counted as part of the vaccine series due to potentially lower immunogenicity in these infants 3 additional doses of vaccine should be administered beginning at age 1 month. Postvaccination testing for both anti-HBs and HBsAg should be performed in all infants after completion of the vaccine series, at age 9 to 18 months this regimen is greater than 95% effective in preventing HBV infection in these infants.
Recommended Reading: Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis B
Kinetics Of Qhbcab And Qhbsag In Hbsag Recurrence And Sustained Hbsag Loss Groups
As shown in Figure 1, during baseline to 1 week after LT, both qHBsAg and qHBcAb were significantly decreased in both sustained HBsAg loss group and HBsAg recurrence group . However, the changes in qHBcAb and qHBsAg in the two groups were not significantly different after 1 week. At each time point between baseline and 24 weeks after LT, the titer of qHBcAb in the sustained HBsAg loss group was higher than that in the HBsAg recurrence group.
Figure 1 The Kinetics of qHBsAg in HBsAg recurrence and sustained HBsAg loss groups. The Kinetics of qHBcAb in HBsAg recurrence and sustained HBsAg loss groups. Box plots showing the median, interquartile range and absolute range of qHBcAb and qHBsAg at baseline and at 1 week, 4 weeks, 12 weeks and 24 weeks in groups .
What Is A Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test
Hepatitis B surface antibody test is part of a panel of blood tests to diagnose HBV infection. Hepatitis B surface antibody test determines the presence and quantity of anti-HBs in the blood serum, which can indicate protection from HBV infection.
Hepatitis B disease affects the liver and commonly spreads through body fluids such as blood, semen, and vaginal secretions.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Titer Labcorp Cost
Hepatitis B And Your Liver
The liver is such an important organ that we can survive only one or two days if it completely shuts down â if the liver fails, your body will fail, too. Fortunately, the liver can function even when up to 80% of it is diseased or removed. This is because it has the amazing ability to regenerate â or create â itself from healthy liver cells that still exist.
If your body were an automobile, your liver would be considered the engine. It does hundreds of vital things to make sure everything runs smoothly:
- Stores vitamins, sugar and iron to help give your body energy
- Controls the production and removal of cholesterol
- Clears your blood of waste products, drugs and other poisonous substances
- Makes clotting factors to stop excessive bleeding after cuts or injuries
- Produces immune factors and removes bacteria from the bloodstream to combat infection
- Releases a substance called âbileâ to help digest food and absorb important nutrients
The word hepatitis actually means inflammation of the liver. Thus, hepatitis B refers to inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis B virus. With early detection and appropriate follow-up medical care, people living with a chronic hepatitis B infection can expect to enjoy a long and healthy life.
Virological And Serological Status
The virological and serological risk factors associated with HBV reactivation are detectable HBV DNA, HBsAg, hepatitis B e antigen and anti-HBc . Patients positive for HBsAg are up to 8 times more likely to experience HBV reactivation than HBsAg negative/anti-HBc positive patients . Amongst HBsAg positive patients, HBeAg positive patients are more likely to experience HBV reactivation than HBeAg negative patients .
You May Like: What Is Hepatic Function Panel
Hepatitis B And Pregnancy
If youâre pregnant, you might pass the virus to your baby at birth. Itâs less likely to happen during your pregnancy.
If your baby gets the virus and isnât treated, they could have long-term liver problems. All newborns with infected mothers should get hepatitis B immune globulin and the vaccine for hepatitis at birth and during their first year of life.
Understanding Your Test Results
Understanding your hepatitis B blood tests can be confusing. It is important to talk to your health care provider so you understand your test results and your hepatitis B status. Are you infected? Protected? Or at risk? The Hepatitis B Panel of blood tests includes 3 tests and all three results must be known in order to confirm your status.
Below is a chart with the most common explanation of the test results, but unusual test results can occur. Please note that this chart is not intended as medical advice, so be sure to talk to your health care provider for a full explanation and obtain a printed copy of your test results. In some cases, a person could be referred to a liver specialist for further evaluation.
More Detailed Information About Hepatitis B Blood Tests
An acute hepatitis B infection follows a relatively long incubation period – from 60 to 150 days with an average of 90 days. It can take up to six months, however, for a person to get rid of the hepatitis B virus. And it can take up to six months for a hepatitis B blood test to show whether as person has recovered from an acute infection or has become chronically infected .
The following graphic from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention represents the typical course of an acute hepatitis B infection from first exposure to recovery.
According to the CDC, a hepatitis B blood test result varies depending on whether the infection is a new acute infection or a chronic infection.
You May Like: What Does It Mean To Have Hepatitis B
Timing And Differential Diagnosis With Hbv
The hepatitis flare is first detected as an increase in ALT levels, typically within 3 to 12 weeks after starting antiretroviral therapy. The differential diagnosis includes direct drug or alcohol hepatotoxicity, a new viral hepatitis infection , or an opportunistic infection. To help distinguish between these conditions, a review of the medication history, prior hepatitis A immunization, and history of recent HCV exposure would be indicated, as well as measurement of serum HBV DNA, HIV RNA, and CD4 cell count.
How Long Do Hep B Antibodies Last
How long does protection from hepatitis B vaccine last? Studies indicate that immunologic memory remains intact for at least 30 years among healthy people who initiated hepatitis B vaccination at > 6 months of age. The vaccine confers long-term protection against clinical illness and chronic hepatitis B virus infection.
You May Like: Hepatitis A Vaccine Schedule For Adults
Scientific Tools And Resources
Interpretation of Hepatitis B Serologic Test Results
One page Summary Table pdf icon describes the four most common tests used in hepatitis B serologic testing and provides guidance to interpret different patterns of test results.
Screening and Referral Algorithm for Hepatitis B Virus Infection among Pregnant Women
This is a clinical algorithm for screening and referral of pregnant women who are HBsAg-positive.
Blood Products And Intravenous Immunoglobulin
Transfusion of blood products or infusion of intravenous immunoglobulin can result in passive transmission of antibodies associated with HBV. This can lead to patients being falsely informed that there is evidence of past HBV or, more importantly, being considered for antiviral prophylaxis in the context of immunosuppression. Baseline anti-HBc should be measured early during the course of disease to avoid this scenario and, if negative, subsequent positive serology can be disregarded in the absence of ongoing risk of acquisition of HBV. Should liver function tests become deranged during the course of immune suppression, HBsAg should be retested, as in any other patient.
You May Like: How Do You Get Rid Of Hepatitis B
Whats The Prognosis For Hepatitis B
Your doctor will know youâve recovered when you no longer have symptoms and blood tests show:
- Your liver is working normally.
- You have hepatitis B surface antibody.
But some people don’t get rid of the infection. If you have it for more than 6 months, youâre whatâs called a carrier, even if you donât have symptoms. This means you can give the disease to someone else through:
- Unprotected sex
- Contact with your blood or an open sore
- Sharing needles or syringes
Doctors donât know why, but the disease does go away in a small number of carriers. For others, it becomes whatâs known as chronic. That means you have an ongoing liver infection. It can lead to cirrhosis, or hardening of the organ. It scars over and stops working. Some people also get liver cancer.
If youâre a carrier or are infected with hepatitis B, donât donate blood, plasma, body organs, tissue, or sperm. Tell anyone you could infect — whether itâs a sex partner, your doctor, or your dentist — that you have it.
Show Sources
CDC: âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for Health Professionals,â âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for the Public.â
Mayo Clinic: âHepatitis B.â
UpToDate: âHepatitis B virus: Screening and diagnosis.â
CDC.
HealthyPeople.gov: âHepatitis B in Pregnant Women: Screening.â
Annals of Internal Medicine: âScreening for Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Nonpregnant Adolescents and Adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement.â
Risk Of Transfusion Transmission
In the US, with testing for HBsAg and anti-HBc, the estimated residual risk of HBV transmission before DNA testing was 1:280,000â1:357,000, significantly higher than that for HIV or HCV. Voluntary minipool testing for HBV DNA has been widely implemented in the US, and is now required by the FDA. Current residual risk estimates are 1:750,000 or less in an era of universal immunization. Minipool HBV DNA assays have similar sensitivity to current HBsAg tests, accounting for the clinically marginal decrease of the window period .
Gregory L. Armstrong, Susan T. Goldstein, in, 2007
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine Cost Cvs