What Does It Mean When Different Types Of Blood Tests For Hepatitis C Give Different Results
The first test your provider probably will perform is called an “antibody” test. A positive result means that you were exposed to the hepatitis C virus at some point in your life.
If the result is positive, your provider will perform a second test called hepatitis C virus RNA to see if the virus is still in your body. If the RNA test result is positive, then you have chronic hepatitis C infection.
So what does it mean if you have a positive result for the first test but a negative result for the second?
What Are The Symptoms And Consequences Of Infection
Approximately 20 percent of persons exposed to the virus develop symptoms which may include jaundice , fatigue, dark-colored urine, stomach pain, loss of appetite and nausea. After the initial infection, 15-25 percent will recover and 75-85 percent will become chronically infected . Approximately 70 percent of persons chronically infected may develop liver disease, sometimes decades after initial infection.
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis, simply put, is liver inflammation. Several things can cause hepatitis, but its most often due to a virus. Hepatitis C is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis C virus . Hepatitis C affects the lives of nearly 60 million people worldwide, and in the United States alone, over 2 million people live with hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C can be a short-term illness, or it can turn into a chronic condition. Hepatitis C is most commonly spread through blood-to-blood contact, often by sharing contaminated needles or from a pregnant parent with HCV passing it on to a newborn. It can also be spread in other ways, such as having sex with someone with HCV and sharing contaminated personal items .
There are also other kinds of viral hepatitis, like hepatitis A and hepatitis B. Hepatitis A usually goes away on its own, and theres a vaccine available. Hepatitis B can turn into a chronic infection, but treatments and a vaccine are also available.
Hepatitis C is a serious infection that can cause complications like liver cancer and cirrhosis if left untreated. Even though hepatitis C medications are available, theyre expensive and often hard to access. To help control the spread of HCV, a vaccine is needed. But due to some nuances of the virus itself, its been difficult for researchers to find an effective hepatitis C vaccine.
Read Also: Where Can I Get My Hepatitis B Vaccine
How Is Hepatitis C Treated
The main aim of treatment for hepatitis C is to cure the infection, if possible, thereby stopping the virus damaging your liver. Maviret A medicine called Maviret is used for the treatment of hepatitis C. It aims to clear the hepatitis C virus from your body. This treatment has a cure rate of more than 90% with 8 weeks of treatment regardless of the type or genotype. Before starting Maviret, you will have tests to assess how much scarring present in your liver.
- If there is no severe scarring in your liver, you will be prescribed a course of Maviret tablets .
- Some people may need to take Maviret for longer .
- Maviret tablets can be prescribed by your GP but is only available from some pharmacies. Read more about Maviret tablets .
However, there are some situations where using Maviret tablets is not suitable and/or you should be cared for in a specialist clinic, eg, if:
- you have severe liver disease
- you also have hepatitis B infection
- you are HIV positive
- previous treatment for hepatitis C has failed.
In these circumstances, the specialist will supervise your treatment. After treatment, you may stay under specialist follow-up because for some people there is a risk of developing liver cancer even many years after the virus has been cured.
Complications Of Hepatitis C

If the infection is left untreated for many years, some people with hepatitis C will develop scarring of the liver .
Over time, this can cause the liver to stop working properly.
In severe cases, life-threatening problems, such as liver failure, where the liver loses most or all of its functions, or liver cancer, can eventually develop.
Treating hepatitis C as early as possible can help reduce the risk of these problems happening.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatic Luciferase Expression
Spread Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is spread through blood-to-blood contact when blood from a person with hepatitis C enters another persons bloodstream.
The most common way people become infected with hepatitis C in Australia is by sharing injecting equipment such as needles, syringes, spoons and tourniquets. It is possible to be infected with hepatitis C after only one risk event.
Hepatitis C may also be spread through:
- tattooing and body piercing with equipment that has not been properly cleaned, disinfected or sterilised such as backyard tattoos’. Registered parlours with appropriate infection control procedures are not a risk
- needlestick injuries in a healthcare setting
- receiving blood transfusions in Australia prior to 1990 before hepatitis C virus testing of blood donations was introduced
- medical procedures, blood transfusions or blood products and mass immunisation programs provided in a country other than Australia
- pregnancy or childbirth there is a 5% chance of a mother with chronic hepatitis C infection passing on the virus to her baby during pregnancy or childbirth.
Breastfeeding is safe, however if nipples are cracked or bleeding cease breastfeeding until they have healed.
Less likely possible routes of transmission of hepatitis C include:
Hepatitis C cannot be transmitted by:
- kissing
- sharing food, cups or cutlery
- shaking hands or day-to-day physical contact.
Can You Prevent Hepatitis
There are many ways to prevent hepatitis, from getting a vaccine to washing your hands well. But it all depends on what type you have. Here are some tips for preventing the three major kinds of this liver disease — hepatitis A, B, and C — and explanations of how one spreads in a different way.
How to prevent hepatitis A: You can get hepatitis A if you eat food or drink water that has the hepatitis A virus in it. You could also get infected if you’re in close physical contact with someone who has the disease or have sex with someone who has it.
The best way to prevent hepatitis A is to get a vaccine. Kids should get a shot around their first birthday.
As an adult, you should get the shot if you:
- Travel to Africa, Asia , the Mediterranean, Eastern Europe, the Middle East, Central and South America, Mexico, and parts of the Caribbean
- Use recreational drugs
- Work in a day-care center, nursing home, or you’re a health care professional
- Are a man who has sex with men
- Have long-term liver disease
- Take blood products to treat hemophilia or other conditions
If you’re planning a trip to a place where there are outbreaks of hepatitis A, keep in mind that the vaccine only starts to work 2 to 4 weeks after you get it. And if you want long-term protection, you’ll need a follow-up shot 6 to 12 months later.
If you haven’t had a hepatitis B shot as an adult, it’s important to get it if you:
- Live with someone who has hepatitis B
- Travel to a country with outbreaks of hepatitis B
Read Also: Hepatitis C Caused By Alcohol
Efficacy Of Hepatitis A Vaccines
Randomised controlled trials show that the vaccines have protective efficacy of nearly 100%.28,29 This is supported by the apparent eradication of hepatitis A from Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities in north Queensland and the Northern Territory since the vaccination program started in these regions.15,17,30
A single dose of Hepatitis A vaccine can confer protection for several years. There is evidence to suggest that a single dose of HAV hepatitis A vaccine can be 100% efficacious in preventing hepatitis A infection in seronegative young children in the study period from 6 weeks to 15 months post vaccination.31 Other studies have demonstrated effectiveness of a single dose in preventing hepatitis A infection up to 7 years after vaccination.25,32
How Common Is Hepatitis C In The United States
In the United States, hepatitis C is the most common chronic viral infection found in blood and spread through contact with blood.14
Researchers estimate that about 2.7 million to 3.9 million people in the United States have chronic hepatitis C.13 Many people who have hepatitis C dont have symptoms and dont know they have this infection.
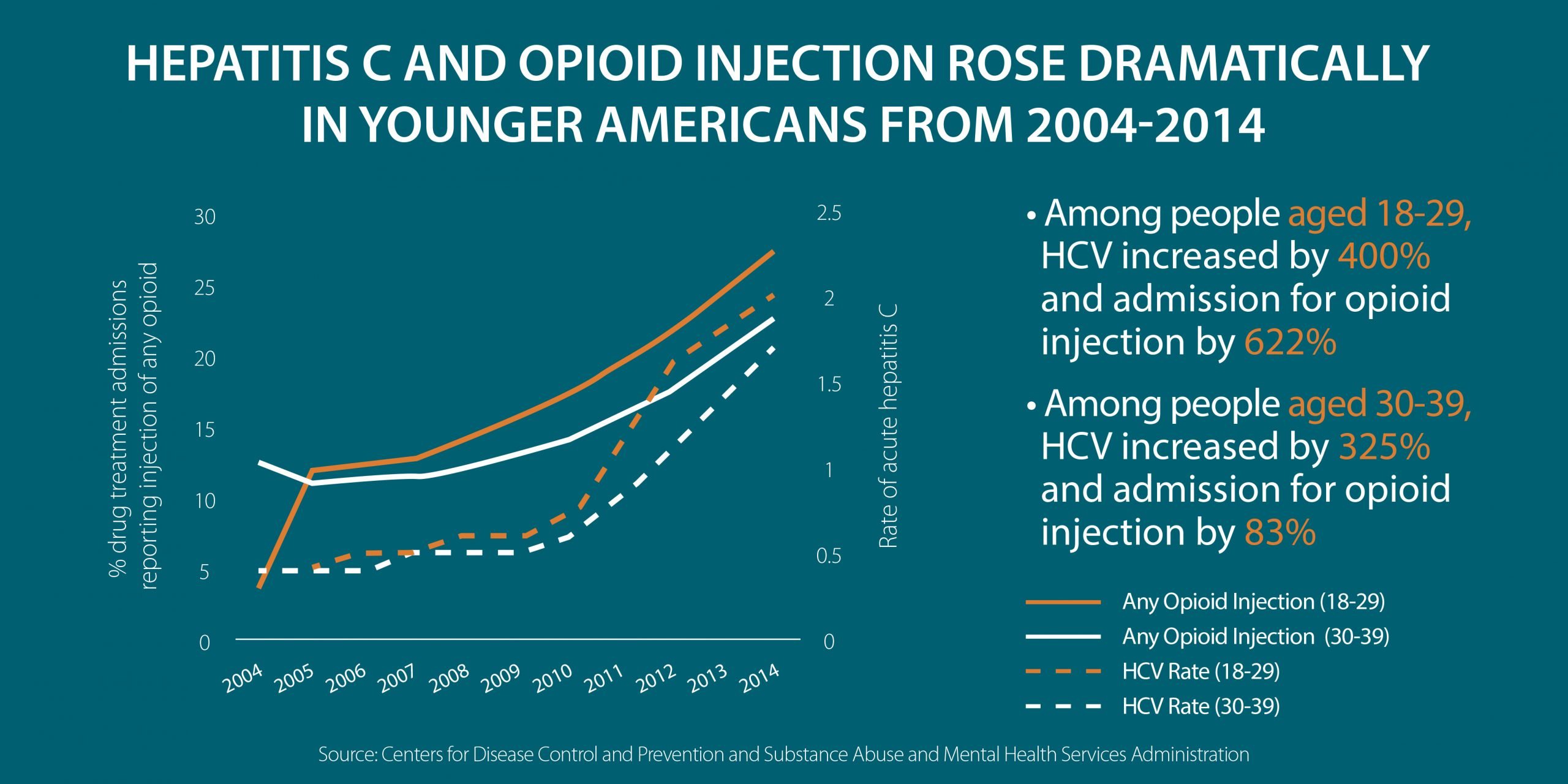
Since 2006, the number of new hepatitis C infections has been rising, especially among people younger than age 30 who inject heroin or misuse prescription opioids and inject them.15,16
New screening efforts and more effective hepatitis C treatments are helping doctors identify and cure more people with the disease. With more screening and treatment, hepatitis C may become less common in the future. Researchers estimate that hepatitis C could be a rare disease in the United States by 2036.17
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Genotype 2 Treatment Guidelines
The Most Common Hepatitis Symptoms
For starters, it’s important to remember that the absence of noticeable symptoms is not an indication of a negative hepatitis status. “As with many other viruses and sexually transmitted illnesses, many people with viral hepatitis won’t have any symptoms at all, or won’t present with symptoms until decades after initial infection,” explains Dr. Pearlman. So, the only true way to know your hepatitis status is to get tested .
So what are the symptoms of hepatitis when they do occur? Acute viral hepatitis common symptoms include things like the following, according to the CDC:
- generalized fatigue
- abdominal pain
- low-grade fever
In the instances that the virus becomes chronic or severe, the symptoms can also include jaundice and dark urine, both a result of liver dysfunction, says Dr. Pearlman. “If not properly managed, consequences can include advanced liver disease or cirrhosis, or even death,” adds Dr. Yoo.
How Long Do Hep A B And Typhoid Immunizations Last
How long do hep a, b and typhoid immunizations last
According to the Canadian Immunization Guide, protection from the hepatitis A vaccine is likely to last at least 20 years and possibly for life. Protection from the hepatitis B vaccine is likely to last for life . Protection from the typhoid vaccine is thought to last for either about three or seven years, depending on the type of typhoid vaccine received . This is assuming all of the recommended doses of these vaccines are received as per the recommended schedules and that the person who received these vaccines is healthy.
If you are wondering if your immunizations are up-to-date and if you are considered to be protected against these diseases, it is recommended that you follow up with your immunizing health care provider or local travel clinic . Your health care provider can review your immunization record, tell you if you are considered up-to-date for these vaccines and recommend and provide any missing vaccines. You can find a list of travel clinics in BC here.
– Immunization Nurse
You May Like: Hepatitis C Antibody Reactive Means
Will My Immunization Be Recorded
Your immunization records are registered in a computerized network known as the Immunization Records and Yellow Cards. While this one is specific to Ontario, each province has their own.
They can use information obtained in these databases to:
- Maintain immunization data
- Inform you whether or when you or your family members need an immunization
- Track how well vaccinations perform to prevent vaccine-preventable infections
You can also share your immunization history with health care providers for the provision of social health services to aid with assessment and treatment and monitor the spread of infectious illnesses.
What Are The Side Effects Of Treatment
The direct acting antiviral regimens used to treat hepatitis C today are extremely well tolerated. You may experience mild side effects like headache or fatigue. For details on the side effects, review the handout specific to medication you take.
In rare instances, providers may recommend the addition of the medication ribavirin for more difficult cases of hepatitis C. Ribavirin may cause additional side effects such as fatigue, shortness of breath, cough, anemia, or rash. Patients who receive ribavirin may need more frequent monitoring for side effects as well as adjustment of the dose if side effects are experienced. For detailed information on ribavirin, patients should review the ribavirin handout.
Also Check: Hepatitis A Vaccine Cost Walmart
Who Should Receive Twinrix
According to Canadian medical advice, the vaccine is required for all those seeking to minimize their hepatitis A and B infection risk. Twinrix is used for vaccinating adults, teenagers, youngsters and babies above one year of age.
In specific, vaccination against hepatitis A is suggested for:
- Travellers to countries or areas with a risk for hepatitis A
- The Canadian armed forces, emergency organization, or any other organization likely to be sent at short notice to high-risk areas for hepatitis A
- Zoo workers, veterinarians, and researchers
- People diagnosed with liver disease
- Hemophiliacs
Hepatitis B vaccination is prescribed for those who:
- Travellers to countries or areas with a risk for hepatitis B
- Nurses, including medical students
- People in contact with someone with hepatitis B
- People who use medication through injections
- Hemophiliacs
- Immigrants and students coming to Canada
Diagnosis Of Hepatitis C
If you are at risk of hepatitis C infection, or think you may have been exposed to hepatitis C in the past, see your doctor for an assessment of your liver health. This will include blood tests and possibly a non-invasive test for liver damage .
There are 2 blood tests used to diagnose hepatitis C. Usually these can be done at the same time but sometimes they will be done separately.
The first test known as a hepatitis C antibody test can tell you whether you have ever been exposed to hepatitis C.
It may take 2 to 3 months from the time of infection until a blood test can detect antibodies to hepatitis C, so there is a window period during which you cannot tell if you are or have been infected. In this time, take precautions to prevent the potential spread of the virus.
The second test is called hepatitis C PCR, which will be done if the antibody test is positive. This determines if the virus is still present in your blood or liver or if you have already cleared the infection.
If you have cleared the virus or had successful treatment to cure it, the PCR test will be negative.
A liver ultrasound or Fibroscan can also be performed to assess if you have any liver damage.
If your doctor is inexperienced in diagnosing hepatitis C you can call the LiverLine on for information, and to find a GP who can help you.
Read Also: What Does Hepatitis Do To The Body
How Can I Protect Myself From Hepatitis C Infection
If you dont have hepatitis C, you can help protect yourself from hepatitis C infection by
- not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- wearing gloves if you have to touch another persons blood or open sores
- making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools and unopened ink
- not sharing personal items such toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
Hepatitis C can spread from person to person during sex, but the chances are low. People who have multiple sex partners, have HIV or other sexually transmitted diseases, or who engage in rough or anal sex have a higher chance of getting hepatitis C. Talk with your doctor about your risk of getting hepatitis C through sex and about safe sex practices, such as using a latex or polyurethane condom to help prevent the spread of hepatitis C.
If you had hepatitis C in the past and your body fought off the infection or medicines cured the infection, you can get hepatitis C again. Follow the steps above, and talk with your doctor about how to protect yourself from another hepatitis C infection.
If you think you may have been exposed to the hepatitis C virus, see your doctor as soon as possible. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent liver damage.
How Hepatitis Is Spread
Hepatitis A: About 20,000 people in the U.S. contract hepatitis A each year. The hepatitis A virus is found in the stool of the infected person. It is spread through contaminated food or water or by certain types of sexual contact.
Children who get hepatitis A often don’t have symptoms, so they can have the virus and not know it. However, they can still spread it easily. Fortunately, children are now routinely vaccinated against hepatitis A.
Most people who get hepatitis A recover completely within two weeks to six months and don’t have any liver damage. In rare cases, hepatitis A can cause liver failure and even death in older adults or people with underlying liver disease.
Hepatitis B: Every year, about 40,000 people in the U.S. become infected with hepatitis B. Acute hepatitis lasts from a few weeks to several months. Many infected people are able to clear the virus and remain virus-free after the acute stage. However, for others, the virus remains in the body, and they develop chronic hepatitis B infection, which is a serious, lifelong condition. About 1.2 million people in the U.S. have chronic hepatitis B. Of these, 15% to 25% will develop more serious health problems, such as liver damage, cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer, and some people die as a result of hepatitis B-related disease.
Hepatitis B cannot be spread by contaminated water, food, cooking, or eating utensils, or by breastfeeding, coughing, sneezing, or close contact such as kissing and hugging.
Also Check: How Long Is Hepatitis C Treatment