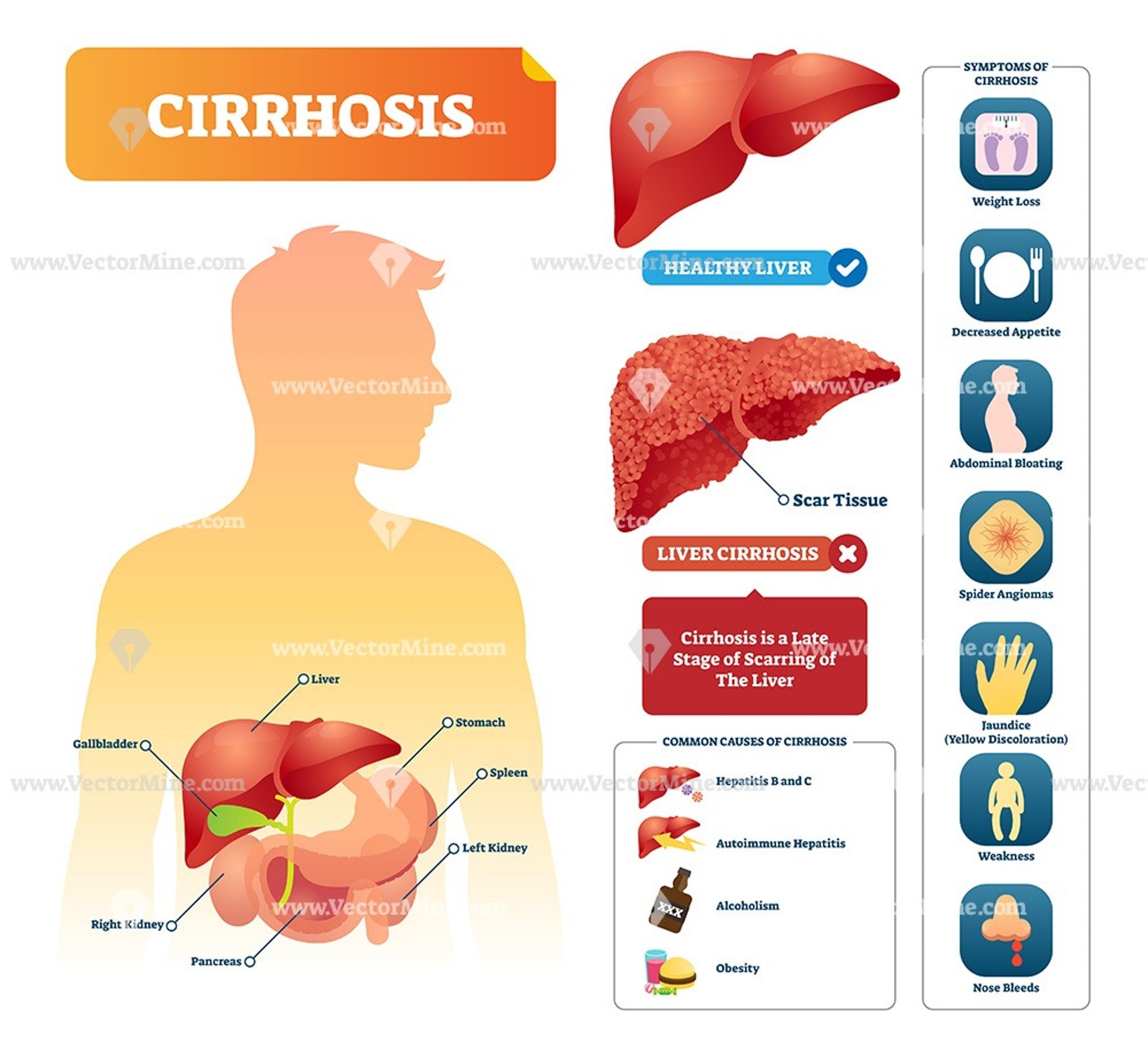
Cirrhosis Of The Liver
Cirrhosis happens when scar tissue permanently replaces the healthy tissue of your liver. Scar tissue affects the normal function of your liver and can eventually cause it to fail.
If you develop cirrhosis as a result of heavy alcohol use, alcoholic hepatitis can get worse. Cirrhosis can also raise your risk of liver cancer.
Hepatitis Cases In Children
The number of cases of hepatitis in children has increased recently. Public health doctors and scientists are looking into what could be causing this.
See a GP if your child has symptoms of hepatitis, including yellowing of the eyes and skin .
Good hygiene, including supervising hand washing in young children, can help to prevent infections that can cause hepatitis.
What Are The Side Effects Of Treatments For Alcoholic Hepatitis
Because alcohol is a drug and is addictive, suddenly stopping drinking is difficult and may cause dangerous side effects. For instance, it can cause alcohol withdrawal symptoms, which include anxiety, confusion, hallucinations and seizures. Patients may be referred to a medically supervised program, or recommended for counseling or a support group to help them stop drinking and to help cope with side effects.
Read Also: Does Hepatitis C Have A Vaccine
Types Of Alcohol Related Liver Disease
- Alcholol Related Steatohepatitis : Fat accumulates inside liver cells, making it hard for the liver to work properly. This early stage of liver disease occurs fairly soon after repeated heavy drinking. Usually it is symptom free but upper abdominal pain on the right side from an enlarged liver may occur. Steatosis goes away with alcohol abstinence.
- Alcoholic Hepatitis: This condition is marked by inflammation, swelling and the killing of liver cells. This scars the liver, which is known as fibrosis. Symptoms may occur over time or suddenly after binge drinking. They include fever, jaundice, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and tenderness. Up to 35 percent of heavy drinkers develop alcohol hepatitis, which can be mild or severe. If it is a mild case, stopping the drinking can reverse it.
- Alcohol Related Cirrhosis: The most serious form of ALD, it occurs when the entire liver is scarred, causing the liver to shrink and harden. This can lead to liver failure. Usually the damage cannot be reversed. Between 10 to 20 percent of heavy drinkers develop cirrhosis typically after 10 or more years of drinking.
Alcohol hepatitis and alcohol cirrhosis previously were called alcohol steatohepatitis , a term that still arises among some circles.
Alcohol Can Also Affect Hepatitis C Treatment
If you are infected with the Hepatitis C virus, the more you drink each week, the more hepatitis C virus accumulates in the liver. That’s because heavy drinking weakens your immune system. This means that alcohol makes your body less able to fight off the virusincreasing the viral burden.
If your liver is working overtime to get rid of alcohol, the virus has more chances to cause damage.
Alcohol can also make your hepatitis C treatment less effective. What’s more, drinking can worsen the side effects of your medication.
Recommended Reading: Can Hiv And Hepatitis Be Passed Through Plasma
Alcohol Drinking Diary And Change Plan
To keep track of how much you drink, use a drinking diary. Record the number of drinks you have every day. At the end of the month, add up the total number of drinks you had during each week.
One way to make any kind of change in your behavior is to come up with a change plan. This exercise has you list the specific goals you would like to achieve, outline the steps and challenges you will meet in reaching those goals, and figure out ways to overcome those challenges.
Dont Miss: The Difference Between Hepatitis B And C
What Is The Prognosis For Patients Who Have Alcoholic Hepatitis
If the patient who has alcoholic hepatitis gives up drinking alcohol completely, the liver may improve, and the long-term prognosis is good if there is no underlying scar in the liver. However, if the patient continues to drink excessively, the liver will continue to get worse and possibly develop cirrhosis, a serious condition that may ultimately lead to liver failure over time. Other health problems may also develop, including infections and malnutrition.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 06/21/2018.
References
Read Also: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Alcohol
How Long Can You Live With Alcohol
If you dont stop drinking after diagnosis, you have a reduced life expectancy. For males in this group, the five-year survival rate is about 70%. For females, its 30%. People with severe alcohol-induced hepatitis and advanced liver disease have poorer outcomes. Up to 40% of people with severe alcohol-induced hepatitis die within six months of diagnosis.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Alcohol-induced hepatitis begins quietly, often without symptoms. Many people fail to recognize the damage that chronic heavy drinking may be doing to their livers. But early recognition is your best hope of catching and reversing the effects of alcohol-induced hepatitis. If you have a history of heavy alcohol use and/or symptoms of liver disease, call your healthcare provider. Theyll check out your liver, assess any possible damage and help you change your habits to change your health future.
Directions For Future Research
A recent National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism conference identified areas of research with the greatest potential for leading to more effective treatment options. Conference recommendations for research within these areas were as follows:
Clinical Studies
-
Determine how variations in the amount and pattern of drinking, combined drinking and smoking, and nutritional deficiencies affect HCVinfected patients risk of liver injury, disease progression, and death.
-
Evaluate the effectiveness of alcohol cessation programs in patients with HCV.
-
Specify how alcohol affects patients response to interferon treatment, including chemical interactions and daytoday changes in virus activity during treatment.
HCV Virology
-
Determine how alcohol affects viral replication, clearance, and persistence and the evolution of new HCV quasispecies.
-
Examine whether alcohol use leads to greater dominance of more harmful genetic variants of HCV.
-
Determine whether alcohol interacts with the HCV viral proteins to alter the viruss genetic activity.
Immunology
-
Identify the effects of alcohol on immune responses to HCV, including changes in quality, behavior, and survival of immune cell populations both within and outside the liver.
Mechanisms of Liver Injury
Model Systems
-
Develop animal models of HCV infection and of alcoholic liver disease that reproduce disease processes found in humans.
Recommended Reading: What Vitamins Are Good For Hepatitis B
Levels Of Alcohol Consumption In Hcv Patients And The Risk Of Further Liver Disease
Several studies have indicated that heavy alcohol consumption accelerates patients progression from chronic HCV to cirrhosis , and liver cancer . Although fewer studies have examined the effects of moderate drinking on the course of liver disease in HCV patients, there is some indication that alcohol consumption in the moderatetoheavy range may increase HCVinfected patients risk of developing liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. Research on whether gender has any effect on alcohol consumption and liver disease progression in HCV patients is very limited.
Cirrhosis
In a study of 2,235 HCVinfected patients, Poynard and colleagues observed that patients who drank heavily tended to show much more advanced liver scarring than those who did not drink as heavily. In addition, the researchers identified a group of rapid fibrosers, who were more likely to be male, heavy drinkers, and infected with HCV after age 40.
Wiley and colleagues observed that HCVinfected patients who drank heavily were significantly more likely to develop cirrhosis than those who were not heavy drinkers. In addition, among patients who did develop cirrhosis, the disease emerged considerably sooner for patients who drank heavily than for those who did not .
Figure 2 Relationship between fibrosis severity and years of HCV infection. Patients who reported significant alcohol consumption experienced markedly faster disease progression than patients who did not report significant alcohol intake.
Liver Cancer
Can You Get Hepatitis From Drinking Alcohol
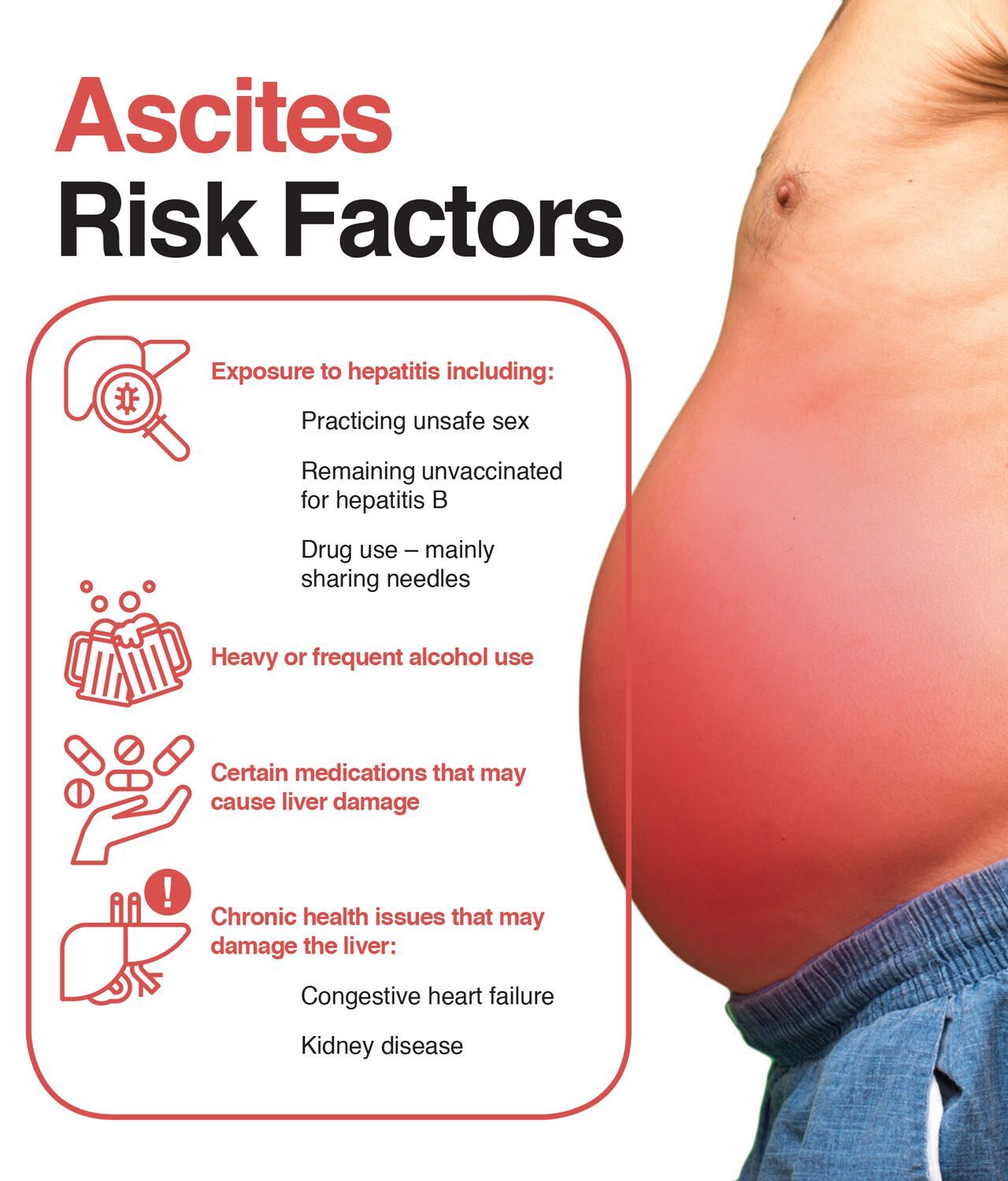
Drinking alcohol in small amounts has many health benefits including preventing Alzheimers disease and kidney stones. However, like with anything else, too much of it can be damaging in more ways than one. One disease heavy drinkers are at risk of developing is alcoholic hepatitis.
Alcoholic hepatitis is an inflammatory condition of the liver caused by heavy alcohol consumption over an extended period of time. The liver is the main source of alcohol breakdown in the body causing it to experience the most damage from heavy alcohol consumption. This can cause the liver to become inflamed, scarred, and fatty. This condition is triggered by binge drinking and continued alcohol use and can result in health problems such as cirrhosis, excessive bleeding and liver failure. About 35 percent of long-time heavy drinkers develop alcoholic hepatitis.
The link between Alcoholic Hepatitis and Hepatitis C
You May Also Like
Scientists are not sure why HCV is more common in alcohol drinkers, but they speculate that alcohol may make it easier for the virus to enter and remain inside the body.
While both conditions cause liver inflammation, there are some differences in the symptoms.
People who have hepatitis C may experience the following:
7 Daily Habits That May Be Damaging Your Liver
5 Foods to Avoid at All Costs
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Long Term Effects
Increased Risk Of Cirrhosis
There is little doubt that people with chronic hepatitis C who drink alcohol have a higher chance of developing cirrhosis. From an epidemiological point of view, more than 90% of heavy drinkers will develop fatty liver disease, of which as many as 20% will develop liver cirrhosis within 10 to 20 years.
Hepatitis C infection runs a similar course, with 75% of infected persons developing chronic disease, while 15-20% will progress to advanced disease within 10 to 30 years.
The combination of these two factors speeds the process dramatically, as well as increasing the severity of liver damageby some estimates, by as much as 200-300%. Furthermore, heavy alcohol users with HCV have a nearly 11-fold greater risk of developing cirrhosis than non-drinkers with HCV.
Interrelation Of Serum Levels Of Alt Hcv Rna Titre And Histological Grading Of Necroinflammation
Since HCV RNA serum levels were not different in the alcohol and alcohol-free groups, we tried to establish whether histological activity of necroinflammation has any correlation with either serum levels of ALT or HCV RNA titre. We did not find any significant correlation between disease activity graded from 1 to 7 and serum levels of ALT , or between disease activity and serum HCV RNA titre . Again, analysis of the interrelation between serum levels of HCV RNA titre and ALT in different patient groups did not demonstrate any significant correlation between them . This indicates that alcohol intake in HCV-infected patients did not exacerbate the underlying disease activity caused by HCV RNA replication.
Also Check: Treatment For Liver Cirrhosis Hepatitis B
You May Like: What Are The Effects Of Hepatitis A
Treatment Options For Alcoholic Hepatitis
Alcohol use both causes and worsens alcoholic hepatitis, so a diagnosis of alcoholic hepatitis means you may want to consider stopping drinking gradually. Quitting drinking can help reduce symptoms and prevent further damage to your liver.
In the early stages of the condition, avoiding alcohol may even help reverse liver damage. Once more significant damage has occurred, the changes to your liver may become permanent.
Even if the damage is too severe to reverse, quitting drinking could prevent further harm to your liver.
Alcoholic hepatitis can lead to severe and lasting liver damage, which can, in turn, cause serious health complications. In some cases, these complications can be life threatening.
Other Risk Factors Of Drinking With Hepatitis C
Apart from alcohol consumption and HCV, other risk factors contribute to alcoholic hepatitis.
These examples include:
- Sex alcoholic hepatitis poses a higher risk to women than to men. The primary liver enzyme responsible for breaking down alcohol is not as common in women as in men. This means that women face more difficulty in metabolizing the substance.
- Obesity heavy drinkers who are overweight face a higher likelihood of alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis.
- Race and Ethnicity Blacks and Hispanics have been linked with an increased risk of the disease.
- Binge drinking the risk increases for men who consume five or more drinks within two hours and women who consume four or more within the same time frame.
- Malnutrition heavy drinking is linked with malnourishment. This is typically due to either poor eating habits or the bodys inability to absorb nutrients. Alcohol and its byproducts can prevent nutrient absorption and result in liver cell damage.
Recommended Reading: Hepato Liver Support For Dogs
Can I Drink Alcohol After Treatment
Healthcare professionals recommend not drinking alcohol after treatment. Even if cured of the disease, there may be liver scarring caused by the viral infection. Alcohol may increase that scarring.
Similarly, alcohol use after hepatitis C treatment has been associated with the risk of liver cancer.
If you believe that you or a loved one is suffering from alcohol abuse, it is best to seek professional medical help. Your healthcare specialist can provide you with a treatment plan that can guide you in your path to recovery.
What Causes Alcoholic Hepatitis
When alcohol gets processed in the liver, it produces highly toxic chemicals. These chemicals can injure the liver cells. This injury can lead to inflammation and, eventually, alcoholic hepatitis.
Although heavy alcohol use can lead to alcoholic hepatitis, experts arent entirely sure why the condition develops in some people but not in others.
Alcoholic hepatitis develops in a minority of people who heavily use alcohol no more than 35 percent, according to the American Liver Foundation. It can also develop in people who use alcohol only moderately.
Because alcoholic hepatitis doesnt occur in all people who heavily use alcohol, other factors may influence the development of this condition.
Risk factors include:
- having genetic factors that affect how the body processes alcohol
- living with liver infections or other liver disorders, such as hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and hemochromatosis
- abdominal CT scan
- ultrasound of the liver
Your doctor may order a liver biopsy to confirm a diagnosis of alcoholic hepatitis. A liver biopsy requires your doctor to remove a tissue sample from the liver. Its an invasive procedure with certain inherent risks, but biopsy results can show the severity and type of liver condition.
Also Check: Medications Used For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C Infection: Disease Characteristics Testing And Treatment
The symptoms and course of hepatitis C vary greatly. Many people who are infected with the virus show no symptoms , whereas some people may experience fatigue, weakness, fever, nausea, abdominal pain, poor appetite, muscle and joint pain, or yellowing of the skin and eyes . About 75 percent of patients who are infected with HCV develop chronic infection . Between 10 and 40 percent of HCV patients develop cirrhosis within 20 to 40 years, and 1 to 3 percent develop liver cancer.
Many patients who develop cirrhosis show no symptoms of the disease and can expect longterm survival . Data from a cohort of European patients with cirrhosis followed for an average of 5 years showed that only 7 percent developed hepatocellular carcinoma, and 18 percent experienced symptomatic liver failure . There currently is no vaccine for hepatitis C.
Testing and Treatment
Blood tests can diagnose HCV infection, either by detecting antibodies to the virus or by detecting the presence and quantity of the viruss genetic material itself . Liver biopsy is quite helpful for evaluating the diseases severity prior to initiating treatment. Liver enzymes have little value in predicting fibrosis.
There are six known genetic variants of HCV, which vary geographically in their rate of occurrence. Genotypes 1 , 2, and 3 constitute the majority of genotypes in the United States.
Eugene R. Schiff and Nuri Ozden
References
END OF SIDEBAR
Abstention Before Interferon Treatment
Treatment Recommendations
How Much Do You Have To Drink To Get Alcohol
Theres no single formula that leads to alcohol-induced hepatitis in everybody. But statistically, youre more at risk if you drink heavily on a regular basis for an extended period of time. Heavy drinking means different things for people assigned male at birth and people assigned female at birth. For males, its about four standard drinks a day or more than 14 drinks per week. For females, its about three drinks per day or more than seven drinks per week.
Heavy drinking can also look like occasional binge drinking more than five drinks in a night for males or four for females. Binge drinking at least five times a month is considered heavy. If you keep up this pace for as few as six months, your risk of developing alcohol-induced hepatitis rises significantly. Most people have been drinking for five years or more, with periods of abstinence.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know When You Have Hepatitis
How Much Alcohol Is Too Much
The more you drink, the worse the damage gets and the faster it happens. There’s no “safe” level of alcohol for people with hepatitis C. The best thing you can do is avoid alcohol entirely.
People with hepatitis C who do not drink are much less likely to develop severe liver disease. This is true even up to 40 years after being infected with the virus. On the flip side, after 40 years of hepatitis C infection, most heavy drinkers have cirrhosis.
If you do drink, limit how much you have. If you have more than two alcoholic drinks daily or drink on most days of the week, take steps to cut back.
Acceleration Of Progression In Liver Disease With Alcohol And Hcv
Molecular and epidemiological evidence support the conclusion that the combination of hepatitis C and alcohol accelerates the progression of liver fibrosis compared to either etiology alone. The combined effect of hepatitis C and alcohol is not simply additive due to different mechanisms of liver injury there is a multiplicative increase in damage . Alcohol-related mechanisms may include direct toxicity of alcohol, condensation of cytoskeletal proteins, alcohol-induced oxidative injury, accumulation of excessive iron further enhancing oxidative injury and neutrophilic infiltration of the liver. HCV-related mechanisms of injury additionally include pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, HCV-induced hepatocellular necrosis, and immunomodulation by the virus . In some studies, but not all, alcohol was shown to increase HCV viral replication . In theory, alcohol could potentially increase the numbers of quasispecies or viral diversity, which might increase risk for resistance emerging during antiviral drug therapy . For these reasons, any alcohol use is strongly discouraged during antiviral treatment.
Heavy to regular moderate use of alcohol has been clearly shown to influence risk for chronic hepatitis C to progress to cirrhosis . In a cross-sectional study of 800 patients with chronic hepatitis C, Monto found that heavy alcohol use was associated with more severe fibrosis, but increases in fibrosis also occurred with low to moderate alcohol use .
You May Like: Hepatitis C Shots For Adults