Looking Further: Hcv Vaccines
Vaccine development for HCV is currently one of the most challenging fields in virology today. Various obstacles that hinder the development of an effective preventive or therapeutic vaccine for HCV include:
Considerable genetic heterogeneity of isolates within and between geographic locales .
Evolution and existence of quasispecies in an individual .
Poorly defined immunological correlates of protection.
Lack of efficient in vitro propagation to isolate the virus.
Despite these obstacles, both preventive as well as therapeutic vaccines for HCV are under development and also under various phases of vaccine trials, but a successful vaccine remains to be developed.
Hep C Transmission And Pcr In Health Care Settings
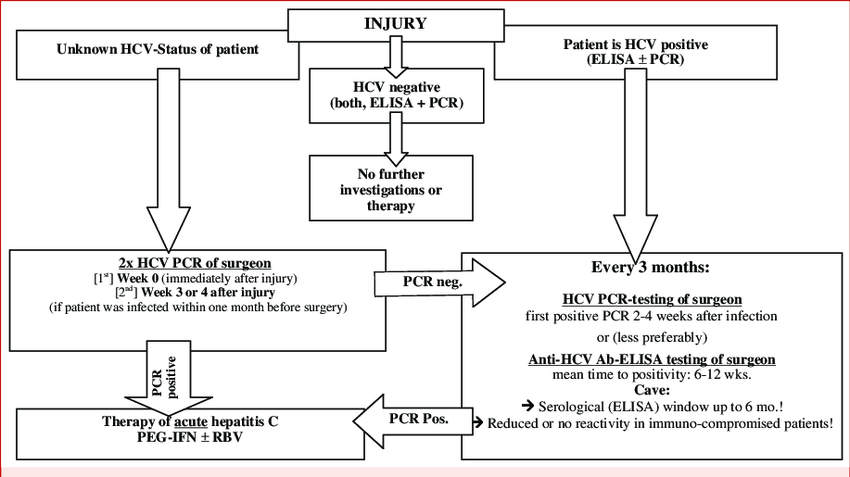
The NSW Ministry of Health recommends that following needlestick and other sharps injury in health care settings, voluntary PCR testing of source individuals should be done.
In NSW, health care workers who perform exposure prone procedures must be aware of their HCV PCR status. Those who are HCV PCR positive must not perform exposure prone procedures .
Exposure prone procedures are those with potential for a health care worker to bleed into a patient as the result of a sharps injury, e.g. surgical procedures in body cavities. The NSW Ministry of Health has a longer and more precise definition to guide health care workers .
Results From The Qualitative Test
Doctors use the qualitative HCV RNA PCR test to determine whether or not the hepatitis C virus is present in the blood.
If the virus is present, the test will be positive. If the test does not detect the virus, the result will be negative.
If the result is positive, a person will then need a quantitative HCV RNA PCR test. For this reason, many doctors now prefer to skip the first test and use the quantitative test straight away.
The quantitative test results show how much HCV is in the body. However, whether low or high, the viral load does not reflect levels of damage to the liver.
Other blood tests, ultrasounds, and, rarely, a liver biopsy will help a doctor determine overall liver health.
After using an HCV RNA PCR test to confirm the presence of HCV, doctors will work out which strain of the virus is active in the body. This helps a doctor plan the course of treatment.
The primary goal of treatment is to bring down the viral load in the body until it is entirely free of the virus. Doctors know this as a sustained virologic response .
SVR occurs when the virus is undetectable for 12 weeks or longer after treatment.
Achieving SVR is the best outcome of treatment, as it often means the person is free from hepatitis C, or that treatment has cured hepatitis C.
Doctors will also combine treatments with other tests that monitor for complications of HCV, including cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Get Hepatitis
Hepatitis C Viral Load / Hcv Rna Quantitative Testing
Hepatitis C
The viral load of hepatitis C refers to the amount of virus present in the bloodstream. The quantitative HCV RNA tests measure the amount of hepatitis C virus in the blood. The result will be an exact number, such as “1,215,422 IU/L.” Many people refer to the quantitative measurement as the hepatitis C “viral load.”
Viral load tests are used to confirm active hepatitis C infection and are used during treatment to help determine response. If you have lower levels of virus in your blood when you start treatment, you may have a better chance of getting rid of the virus.
What Is Pcr Testing
RNA testing refers to an advanced technology that is used to detect ribonucleic acid from the hep C virus .
Several types of RNA technologies exist with the most commonly-used version being the Polymerase Chain Reaction test. Less commonly used versions include the transcription mediated amplification test which is used as a screening test by Australian blood banks, and the branched chain DNA test which is generally used as a research tool.
Unlike the HCV antibody test that looks for signs that the body has at some time mounted an immune response to HCV, the PCR test looks for current presence of the virus.
With hep C, there are 3 types of PCR tests:
- PCR viral detection test: it looks for the virus
- PCR viral load test: it looks for the virus and estimates how many HCV viruses per millilitre of blood
- PCR genotype test: it looks for the particular genotype of HCV.
You May Like: Where Can I Get Tested For Hepatitis
Availability Pcr Viral Detection Test In Diagnosis
Detection of hepatitis C viral RNA if at least 1 of the following criteria is satisfied:
the patient is hepatitis C seropositive
the patients serological status is uncertain after testing
the test is performed for the purpose of:
To a maximum of 1 of this item in a 12 month period.
Hepatitis C Quantitative Pcr
Hepatitis C virus is a single stranded RNA virus. Hepatitis C virus is a major cause of chronic liver disease in the United States. Approximately 4 million people in the United States are currently infected. Of those known to be infected, 2.7 million have chronic liver disease. An estimated 40,000 new infections are suspected each year. Of the six different HCV genotypes, genotype 1 is most common, followed by 2 and 3.
Once HCV infection has been established, quantitative HCV PCR can provide prognostic information. Predictors of response to antiviral therapy include viral load of less than 2,000,000 IU/mL, genotype other than 1, shorter duration of infection, female gender, and low body weight. The HCV positive patient with negative viral load should have the test repeated in 3 to 4 months, because some patients with active infection have intermittently undetectable viral loads.
Cure is defined as a sustained viral response, which means undetectable HCV RNA using a sensitive PCR assay with a lower limit of detection and lower limit of quantitation of 15 IU/mL. Up to date guidelines can be found at www.hcvguidelines.org.
Samples having no HCV target detected are reported as not detected. Samples having detectable and quantifiable HCV target are reported as the numeric value up to 200 million IU/mL. The unit of measurement for the Hepatitis C Virus RNA changed from copies/mL to IU/mL in March 2001.
Reference
Read Also: Hepatitis B And Liver Cancer
Hepatitis C Virus Quantitative Real
The Quantitative, real-time PCR test measures the IU of the HCV RNA per millimeter of plasma or serum. This test is typically only done for known HCV positive individuals. If you are unsure or if you just want to screen for this virus, you may want to order the Hepatitis C Virus Antibody test.
Test results may take 3-5 business days.
Tests After The Diagnosis
Once the doctor knows you have hep C, theyâll do tests to find out more about your condition. This will help determine your treatment. They could include:
- Genotype tests to find out which of the six kinds of hepatitis C you have.
- Liver function tests. They measure proteins and enzymes levels, which usually rise 7 to 8 weeks after youâre infected. As your liver gets damaged, enzymes leak into your bloodstream. But you can have normal enzyme levels and still have hepatitis C.
- Tests to check for liver damage. You might get:
- Elastography. Doctors use a special ultrasound machine to feel how stiff your liver is.
- Liver biopsy. The doctor inserts a needle into your liver to take a tiny piece to examine in the lab.
- Imaging tests. These use various methods to take pictures or show images of your insides. They include:
Don’t Miss: What Are The Ways You Can Get Hepatitis C
Who Should Have A Test For Hepatitis C
In the United States, the recommend that most adults over 18 years, and pregnant women undergo screening at least once.
A doctor may also recommend testing at least once for people who:
- have HIV
- have ever injected drugs or shared needles or other equipment, even if it was only once, a long time ago
- have had certain medical conditions or undergone transplants and other treatments in the past
- have had a needlestick or other injury while working in healthcare or public safety setting
- were born to a mother who had HCV
A healthcare professional may advise a person to have regular screening if they:
- currently inject drugs, and share needles and other equipment
- have specific medical conditions
People who have been in prison or have tattoos and piercings may require HCV testing, depending on the circumstances.
If a person thinks they have had exposure to someone who has HCV, they should speak to their doctor about screening.
What Your Hepatitis C Virus Quantitative Real
When your results show a high viral load, this normally indicates that the infection level is higher. However, for hepatitis C, a high viral load is not related to how you feel and how damaged your liver is. This number is the perfect indicator of how well a treatment is being successful.
If your viral load is less than 615 international units per liter then, your system does not contain any detectable hepatitis C virus. This result could even indicate that the levels are too low to be detected.
If the viral load is higher than 800,000 international units per liter means that the viral count is still high and the treatment needs to be adjusted. If the levels are below that number this indicates a successful treatment. After a period of eight to twelve weeks, if the viral load became undetectable, this marks the end of the treatment. You will no longer need to be treated for hepatitis C but, still need to be tested after a while to check for a relapse.
Recommended Reading: Foods To Avoid With Hepatitis C
How It Is Done
The health professional taking a sample of your blood will:
- Wrap an elastic band around your upper arm to stop the flow of blood. This makes the veins below the band larger so it is easier to put a needle into the vein.
- Clean the needle site with alcohol.
- Put the needle into the vein. More than one needle stick may be needed.
- Attach a tube to the needle to fill it with blood.
- Remove the band from your arm when enough blood is collected.
- Put a gauze pad or cotton ball over the needle site as the needle is removed.
- Put pressure on the site, and then put on a bandage.
Taking A Hepatitis C Test
Hepatitis C testing is conducted on a sample of blood. Blood samples can be collected by a doctor, nurse, technician, or other health care provider from an adult patients vein using a small needle or a skin prick on a childs heel.
For an at-home hepatitis C test, patients collect a blood sample according to the manufacturers directions. Instructions provided in the test kit detail the steps to obtain a small sample of blood and mail it for testing.
You May Like: Hepatitis C High Viral Load
Getting Tested For Hepatitis C
A blood test, called an HCV antibody test, is used to find out if someone has ever been infected with the hepatitis C virus. The HCV antibody test, sometimes called the anti-HCV test, looks for antibodies to the hepatitis C virus in blood. Antibodies are chemicals released into the bloodstream when someone gets infected.
Test results can take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks to come back. Rapid anti-HCV tests are available in some health clinics and the results of these tests are available in 20 to 30 minutes.
What The Qualitative Results Mean
The qualitative results indicate that HCV is present in your blood. The test result will be either detected or undetected.
Detected means that you do have the virus in your blood. Undetected means that you dont have the virus in your blood, or you have a tiny amount that cant be detected by this test.
The qualitative test results may still be positive even if your viral load has decreased drastically due to treatment.
Read Also: Can You Give Yourself Hepatitis B
What Is The Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver. There are five different types of hepatitis virus that attack the liver. Hepatitis C is the most serious type that can be transmitted through being exposed to contaminated blood. This virus is rarely transmitted through sexual contact. It is either acute or chronic but, there is no vaccine that can help protect us from it. Hepatitis C cannot be transmitted through coughing or sneezing, sharing utensils, hugging and kissing as well as holding hands.
Unlike other kinds of hepatitis, being infected with hepatitis C does not protect you from being re-infected by it. This virus undergoes a lot of changes when it replicates in our system, this will prevent our immune system to build up an appropriate immune response for future infections.
The quantitative real time PCR hepatitis C virus test measures the viral load in infected individuals. The count will come as number of international units per mL of blood. It is used measure the amount of viral RNA particles in the blood. It is also used to diagnose an active infection as well as determine the bodys response to therapy, by comparing the before and after count of the virus.
Cdc Recommendations For Hepatitis C Screening Among Adults In The United States
- Universal hepatitis C screening:
- Hepatitis C screening at least once in a lifetime for all adults aged 18 years and older, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is less than 0.1%*
- Hepatitis C screening for all pregnant women during each pregnancy, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is less than 0.1%*
- Any person who requests hepatitis C testing should receive it, regardless of disclosure of risk, because many persons may be reluctant to disclose stigmatizing risks
Read Also: Where To Get Tested For Hepatitis B
Hepatitis C Testing And Diagnosis
Doctors will start by checking your blood for:
Anti-HCV antibodies: This blood test is the first — and sometimes only — one you may get. Also called the ELISA screen, it checks for antibodies that your body releases to fight the virus. These are proteins your body makes when it finds the hep C virus in your blood. They usually show up about 12 weeks after infection. Your test will be either negative or positive for antibodies. It usually takes a few days to a week to get results, though a rapid test is available in some places.
What the results mean
Negative . This is when your blood shows no signs of HCV antibodies. Most of the time, thatâs because you never came in contact with the virus and you do not have hep C.
Sometimes, your negative result can be false, meaning you have HCV. That may happen if you:
- Took the test too soon after your exposure. This test checks for only HCV antibodies, which can take several months to appear.
- Have HIV, a donated organ, or other conditions that weaken your immune system, which can suppress your antibodies
- Get hemodialysis for kidney problems
If youâve been exposed in the last 6 months, youâll need to be retested.
Positive . This means youâve been infected with HCV. But false positives are surprisingly common. More than 1 in 5 people who test positive donât actually have hepatitis C. Possible reasons include:
What the results mean
What Is Hepatitis C Test
Hepatitis C Test is a blood test that is used for the detection of the Hepatitis C virus. There are several types of Hepatitis C test that is used by doctors for the diagnosis of Hepatitis C. The varied Hepatitis C tests are
Hepatitis C Antibody Test : Hepatitis C antibody test is used by doctors to ascertain whether or not a person has been affected by the HCV at any point of his/her life by detecting Hepatitis C antibodies in the blood.
Hepatitis C RNA Qualitative Test : Also referred to as PCR test, this test screens for current infection of the virus.
Hepatitis C RNA Quantitative Test: As the name suggests it is a quantitative test and measures the amount of Hepatitis C virus in the body. The Hepatitis C RNA Quantitative Test is also referred to as viral load test.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Is It Curable
Can I Take The Test At Home
At-home hepatitis C tests are available that allow patients to collect a blood sample at home and mail it to a laboratory for testing. Test samples are collected through pricking a finger with a sharp object, called a lancet, thats included in the test kit.
At-home HCV testing is a form of hepatitis C antibody testing and does not test for hepatitis C RNA or the strains genotype. Testing for hepatitis C at home is not a substitute for testing performed by a health care professional, and positive test results may need to be confirmed by laboratory-based testing.