Can Bleach Or Cleaner Kill Hepatitis A
Disinfectant that contains bleach can kill the hepatitis A virus on hard non-porous surfaces like toilet seats. However, freezing does not kill HAV.
If you cook food that is contaminated for one minute at cooking temperatures higher than 185ºF , it will kill HAV. However, food can be contaminated after cooking, so it is very important to wash your hands well with soap and water.
Persons With Chronic Diseases
Refer to Immunization of Persons with Chronic Diseases in Part 3 for additional general information about vaccination of people with chronic diseases.
Chronic renal disease and patients on dialysis
HA vaccine is recommended for people with chronic renal disease or undergoing dialysis if they are at increased risk of HA infection or severe HA . A study assessing the immune response of hemodialysis patients to standard doses of HA vaccine demonstrated a good HA antibody response and no serious adverse effects.
Chronic liver disease
HA immunization is recommended for susceptible persons with chronic liver disease, including those infected with hepatitis C and chronic HB carriers, because they are at risk of more severe disease if infection occurs. Vaccination should be completed early in the course of the disease, as the immune response to vaccine is suboptimal in advanced liver disease.
Non-malignant hematologic disorders
How Can I Tell If I Have The Disease
If you have hepatitis A you might get a sudden fever or headache and feel tired. You might not want to eat as much as usual, and you may feel queasy. You may vomit or have stomach pain. Some people with the disease have chills, aching muscles and joints, cough, diarrhea, constipation, or itchy skin.
Later in the disease you may have jaundice , and your feces may be pale or clay colored. Rarely, the brain can be affected. This can cause confusion, unusual eye and body movements, and even coma.
Your doctor can do a blood test to see if you have the disease. Other things your doctor may look for are a painful and large liver, spleen, or lymph nodes, and a slow heart rate.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Antibody Titer Test
Who Is At Risk
Anyone who has not been vaccinated or previously infected can get infected with the hepatitis A virus. In areas where the virus is widespread , most hepatitis A infections occur during early childhood. Risk factors include:
- poor sanitation
- living in a household with an infected person
- being a sexual partner of someone with acute hepatitis A infection
- use of recreational drugs
- travelling to areas of high endemicity without being immunized.
Concurrent Administration Of Vaccines

HA vaccine may be administered concomitantly with other vaccines or with Ig. Different injection sites and separate needles and syringes must be used for concurrent parenteral injections.
If concurrently providing HA-containing vaccine and Ig, separate anatomic injection sites should be used for each injection.
Passive immunization with human Ig preparations can interfere with the immune response to measles-mumps-rubella , measles-mumps-rubella-varicella and univalent varicella vaccines . These vaccines should be given at least 14 days prior to administration of a human Ig preparation, or delayed until the antibodies in the Ig preparation have degraded. Refer to Blood Products, Human Immunoglobulin and Timing of Immunization in Part 1 for additional information.
Refer to Timing of Vaccine Administration in Part 1 for additional information about concurrent administration of vaccines.
Read Also: What Should You Eat If You Have Hepatitis C
How Is The Virus Spread
Hepatitis A virus is usually spread from person to person by putting something in the mouth that has been contaminated with the stool of a person with hepatitis A. This type of transmission is called the “fecal-oral” route. For this reason, the virus is more easily spread in areas where there are poor sanitary conditions or where good personal hygiene is not observed.
Most infections in the United States result from contact with a household member or sex partner who has hepatitis A.Hepatitis A virus may also be spread by consuming food or drink that has been handled by an infected person. Waterborne outbreaks are infrequent and are usually associated with sewage-contaminated or inadequately treated water. Casual contact, as in the office, factory or school setting, does not spread the virus.
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis
Each type of hepatitis is treated differently.
Hepatitis A often goes away on its own and home treatment is all that is needed to help the liver recover, such as:
- Rest
- Avoiding alcohol
- Avoiding certain medicines that can be harmful to the liver
Hepatitis B often goes away on its own in about 6 months, and can also be treated at home with the above remedies. Other treatments for hepatitis B include:
- Antiviral medications
- Liver transplant in severe cases
Treatment for hepatitis C is effective on certain forms of the hepatitis C virus. The choice of medications depends on the type of hepatitis C you have, whether you have been treated for the illness before, how much liver damage has occurred, any other underlying medical issues, and other medicines you take. Treatment for hepatitis C usually involves 8 to 12 weeks of oral antiviral medications, such as:
- Elbasvir-grazoprevir
- Sofosbuvir-velpatasvir-voxilaprevir
Also Check: Is Hepatitis A Virus Or Bacteria
How Many People Have Hepatitis A
Since the release of the first vaccine in 1995, the rate of new HAV infections in the United States declined by more than 95% from 1996 to 2011. From 2012 through 2016, the number of hepatitis A cases fluctuated because large foodborne outbreaks occurred. From August 2016 through August 2020, 33 states reported hepatitis A outbreaks spread through person-to-person contact resulting in over 33,000 infections with high numbers of hospitalizations and deaths.
Globally, HAV infection is most common in countries with poor sanitary conditions and hygienic practices and transitional economies according to the World Health Organization .
Contaminated Food And Water
Hepatitis A is most commonly passed on by eating food prepared by someone with the virus whose hands have not been washed properly. You can also get it by drinking dirty water and by eating raw or undercooked shellfish from dirty water.
You can protect yourself by:
- Washing your hands each time you go to the toilet, before you prepare or eat food, after coughing or sneezing, or handling rubbish or other dirty items.
- Peeling and washing all your fresh fruit and vegetables avoiding raw or undercooked meat and fish avoiding all drinks if youre not sure if theyre safe with or without ice.
- If tap water isnt safe and bottled water isn’t available, boil tap water before drinking it.
- People living in places with poor sanitation and hygiene are at a greater risk of hepatitis A infection. You may also be exposed to hepatitis A through your work, for example, sewage workers, staff in institutions where levels of personal hygiene may be poor , people working with animals that may be infected with hepatitis A and daycare centres.
You May Like: Is There A Cure For Hepatitis C Now
Hepatitis A Vaccine And Travel
If youâre going to a country where hepatitis A is common and youâve never had the virus or the vaccine, start the vaccination process as soon as you can. It takes 2 to 4 weeks after the first dose for the vaccine to work, but even one shot a few days before you leave will give you some protection.
People who are allergic to something in the vaccine and children younger than 6 months might instead get a shot of immune globulin , which will protect against hepatitis A for up to 2 months.
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- Do I need treatment?
- What treatment is best for me?
- Will I need be hospitalized?
- Are there any medicines I should avoid taking?
- Are there foods I should avoid eating?
- Can I drink alcohol?
- How can I protect my family from getting hepatitis A?
- If Ive had hepatitis A, am I at higher risk of getting other types of hepatitis?
- Will I have permanent liver damage?
- How soon before I travel should I be vaccinated?
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatic Steatosis Mean
What Is Hepatitis E
Hepatitis E, also called enteric hepatitis , is similar to hepatitis A, and more prevalent in Asia and Africa. It is also transmitted through the fecal-oral route. It is generally not fatal, though it is more serious in women during pregnancy and can cause fetal complications. Most patients with hepatitis E recover completely.
How Do People Get Sick
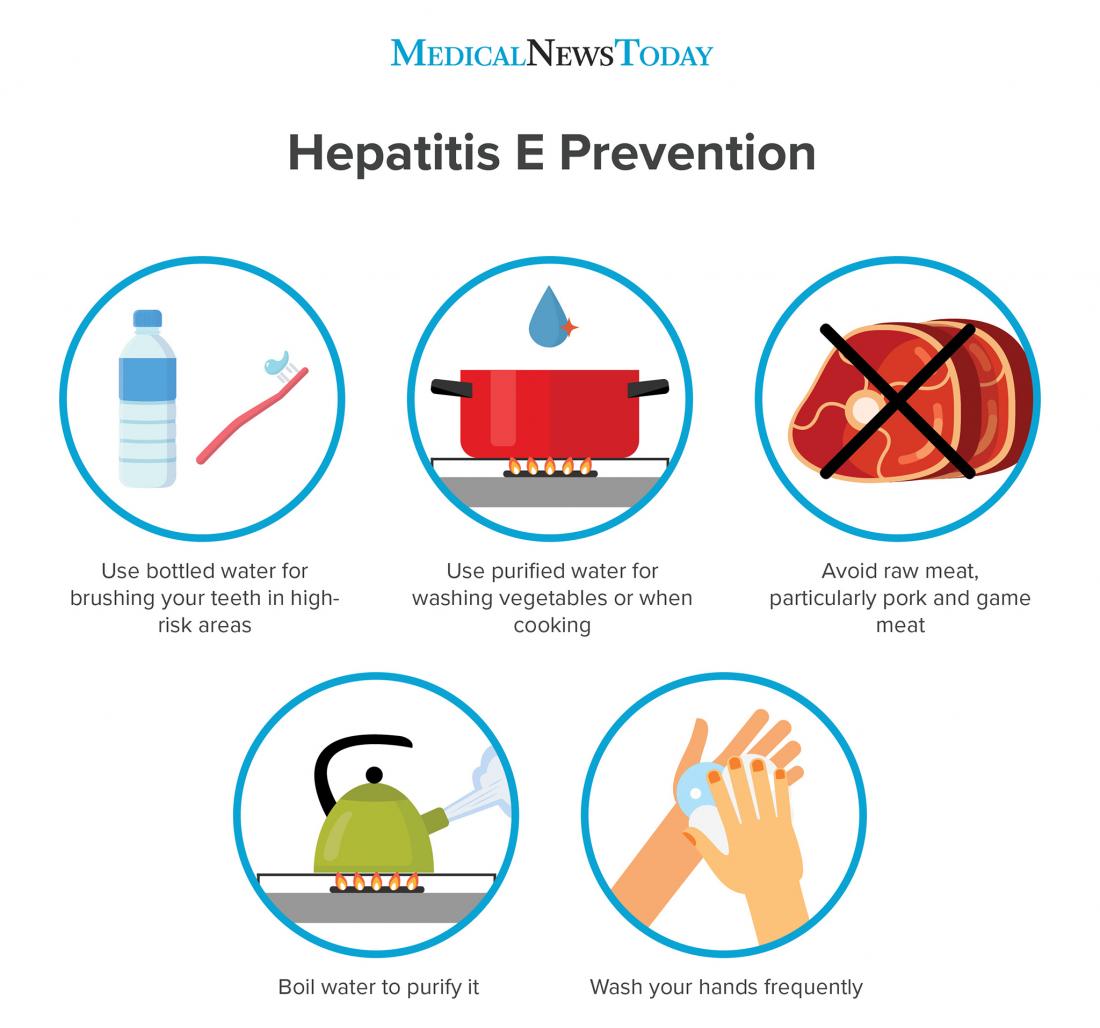
Hepatitis viruses are spread from person to person through contact with infected feces , either directly or indirectly . People can carry the virus without showing symptoms, then spread it to other people, foods or surfaces.
People can get Hepatitis A after eating contaminated food and beverages. Food and drinks can become contaminated through:
- a contaminated food handler
- hands that were not washed properly after using the washroom
- contamination during harvest, manufacturing and processing
Common food sources of Hepatitis A include:
- contaminated water
Recommended Reading: How You Contract Hepatitis B
Common And Local Adverse Events
HA vaccine
HA vaccine is well tolerated. Reactions are generally mild and transient, and are usually limited to soreness and redness at the injection site. Other less frequent reactions include headache, irritability, malaise, fever, fatigue and gastrointestinal symptoms. Injection site reactions occur less frequently in children than in adults as do mild, systemic events . No significant difference in reactions is evident between initial and subsequent doses of vaccine or in the presence of pre-existing immunity.
HAHB vaccine
Refer to Hepatitis B Vaccine in Part 4 for information about HAHB vaccine.
Ig
Injection site reactions following receipt of standard human Ig include tenderness, erythema and stiffness of local muscles, which may persist for several hours. Mild fever or malaise may occasionally occur.
Why Isn’t Hepatitis A Vaccine Required For Food Service Workers
While food service employers can offer hepatitis A vaccine to their employees if they wish, most public health authorities prefer not to make it mandatory for the following reasons:
- There is no evidence that food service workers are at any greater risk of acquiring hepatitis A than are people in other occupations.
- Only 2-3 percent of all hepatitis A cases are acquired through restaurant food.
- Employee turnover in some segments of the food service industry is high, making it impractical to vaccinate staff.
- Emphasis on careful hand washing, use of disposable gloves and not working when ill are measures that can greatly minimize the risk of spreading hepatitis A and a number of other infections.
- Hepatitis A vaccine would be strongly recommended for food service workers in a county or region where a community-wide outbreak has been recognized.
Don’t Miss: How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis C
Treatments For Hepatitis A
There’s currently no cure for hepatitis A. But it usually gets better on its own within a couple of months. You can usually look after yourself at home.
While you’re ill, it’s a good idea to:
- get plenty of rest
- take painkillers, such as paracetamol or ibuprofen, for any aches and pains ask your GP for advice about this, as you may need to take lower doses than normal or avoid certain medications until you have recovered
- maintain a cool, well-ventilated environment, wear loose clothing and avoid hot baths or showers to reduce any itching
- eat small, light meals to help reduce nausea and vomiting
- avoid alcohol to reduce the strain on your liver
- stay off work or school and avoid having sex until at least a week after your jaundice or other symptoms started
- practise good hygiene, such as washing your hands with soap and water regularly
Speak to your GP if your symptoms are particularly troublesome or have not started to improve within a couple of months.
They can prescribe medications to help with itchiness, nausea or vomiting, if necessary.
For most people, hepatitis A gets better within 2 months and there are no long-term effects.
Once it passes, you normally develop life-long immunity against the virus.
In around 1 in every 7 people with the infection, the symptoms may come and go for up to 6 months before eventually disappearing.
Life-threatening complications such as liver failure are rare, affecting less than 1 in every 250 people with hepatitis A.
What You Need To Know
Hepatitis A is a liver disease caused by the hepatitis A virus. Hepatitis A virus is transmitted through the fecal-oral route. If a person with hepatitis A does not wash their hands well after going to the bathroom they can contaminate objects, food, or drinks. Someone else can be infected when they put these items into their mouth.
Vaccination is a safe and effective way to prevent hepatitis A.
In addition to vaccination, consistent, thorough hand washing after going to the bathroom and before preparing or eating food is the most effective way to prevent getting hepatitis A.
Also Check: Where To Get Tested For Hepatitis
How Is Hepatitis A Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will listen to your symptoms and will take a blood test to confirm the diagnosis of hepatitis A. If the test finds immunoglobulin M antibodies, you have an acute hepatitis A. If there are antibodies, but not IgM antibodies, you are immune to the virus either because you had a case of it and recovered, or you got the hepatitis A vaccine.
What Is The Prognosis/outlook For Patients Who Have Hepatitis A
Most cases of hepatitis A are short-lived, but the disease doesnt always look the same for everyone. Some people have short illnesses that only last a few weeks and have mild symptoms. Others can be very ill for several months. Hepatitis A is rarely fatal, but death has happened due to liver failure brought on by HAV. This tends to happen more often in people who are over 50 years old or and in people who have another liver condition.
Don’t Miss: How To Know You Have Hepatitis
How Is Hepatitis A Transmitted
HAV is highly contagious. It is spread primarily when a person ingests the virus from food, drinks, or objects that have been contaminated by small amounts of stool from an infected person sex with an infected person, particularly if it involves anal-oral contact and through injection drug use. In crowded, unsanitary conditions, HAV can be spread quickly and cause outbreaks by exposure to contaminated water or food .
Transmission Of Hav Within The United States
In the United States, transmission of HAV is typically person-to-person through the fecaloral route and occurs among high-risk groups and populations likely to develop severe disease, including travelers to endemic countries, MSM, persons who use illicit drugs, and persons with chronic liver disease. Foodborne, waterborne, and blood transfusion and organ transplantationassociated outbreaks are rare but continue to occur .
Among cases of HAV infection with risk factor data reported in the United States, 46% are attributable to international travel to endemic countries . The risk of developing hepatitis A infection among susceptible travelers ranges from 3 to 20 per 1000 travelers . The proportion of cases attributable to international travel includes cases who did not travel but reported exposure to a traveler . Vaccination has been recommended for international travelers since 1996, but awareness and uptake of the vaccine prior to travel has been lacking, with up to 65% of U.S. international travelers reportedly unaware that vaccination prior to travel was available or recommended, and vaccine coverage among travelers 16% in 2015 .
Don’t Miss: What Is The Medicine For Hepatitis B
Hepatitis C: How Does It Spread
It spreads through infected blood. In the U.S., sharing needles or other items used to inject drugs is the most common cause of infection. Getting a tattoo or body piercing with an infected needle is another means of exposure. A mother may pass the virus to their child at birth. In rare cases, unprotected sex spreads hepatitis C, but the risk appears small. Having multiple sex partners, HIV, or rough sex seems to raise risk for spreading hepatitis C.
More About Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A virus infection can cause a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a severe illness lasting several months. People with liver disease, including chronic hepatitis B or C infection, are at greater risk of developing severe disease as a result of hepatitis A infection. People over 50 years old are also at greater risk of developing severe disease. Unlike hepatitis B and C, hepatitis A does not cause a chronic infection.
Read Also: How Do You Contact Hepatitis C
Hepatitis A Vaccine And International Travel
Who should get the hepatitis A vaccine before traveling internationally?
All unvaccinated people, along with those who have never had hepatitis A, should be vaccinated before traveling to countries where hepatitis A is common. Travelers to urban areas, resorts, and luxury hotels in countries where hepatitis A is common are still at risk. International travelers have been infected, even though they regularly washed their hands and were careful about what they drank and ate. Those who are too young or cant get vaccinated because of a previous, life-threatening reaction to the hepatitis A vaccine or vaccine component should receive immune globulin. Travelers to other countries where hepatitis A does not commonly occur are not recommended to receive hepatitis A vaccine before travel.
How soon before travel should I get the hepatitis A vaccine?
You should get the first dose of hepatitis A vaccine as soon as you plan international travel to a country where hepatitis A is common. The vaccine will provide some protection even if you get vaccinated closer to departure. For older adults , people who are immunocompromised, and people with chronic liver disease or other chronic medical conditions the health-care provider may consider, based on several factors, giving an injection of immune globulin at the same time in different limbs.
What should I do if I am traveling internationally but cannot receive hepatitis A vaccine?
Who Should Receive Immune Globulin To Prevent Hepatitis A
For individuals who should not get the vaccine, or if vaccine is not available, a “shot” called an immune globulin can be given. Immune globulin is a sterile preparation of antibodies that can lower the risk of infection for about 3 to 5 months. Also, people with a weakened immune system or chronic liver disease should be given one dose of immune globulin.
Household members, day-care contacts or others in close personal contact with an infected person should call a doctor or their local health department to obtain information about receiving preventive treatment to reduce the risk of becoming ill. In normal working and classroom situations , contacts do not need to receive immune globulin or vaccine.
Don’t Miss: How Much Does It Cost To Treat Hepatitis C