Patient Population And Clinical End Points
Individual patient data were retrieved for the meta-analysis by the Meta-Analysis Group In Cancer in 1996. All seven clinical trials were included in the economic analysis. Five of these trials directly compared hepatic arterial infusion with intravenous chemotherapy , and two compared hepatic arterial infusion with symptom palliation or ad libitum intravenous chemotherapy . The total number of patients included in these trials was 654. We will hereafter refer to the group of patients assigned to receive hepatic arterial infusion as the HAI group and to the group of patients who received either symptom palliation or intravenous chemotherapy as the control group.
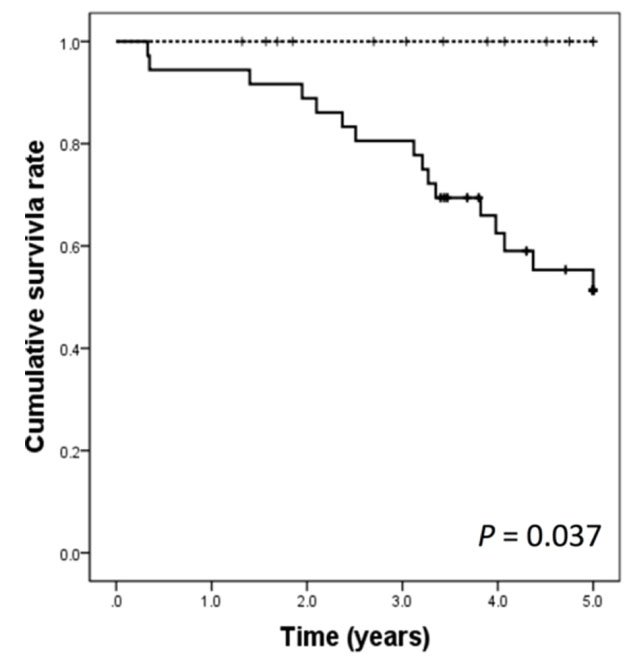
Fig. 1.
Overall survival curves among patients treated with hepatic arterial infusion compared with control patients. Survival time was discounted at a 5% yearly rate. P value is two-sided.
The Role Of Hepatic Artery Infusion
When colorectal cancer spreads, it frequently results in metastatic tumors in the liver. When possible, the liver tumors are surgically removed, and chemotherapy destroys the remaining cancer cells. Sometimes the tumors cant be removed because of their location or size, or the available treatments simply cant slow the disease. At this point, some people are told by their doctors that chemotherapy is their only option. Or worse, that nothing more can be done.
However, there is another option. It just hasnt been widely available because it requires specialized training in surgical and medical oncology.
Hepatic arterial infusion delivers chemotherapy through a pump thats implanted in the abdominal wall. We then use a catheter to deliver high doses of chemotherapy through the hepatic artery, which directly feeds metastatic tumors in the liver, said Peter Allen, MD, a Duke surgical oncologist. Even though the HAI pump delivers chemotherapy directly to the liver at concentrations that are hundreds of times higher than whole-body chemotherapy, it does not increase the side effects beyond those associated with whole-body chemotherapy.
If the liver tumors can be removed doctors use the term resected the pump may be implanted at the time of surgery and used to delay or prevent recurrence of cancer. If the liver tumors cannot be removed, the pump may be inserted to help control the tumor or, even better, shrink its size so it can be surgically removed in the future.
Comparison Of Outcome Of Haic And Sorafenib In Patients With Hcc Advanced Stage
Recently, a few centers reported the outcomes of an interesting, randomized phase II trial comparing sorafenib alone with sorafenib plus HAIC with cisplatin in advanced HCC. The median survivals in the Sor and SorCDDP arms were 8.7 and 10.6 months. The HR stratified by the allocation factors, including the presence/absence of portal vein tumor thrombosis and extrahepatic metastases , was 0.60 . The crude HR was 0.68 . In brief, the administration of sorafenib before HAIC could lead to better clinical outcomes considering the sensitized and synergistic effect with cisplatin and the antiangiogenic activity of sorafenib. In a Korean study by Song and colleagues , on advanced-stage HCC and PVTT, 50 patients were treated with HAIC and 60 patients were treated with sorafenib. The median OS was significantly longer in the HAIC group than in the sorafenib group . The median time to progression was also significantly longer in the HAIC group than in the sorafenib group . So, HAIC shows more favorable responses compared to sorafenib .
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Vaccine Side Effects
What Gets Stored In A Cookie
This site stores nothing other than an automatically generated session ID in the cookie no other information is captured.
In general, only the information that you provide, or the choices you make while visiting a web site, can be stored in a cookie. For example, the site cannot determine your email name unless you choose to type it. Allowing a website to create a cookie does not give that or any other site access to the rest of your computer, and only the site that created the cookie can read it.
Hai Provides A Significant Survival Advantage
HAI involves surgically implanting a pump about the size of a hockey puck under the skin between the ribs and pelvis. This occurs during the same surgery as the tumor resection. The pump delivers chemotherapy to the liver through the hepatic artery, which supplies most of the blood to colorectal liver metastases. The agents deployed have a high first-pass extraction in the liver, allowing the use of high doses with limited systemic impact.
From 1992 to 2012, we evaluated 2,368 people who had complete tumor resection and compared survival rates for the group that received perioperative HAI with the group that did not. All of them also received standard systemic chemotherapy.
For the HAI group , median overall survival was 67 months compared with 44 months for the non-HAI group . Five-year overall survival was 53 percent for the HAI group compared with 38 percent for the group that did not receive a pump , and ten-year survival rates were 38 percent and 23 percent , respectively.
We also examined data for the most recent cohort of 1,442 people to see if our findings would hold, given that during the 21-year period, more-modern systemic chemotherapy agents became available. The results were similar: The median overall survival was 67 months with HAI and 47 months without .
Additionally, we identified who was most likely to benefit from HAI those with node-negative colorectal cancer and a low clinical risk score .
Read Also: Hepatitis C Reactive Test Results
Hepatic Arterial Infusion In The Metastatic Setting
Early studies using HAI FUDR without systemic chemotherapy demonstrated increased objective response rates compared to systemic chemotherapy with intravenous FUDR or 5-FU alone , but did not show an increase in overall survival . Using HAI 5-FU alone , response rates are somewhat lower and survival is 19.2 months . In a randomized study comparing HAI plus systemic bolus 5-FU/leucovorin or HAI alone , there was an increase in survival in the combined group , but no significant increase in response rate . More recently, newer systemic agents such as irinotecan and oxaliplatin have been evaluated with HAI. A study using HAI FUDR plus systemic irinotecan in previously treated patients produced a response rate of 74% and a median survival of 21 months . Another study using HAI with systemic oxaliplatin combined with irinotecan or 5-FU/LV demonstrated further improvement. Of those who received HAI FUDR plus oxaliplatin and CPT, 19 out of 21 had a partial response and median survival was 35.8 months . In a Chinese study in which half of the patients had extrahepatic disease, HAI FUDR plus systemic mFOLFOX6 produced a response rate of 68.6% and a median survival of 25 months .
Fig. 1
For additional information:
Promising Results In Metastatic Liver Cancer
The early results are promising. So far, the Duke team has been successful in converting tumors from ones that couldnt be surgically removed to tumors that could be removed, theyve given more time to people who were told they only had less than a year to live, and they have been able to prevent or delay the recurrence of liver cancer.
Don’t Miss: The Cost Of Hepatitis C Treatment
A Case Report Of Long
Kobe Van BaelBart Neyns
1Department of Surgery, Laarbeeklaan 101, 1090 Brussels, Belgium
2Department of Medical Oncology, Laarbeeklaan 101, 1090 Brussels, Belgium
3Department of Radiotherapy, Laarbeeklaan 101, 1090 Brussels, Belgium
Abstract
1. Introduction
The 5-year survival rate of patients with advanced colorectal cancer that has metastasized to the liver is determined by the possibility of resection of the primary tumor and liver metastases . Up to 50% of patients with CRC develop LM synchronously or metachronously during the course of their disease. In a majority of stage IV CRC patients, the LM determines the life expectancy .
Contemporary neoadjuvant systemic chemotherapy allows for resection of initially unresectable CRC-LM in about 522% of patients. Despite a high rate of recurrence, 5- and 10-year overall survival are, respectively, 33% and 23% with a wide use of repeat hepatectomies and extrahepatic resections . This strategy has become incorporated in the treatment of CRC with LM, although randomized studies that demonstrate the superiority of this approach are lacking.
We here report on a case where HAI of 5-FU-based chemotherapy could downstage the initially unresectable CRC-LM and rendered the patient amenable for hepatectomy achieving an overall survival of more than 5 years.
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
Conflict of Interests
No author has any commercial association that might create a conflict of interests in connection with this paper.
References
Hepatic Arterial Infusion With Systemic Chemotherapy
When combined with systemic chemotherapy, hepatic arterial infusion leads to higher response rates compared to systemic chemotherapy alone. There are several major benefits to including HAIP chemotherapy in late-stage cancer treatment plans:
- Higher resection rates of previously unresectable tumors
- Lower recurrence rates
Recommended Reading: Difference Between Hepatitis A And B
Economic Implications Of Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy In Treatment Of Nonresectable Colorectal Liver Metastases
Correspondence to:
Supported in part by the Association pour la Recherche contre le Cancer .
Collaborators of the Hepatic Arterial Infusion Meta-Analysis Project: P. Rougier, A. Laplanche, M. Huguier, and J. M. Hay R. Carlson, W. Brown, D. Hohn, and A. E. Venook T. G. Allen-Mersh and S. Earlam N. E. Kemeny and M. Mazumdar M. J. O’Connell, S. Wieand, and K. Martin A. E. Chang and V. K. Sondak M. M. Kemeny P. Piedbois, I. Durand-Zaleski, J.-P. Le Bourgeois, and Y. Piedbois , E. Levy and B. Roche M. Buyse .
Board of the Meta-Analysis Group In Cancer: N. Wolmark P. Piedbois M. Buyse R. Carlson Y. Rustum C. E. Erlichman .
We are indebted to Dr. P.-P. Sagnier and Dr. B. Hillner for their helpful comments on the manuscript. We also thank Mr. B. Sullivan for his help in retrieving cost data.
JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer Institute
Chemotherapy With Hepatic Arterial Infusion
A new chemotherapy technique called HAI, in combination with traditional chemotherapy, has been shown to dramatically increase survival for patients with liver cancer, including those with recurrent disease. HAI involves delivering a high dose of chemotherapy drugs directly to the liver through a tiny pump implanted under the skin in the lower abdomen. Additional chemotherapy medicine is injected into the pump, as needed, on an outpatient basis. HAI therapy may be used to shrink tumors before surgery, or after surgery to prevent recurrence.
Read Also: Royal Canin Hepatic Wet Food
What Are The Benefits Of Tace
In one large study involving several institutions in Italy, chemoembolization did not seem to impact overall survival. Patients who did not undergo TACE lived as long as patients who received TACE, even though the tumors were more likely to shrink in size in patients who were treated. Does this mean that TACE or intra-arterial chemotherapy does not work? Maybe, maybe not.
Studies in Japan, however, have shown that TACE can downstage HCC. In other words, the tumors shrank enough to lower the stage of the cancer. From the practical point of view, shrinking the tumor creates the option for surgery in some of these patients. Otherwise, these patients had tumors that were not operable because of the initial large size of their tumors. More importantly, these same studies showed an improvement in survival in patients whose tumors became considerably smaller. In the U.S., trials are underway to see whether doing TACE before liver transplantation increases patient survival as compared to liver transplantation without TACE.
Also Check: How Long Is Hepatitis C Treatment
Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy
A microcatheter was selectively placed into the tumor blood supply artery. If necessary, the gastroduodenal artery was occluded. The microcatheter was then connected to the artery infusion pump to administer the following treatment : 85 mg/m2 OXA intra-arterial infusion on day 1, 400 mg/m2 LV intra-arterial infusion on day 1, and 400mg/m2 5-FU bolus infusion on day 1, and 2400 mg/m2 5-FU continuously infused over 46 h . Patients received six to eight courses of treatment, and the therapy was discontinued if it was not well-tolerated for another course of HAIC.
Also Check: Hepatitis B And Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
Duke Surgeons Expertise With Hai Pumps
Drs. Lidsky and Allen and their Duke colleagues have implanted more than 60 pumps in people with liver metastases from colorectal cancer since they started offering the procedure in conjunction with whole-body chemotherapy in late 2018. In many cases, they also work alongside Duke surgical oncologist Sabino Zani, MD, who uses minimally invasive techniques, including robotic surgical approaches to implant the pump. The minimally invasive approach, which requires smaller incisions than traditional surgery, allows people to spend less time in the hospital, and recover faster.
Role Of Hai Chemotherapy In Current Guidelines
Current National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines for metastatic CRC recommend that if metastatic disease is limited to the liver and is amenable to resection, surgery should be pursued as first line therapy. Adjuvant HAI with systemic therapy can follow, or adjuvant systemic chemotherapy alone. For patients with initially unresectable, liver-dominant disease, HAI with systemic chemotherapy can be pursued or systemic therapy alone. There is increasing popularity to consider earlier initiation of HAI in patients with initially unresectable disease who are chemotherapy-naive to increase resection rates . There is currently no role for HAI therapy in the neoadjuvant setting for patients with resectable disease. European Society for Medical Oncology guidelines do not currently recommend HAI .
Read Also: Where Can I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine For Free
Rationale For Hepatic Artery Infusion Chemotherapy
There are approximately 150,000 new cases of colorectal carcinoma diagnosed annually in the United States . Approximately 25% of patients present with metastatic disease at the time of diagnosis and over 50% will develop metastasis to the liver at some point in their lifetime . Five-year overall survival in metastatic colorectal cancer confined to the liver is approximately 20%, although complete resection can increase 5-year survival to over 50% in selected series .
Liver resection provides the only chance for cure in patients with colorectal liver metastases , however, only 1520% of patients with CRC metastases confined to the liver are deemed resection candidates at presentation. Most patients with CRC die from metastatic disease, and two-thirds of CRC deaths are due to liver metastases .
HAI therapy has evolved in the last three decades with improved surgical techniques and discovery of new systemic agents. It is now an acceptable first line option in the United States for unresectable CRLM and a treatment option in the adjuvant setting however, it remains infrequently used. Reasons for this include lack of widespread expertise with HAI therapy, requirement of a multidisciplinary team to manage therapy, and more widespread use of systemic chemotherapy in first-line settings .
Delivering Therapy Directly To The Liver Delays Overall Survival And Time
We were unable to process your request. Please try again later. If you continue to have this issue please contact .
Hepatic arterial infusion significantly increases survival in patients with colorectal cancer that has metastasized to the liver compared with systemic chemotherapy, according to the results of a study by the Cancer and Leukemia Group B .
|
Nancy E. Kemeny |
Patients who received fluoropyrimidines through HAI had increased overall survival, response rates and time to hepatic progression compared with those who received fluoropyrimidines systemically, said lead researcher Nancy E. Kemeny, MD, attending physician in the department of medicine at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
It was a similar chemotherapy agent with a different means of delivery, Kemeny said. Giving a similar drug but changing the method of delivery increases survival and quality of life.
In HAI, chemotherapy is delivered directly to the liver through a pump inserted in the abdomen. The blood supply for hepatic metastases is primarily from the hepatic artery, rather than the portal vein, which supplies a healthy liver.
Direct vs. indirect
They included 135 colorectal cancer patients with unresectable liver metastases whom they randomized to receive fluorouracil and leucovorin systemically, or floxuridine plus leucovorin and dexamethasone through HAI.
Ongoing validation
Also Check: Is There A Vaccine For Hepatitis B
Is Nuclear Medicine Helpful In Placement Of Arterial Perfusion Catheters
The use of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy can serve as an adjuvant treatment following surgery or may be used for patients with unresectable disease. Occasional unrecognized systemic shunting, catheter dislodgment, and unintended perfusion of an area not suitable for highly toxic chemotherapeutic drugs hamper placement of hepatic arterial perfusion catheters. Arterial catheter injection of 99mTc-macroaggregated albumin results in temporary microembolization and provides an imaging map of the true area of perfusion of the catheter. After a baseline scan, if there has been a significant change in perfusion, further therapy with chemotherapy would entail significant risk for gastrointestinal toxicity.
In , 2016
Our Experts Are Leaders In Hepatic Arterial Infusion Pump Therapy
Washington University specialists at Siteman have made incredible strides in research and implementing hepatic arterial infusion pump chemotherapy into certain advanced cancer treatment plans. Our multidisciplinary team consists of exceptional surgical, medical and radiation oncologists who work together to deliver HAI care.
What is hepatic arterial infusion?
Hepatic arterial infusion is a type of cancer treatment in which surgeons implant a special pump to deliver specialized chemotherapy drugs directly to metastatic tumors in the liver. Via the pump, a catheter is connected to the hepatic artery, which supplies blood to tumors within the liver. Because the chemotherapy is delivered directly to the liver, high doses that are effective against tumors can be used without causing damage to the rest of the body. This reduces side effects and makes HAIP chemotherapy very effective in treating advanced tumors in the liver.
The HAI pump, which is about the size and shape of a hockey puck, will likely need to be refilled every 2 to 4 weeks. The pump releases chemotherapy at a set rate and delivers a constant dose of chemotherapy to the liver, which also increases the effectiveness of the treatment.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis C Virus Infection