Is Hepatitis Testing Recommended For People With Hiv
Yes. Everyone living with HIV should be tested for HBV and HCV when they are first diagnosed with HIV and begin treatment. People living with HIV who have ongoing risk factors for getting hepatitis B or hepatitis C should be tested annually.
In addition, new HCV screening recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention call for:
- One-time screening for all adults 18 years and older
- Screening of all pregnant women during every pregnancy
- Testing for all persons with risk factors, with testing continued periodic testing those with ongoing risk.
Question 7 What Proportion Of Hcv Antibody
Among specimens with reactive HCV antibody results, approximately 52% have detectable HCV RNA at a level of > 15 IU/mL on reflex testing. However, the frequency varies markedly based on the strength of the signal of the antibody test, or signal-to-cutoff ratio. Specimens with an S/C ratio of at least 1.0 are considered reactive for HCV antibody7 and thus undergo reflex testing for HCV RNA. Analysis of approximately 200,000 specimens submitted to Quest Diagnostics for HCV antibody testing with reflex to HCV RNA testing demonstrate that the frequency of positive reflex results increases with increasing S/C ratio:
Clinical Features And Natural History
Persons with acute HCV infection are typically either asymptomatic or have a mild clinical illness like that of other types of viral hepatitis . Jaundice might occur in 20%30% of persons, and nonspecific symptoms might be present in 10%20% of persons. Fulminant hepatic failure following acute hepatitis C is rare. The average time from exposure to symptom onset is 212 weeks . HCV antibodies can be detected 410 weeks after infection and are present in approximately 97% of persons by 6 months after exposure. HCV RNA can be detected as early as 12 weeks after exposure. The presence of HCV RNA indicates current infection .
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis A
Hcv Core Antigen Testing
The hepatitis C core antigen is a viral protein. Since the core antigen is part of hepatitis C virus, it can usually be found in the bloodstream two weeks after infection.
Since HCV core antigen testing is simpler and less expensive than viral-load testing, some experts suggest using it in resource-limited settings. Core antigen testing can be usedoften with HCV antibody testingto detect acute HCV or to confirm chronic HCV infection. HCV core antigen testing can also be used to measure treatment outcome. Although it does not detect low levels of HCV , usually the hepatitis C viral load is much higher in people who relapse after HCV treatment.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Catch Hepatitis C
Rna Or Viral Load Test
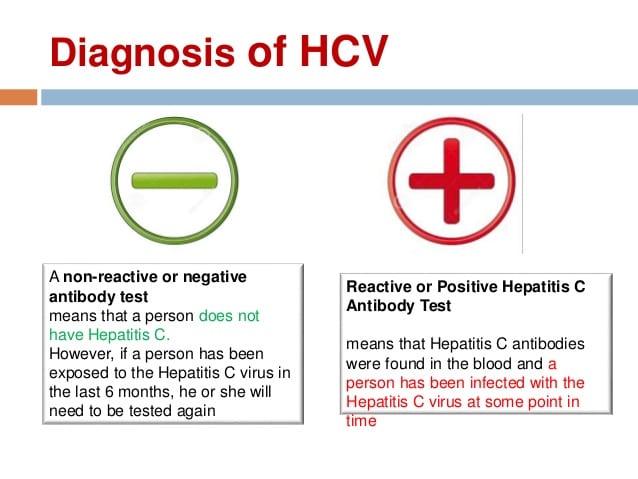
If you test positively for hepatitis C antibodies, you will need to get an RNA or viral load test. The RNA test is a blood test that checks to see if hepatitis C is active in your body.
- Negative
- If your RNA test result is negative, you do not have hepatitis C.
Supported by an independent educational grant from Merck & Co., Inc.
Recommended Reading: What Are The First Symptoms Of Hepatitis C In Adults
Hepatitis C: Diagnosis And Treatment
THAD WILKINS, MD JENNIFER K. MALCOLM, DO DIMPLE RAINA, MD and ROBERT R. SCHADE, MD, Medical College of Georgia, Augusta, Georgia.
Am Fam Physician. 2010 Jun 1 81:1351-1357.
An estimated 170 million persons, or 3 percent of the worlds population, are chronically infected with the hepatitis C virus .1 In the United States, the prevalence of hepatitis C antibody is 2 percent in adults 20 years and older, but the prevalence is higher in groups at increased risk .2,3 HCV, a single-stranded RNA virus, is transmitted through percutaneous exposure to infected blood.4 HCV is categorized into nine genetically distinct genotypes.5 In the United States, 72 percent of patients with HCV infection have genotype 1 16 to 19 percent have genotype 2 8 to 10 percent have genotype 3 and 1 to 2 percent have other genotypes.6 This article focuses on chronic HCV infection in adults and excludes special groups, such as children, pregnant women, transplant recipients, and persons coinfected with hepatitis B virus or human immunodeficiency virus .
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Persons who are not at increased risk should not be screened for HCV infection.
HCV = hepatitis C virus.
*Recommendation for treatment is C because the outcome is a surrogate marker rather than mortality.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Persons who are not at increased risk should not be screened for HCV infection.
HCV = hepatitis C virus.
False Reactive Test Results
What if I have a false reactive test result?
Every donation given to Canadian Blood Services is tested for infectious diseases caused by the hepatitis viruses B and C, HIV, syphilis and another uncommon virus called HTLV .
A false reactive test result means your initial screening test was reactivein other words, suggested the presence of something that would prevent you from donating bloodand a more precise follow-up test was negative. Almost all false reactive results occur because of interference with a test and are not necessarily due to testing positive for an infection.
FAQS
How does Canadian Blood Services test blood?
We follow a two-stage testing method that is used in laboratories worldwide. In the first stage, a sensitive screening test looks for the possible presence of infection. If the screening test shows no reaction, the blood is considered free of infection and no further testing is done. However, if the screening test is reactive, further testing is done to sort out whether the reactive result was due to an infection in the blood or interference with the test. The second test identifies markers in the blood that are found only when infection is present.
Do I need to go to my doctor for repeat testing?
Yes. Repeat testing should be discussed with your doctor because he/she is in the best position to offer you personal medical advice.
Do my partner, children, or friends need to worry if I’ve had a false reactive result?
Recommended Reading: What Virus Causes Hepatitis A
Home Screening Tests For Hepatitis C
At-home screening tests provide privacy if you prefer not to go to a doctor or clinic for testing. These tests typically look for antibodies to hepatitis C, but they may not always test for active viral infection. Make sure you know what type of test youll be taking before you buy.
Many at-home tests have close to or the same reliability as blood tests received by a medical professional.
If youve recently been exposed to hepatitis C, wait several weeks before testing at home.
Question 6 Why Didnt The Test Reflex To Hcv Genotype When My Patient Had A Detectable Viral Load
The LiPA usually requires a minimum viral load of 300 IU/mL to successfully obtain a genotype. Since the viral load assay used in this reflex test has a much lower limit of quantitation, it is possible for the patient to have a detectable viral load and not have a reportable genotype result. Therefore, this test code does not reflex to HCV genotype if the patients viral load is < 300 IU/mL.
You May Like: How Do You Prevent Hepatitis C
Also Check: How Do You Contact Hepatitis B
How Does Hepatitis C Progress
When someone is first infected with hepatitis C, most likely they have no symptoms and are unaware. Occasionally people experience fatigue, loss of appetite, weakness or sometimes having a yellow color in their skin or eyes. Although having any symptoms at all is rare, if they do occur, they usually go away within a few weeks.
Around 15-25% of people who are infected will spontaneously fight off the virus on their own and they will not have a chronic hepatitis C infection and no long term damage occurs.
But around 75-85% of people will develop chronic infection. Most of the time, people with chronic hepatitis C have no symptoms at the time of infection and no symptoms for years or even decades of chronic infection. The virus will be with them until they are successfully treated with hepatitis C medications.
Around 10-20% of people with chronic infection will slowly have gradual damage in the liver over years and will eventually develop cirrhosis . This can take 20 years or more from the time of the initial infection.
Cirrhosis is the replacement of liver cells with permanent scar tissue. Cirrhosis can lead to problems such as bleeding from veins in the esophagus, fluid buildup in the belly, and damaged brain function.Approximately 15% of people with cirrhosis will develop liver cancer during their lifetime. Drinking excessively can double the chance of liver cancer in people infected with HCV.
Also Check: How Long Hepatitis C Virus Survive Outside Body
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis C testing is performed by a doctor. Testing requires a blood sample, which can be collected in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Blood is often drawn from a vein in the arm or, in children, taken by pricking the skin. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
You May Like: How Does Someone Catch Hepatitis C
Determining The Prevalence Threshold For The Recommendations
Although the intent of public health screening is usually to identify undiagnosed disease, many persons previously diagnosed with hepatitis C are not appropriately linked to care and are not cured of their HCV infection, thereby representing an ongoing source of transmission. Therefore, the prevalence threshold of 0.1% should be determined on the basis of estimates of chronic hepatitis C prevalence, regardless of whether hepatitis C has been diagnosed previously.
What Are The Side Effects Of Treatment
The direct acting antiviral regimens used to treat hepatitis C today are extremely well tolerated. You may experience mild side effects like headache or fatigue. For details on the side effects, review the handout specific to medication you take.
In rare instances, providers may recommend the addition of the medication ribavirin for more difficult cases of hepatitis C. Ribavirin may cause additional side effects such as fatigue, shortness of breath, cough, anemia, or rash. Patients who receive ribavirin may need more frequent monitoring for side effects as well as adjustment of the dose if side effects are experienced. For detailed information on ribavirin, patients should review the ribavirin handout.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Rapid Test Kit
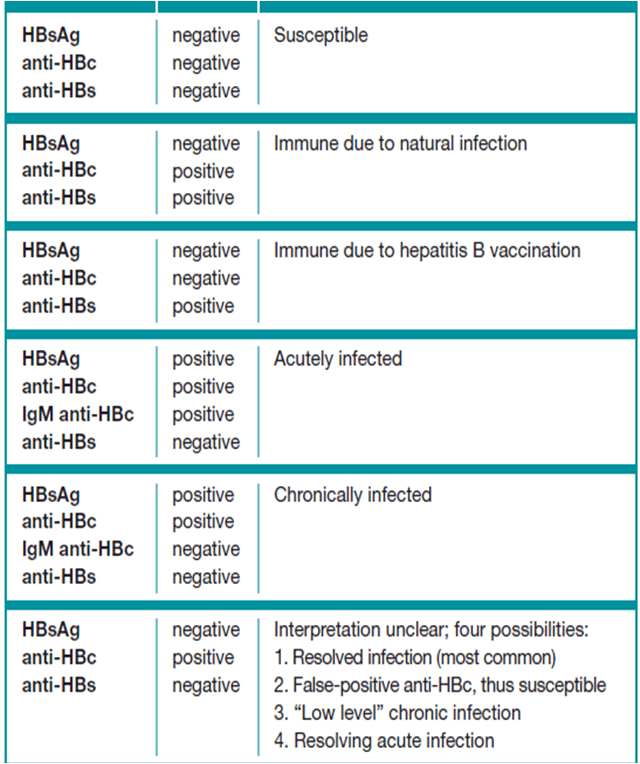
Results Of The Hbcab Test
There are two variations of antibodies. The IgM antibody is the largest antibody and the first produced in an infection. It shows that you may have a current, active infection. Sometimes it persists for years, but it usually drops to undetectable levels.
The HBcAb IgG variant is produced later in the course of the infection, and its likely that you will have a positive HBcAb IgG test the rest of your life.
The screening panel usually has a test that is for total HBcAb, which includes both IgM and IgG. The IgM test may be ordered to help determine if you have an acute infection.
A positive HBcAb test must be interpreted along with the results of the other tests. You may have an active or chronic infection, or you may be immune to hepatitis B due to past infection. Discuss the results with your healthcare provider. In any case, a positive HBcAb test means your blood or organs cannot be donated to a recipient.
What Is The Risk That Hcv Infected Women Will Spread Hcv To Their Newborn Infants
About 5 out of every 100 infants born to HCV infected women become infected. This occurs at the time of birth, and there is no treatment that can prevent this from happening. Most infants infected with HCV at the time of birth have no symptoms and do well during childhood. More studies are needed to find out if these children will have problems from the infection as they grow older. There are no treatments or guidelines for the treatment of infants or children infected with HCV. Children with elevated ALT levels should be referred for evaluation to a specialist familiar with the management of children with HCV-related disease.
Also Check: What Does Hepatitis Do To The Body
Also Check: How Do You Get Viral Hepatitis
What Does High/low Viral Load Mean
Viral load is the amount of virus present in the bloodstream. It is expressed as the amount of viral genetic material per milliliter of blood. The amount of virus does not predict how severe the liver disease is or will become. The level of the viral load does not tell us anything about the risk of liver damage or how sick someone is. In hepatitis C, it matters if virus is present or absent. Some treatment regimens can be shortened if the patient has a low viral load to start with, but most often, treatment regimens are the same for people with high hepatitis C viral loads or low viral loads.
The RNA test is essential for making the diagnosis of hepatitis C infectionhaving a positive RNA test is the definition of having infection. After the diagnosis is made, the RNA level does not need to be checked over and over unless it is checked during the time that the patient is undergoing treatment. During treatment, regular RNA tests are done to follow the dropping virus level until it reaches an undetectable state. But before treatment and after treatment, repeated RNA testing is not necessary.
Recommended Reading: How Can I Get Hepatitis
Additional Tests You Might Need
Once youve been diagnosed with Hepatitis C, your doctor will likely order a number of tests to find out about the health of your liver and decide on a treatment plan thats most appropriate for you.
Hepatitis C genotype
The Hepatitis C genotype refers to a specific strain or type of the Hepatitis C virus. There are six major types of Hepatitis C around the world: genotypes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. In the United States, genotypes 1, 2, and 3 are common:
- Genotype 1: Most Americans with Hepatitis C have this type
- Genotype 2: About 10% of Americans with Hepatitis C have this type
- Genotype 3: About 6% of Americans with Hepatitis C have this type
The genotype of Hepatitis C does not change over time, so you only need to get tested once.
Genotype tests are done before a person starts treatment. Hepatitis C treatment works differently for different genotypes, so knowing your genotype helps your doctor choose the best treatment for you.
Testing for Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B
Your doctor may test to see if your body is immune to Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B. If these tests show no prior exposure or protection, he or she will recommend that you be vaccinated against these two viruses to eliminate the chance of becoming infected.
Liver function tests or liver enzymes
- ALT
Liver function tests also include ALP and total bilirubin, among other things.
Tests to measure liver scarring or fibrosis
- Liver Biopsy
Also Check: Is There A Vaccine For Hepatitis C
How Is The Hbcab Test Done
This is a blood test. A clinician will fill a tube with blood taken from a vein in your arm through which a needle is inserted. If you are giving blood, a sample will be taken from the blood youre donating. The blood is sent to a lab, where it is tested. Sometimes HBcAb will be added on to lab orders when results from other tests indicate there may be a hepatitis B infection.
Do Medical Conditions Outside The Liver Occur In Persons With Chronic Hepatitis C
A small percentage of persons with chronic hepatitis C develop medical conditions outside the liver . These conditions are thought to occur due to the bodyâs natural immune system fighting against itself. Such conditions include: glomerulonephritis associated with kidney disease, essential mixed cryoglobulinemia, and porphyria cutanea tarda-a skin condition.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does It Take To Cure Hepatitis C
Pregnancy And Hepatitis C
Should pregnant women be tested for HCV antibodies?
Yes. All pregnant women should be screened for anti-HCV during each pregnancy, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is < 0.1% . Pregnant women with known risk factors should be tested during each pregnancy, regardless of setting prevalence. Any pregnant women testing positive for anti-HCV should receive a PCR test for HCV RNA to determine current infection status.
Can a mother with hepatitis C infect her infant during birth?
The overall risk of an infected mother transmitting HCV to her infant is approximately 4%8% per pregnancy . Transmission occurs during pregnancy or childbirth, and no prophylaxis is available to protect the newborn from infection. The risk is significantly higher if the mother has a high HCV viral load, or is coinfected with HIV with which the rate of transmission ranges from 8%15% . Most infants infected with HCV at birth have no symptoms.
Should a woman with hepatitis C be advised against breastfeeding?
When should children born to HCV-infected mothers be tested to see if they were infected at birth?
Hepatitis C Testing Strategy
The goal of hepatitis C screening is to identify persons who are currently infected with HCV. Hepatitis C testing should be initiated with a U.S. Food and Drug Administration -approved anti-HCV test. Persons who test anti-HCV positive are either currently infected or had past infection that has resolved naturally or with treatment. Immunocompetent persons without hepatitis C risks who test anti-HCV negative are not infected and require no further testing. Persons testing anti-HCV positive should have follow-up testing with an FDA-approved nucleic acid test for detection of HCV RNA. NAT for HCV RNA detection determines viremia and current HCV infection. Persons who test anti-HCV positive but HCV RNA negative do not have current HCV infection. CDC encourages use of reflex HCV RNA testing, in which specimens testing anti-HCV positive undergo HCV RNA testing immediately and automatically in the laboratory, using the same sample from which the anti-HCV test was conducted. Hepatitis C testing should be provided on-site when feasible.
Also Check: What Is The Definition Of Hepatitis C