Who Is At Risk For Infection
Anyone who is not immune to hepatitis A can get hepatitis A infection. Food-borne outbreaks occur sporadically throughout the USA. Certain groups of people do have a higher risk of developing HAV infection and should be vaccinated:
- Persons experiencing homelessness
- People who eat raw or under-cooked shellfish
How Common Is Hepatitis A
In the United States, hepatitis A has become relatively uncommon. After the hepatitis A vaccine became available in 1995, the rate of hepatitis A infections declined by 95 percent in the United States. The number of reported cases of hepatitis A fell to 1,239 in 2014, the lowest yearly number of cases reported since the disease could be tracked.1 However, the number of reported cases increased to 3,366 in 2017, almost 3 times higher, mostly due to outbreaks among people who use drugs and people experiencing homelessness.1 Early reports suggest that the numbers of cases and outbreaks of hepatitis A increased further during 2018 and continue at these higher rates in 2019.2
Hepatitis A is more common in developing countries where sanitation is poor and access to clean water is limited. Hepatitis A is more common in parts of Africa, Asia, Central and South America, and Eastern Europe than it is in the United States.
How Long Do The Hepatitis A And B Vaccines Protect You
During your lifetime, you need:
- One series of the hepatitis A vaccine
- One series of the hepatitis B vaccine
Most people dont need a booster dose of either vaccine. But if you have had dialysis, a medical procedure to clean your blood, or have a weakened immune system, your doctor might recommend additional doses of the hepatitis B vaccine.
Recommended Reading: How To Prevent Hepatitis B
What Is Chronic Viral Hepatitis
Patients infected with HBV and HCV can develop chronic hepatitis. Doctors define chronic hepatitis as hepatitis that lasts longer than 6 months. In chronic hepatitis, the viruses live and multiply in the liver for years or decades. For unknown reasons, these patients’ immune systems are unable to eradicate the viruses, and the viruses cause chronic inflammation of the liver. Chronic hepatitis can lead to the development over time of extensive liver scarring , liver failure, and liver cancer. Liver failure from chronic hepatitis C infection is the most common reason for liver transplantation in the U.S. Patients with chronic viral hepatitis can transmit the infection to others with blood or body fluids as well as infrequently by transmission from mother to newborn.
Viral Hepatitis Definition And Overview
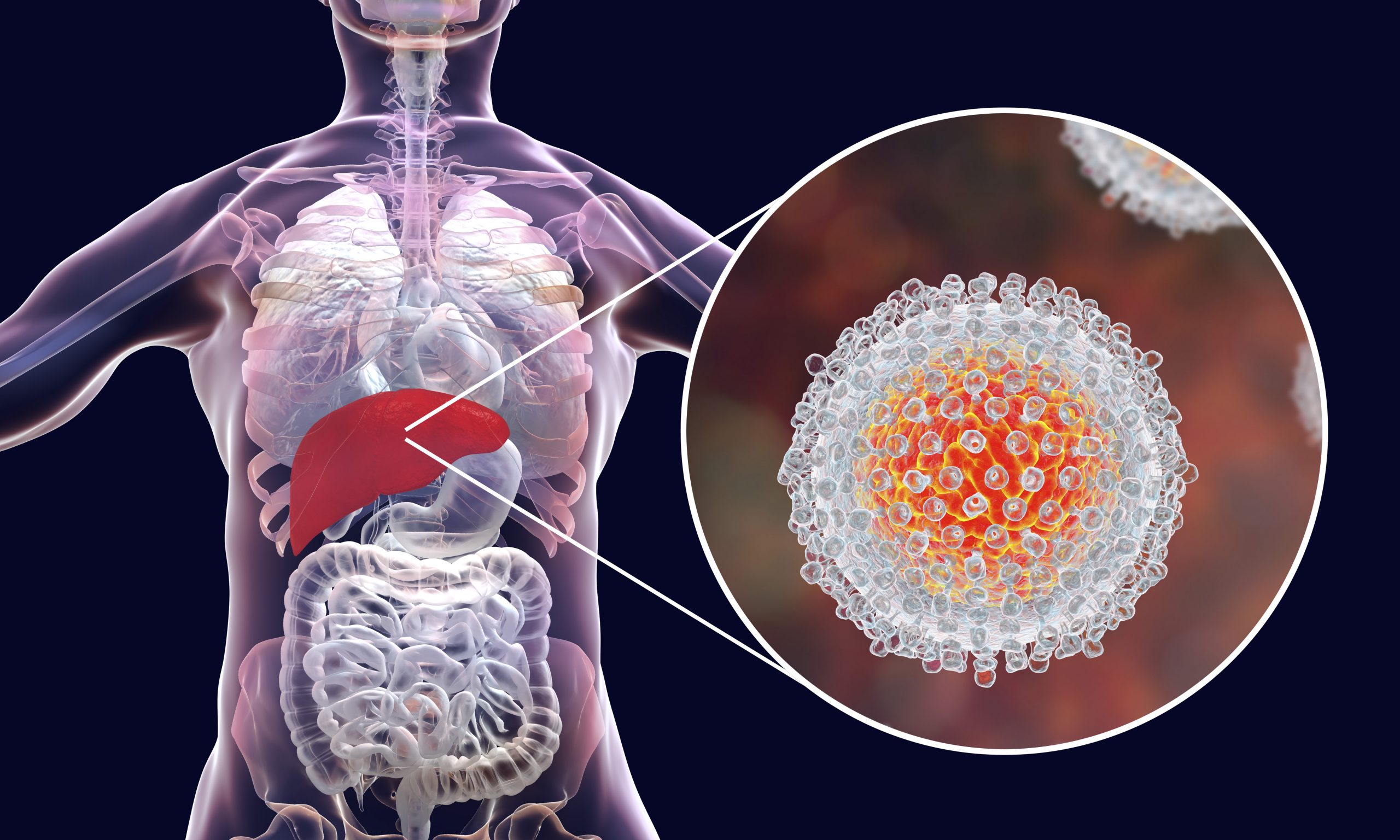
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Many illnesses and conditions can cause inflammation of the liver, for example, drugs, alcohol, chemicals, and autoimmune diseases. Many viruses, for example, the virus causing mononucleosis and the cytomegalovirus, can inflame the liver. Most viruses, however, do not attack primarily the liver the liver is just one of several organs that the viruses affect. When most doctors speak of viral hepatitis, they are using the definition that means hepatitis caused by a few specific viruses that primarily attack the liver and are responsible for about half of all human hepatitis. There are several hepatitis viruses they have been named types A, B, C, D, E, F , and G. As our knowledge of hepatitis viruses grows, it is likely that this alphabetical list will become longer. The most common hepatitis viruses are types A, B, and C. Reference to the hepatitis viruses often occurs in an abbreviated form The focus of this article is on these viruses that cause the majority of human viral hepatitis.
Hepatitis viruses replicate primarily in the liver cells. This can cause the liver to be unable to perform its functions. The following is a list of major functions of the liver:
Recommended Reading: What Organ Does Hepatitis B Affect
Relationship Between Hepatitis C Virus And Liver Cancer
Hepatitis C virus are causing acute and chronic infections that is a major cause of hepatocellular carcinoma , advanced hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis.
A major cause of death in HCC patients with chronic HCV infection. The pathogenesis of HCC associated with HCV, that virus play direct and indirect roles.
A major risk for the development of HCC is persistent infection with HCV and the highest risk for HCC development is associated with co-infection of HBV with HDV, HCV or HIV.
The risk factors lead to development of HCC in chronic HCV is synchronous liver diseases, viral genotype, lifestyle factors and presence of obesity and diabetes mellitus. The lifestyle factors such as smoking, alcohol use and coffee drinking accelerated progression to HCC in HCV.
The purpose of HCV treatment is to eliminate the infection, reduce the transmission to other people and decrease the risk of HCC development.
Diagnosis Of Acute Viral Hepatitis
-
Blood tests
Doctors suspect acute viral hepatitis based on symptoms. During the physical examination, a doctor presses on the abdomen above the liver, which is tender and somewhat enlarged in about half of the people with acute viral hepatitis.
Doctors suspect fulminant hepatitis if
-
People are very ill and develop jaundice very quickly.
-
Mental function quickly deteriorates.
-
Blood tests to determine how quickly blood clotsâprothrombin time or international normalized ratio âare abnormal.
-
People who have liver disease start worsening rapidly.
These blood tests can detect parts of specific viruses or specific antibodies produced by the body to fight the viruses. involves white blood cells that travel through the bloodstream and into tissues, searching for and attacking microorganisms and… read more â are proteins produced by the immune system to help defend the body against attack by viruses and other foreign invaders.)
To determine whether the cause may be something other than a virus, the doctor may ask whether people take any drugs that can cause hepatitis and how much alcohol they drink.
Occasionally, if the diagnosis is unclear, a liver biopsy is done: A sample of liver tissue is removed with a needle and examined.
Don’t Miss: Chronic Hep C Without Hepatic Coma Icd 10
How Can I Avoid Getting Hepatitis A
There is a safe and effective vaccine that can protect you from getting hepatitis A. The vaccine is usually given in two doses six months apart. The vaccine will give you protection for up to 20 years. A combined vaccine for hepatitis A and hepatitis B is also available. Since up to 40% of the reported cases of hepatitis A occur in travellers, it is advisable to protect yourself with a hepatitis A vaccination six weeks before you leave.
Consider these additional safety precautions:
- Wash your hands frequently and thoroughly especially after using the washroom, before preparing food and before eating.
- Avoid raw or undercooked food.
- If you are travelling to countries with high rates of hepatitis A:
- Drink bottled or boiled water and use it for brushing your teeth.
- Drink bottled beverages without ice.
- Avoid uncooked food including salads.
- Avoid food from street vendors.
- Peel and wash fresh fruits and vegetables yourself.
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis A
Although anyone can get hepatitis A, you are at higher risk if you:
- Travel to developing countries
- Abdominal pain
- Yellowish eyes and skin, called jaundice
The symptoms usually last less than 2 months, although some people can be ill for as long as 6 months.
You are at a higher risk of getting a more severe infection from hepatitis A if you also have HIV, hepatitis B, or hepatitis C.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vaccine Cost Cvs
Treatment And Prevention Of Hepatitis A
Because hepatitis A virus infections can have serious health consequences, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends providing post-exposure prophylaxis for unvaccinated people who have consumed any contaminated food or water within two weeks of exposure.
PEP consists of:
- Hepatitis A vaccine for people between the ages of 1 and 40 years
- Hepatitis A virus-specific immunoglobulin for people outside of this age range, but the hepatitis A vaccine can be substituted if IG is not available.
- Those with evidence of previous vaccination or who can confirm previous hepatitis A illness do not require PEP.
If you are unsure if you have been vaccinated against hepatitis A, contact your health professional to check your immunization records. If you have been vaccinated, no further action is needed. If you have never received the hepatitis A vaccine, getting a single dose within two weeks of exposure can protect against illness. If you are unable to determine whether you have already been vaccinated, receiving an additional dose of vaccine is not harmful if you have already been vaccinated.
How Does Viral Hepatitis Affect Pregnancy
Hepatitis B and C can cause problems during pregnancy and can be passed to your baby. The risk of passing the virus to your baby is higher with hepatitis B than C.
Research shows that pregnant women with hepatitis B or C may have a higher risk for certain pregnancy complications:2
- Gestational diabetes
- Low-birth-weight baby
- Premature birth . Premature birth is the leading cause of infant death and raises the risk of health and developmental problems at birth and later in life.
Talk to your doctor if you think you may be pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Some antiviral medicines that treat hepatitis C, such as ribavirin, can cause serious birth defects if taken during pregnancy.
Recommended Reading: Drinking Alcohol With Hepatitis C
How Long Does The Hepatitis A Vaccine Last
We dont know exactly how long the protection of the vaccine lasts, but studies have indicated that it lasts at least 20 years in some people and it could last as long as 40 years or more. Having only one dose of the recommended two-dose vaccine has shown to provide protection for at least 10 years.
Who Is Likely To Be Affected By Hepatitis A
Certain people are more at risk than others for hepatitis A. These include:
- People who use recreational drugs, both injected and non-injected types.
- Men who have sex with men.
- People who have close contact with someone who already is infected.
- People who have close contact with someone adopted from a country where hepatitis A is common, or people who travel to countries where hepatitis A is common.
- People who work with non-human primates.
- People who have clotting factor issues, including hemophilia.
- People who work in child care, or children who are in childcare.
Recommended Reading: How Contagious Is Hepatitis C Sexually
Whats The Best Way To Stop The Spread Of Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A vaccination is the best way to prevent hepatitis A. The hepatitis A vaccine is given in 2 doses, usually about 6 months apart.
Other ways to stop the spread of HAV are:
- Always washing your hands with soap and warm water immediately after using the bathroom or changing a diaper
- Always washing your hands with soap and warm water before preparing or eating food
What Is Hepatitis E
Hepatitis E, also called enteric hepatitis , is similar to hepatitis A, and more prevalent in Asia and Africa. It is also transmitted through the fecal-oral route. It is generally not fatal, though it is more serious in women during pregnancy and can cause fetal complications. Most patients with hepatitis E recover completely.
Also Check: What Are The Ways You Can Get Hepatitis C
What Is The Virus That Causes Hepatitis
In the United States, viral hepatitis is most commonly caused by hepatitis A virus , hepatitis B virus , and hepatitis C virus . These three viruses can all result in acute disease with symptoms of nausea, abdominal pain, fatigue, malaise, and jaundice.
Also to know is, what is virus hepatitis?
Viral hepatitis is an infection that causes liver inflammation and damage. Inflammation is swelling that occurs when tissues of the body become injured or infected. Inflammation can damage organs. The hepatitis B, C, and D viruses can cause acute and chronic, or long-lasting, infections.
what is viral hepatitis symptoms? Symptomsof chronic viral hepatitis can take decades to develop. Symptoms of hepatitis can include: fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, light-colored stools, joint pain, and jaundice.
Beside this, what are the causes of hepatitis?
Hepatitis refers to an inflammatory condition of the liver. It’s commonly caused by a viral infection, but there are other possible causes of hepatitis. These include autoimmune hepatitis and hepatitis that occurs as a secondary result of medications, drugs, toxins, and alcohol.
How long is viral hepatitis contagious?
You are most contagious soon after you are infected and before symptoms appear. Adults who are otherwise healthy are no longer contagious 2 weeks after the illness begins. Children and people who have weak immune systems may be contagious for up to 6 months.
You May Like Also
Can Hepatitis A Be Treated
There is no drug treatment for hepatitis A. The disease will eventually run its course and an infected person will recover completely although recovery time varies for each person. Recovery from this virus infection means that you are protected for life from getting it again.
The following are some ways of dealing with the symptoms:
- You will feel tired and may have very little energy. You may need to take time off from daily activities, work or school to recover.
- Nausea and vomiting may cause you to lose your appetite. Try to eat small snacks and soft foods such as soup or toast.
- You may look yellow. Once you become yellow, you are no longer infectious. There is no need to isolate yourself. Let people around you know it is OK to be near you.
- Try not to drink alcohol. Your liver may not be able to process alcohol and alcohol may make your symptoms worse.
- Talk to your doctor before taking over-the-counter medications or complementary medicine. None of the alternative therapies have proved helpful in treating hepatitis A.
Recommended Reading: Where Can I Get Tested For Hepatitis
Does Viral Hepatitis Affect Women Differently Than Men
Yes, certain types of viral hepatitis affect women differently than men.
Hepatitis A affects women and men in similar ways.
Hepatitis B affects women differently than men:
- Birth control. Women with severe liver damage may not be able to use birth control.1 This is because a damaged liver may have problems breaking down estrogen.
- Pregnancy. The risk of passing hepatitis B to your baby during pregnancy is high. Hepatitis B raises your risk for pregnancy complications.2 Talk to your doctor about taking hepatitis B medicine to lower the risk of passing hepatitis B to your baby. Certain hepatitis B medicines are safe to take during pregnancy but are not recommended for everyone. Learn more about hepatitis B during pregnancy.
Hepatitis C affects women differently than men:
How Many People Have Hepatitis A
Since the release of the first vaccine in 1995, the rate of new HAV infections in the United States declined by more than 95% from 1996 to 2011. From 2012 through 2016, the number of hepatitis A cases fluctuated because large foodborne outbreaks occurred. From August 2016 through August 2020, 33 states reported hepatitis A outbreaks spread through person-to-person contact resulting in over 33,000 infections with high numbers of hospitalizations and deaths.
Globally, HAV infection is most common in countries with poor sanitary conditions and hygienic practices and transitional economies according to the World Health Organization .
Also Check: How Is Hepatitis C Contracted
How Hepatitis A Is Spread
Hepatitis A is most commonly spread when someone eats food or drinks water that contains the hepatitis A virus. This is more likely when travelling outside Canada in areas of the world where hepatitis A is more common. Contaminated sources may include:
- ice
- raw or frozen fruits and vegetables
Hepatitis A can also spread:
- from person to person through:
- sexual contact with an infected person
- contact with the feces of an infected person
- blood transfusions or sharing needles for drug use
- changing diapers or cleaning up stool from an infected person
Even if you do not have symptoms, you can still infect others. Infected infants and children are more likely to be without symptoms than infected adults.
You can spread the virus starting 2 weeks before you show any symptoms. You can continue to infect others until about a week after you get jaundice .
Who Gets Viral Hepatitis
Viral hepatitis is common in the United States and affects women and men. Hepatitis B and C are more common than hepatitis A.
- In 2015, hepatitis A affected an estimated 2,500 Americans.6 The percentage of people with hepatitis A has gone down by 95% since the hepatitis A vaccine became available in 1995.
-
Chronic hepatitis B may affect more than 1 million Americans.6 Asian-Americans and Pacific Islanders have the highest rates of hepatitis B infection. About 50% of the people living with Hepatitis B are Asian-Americans and Pacific Islanders.7
Within this high-risk group, hepatitis B is usually passed from a mother to her baby during pregnancy. Babies born with hepatitis B are likely to have it their entire lives and are at higher risk of liver damage and liver cancer.
- Hepatitis C is the most common type of viral hepatitis infection in the United States. An estimated 3.5 million Americans have chronic hepatitis C.6 The CDC recommends that everyone born between 1945 and 1965 get tested at least once for hepatitis C because it is so common in this age group.8
Also Check: How Can Hepatitis C Be Transmitted Sexually
What Causes Hepatitis A And How Is It Contracted
People develop hepatitis A infection after contracting HAV. This virus is typically transmitted by ingesting food or liquid contaminated with fecal matter that contains the virus. Once transmitted, the virus spreads through the bloodstream to the liver, where it causes inflammation and swelling.
In addition to transmission from eating food or drinking water containing HAV, the virus can also be spread by close personal contact with an infected person. HAV is contagious, and a person who has hepatitis A can easily pass the disease to others living in the same household.
You can contract hepatitis A by:
- eating food prepared by someone with the hepatitis A virus
- eating food handled by preparers who dont follow strict hand-washing routines before touching food that you eat
- eating sewage-contaminated raw shellfish
- not using condoms when having sex with someone who has the hepatitis A virus
- drinking polluted water
- coming in contact with hepatitis A-infected fecal matter
If you contract the virus, you will be contagious two weeks before symptoms even appear. The contagious period will end about one week after symptoms appear.