Hepatitis C And Itchy Feet
Edema caused by chronic hepatitis C can result in swollen feet & ankles.
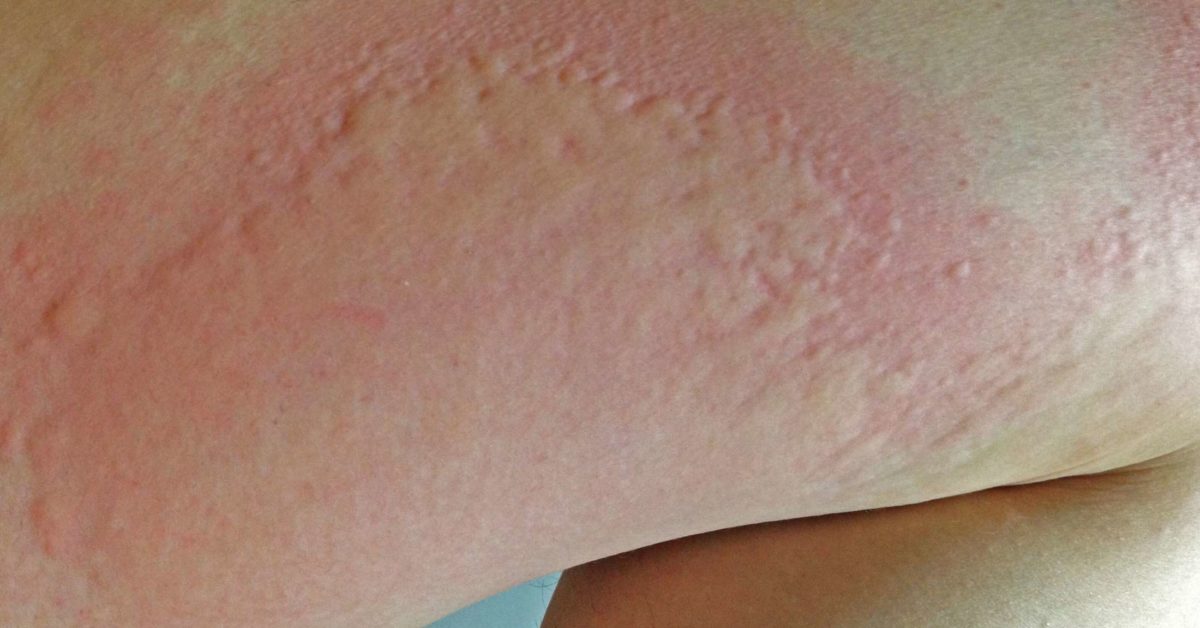
Around 20% of patients with late stage hepatitis C suffer from pruritus, severe itching of the skin.
The itching may be localized to the feet or hands or be widespread on the body.
Itchy feet in hep C patients may be caused by a buildup of toxins the liver is unable to eliminate. Itching can also manifest in non-late-stage patients arising from dry skin or side effects from treatment.
Hepatitis C And Arthritis
The same virus causing hepatitis can also cause rheumatoid arthritis, inflammation of the joints, and pain and weakness in the muscles and connective tissue. This pain can occur in the feet, ankles, knees and elsewhere in the body.
The hepatitis C virus activates the bodys immune system which is constantly engaged in fighting the infection, leading to many potential symptoms including joint and muscle pain.
Treatment for symptoms of arthritis caused by HCV will depend on how severe the liver damage is, overall health, lifestyle and other factors.
How Is Hepatitis C Diagnosed
Blood tests for hepatitis C
There are several blood tests for the diagnosis of hepatitis C infection. Blood can be tested for antibody to hepatitis C . It takes about 8-12 weeks on average, and up to 6 months, for antibodies to develop after the initial infection with hepatitis C, so screening for antibodies may miss a few newly infected individuals. Having antibodies is not an absolute indication of active, multiplying hepatitis C virus, but if the antibody test is positive , the statistical probability of active infection is greater than 99%.
Several tests are available to measure the amount of hepatitis C virus in a person’s blood . The hepatitis C virus’s RNA can be identified by a type of test called polymerase chain reaction that detects circulating virus in the blood as early as 2-3 weeks after infection, so it can be used to detect suspected acute infection with hepatitis C early infection. It also is used to determine whether active hepatitis is present in someone who has antibodies to hepatitis C, and to follow the viral load during treatment.
Blood tests are also performed to identify the genotypes of HCV. Genotypes respond differently to different treatment, so this information is important in selection of the most appropriate treatment regimen.
Estimation of liver fibrosis using blood tests also is quite reliable in diagnosing clinically significant scarring these include FIB-4, FibroSure, Fibrotest, and aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index .
Also Check: What Is The Definition Of Hepatitis B
Some People Have It And May Never Know It As They Are Affected By Any Sorts Of Symptoms
. 1 cause of liver cancer and liver transplants. Webmd tells you why more and more people are being cure cured without shots or toxic side effects. Hepatitis c can cause many symptoms including skin issues such as jaundice, itching, and blood spots. Hepatitis is the name of a group of diseases that affect the liver. Hepatitis is a condition that causes inflammation of your liver.
Hepatic steatosis is essentially fatty liver. Learn how to identify a hepatitis c rash here. Some people have it and may never know it as they are affected by any sorts of symptoms.
Treatment for hepatitis c is rapidly evolving. Hepatitis c can cause many symptoms including skin issues such as jaundice, itching, and blood spots. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
They can also be caused by hepatitis c treatment and liver damage. 1 cause of liver cancer and liver transplants. It can remain silent until there is severe damage to your liver.
Learn how to identify a hepatitis c rash here. Some people have it and may never know it as they are affected by any sorts of symptoms. Webmd tells you why more and more people are being cure cured without shots or toxic side effects.
What Are The Symptoms And Signs Of Viral Hepatitis
The period of time between exposure to hepatitis and the onset of the illness is called the incubation period. The incubation period varies depending on the specific hepatitis virus. Hepatitis A virus has an incubation period of about 15 to 45 days Hepatitis B virus from 45 to 160 days, and Hepatitis C virus from about 2 weeks to 6 months.
Many patients infected with HAV, HBV, and HCV have few or no symptoms of illness. For those who do develop symptoms of viral hepatitis, the most common are flu-like symptoms including:
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Is More Infectious Than Hiv
There Are Several Different Causes Of Fatty Liver And In Many Cases It Is Preventable Or Curable
Hepatitis c, a virus that attacks the liver, is a tricky disease. They can also be caused by hepatitis c treatment and liver damage. There are several different causes of fatty liver, and in many cases, it is preventable or curable. It’s brought on by a vir. The standard treatment for hepatitis c, interferon and ribavirin, cures just 45% of those who receive it. Know what to look for and how this rash is treated. Hepatitis involves an inflammation of the liver, which diminishes the liver’s ability to function. Hepatitis c can cause many symptoms including skin issues such as jaundice, itching, and blood spots. Learn how to identify a hepatitis c rash here. Each one is caused by a virus that infects the li. Hepatic steatosis is essentially fatty liver. Some people have it and may never know it as they are affected by any sorts of symptoms. 1 cause of liver cancer and liver transplants.
. Hepatitis c is a viral infection that causes inflammati. Skin rashes may be a sign of hepatitis c. The most common types in the united states and most of the rest of the world are hepatitis a, hepatitis b and hepatitis c. Va hsr& d research topics the.gov means it’s official. They can also be caused by hepatitis c treatment and liver damage.
Hepatic steatosis is essentially fatty liver. Va hsr& d research topics the.gov means it’s official. Hepatitis c, a virus that attacks the liver, is a tricky disease.
Is Liver Transplantation An Option For A Person With Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is the leading reason for 40% to 45% of liver transplants in the U.S. Hepatitis C usually recurs after transplantation and infects the new liver. Approximately 25% of these patients with recurrent hepatitis will develop cirrhosis within five years of transplantation. Despite this, the five-year survival rate for patients with hepatitis C is similar to that of patients who are transplanted for other types of liver disease.
Most transplant centers delay therapy until recurrent hepatitis C in the transplanted liver is confirmed. Oral, highly effective, direct-acting antivirals have shown encouraging results in patients who have undergone liver transplantation for hepatitis C infection and have recurrent hepatitis C. The choice of therapy needs to be individualized and is rapidly evolving.
You May Like: How Do You Test For Hepatitis C
What Are The Risk Factors For Hepatitis C
In the United States, having been born between 1945 and 1965, and the use of illicit injection drugs are the two most common factors associated with hepatitis C. Other risk factors include
- having received blood transfusions prior to 1990,
- hemodialysis, and
- having greater than 10-lifetime sex partners.
Population studies show that hepatitis C is more common among males, non-Hispanic blacks, those with low income, and those with less than a high school education.
People who have HIV/AIDS have an increased risk for hepatitis C, because both these diseases are transmitted in the same ways, through blood and body fluids. If someone has both infections, that person is said to be co-infected with HIV and HCV.
Do You Need Vaccinations Before Traveling Abroad
The CDC divides travel vaccinations into three categories: 1) routine, 2) recommended, and 3) required. The only vaccine classified as “required” by International Health Regulations is the yellow fever vaccination for travel to certain countries in sub-Saharan Africa and tropical South America.
“Routine” vaccinations are those that are normally administered, usually during childhood, in the United States. These include immunizations against:
- tetanus
You May Like: What Is A Hepatitis Panel
Key Points About Hepatitis In Children
-
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. It can damage and destroy liver cells.
-
Hepatitis in children can be caused by many things. Your child can get hepatitis by being exposed to a virus that causes it.
-
There are 5 main types of the hepatitis virus: A, B, C, D, and E.
-
The most common symptoms of hepatitis include a yellowish color to the skin and whites of the eyes and flu-like symptoms.
-
Some children don’t have any symptoms.
-
Getting vaccinated and having good hygiene can prevent hepatitis.
Hepatitis C Testing And Diagnosis
Doctors will start by checking your blood for:
Anti-HCV antibodies: These are proteins your body makes when it finds the hep C virus in your blood. They usually show up about 12 weeks after infection.
It usually takes a few days to a week to get results, though a rapid test is available in some places.
The results can be:
- Nonreactive, or negative:
- That may mean you donât have hep C.
- If youâve been exposed in the last 6 months, youâll need to be retested.
If your antibody test is positive, youâll get this test:
HCV RNA: It measures the number of viral RNA particles in your blood. They usually show up 1-2 weeks after youâre infected.
- The results can be:
- Negative: You donât have hep C.
- Positive: You currently have hep C.
You might also get:
Liver function tests: They measure proteins and enzyme levels, which usually rise 7 to 8 weeks after youâre infected. As your liver gets damaged, enzymes leak into your bloodstream. But you can have normal enzyme levels and still have hepatitis C. Learn the reasons why you should get tested for hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: How Us Hepatitis C Transmitted
Serological Tests For Hepatitis
- IgMantibodies appear early in acute infection.
- IgG appears later.
- Anti-HBs antibodies becomes detectable in late convalescence. It indicates immunity following infection and remains detectable for life. It is not seen in chronic carriers.
- HBsAg can be present in acute and chronic HBV infection. Persistence in the blood for greater than six months is suggestive of chronic infections.
- HBe is a secreted protein of unknown function. Expression is greatest when the virus is rapidly replicating. Anti-HBe antibodies become detectable as viral replication falls. It indicates low infectivity in a carrier.
- Anti-HCV antibodies indicate prior exposure or infection. The third generation assays for these antibodies are highly sensitive and specific and can detect antibodies within 4 to 10 weeks of infection.
- PCR for HCV particles is the most specific test. PCR can be used to diagnose acute HCV infection before antibodies develop.
Immunosuppressive medications may reactivate HBV or HCV. For example:
- Chemotherapy for cancer
- Long term systemic steroids
Patients are often tested for chronic hepatitis before starting these medications. Hepatitis treatment such as lamivudine may be prescribed one to two weeks before the immunosuppressive and continued long term. Antiviral therapy should be started immediately after an HBV flare is recognised as antiviral therapy takes time to work and may not prevent progression to liver failure if delayed.
How Is Monitoring Done After Treatment For Hepatitis C
Once patients successfully complete treatment, the viral load after treatment determines if there is an SVR or cure. If cure is achieved , no further additional testing is recommended unless the patient has cirrhosis. Those who are not cured will need continued monitoring for progression of liver disease and its complications.
While cure eliminates worsening of fibrosis by hepatitis C, complications may still affect those with cirrhosis. These individuals still need regular screening for liver cancer as well as monitoring for esophageal varices that may bleed.
Because hepatitis B co-infection may reactivate or worsen even after treatment for HCV, monitoring for hepatitis symptoms may be needed after the end of therapy.
Read Also: How To Contract Hepatitis B And C
What Is Hepatitis C Infection How Many People Are Infected
Hepatitis C virus infection is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus . It is difficult for the human immune system to eliminate hepatitis C from the body, and infection with hepatitis C usually becomes chronic. Over decades, chronic infection with hepatitis C damages the liver and can cause liver failure. In the U.S., the CDC has estimated that approximately 41,200 new cases of hepatitis C occurred in 2016. When the virus first enters the body there usually are no symptoms, so this number is an estimate. About 75%-85% of newly infected people become chronically infected. In the U.S., more than 2 million people are estimated to be chronically infected with hepatitis C. Infection is most commonly detected among people who are 40 to 60 years of age, reflecting the high rates of infection in the 1970s and 1980s. There are 8,000 to 10,000 deaths each year in the U.S. related to hepatitis C infection. HCV infection is the leading cause of liver transplantation in the U.S. and is a risk factor for liver cancer. In 2016, 18,153 death certificates listed HCV as a contributing cause of death this is believed to be an underestimate.
Those who have cirrhosis from HCV also have a yearly risk of liver cancer of about 1%-5%.
What Are The Common Types Of Viral Hepatitis
Although the most common types of viral hepatitis are HAV, HBV, and HCV, some clinicians had previously considered the acute and chronic phases of hepatic infections as “types” of viral hepatitis. HAV was considered to be acute viral hepatitis because the HAV infections seldom caused permanent liver damage that led to hepatic failure. HBV and HCV produced chronic viral hepatitis. However, these terms are outdated and not currently used as frequently because all of the viruses that cause hepatitis may have acute phase symptoms . Prevention techniques and vaccinations have markedly reduced the current incidence of common viral hepatitis infections however, there remains a population of about 1 to 2 million people in the U.S. with chronic HBV, and about 3.5 million with chronic HCV according to the CDC. Statistics are incomplete for determining how many new infections occur each year the CDC documented infections but then goes on to estimate the actual numbers by further estimating the number of unreported infections .
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis C
Types D, E, and G Hepatitis
Individuals who already have chronic HBV infection can acquire HDV infection at the same time as they acquire the HBV infection, or at a later time. Those with chronic hepatitis due to HBV and HDV develop cirrhosis rapidly. Moreover, the combination of HDV and HBV virus infection is very difficult to treat.
- HIV patients
- People with hemophilia who receive blood clotting factors
Also Check: Hepatitis B How Long Does It Last
Can You Prevent Hepatitis C Infection
Thereâs no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C. To avoid getting the virus:
- Use a latex condom every time you have sex.
- Don’t share personal items like razors.
- Don’t share needles, syringes, or other equipment when injecting drugs.
- Be careful if you get a tattoo, body piercing, or manicure. The equipment may have someone else’s blood on it.
Deterrence And Patient Education
Patient education is key to preventing and controlling hepatitis, especially viral and alcoholic hepatitis. Patients who have viral hepatitis must obtain education educated regarding the importance of routine follow-up and the importance of monitoring the disease progression and development of complications. They should learn about the importance of personal hygiene, including frequent handwashing. People who are traveling to endemic areas should be advised not to drink untreated water or ingest shellfish or raw seafood, and fruits and veritable should always be eaten after being cooked or after being peeled. Patients who have hepatitis A should not handle food for others until they stop shedding the virus. Patients should receive instruction about not sharing any articles, including toothbrushes, razors, or needles that have the potential for contamination with saliva, semen, or blood. All the patients should avoid using hepatotoxic agents, including alcohol and acetaminophen. Patients who are having a disease progression with liver disease should be referred to a gastroenterologist or hepatologist promptly. Patients with features of liver damage that includes liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and features of portal hypertension should be monitored with routine labs.
Vaccination
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis D
Hepatitis E
Hepatitis G
You May Like: Who Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Evaluation Of Seasonal Changes In Itch
We first distributed a questionnaire on pruritus in the winter and received answers from 450 patients. Then, we distributed the same questionnaire to the 450 patients a second time in the summer , and responses were received from 303 patients. We investigated the differences in itch severity between summer and winter in 303 patients. Furthermore, we compared patients who had pruritus all year with other patients and examined the relationships between patients blood test/background factors and pruritus.
Living With Hepatitis C Infection
Many people are living with hepatitis C. If you have hepatitis C, there are several important things that you can do to help yourself and others such as:
- Eat a healthy diet and get plenty of rest.
- To avoid further liver damage:
- Do not drink alcohol.
- Do not take medicine that can cause liver damage .
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis A & B if you are not already immune.
- Do not to pass the infection to anyone else by taking the following precautions, such as:
- Do not share toothbrushes or razors with others.
- Do not to let anyone else come into contact with your blood, urine or feces.
- Use condoms during sexual activity.
- Limit the number of sex partners you have.
- If you use injection drugs, do not share needles or syringes with anyone else.
- It is best to not get tattoos or body piercings.
Although often uncomfortable, you should notify your partner of your hepatitis C prior to having sex. You also must notify all your health care professionals of your infection, so they can take precautions.
Also Check: What Does Hepatitis B Come From