How Can I Prevent Spreading Hepatitis C To Others
If you have hepatitis C, follow the steps above to avoid spreading the infection. Tell your sex partner you have hepatitis C, and talk with your doctor about safe sex practices. In addition, you can protect others from infection by telling your doctor, dentist, and other health care providers that you have hepatitis C. Dont donate blood or blood products, semen, organs, or tissue.
Virus Release And Extracellular Particles
Analysis of cell supernatant by gradient density centrifugation demonstrated that the MVs subpopulations are different, depending on the cell line. It is known, that MVs are intensively released by primary hepatocytes and immortalized cells of hepatic origin. The release from hepatocytes might be increased by an undergoing lipotoxicity. Thus, MVs are actively used by the hepatocytes as delivery system and the amounts of MVs might be increased in response to lipotoxicity and likely other complications. In this regard, we speculate that during acute phase of infection the virus can trigger the MV release and that might be an additional pathway for the virus. How MVs containing virus particles can influence HCV distribution along the density gradient? In fact, MV containing different amount of viruses may contribute to observed diversity of buoyant densities of HCV, especially when plasma is investigated.
It is known, that the diffusion of spherical particle through a viscous liquid is dependent on the particle diameter. It is described by Stokes-Einstein equation:
Math.
D = diffusion constant, k = Boltzmann constant, T = temperature , = solvent viscosity, r = radius of spherical particle.
Another parameter that influences the diffusion is the mass of spherical particle and the equation counting these parameters looks as follows:
Math.
where: D = diffusion = radius of the spherical particle M = mass of the particle = viscosity of the medium.
You Can Have It And Not Know It
What is Hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C is a liver disease caused by the hepatitis C virus . HCV is far more infectious than HIV. Presently, there is no vaccine to prevent HCV infection.
In 2011, it is estimated that over 220,000 people in Canada were infected with HCV. In 2012, 10,180 new cases of hepatitis C were reported in Canada. It has been estimated that over 40% of people living with chronic hepatitis C don’t even know they are infected.
About 15 to 25 percent of adults will recover within 6 months of becoming infected . The remaining 75 to 85 percent are unable to clear the virus and will become chronically infected. Chronic hepatitis C is treatable and in some instances can be cured.
Why is hepatitis C a health concern?
Many people infected with HCV do not know they have the virus because symptoms can take two to six months to appear and the majority of people will not develop symptoms. During this time, they can spread the infection to others. You may not know you have this infection until damage has already been done to your liver. Potential complications from chronic hepatitis C include cirrhosis of the liver, liver failure, liver cancer and premature death.
Why do I need my liver?
How is hepatitis C virus spread?
Organization:
The most common risk factors for HCV infection include:
What are the symptoms of hepatitis C?
How can I find out if I have hepatitis C?
How can I protect myself and others against HCV?
What if I have hepatitis C?
Remember:
Read Also: Hepatitis C Ab W Reflex Hcv Rna Quant Rt Pcr
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis C
Doctors treat hepatitis C with antiviral medicines that attack the virus and can cure the disease in most cases.
Several newer medicines, called direct-acting antiviral medicines, have been approved to treat hepatitis C since 2013. Studies show that these medicines can cure chronic hepatitis C in most people with this disease. These medicines can also cure acute hepatitis C. In some cases, doctors recommend waiting to see if an acute infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
Your doctor may prescribe one or more of these newer, direct-acting antiviral medicines to treat hepatitis C:
You may need to take medicines for 8 to 24 weeks to cure hepatitis C. Your doctor will prescribe medicines and recommend a length of treatment based on
- which hepatitis C genotype you have
- how much liver damage you have
- whether you have been treated for hepatitis C in the past
Your doctor may order blood tests during and after your treatment. Blood tests can show whether the treatment is working. Hepatitis C medicines cure the infection in most people who complete treatment.
Hepatitis C medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Check with your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
Hcv Morphology And Parameters
HCV is a small, enveloped, positive single-stranded RNA virus that belongs to the Flaviviridae family, genus Hepacivirus. Analysis of viruses from plasma and from cell culture supernatant indicated that enveloped particles are icosahedral and 56-65 nm in diameter, while and the viral core is about 45 nm. Viral spikes on the membrane of the virion are about 6 nm and they are formed by heterodimers of E1 and E2 glycoproteins. In fact, the population of the extracellular HCV particles is heterogeneous. Particles are pleomorphic and size, buoyant density, and infectivity might differ significantly. A large majority of particles is non-infectious. Interestingly, the buoyant densities of infectious particles isolated from serum and from cell culture medium are different. A significant amount of the particles are associated with cellular lipoproteins making that a hallmark mark of HCV. The pattern of virus-associated lipoproteins might differ and several of those are associated with HCV most frequently: low density lipoproteins , very low-density lipoproteins and apolipoproteins A1, B, C and E . The viral particles associated with lipoproteins are called lipoviral particles . More details on LVP are given in Virus assembly and release section. Detailed update on HCV-associated lipoproteins is given in the review by Grassi et al.
Read Also: How Hepatitis C Affects The Body
How Long Does It Last
Hepatitis A can last from a few weeks to several months.
Hepatitis B can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious, life-long condition. More than 90% of unimmunized infants who get infected develop a chronic infection, but 6%10% of older children and adults who get infected develop chronic hepatitis B.
Hepatitis C can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious, life-long infection. Most people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop chronic hepatitis C.
Medications For Hepatitis C
Many different medications can treat hepatitis C. Treatments most often include antivirals, with Riboviria sometimes prescribed if previous treatments were ineffective.
Medications called direct-acting antivirals work to fully remove the hepatitis C virus from your body while helping prevent liver damage at the same time.
A few brand names of these medications include:
- Zepatier
6 different genotypes , or strains, of hepatitis C.
Once your doctor or other healthcare professional knows your genotype, theyll have a better idea of which medication will work best for you. Some strains have developed a resistance to some medications, so your genotype can affect your treatment options.
Don’t Miss: Can You Donate Blood If You Had Hepatitis A
Why Do So Many People In The Us Have Hepatitis C
Like the slow, silent serial killers found in society, the hepatitis C virus has slowly and methodically infected many people. Initially people infected with hepatitis C do not realize they are infected with the hepatitis C virus until, for many individuals, the disease becomes untreatable and death is the outcome. However, serial killers in society are caught and stopped. Usually when their pattern of attacks are recognized and then publicized so people understand how to protect themselves from attack, or if being attacked, how to defend themselves. The killer, hepatitis C virus, is now better understood so that an initial outcry may be heard and heeded.
Identification Of The Hepatitis C Virus
HCV was first recognized in 1989 using recombinant technology to create peptides from an infectious serum that were then tested against serum from individuals with non-A, non-B hepatitis. This approach resulted in the isolation of a section of the HCV genome. Subsequently, the entire HCV genome was sequenced. HCV is a member of the family of flaviviridae. Flaviviruses are positive, single-stranded RNA viruses. The HCV genome encodes a gene for production of a single polypeptide chain of approximately 3000 amino acids. This polypeptide gives rise to a number of specific proteins. The Env proteins are among the most variable parts of the peptide chain and are associated with multiple molecular forms in a single infected person. The mutations affecting this portion of the HCV genome seem to be critical for escape of the virus from the host immune response. The HCV protein NS5a contains an interferon-response element. Evidence from several studies suggest that mutational variation in the HCV genome encoding this protein are associated with resistance to interferon, the main antiviral agent used in treatment of HCV. Other proteins encoded by the HCV genome include the NS3 region that codes for a protease and the NS5b region that codes for an RNA polymerase. Drugs that target the HCV protease or polymerase are now undergoing trials as therapeutic agents to treat HCV infection.
Stuart C. Ray, David L. Thomas, in, 2015
Also Check: How Does Someone Get Hepatitis B
Living With Hepatitis C Infection
Many people are living with hepatitis C. If you have hepatitis C, there are several important things that you can do to help yourself and others such as:
- Eat a healthy diet and get plenty of rest.
- To avoid further liver damage:
- Do not drink alcohol.
- Do not take medicine that can cause liver damage .
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis A & B if you are not already immune.
- Do not to pass the infection to anyone else by taking the following precautions, such as:
- Do not share toothbrushes or razors with others.
- Do not to let anyone else come into contact with your blood, urine or feces.
- Use condoms during sexual activity.
- Limit the number of sex partners you have.
- If you use injection drugs, do not share needles or syringes with anyone else.
- It is best to not get tattoos or body piercings.
Although often uncomfortable, you should notify your partner of your hepatitis C prior to having sex. You also must notify all your health care professionals of your infection, so they can take precautions.
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis C
People more likely to get hepatitis C are those who
- have injected drugs
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- have hemophilia and received clotting factor before 1987
- have been on kidney dialysis
- have been in contact with blood or infected needles at work
- have had tattoos or body piercings
- have worked or lived in a prison
- were born to a mother with hepatitis C
- are infected with HIV
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have or had sex with men
In the United States, injecting drugs is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.13
Don’t Miss: How Long Is Hepatitis C Treatment
The Natural History Of Hepatitis C Virus Infection
Stephen L. Chen12, Timothy R. Morgan12
1. Gastroenterology Section, VA Medical Center, Long Beach, California2. Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University of California-Irvine, Irvine, California
Citation:Int J Med Sci
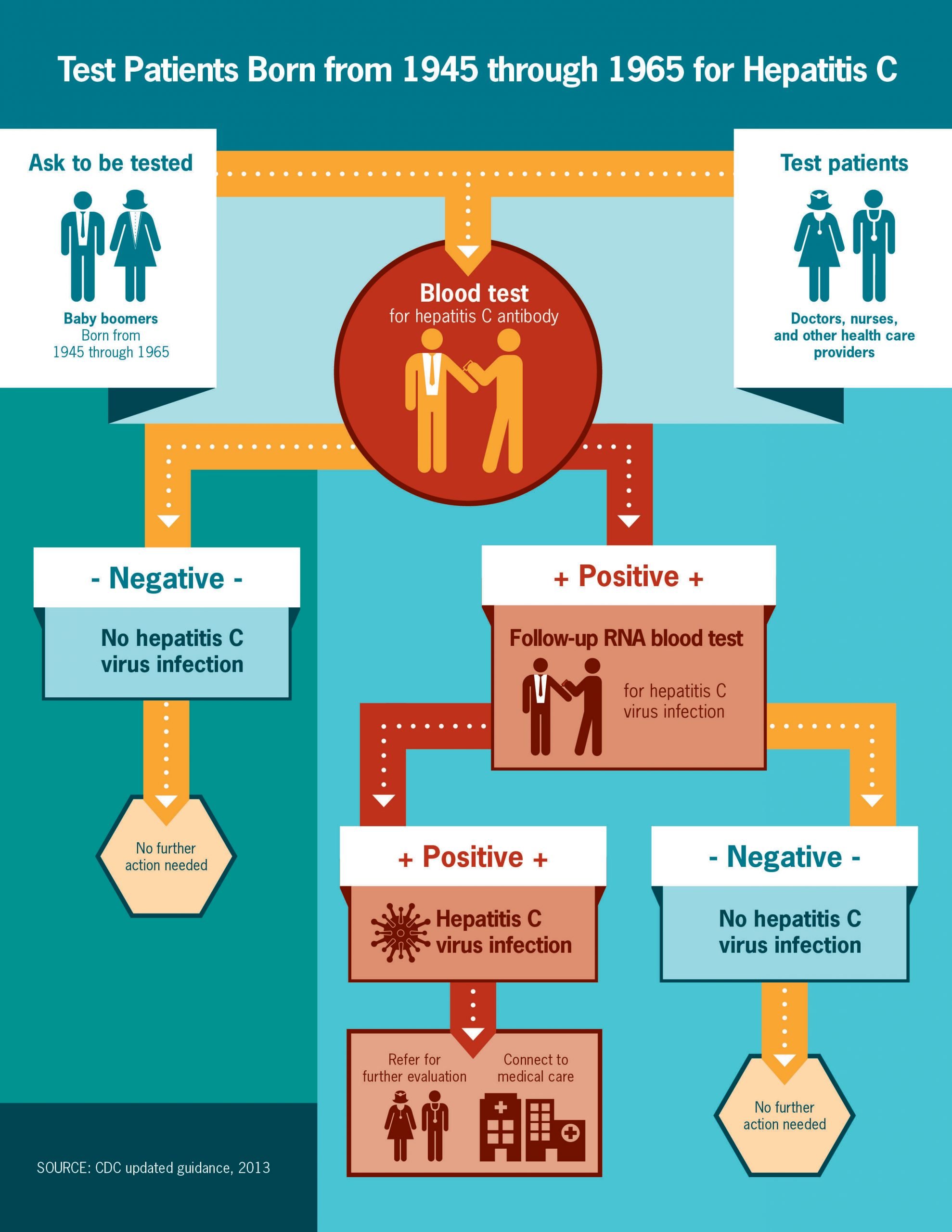
Why It Is Done
Hepatitis C virus testing is done to:
- Find out if a hepatitis C infection is the cause of abnormal liver function tests.
- Screen people who have an increased chance of getting or spreading a hepatitis C infection.
- Screen potential blood donors and donor organs to prevent the spread of hepatitis C.
- Screen people born from 1945 to 1975. People in this age group are more likely to have hepatitis C and not know it.
- Identify the type of hepatitis C virus causing the infection.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine During Pregnancy
Ive Never Used Iv Drugs Or Been Stuck With A Dirty Needle How Did I Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is usually spread through direct contact with the blood of a person who has the disease. It can also be transmitted by needles used for tattooing or body piercing. In rare cases, hepatitis C can be passed from a mother to her unborn baby. This virus can be transmitted through sex and sharing razors or toothbrushes. These occurrences are also rare. Many times, the cause of hepatitis C is never found.
What Is The Treatment For People With Acute Hepatitis C Infection
When people first get hepatitis C, the infection is said to be acute. Most people with acute hepatitis C do not have symptoms so they are not recognized as being infected. However, some have low-grade fever, fatigue or other symptoms that lead to an early diagnosis. Others who become infected and have a known exposure to an infected source, such as a needlestick injury, are monitored closely.
Treatment decisions should be made on a case-by-case basis. Response to treatment is higher in acute hepatitis infection than chronic infection. However, many experts prefer to hold off treatment for 8-12 weeks to see whether the patient naturally eliminates the virus without treatment. Approaches to treatment are evolving. Patients with acute hepatitis C infection should discuss treatment options with a health care professional who is experienced in treating the disease. There is no established treatment regimen at this time.
How effective is hepatitis C treatment? Is hepatitis C curable?
If the hepatitis C RNA remains undetectable at the end of the treatment and follow-up period, this is called a sustained virologic response and is considered a cure. Over 90% of people treated with DAAs are cured. These people have significantly reduced liver inflammation, and liver scarring may even be reversed.
About 5% of people who are treated for HCV infection are not cured by some of the older regimens. These people may still have options for cure with the newer regimens.
Read Also: How Much Is Hepatitis B Vaccine
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- Do I need treatment?
- What treatment is best for me?
- What medicines should I take?
- Are there any medicines I should avoid?
- How can I cope with the side effects of treatment?
- Is there a therapist I can talk to?
- How long will my treatment last?
- Can hepatitis C be cured?
- Are organ transplants and blood transfusions safe?
- Is it safe for me to get pregnant?
Cost Of Hepatitis C Medicines
The newer direct-acting antiviral medicines for hepatitis C can be costly. Most government and private health insurance prescription drug plans provide some coverage for these medicines. Talk with your doctor about your health insurance coverage for hepatitis C medicines.
Drug companies, nonprofit organizations, and some states offer programs that can help pay for hepatitis C medicines. If you need help paying for medicines, talk with your doctor. Learn more about financial help for hepatitis C medicines.
Also Check: What Are The First Symptoms Of Hepatitis C In Adults
How Is Hepatitis C Transmitted
Because HCV is primarily spread through contact with infected blood, people who inject drugs are at increased risk for HCV infection. HCV can also be transmitted from an infected mother to child at the time of birth, from unregulated tattoos or body piercings, and from sharing personal items that may be contaminated with infected blood, even in amounts too small to see. Much less often, HCV transmission occurs through sexual contact with an HCV-infected partner, especially among people with multiple sex partners and men who have sex with men. Currently in the United States, health care related transmission of HCV is rare, but people can become infected from accidental needle sticks and from breaches in infection control practices in health care facilities.
What Are The Complications Of Undiagnosed Hepatitis C
- Hepatitis C is known to be associated with two skin conditions, lichen planus and porphyria cutanea tarda.
- Diabetes, heart disease, and arterial blockage are more common among patients with chronic hepatitis C infection than in the general population. It may be that liver damage and chronic inflammation caused by hepatitis C may affect the levels of blood fats and blood sugar.
- Low platelet counts may occur as a result of the destruction of platelets by antibodies.
Don’t Miss: Where Do I Get A Hepatitis A Vaccine
Hcv Pseudotype Virus Particles
The HCV pseudotyped particles were constructed with chimeric genes expressing HCV envelope E1 and E2 proteins and the transmembrane and cytoplasmic tail of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein. The pseudotyped particles allowed a detailed study of the role of HCV receptors in the early steps of HCV infection in Huh7 cells and primary human hepatocytes. The system is useful for testing of new antiviral drugs.
Extrahepatic Manifestations Associated With The Hcv Infection
At least, one clinically significant extrahepatic manifestation occurs in 38% to 76% of HCV infected patients with chronic HCV. The most frequent associated pathology is a mixed cryoglobulinemia. It is detected in 19% to 50% of HCV infected patients, while only 15% of them are symptomatic. The cryoglobulins are immunoglobulins which precipitate at a temperature below 37 °C. They are produced by HCV activated B cells. The cryoglobulins deposed in small and medium vessels are the cause of systemic vasculitis which can manifest in level joint, skin, renal or peripheral nerves. Other observed extrahepatic manifestations are the following: lymphoma, thyroid disorders, diabetes, xerostomia and xerophthalmia. The HCV infection cure leads to a gradual decrease of the cryoglobulin level in serum, followed by the remission of cryoglobulin-related symptoms and pathologic lesions. Interestingly, as a result of treatment the incidence of type 2 diabetes is also reduced by approximately two thirds.
You May Like: Is There Now A Cure For Hepatitis C