Concurrent Administration Of Vaccines
HB-containing vaccines may be administered concomitantly with other vaccines or with HBIg. Different injection sites and separate needles and syringes must be used for concurrent parenteral injections.
Refer to Timing of Vaccine Administration in Part 1 for additional information about concurrent administration of vaccines.
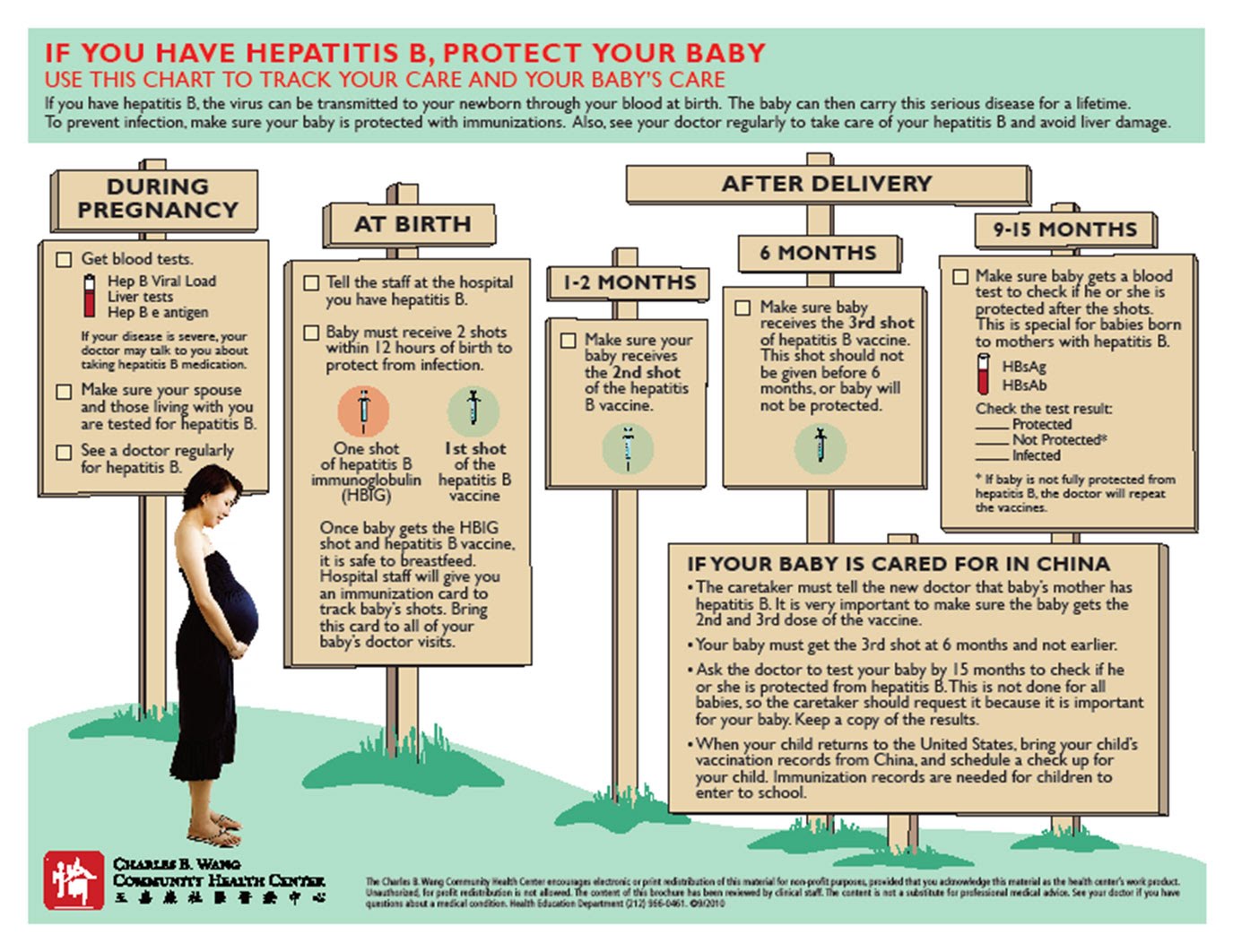
Hepatitis B Vaccination In Pregnancy
Hepatitis B infection in pregnant women may result in severe disease for the mother and chronic infection for the baby.
This is why the hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for pregnant women who are in a high-risk category.
There’s no evidence of any risk from vaccinating pregnant or breastfeeding women against hepatitis B.
And, as it’s an inactivated vaccine, the risk to the unborn baby is likely to be negligible .
Appendix : Legal Permissions To Collect Personal Information
PHE has been given responsibility by the Secretary of State for Health and Social Care to act to protect and improve the nations health and reduce health inequalities. To do this, the law on data protection allows us to use personal information. We are trained to use personal information and treat this in the strictest confidence, in compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation and the NHS Caldicott principles. Our staff have the same duty as other healthcare professionals to maintain confidentiality.
PHEIDPS programme and National Infection Service has legal permission to collect and process patient identifiable information without the need to seek consent from individual patients under Regulation 3 of the Health Service Regulations 2002.
The service also conforms to the requirements of the Data Protection Act .
For queries or further information from healthcare professionals about information governance and data protection please contact:
Also Check: Who Needs To Be Tested For Hepatitis C
Safety Of Immunization In Pregnancy For The Fetus And Infant
There is no theoretical reason to anticipate adverse events in the fetus or infant following vaccination with inactivated vaccines during pregnancy. There are no published data indicating that currently authorized inactivated vaccines are teratogenic or embryotoxic or have resulted in specific adverse pregnancy outcomes.
The National Advisory Committee on Immunization has concluded that vaccines that contain thimerosal are safe in pregnancy and should be used if indicated.
In general, live attenuated viral or bacterial vaccines are contraindicated in pregnancy, as there is a theoretical risk to the fetus however, when benefits outweigh this theoretical risk, vaccination with a live attenuated vaccine may be considered .
Immunization Of Household Contacts Of Pregnant Women
Pregnancy in a household does not affect immunization indications for any other members of the household. Indeed, pregnancy should be used as an opportunity to update immunization of susceptible household contacts, including live vaccines such as rotavirus, MMR, MMRV, varicella, zoster and LAIV.
In the unlikely event of a household contact being vaccinated against smallpox, extreme precautions should be taken to prevent transfer of the vaccinia virus to unvaccinated household and other close contacts, pregnant or not. Such precautions can include isolation of the vaccinee from pregnant household contacts until the vaccine scab falls off.
Recommended Reading: What Medication Cures Hepatitis C
Acute And Chronic Infection
Within the first 6 months after exposure to HCV, nearly 75% of exposed persons will remain asymptomatic. Others may develop nonspecific abdominal pain, nausea, anorexia, jaundice, or malaise. Without treatment, up to 60% will progress to chronic HCV infection. Chronic HCV infections are a major cause of chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma around the world.
HCV infection in pregnancy can lead to a variety of sequelae. During pregnancy, the maternal immune response is dampened, which is believed to offset the immune-mediated hepatocyte damage from HCV. Clinically, this often results in a decrease in serum maternal liver enzymes, such as alanine aminotransferase , during the second half of pregnancy and a rise in the HCV viral load. Thus, it is not recommended to trend liver function during pregnancy.
Other associations of HCV infection in pregnancy include gestational diabetes, especially in the setting of excessive weight gain in pregnancy. There is also 20 times the odds of developing intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. HCV infection in pregnancy has consistently been associated with poorer fetal outcomes, including fetal growth restriction and low birth weight. A growth scan in the third trimester is recommended for women with HCV infection in pregnancy.
Delivery Suite And Postnatal Management Of Women With Lower Infectivity
There should be agreed protocols in place to ensure an MDT approach to caring for women with HBV when they present in labour.
Actions required
- informing the screening team of the womans admission
- arranging administration of monovalent hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of the babys birth
- completion of the PHCR red book hepatitis vaccination page
- notify screening team of birth and returning notes and checklist to the team
Read Also: Treatment To Cure Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Vaccine On The Nhs
A hepatitis B-containing vaccine is provided for all babies born in the UK on or after 1 August 2017. This is given as part of the 6-in-1 vaccine.
Hospitals, GP surgeries and sexual health or GUM clinics usually provide the hepatitis B vaccination free of charge for anyone at risk of infection.
GPs are not obliged to provide the hepatitis B vaccine on the NHS if you’re not thought to be at risk.
GPs may charge for the hepatitis B vaccine if you want it as a travel vaccine, or they may refer you to a travel clinic for a private vaccination. The current cost of the vaccine is around £50 a dose.
Delivery And Receipt Of Hbig And Hepatitis B Delivery Suite Box
The request for HBIG will prompt delivery to the screening coordinator of the PHE hepatitis B delivery suite box containing instructions for HBIG or vaccination, maternal serology sample and neonatal HBVDBS.
HBIG will be delivered by a logistics company in cold chain to the hospital pharmacy department approximately 7 weeks prior to the EDD. The HBIG pack will consist of:
- the HBIG vial
- a delivery note which quotes PHE Ref No: XXXX
- an information leaflet for pharmacy which states the HBIG has been issued for a named baby
The screening coordinator is responsible for matching up the named baby HBIG vial from pharmacy with the named baby hepatitis B delivery suite box and ensure these are stored securely according to local arrangements so that they are available for that named baby at all hours of the day to the delivery suite team. The storage location of the HBIG and delivery suite box should be documented in the maternal notes.
Also Check: How Is Hepatitis C Virus Transmitted
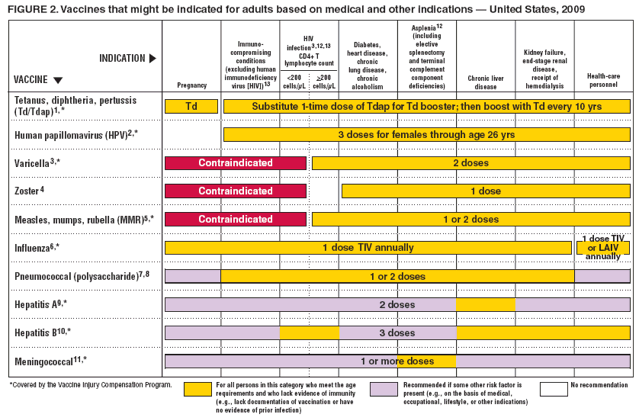
Vaccines That May Be Indicated
Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine
Hib vaccine should be considered in pregnancy if indicated for a medical condition at high risk for Hib disease. Although Hib vaccine has not been studied in pregnancy, there is no theoretical reason to suspect that adverse events to mother or infant will occur. Refer to Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine in Part 4 and Immunization of immunocompromised persons and Immunization of persons with chronic diseases in Part 3 for additional information.
Hepatitis A vaccine
Hepatitis A can cause severe disease in pregnancy, and the vaccine should be considered for pregnant women when indicated for post-exposure prophylaxis, for travel to endemic areas or for other exposure risks. The efficacy and safety of hepatitis A vaccines given during pregnancy has not been studied in clinical trials, but there is no evidence of, or theoretical reason to suspect an increased risk of adverse events to the mother or the infant. Refer to Hepatitis A vaccine in Part 4 for additional information.
Meningococcal vaccine
Conjugate quadrivalent meningococcal vaccine and meningococcus B vaccine should be considered in pregnancy, if indicated in circumstances such as a medical condition at high risk for meningococcal disease travel to a high risk area post-exposure prophylaxis or during an outbreak. Although these vaccines have not been studied in pregnancy, there is no theoretical reason to suspect that adverse events to mother or infant will occur.
Eligibility For Nhs Treatment
The diagnosis and treatment of viral hepatitis is included in the list of services exempt from charges irrespective of residency and status, including asylum seekers, refugees and their dependants. In addition, failed asylum seekers are exempt for charges for maternity care as well as diagnosis and treatment of communicable diseases.
These mothers and their infants should be treated according to the clinical guidelines and HBIG, and vaccination ordered and prescribed accordingly.
Further information on NHS entitlements and immunisation for migrants.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Virus Surface Ab
Management Of A Baby Whose Mother Is Hepatitis B Negative But Another Household Member Is Hepatitis B Infected
Newborn infants born to a hepatitis B negative woman but known to be going home to a household with another hepatitis B infected person may be at immediate risk of exposure to hepatitis B virus. In these situations, a monovalent dose of hepatitis B vaccine can be offered before discharge from hospital to provide some protection before routine immunisations begin. Infants should then continue the routine childhood schedule commencing at 8 weeks.
If infants have received the routine schedule and there has not been any known significant exposure to the infected household member then they do not require testing at 12 months of age because they have not been exposed vertically.
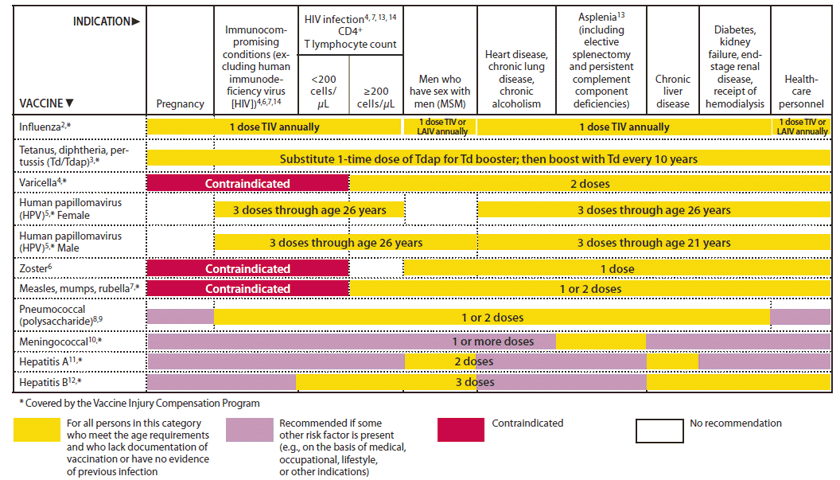
Which Vaccines Can I Receive While I Am Pregnant
The following vaccines are considered safe to give to women who might be at risk of infection:
- Hepatitis B: Pregnant women who are at high risk for this disease and have tested negative for the virus can receive this vaccine. It is used to protect the mother and baby against infection both before and after delivery.
- Influenza: This vaccine can prevent serious illness in the mother during pregnancy. You can receive the vaccine at any stage of your pregnancy. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends all pregnant women should receive the flu shot.
- Tetanus/Diphtheria/ : Tdap should be administered during pregnancy, preferably during the third trimester or late second trimester . If you or your family members did not receive this vaccination during pregnancy, Tdap should be administered immediately postpartum while in the hospital to ensure pertussis or whooping cough immunity and reduce the risk of transmission to the newborn. The CDC recommends that all pregnant women receive this vaccine, please accept this vaccine for the safety of you and your baby.
Read Also: How Does One Catch Hepatitis B
Persons New To Canada
Health care providers who see persons newly arrived in Canada should review the immunization status and update immunization for these individuals, as necessary. In many countries outside of Canada, HB vaccine is in limited use.
All persons from a country that is endemic for HB should be assessed and vaccinated against HB if not immune and not infected. Individuals born in developing countries are more likely to be carriers of HB, necessitating vaccination of their sexual and household contacts based on review of their serologic test results. HB vaccine is recommended for all household contacts whose families have immigrated to Canada from areas in which there is a high prevalence of HB and who may be exposed to HB carriers through their extended families or when visiting their country of origin.
Children adopted from countries in which there is a high prevalence of HB infection should be screened for HBsAg and, if positive, household or close contacts in the adopting family should be immunized before adoption or as soon as possible thereafter. Adults going to pick-up children from these countries should be vaccinated before departure. Refer to Immunization of Persons New to Canada in Part 3 for additional information.
What Are The Risks When You Are Given A Blood Product Eg Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin
As with any medical procedure, blood products such as hepatitis B immunoglobulin carry some risks. Some of the risks are:
- severe inflammatory reactions: these are very rare and can be treated
- mild inflammatory reactions: any vaccine/injection may cause a rash or rise in temperature
- infection from the injection. However, serious infections from blood products are extremely rare because of the careful selection and testing of donors.
The chance of serious problems is low. Although there have been rare reports of variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease being spread by blood, any person with a known risk of contracting vCJD is excluded from donating blood.
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis The Same As Hiv
Actions For Chrd Or Chis
To support scheduling of the 4-week and 12-months dose and testing the CHRD or CHIS could
- schedule a paper or email reminder to the practice when the baby is approaching 2 weeks old alerting them to arrange an appointment for the 4-week dose
- include in the text of the reminder that:
- the vaccination is post exposure treatment to prevent chronic infection, liver disease and cancer so it is important that vaccine is given on time
- the practice can claim reimbursement for the dose from NHS Business Services Authority using form FP43
Women Who Are Living With Hepatitis B
Women who are living with hepatitis B should be offered screening in the current pregnancy to provide a failsafe mechanism to ensure a current result is available on the trusts reporting system. It should not be presumed that women who are living with hepatitis B fully understand their condition, the implications for their current pregnancy and the current treatment and care regimes available in the UK.
Also Check: Does Hepatitis C Have A Vaccine
Safety Of Immunization In Pregnancy For The Mother
Inactivated vaccines are considered to be safe when administered in pregnancy. Reactions following vaccination with inactivated vaccines are usually limited to the injection site. No increase in anaphylactic reactions or events that might induce preterm labour has been observed following immunization with inactivated vaccines.
Benefits Of Early Detection And Interventions
The USPSTF found convincing evidence that universal prenatal screening for HBV infection substantially reduces perinatal transmission of HBV and the subsequent development of chronic HBV infection. The USPSTF found adequate evidence that vaccination of all infants against HBV infection and providing postexposure prophylaxis with hepatitis B immune globulin at birth to infants of mothers infected with HBV substantially reduce the risk for acquisition of HBV infection in infants.
Don’t Miss: Where To Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Management Of Close Family Contacts Of A Hepatitis B Infected Pregnant Woman
Sexual partners of infected women are most at risk of HBV transmission, and they and close family and household contacts should be vaccinated and tested as per Green Book guidance.
Actions required
The screening team should inform the GP of the mother so that the family contacts can be tested and vaccinated appropriately:
- advice given to the mother and her partner that protection such as condoms should be used until he is immunised or found to be infected
- all close family /household and sexual contacts should have blood taken at the time of the first dose of vaccine to determine if they have already been infected
- contacts shown to be HBsAg, anti-HBs or anti-HBc positive do not require further immunisation otherwise a hepatitis B immunisation schedule should be followed
- post vaccination testing for immune response is not required in healthy contacts
- contacts shown to be HBsAg positive that is, have evidence of current hepatitis B infection should be referred for specialist management
Management Of Lower Infectivity Pregnancies
Following the screening assessment consultation, the screening team should refer the woman to the specialist team as per local arrangements dependant on whether she is a new diagnosis or known HBV positive woman.
- lower infectivity, known positive within 18 weeks as per NHS England referral to treatment target
- lower infectivity, new diagnosis within 6 weeks regardless of infectivity status IDPS Standard SO6
Actions required
The screening team should:
- refer pregnant woman to the specialist team
- notify the GP, Health Visitor, Child Health Information Service and Health Protection Team of the positive result and plans for care
- create a neonatal alert to ensure timely administration of neonatal vaccination on delivery suite within 24 hours of delivery
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Can You Get Rid Of It
Hepatitis A Adult Vaccine / Hepatitis B Adult Vaccine Pregnancy Warnings
The manufacturer makes no recommendation regarding use during pregnancy.AU TGA pregnancy category: B2US FDA pregnancy category: Not assigned:-There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of this vaccine in pregnant women, but available data do not indicate an increase in major birth defects or miscarriage when given within 28 days prior to conception or during pregnancy.-An animal developmental toxicity study showed no adverse effects on fetal or pre-weaning development when given prior to mating and during gestation.
How Do I Know If A Vaccine’s Ingredients Are Safe
All vaccines are tested for safety under the supervision of the Food and Drug Administration . The vaccines are checked for purity, potency, and safety, and the FDA and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention monitor the safety of each vaccine for as long as it is in use. Some people might be allergic to an ingredient in a vaccine, such as eggs in the influenza vaccine, and should not receive the vaccine until they have talked to their doctors.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer