What Is The Normal Range For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are measured in blood samples in milli-International Units/milliliter mIU/mL). The ranges for hepatitis B surface antibodies are:
- Anti-HBs greater than 10-12 mIU/mL: Protected against hepatitis B virus infection, either from vaccination or successful recovery from a previous HBV infection.
- Anti-HBs less than 5 mIU/mL: Negative for HBV infection, but susceptible and hence requires vaccination.
- Anti-HBs from 5-12 mIU/mL: Inconclusive results and the test should be repeated.
However, there is no standardization of these values so it is advisable to check the manufacturers values it is the reason values are mainly reported as positive or negative.
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Surface Antibody And Antigen
An antigen is a substance that induces antibody production. Hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
Hepatitis B Blood Tests
The Hepatitis B Panel of Blood Tests
Only one sample of blood is needed for a hepatitis B blood test, but the Hepatitis B Panel includes three parts. All three test results are needed to fully understand whether a person is infected or not. Below is an explanation of the 3-part Hepatitis B Panel of blood test results.
Read Also: What Vitamins Are Good For Hepatitis B
Data Analysis And Statistics
All analyses were done using nonparametric statistical software with penalized maximum likelihood to remove first-order bias. A p-value < 0.05 for two-sided tests was considered statistically significant. Continuous variables were expressed as means plus/minus standard deviation or mean , categorical variables as numbers . Conditional logistic regression analysis was used to estimate risk ratios and 95% confidence intervals for loss of anti-HBs putative associated factors included age, sex, type of rheumatic disease, conventional DMARDs, biologic DMARDs , comorbidity, and baseline anti-HBs titer.
What Is A Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test
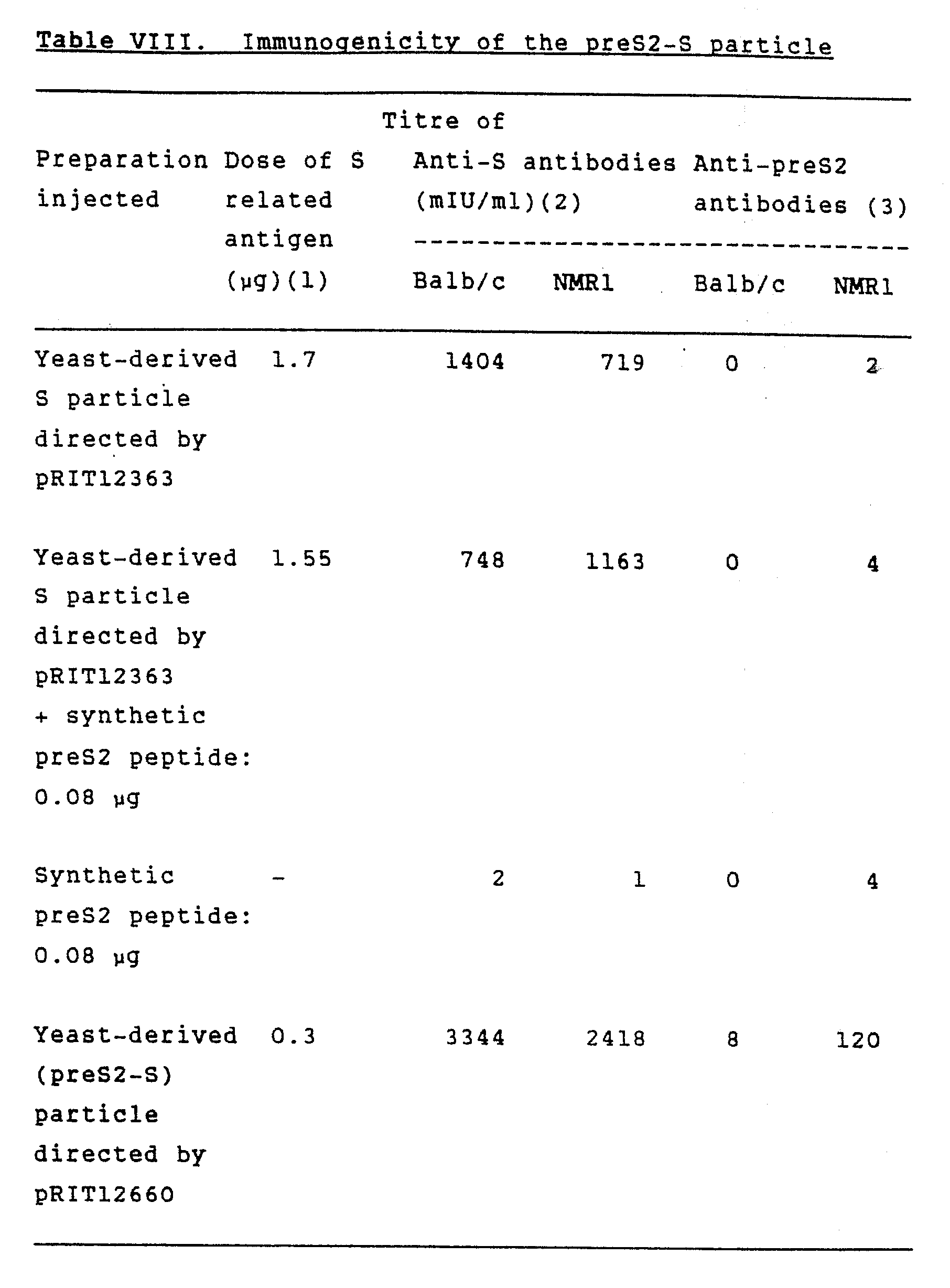
Hepatitis B surface antibody test is part of a panel of blood tests to diagnose HBV infection. Hepatitis B surface antibody test determines the presence and quantity of anti-HBs in the blood serum, which can indicate protection from HBV infection.
Hepatitis B disease affects the liver and commonly spreads through body fluids such as blood, semen, and vaginal secretions.
Don’t Miss: My Husband Has Hepatitis A Can I Get It
Hbv Viral Load Determination
HBV viral loads from stored sera were determined using a real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay with a lower limit of detection of 100 copies/mL . Briefly, HBV DNA was extracted from stored serum specimens using the MagNA Pure Compact System and Total Nucleic Acid Extraction Kit I according to the manufacturer’s instructions . Subsequently, a 118-bp fragment of the core gene was amplified, and HBV viral loads were determined by comparison to a set of HBV DNA standards amplified in parallel with the samples being tested.
Demographic Characteristics And Clinical Status
The analytic samples drawn from 294 patients with HBsAg/anti-HBs+serostatus at baseline, comprised 23 cases and 311 matched controls Table shows their demographic and clinical characteristics. Mean age and rheumatic disease types were similar between case and control groups. No patients with HBsAg/anti-HBs+serostatus had detectable HBV DNA at enrolment. Compared with controls, cases had lower baseline serum anti-HBs titers, more prevalent comorbidities , and relatively higher accumulated doses of sulfasalazine, leflunomide, and prednisolone. Most people in both groups used anti-TNF agents . No study subjects were kidney transplant recipients.
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of cases and controls treated with biologic DMARDs
No cases had clinical HBV reactivation during follow-up , and no cases developed alanine transaminase elevation, or received any anti-viral treatment during median follow-up of 30months after anti-HBs loss. Only one of the 16/23 cases whose serum HBV DNA was monitored after anti-HBs loss ever had a detectable viral load , which was observed only once, with no recurrence as of August 2020.
You May Like: How Is Hepatitis C Transmitted
Measures Of Immune Response And Duration Of Immunity/protection
In high-risk individuals who have had titers checked after primary HB immunization, a small percentage of apparently healthy recipients do not mount a detectable response to the vaccine. This failure to respond is related to factors such as age , male gender, smoking, obesity, HIV infection, or chronic disease. Persons > 40 years of age have an immune response < 90%, whereas only 65%75% of persons > 65 years of age develop protective anti-HBs antibody levels.29 For persons with these risk factors and who are at high risk of HB exposure, a postvaccination serology 16 months after the last dose should be done. Patients without detectable anti-HBs titers after primary series should begin a standard three-dose series and have serology 1 month after each dose for up to three doses until they seroconvert, or may wait until the three additional doses are administered before being tested. A similar approach can be taken for health care providers who have received a complete HB series but have undetectable anti-HBsAg titers.
MICHAEL R. CHARLTON, K. V. NARAYANAN MENON, in, 2005
Defective Surface Antigen Mutation And Hbv Biology
HBsAg mutants were first identified in individuals vaccinated against HBV but who were infected despite the presence of protective anti-HBs antibodies. Those immune escape mutants with aa substitutions within a-determinants were found in different clinical settings, including vaccines, transplant patients receiving hyperimmunoglobulins, and immunocompromised patients with HBV reactivation. Such mutant HBsAg commonly showed reduced binding to anti-HBs antibodies and decreased reactivity in established HBsAg detection assays. The most widely known mutation is the sG145R mutation, which has been shown to be replication competent, may persist stably over time, and may be transmitted vertically or horizontally. The sG145R mutation induces a strongly impaired anti-HBs antibody response, which could not efficiently clear HBsAg in an HBV hydrodynamic injection mouse model. A similar result was also observed for another immune escape mutation, sK122I, indicating that such a defective surface antigen mutation may impair HBsAg neutralization and clearance during HBV infection. In addition, sG145R, sK122I, and other immune escape mutants occurring in the a-determinant of SHBs, such as the sT123N mutation, could affect HBsAg secretion.
Recommended Reading: Initial Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Understanding The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test
- Get link
The hepatitis B surface antibody test , looks for antibodies that your immune system makes in response to the surface protein of the hepatitis B virus. The hepatitis B surface antibody is also referred to as anti-HBs and should not be confused with HBsAg, which stands for hepatitis B surface antigen.& nbsp
Question 1 What Is The Clinical Indication For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quantitation
Hepatitis B surface antibody quantitation is used to determine hepatitis B immune status, ie, to determine if the patient has developed immunity against the hepatitis B virus. Such immunity may develop following exposure to the hepatitis B virus or its vaccine.
Patients at higher risk of exposure to the virus include:
- Infants born to infected mothers
- Sex partners of infected persons
- People with more than 1 sex partner in the last 6 months
- People with a history of sexually transmitted infection
- Men who have sex with men
- Injection drug users
- Household contacts of an infected person
- Healthcare and safety workers who have contact with blood and body fluids
- People who have lived or traveled in an area in which hepatitis B is common
- People who live or work in a prison
Testing is not recommended routinely following vaccination. It is advised only for people whose subsequent clinical management depends on knowledge of their immune status. These people include:
- Chronic hemodialysis patients
- Immunocompromised people, including those with HIV infection, hematopoietic stem-cell transplant recipients, and people receiving chemotherapy
- Infants born to women who test positive for the hepatitis B surface antigen
- Sex partners of people who test positive for the hepatitis B surface antigen
- Healthcare and public safety workers who have contact with blood or body fluids
Also Check: Can Hepatitis C Go Away On Its Own
Question 7 Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Antibody Always Acquired After A Completed Vaccination Protocol
No. After 3 intramuscular doses of vaccine, > 90% of healthy adults and > 95% of those < 19 years of age develop immunity .1 However, there is an age-specific decline in development of immunity. After age 40 years, about 90% of people become immune, but by age 60 years, only 75% of people become immune.1 Larger vaccine doses or an increased number of doses are required to induce immunity in many hemodialysis patients and in other immunocompromised people.1
References
This FAQ is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. A clinicians test selection and interpretation, diagnosis, and patient management decisions should be based on his/her education, clinical expertise, and assessment of the patient.Document FAQS.105 Revision: 0
Quest, Quest Diagnostics, the associated logo, Nichols Institute, and all associated Quest Diagnostics marks are the registered trademarks of Quest Diagnostics. All third-party marks®’ and ‘are the property of their respective owners. © 2000- 2021 Quest Diagnostics Incorporated. All rights reserved.Image content features models and is intended for illustrative purposes only.
Hbv Dna Hbv Genotype And Hbv Drug Resistance Assays
Specimen: Serum or plasma
Container: Red-top tube, yellow-top tube , gel-barrier tube, plasma preparation tube, or lavender tube
Collection method: Routine venipuncture
The specimen should be transfused to separate plasma/serum from cells within 6 hours and kept frozen when testing cannot be done promptly.
The tests use PCR amplification, DNA probe hybridization, and sequencing method.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Catch Hepatitis A
How Is The Hbcab Test Done
This is a blood test. A clinician will fill a tube with blood taken from a vein in your arm through which a needle is inserted. If you are giving blood, a sample will be taken from the blood you’re donating. The blood is sent to a lab, where it is tested. Sometimes HBcAb will be added on to lab orders when results from other tests indicate there may be a hepatitis B infection.
Defective Surface Antigen Mutations And The Host
Defective surface antigen mutations have been found in acute hepatitis B infection, chronic hepatitis B infection, and occult HBV infection and are associated with advanced liver disease, including liver cirrhosis, fulminant hepatitis B, and HCC. It has been questioned whether HBV mutants arise due to viral adaptation to inflammation and decreased liver function or, alternatively, causally contribute to liver pathogenesis. The mechanism of defective surface antigen mutations to HCC development has been widely elucidated. Here, we will emphasize in our discussion the relationship between defective surface antigen mutations and fulminant hepatitis B, as well as occult HBV infection.
Don’t Miss: New Medicine To Treat Hepatitis C
Defective Surface Antigen Expression And Fulminant Hepatitis
There is increasing evidence that defective surface antigen expression may play a role in the pathogenesis of fulminant hepatitis . preS deletions, particularly those unable to synthesize the MHBs protein, have been associated with cases of FH, suggesting the potential pathogenic role of preS deletions. A mutation in the CAAT element of the S promoter has been found in the HBV genome isolated from an FH patient. This mutation led to excessive LHBs expression over MHBs and SHBs proteins and resulted in virus retention and misassembly. Obviously, the accumulation of LHBs may be due to hepatocyte injury, as shown in transgenic mice with LHBs expression. One of our previous studies also identified deletions within the preS regions from HBV strains isolated from a patient with HBV-associated FH. In addition, a hepatitis B immune globulin -escape mutant sG145R on the HBsAg, causing 30% inhibition of virion secretion, has been identified from a study on FH strains, suggesting the potential role of defective surface antigen expression in the fulminant clinical course of HBV infection.
Results Of The Hbcab Test
There are two variations of antibodies. The IgM antibody is the largest antibody and the first produced in an infection. It shows that you may have a current, active infection. Sometimes it persists for years, but it usually drops to undetectable levels.
The HBcAb IgG variant is produced later in the course of the infection, and it’s likely that you will have a positive HBcAb IgG test the rest of your life.
The screening panel usually has a test that is for total HBcAb, which includes both IgM and IgG. The IgM test may be ordered to help determine if you have an acute infection.
A positive HBcAb test must be interpreted along with the results of the other tests. You may have an active or chronic infection, or you may be immune to hepatitis B due to past infection. Discuss the results with your healthcare provider. In any case, a positive HBcAb test means your blood or organs cannot be donated to a recipient.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Mode Of Transmission
Question 3 How Is The Quantitative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test Performed
An immunometric technique is used. The anti-HBs binds to HBsAg ad and ay subtypes, which are coated on the test wells. Binding of a horseradish peroxidase-labeled HBsAg conjugate to the anti-HBs completes the sandwich formation. Unbound materials are then washed away. In the next step, the horseradish peroxidase catalyzes oxidation of a luminogenic substrate, producing light. Light signals are detected and quantified. Intensity of the light is proportional to the amount of anti-HBs present in the patient sample. The result is standardized to an international unit system and reported as milliinternational units per milliliter .
Other Classes Of Hbsag Secretion Inhibitors
There are also other types of HBsAg secretion inhibitors. Immunosuppressive Mycophenolate active compound, MPA, is a monophosphate dehydrogenase inhibitor. It can inhibit HBsAg secretion in HepG2.2.15 cell line at low concentrations . The mechanism of HBsAg secretion inhibition by MPA underlies its potential to depleting cellular exogenous guanosine source and subsequently viral DNA polymerase inactivation .
Two mAbs C4G4 and D2H2 have been demonstrated to target two circularized epitopes within the HBsAg loop domain . A bispecific antibody, C4D2-BsAb, engineered from C4G4 and D2H2 mAbs has been shown to recognize two HBsAg loop domain epitopes in one time. This prevents interaction of HBV with its cellular surface receptor. Accordingly, pre-treatment of HepRG cells and treatment of cell line producing HBsAg, PLC/PRF/5, have shown remarked decrease of HBsAg secretion . C4D2-BsAb targets circularized epitopes within HBsAg loop domain, and it can be used for prevention therapy approaches . However, investigation of infected chimpanzees revealed short lasting of HBsAg suppression with antibodies . The C4D2-BsAb action may be through induction of conformational changes as well as conflicting with virusreceptors interactions.
You May Like: What Is Hepatic Steatosis Of The Liver
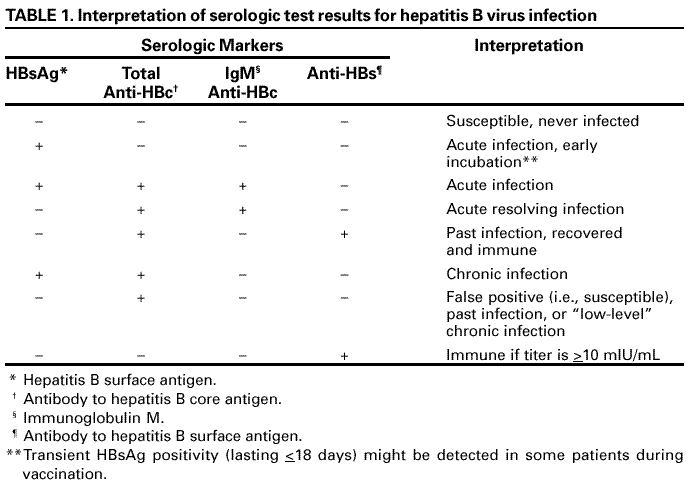
What Do Hepatitis B Test Results Mean
Hepatitis B test results help determine if HBV infection is negative or positive, and if positive, whether the infection is acute or chronic, or if recovery is complete. A combination of results are considered to identify and classify HBV infection status.
The following are some interpretations of hepatitis B test results:
Table: Hepatitis B test results and interpretations
| Test |
|---|
Question 5 What Is The Natural History Of Hepatitis B Surface Antibody During Acute Hepatitis B Infection And Convalescence

HBsAg can be detected in the blood 4 to 10 weeks after exposure. This corresponds to onset of symptoms and viremia detectable by nucleic acid amplification methods. Most hepatitis B infections are self-limited and are associated with disappearance of HBsAg within 4 weeks of onset of symptoms. The anti-HBs then appears and increases to a plateau level that persists indefinitely.2
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis B Virus Be Cured
Biology Of Hbv Surface Antigen
Three viral envelope/surface proteins – large surface antigens , middle surface antigens , and small surface antigens – are expressed from a single open reading frame , but they are translated from two different mRNAs. LHBs are encoded by the 2.4 kb subgenomic RNA, and MHBs and SHBs are encoded by the 2.1 kb subgenomic RNA. Subgenomic RNAs of 2.4 kb and 2.1 kb are driven by preS1 and preS2/S promoters, respectively, allowing variable regulation of protein expression. The preS1 promoter is situated within the upstream region of the S-ORF, whereas the preS2 promoter corresponds to the preS1 domain. Therefore, the transcription of the 2.1 kb subgenomic RNA is also regulated by the preS1 domain .
Hepatitis B Serologic Testing And Hbv Dna
HBV serology and DNA assays were done every 6months according to Taiwan Rheumatology Association recommendations . HBV assays included serum HBsAg, anti-HBs and anti-HBc, measured by Architect i2000SR chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay . HBV immunization history of people with anti-HBs+/anti-HBcserostatus was not ascertained.
Anti-HBs titer < 10 mIU/ml was defined as seronegative. Low anti-HBs titer was defined as 10100 mIU/ml, based on evidence of significantly increased likelihood of anti-HBs loss and detectable HBV DNA at anti-HBs titers below 100 mIU/ml and protection against HBV reactivation above this threshold . Serum HBV DNA viral load was quantified by Abbott RealTime HBV , with a minimal sensitivity of 10 IU/ml. HBV DNA titer 10 mIU/ml was defined as detectable viral load , while the criteria defining clinical HBV reactivation at any serial 6-monthly follow-up check, were HBV replication 2 log increase from baseline or a new appearance of HBV DNA to 100IU/ml in people with previously stable or undetectable levels .
Read Also: How Do They Treat Hepatitis C