Hepatitis C: Who Is At Risk
People who have injected illegal drugs at any time, even one time, many years ago, could be walking around with chronic hepatitis C. Because there are often no symptoms, many former drug users may not realize they have the infection. People who received a blood transfusion before 1992 also have a higher risk. Before that year, donated blood was not screened for the hepatitis C virus.
Can The Results Of Liver Panel Tests Point To The Presence Of Hepatitis C
A liver panel usually includes tests called AST, ALT, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, and some others. Abnormal results could show up in many different conditions, not just hepatitis C. And even if the results of a liver panel are normal, you might still have hepatitis C. So, the liver panel alone cannot tell your provider the answer.
Hepatitis C can be diagnosed only by blood tests that are specific to hepatitis C:
In short, if the results of one or more tests on a liver panel are abnormal, generally speaking, the tests should be repeated and confirmed. If the results remain abnormal, your provider should be prompted to look for the cause.
More important than using the liver panel, if you have risks of having been infected with hepatitis C then you should have the specific hepatitis C antibody test to determine if you have hepatitis C infection.
Chronic Hepatitis B Infection
If you develop chronic hepatitis B, youll be given treatment to reduce the risk of permanent liver damage and liver cancer. Treatment does not cure chronic hepatitis B and most people who start treatment need to continue for life.
Without treatment, chronic hepatitis B can cause scarring of the liver , which can cause the liver to stop working properly.
A small number of people with cirrhosis develop liver cancer, and these complications can lead to death. Other than a liver transplant, there is no cure for cirrhosis. However, treatments can help relieve some of the symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Reactive
Hiv And Hepatitis C Coinfection
HCV infection is common among people with HIV who also inject drugs. Nearly 75% of people living with HIV who report a history of injection drug use are co-infected with HCV. All people who are diagnosed with HIV are recommended to be tested for HCV at least once. People living with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HCV infection. Fortunately, direct acting antivirals that are used to treat HCV work equally well in people with and without HIV infection. For more information about HIV and HCV coinfection, visit the HIV.govs pages about hepatitis C and HIV coinfection.
- have been on kidney dialysis
- have been in contact with blood or infected needles at work
- have had tattoos or body piercings
- have worked or lived in a prison
- were born to a mother with hepatitis C
- are infected with HIV
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have or had sex with men
In the United States, injecting drugs is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.13
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
All newborn babies should get vaccinated. You should also get the shot if you:
- Come in contact with infected blood or body fluids of friends or family members
- Use needles to take recreational drugs
- Have sex with more than one person
- Are a health care worker
- Work in a day-care center, school, or jail
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine Side Effects
How Can You Prevent The Spread Of Hepatitis C
Now that you know how you get hepatitis C, you can take steps to protect yourself from the virus. For instance:
- Avoid sharing needles or other paraphernalia related to intravenous drugs.
- Wear gloves if youre a health care worker or otherwise exposed to needles or potentially infected blood.
- Use barrier methodsaka condomsoutside of sexually monogamous relationships.
- Dont share toothbrushes or other dental equipment, nail clippers, or shaving tools.
- If youre getting a tattoo or piercing, make sure the artist or piercer uses sterile ink and needles.
If you have the hepatitis C virus, you can prevent passing it along to others by following those same steps, in addition to:
- Covering any open sores or wounds.
- Telling all your health and dental care providers you have the virus.
- Avoiding donating blood.
Hepatitis C: How Does It Spread
It spreads through infected blood. In the U.S., sharing needles or other items used to inject drugs is the most common cause of infection. Getting a tattoo or body piercing with an infected needle is another means of exposure. A mother may pass the virus to their child at birth. In rare cases, unprotected sex spreads hepatitis C, but the risk appears small. Having multiple sex partners, HIV, or rough sex seems to raise risk for spreading hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C And Liver Damage
Differences In Hepatitis B And C Treatments
Guidelines for the medical treatment of a co-infection with hepatitis B and C have not been clearly set, according to Ibrahim Hanouneh, MD, a hepatologist at the Cleveland Clinic. There are scant data and no standard-of-care recommendations, he says. But limited research suggests treatment for hepatitis C is still effective even in the presence of the hepatitis B virus, he adds.
Medications for hepatitis C have improved dramatically in recent years. Not only are newer hepatitis C drugs easier for people to take, with fewer and less severe side effects, but they’re also effective, Alqahtani says, and cure rates are excellent.
For chronic hepatitis B infection, however, there’s currently no cure. Treatment involves slowing the progression of the virus and monitoring people for signs of liver damage, according to the CDC.
For this reason, Alqahtani says, doctors try to determine which virus is dominant in people with co-infection. We check the liver to see which virus is more active,” he says. “If its hepatitis C, we treat that virus first.” Once it’s cured, he says, the focus of treatment shifts to controlling hepatitis B.
Treatment for co-infection comes with specific concerns that should be monitored by your healthcare team, including:
- Liver transplant may be an option: People who develop severe cases of co-infection that result in liver failure may be candidates for liver transplant, Alqahtani says.
When Should I Contact A Health
Any infant, child, or adult that has not been vaccinated against HBV should be vaccinated especially if they have had any close association with HBV-infected individuals.
An individual with chronic hepatitis B infection is advised to
- have follow-up every 6-12 months to maximize their health,
- get vaccinated against hepatitis A, and
Discuss diet, lifestyle changes, and ways to prevent transmission of their disease to others with your health-care professional.
Recommended Reading: Genotype Test For Hepatitis C
What Do Doctors Do
A doctor who thinks someone may have hepatitis may ask questions like these:
- Has the person been around anyone who works in health care or childcare?
- Did the person stick himself or herself with a dirty needle or get a tattoo with a dirty needle?
- Did the person have contact with the bodily fluids of someone who has hepatitis?
- Did the person have a blood transfusion as a baby?
- Have any of the person’s family members had hepatitis?
- Could the person have eaten food that was contaminated with hepatitis A?
The doctor can order a blood test to see if someone has hepatitis and which type, then help the person get the right care.
Which Is The Worst Hepatitis
With the newest forms of antiviral treatment, most people can be cured from hepatitis C. With each generation there have been new advancements in medication that will cure you! Not long ago treatment was limited to injections like Interferon Alpha 2b or pegylated interferons alpha-2b/pregnancy related version called PEG Intensived 26A. These medications need to be Subcutaneous injection which is not pleasant at all for someone who has had countless shots before with little relief plus side effects are another thing altogether too scary sounding one moment Im healthy as ever then BAM instant stomach acheor muscle pain across my whole back and shoulders? What?? Ribavirin.
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis C Antibody Test
Recommended Reading: Unspecified Hepatic Cirrhosis Type Hcc
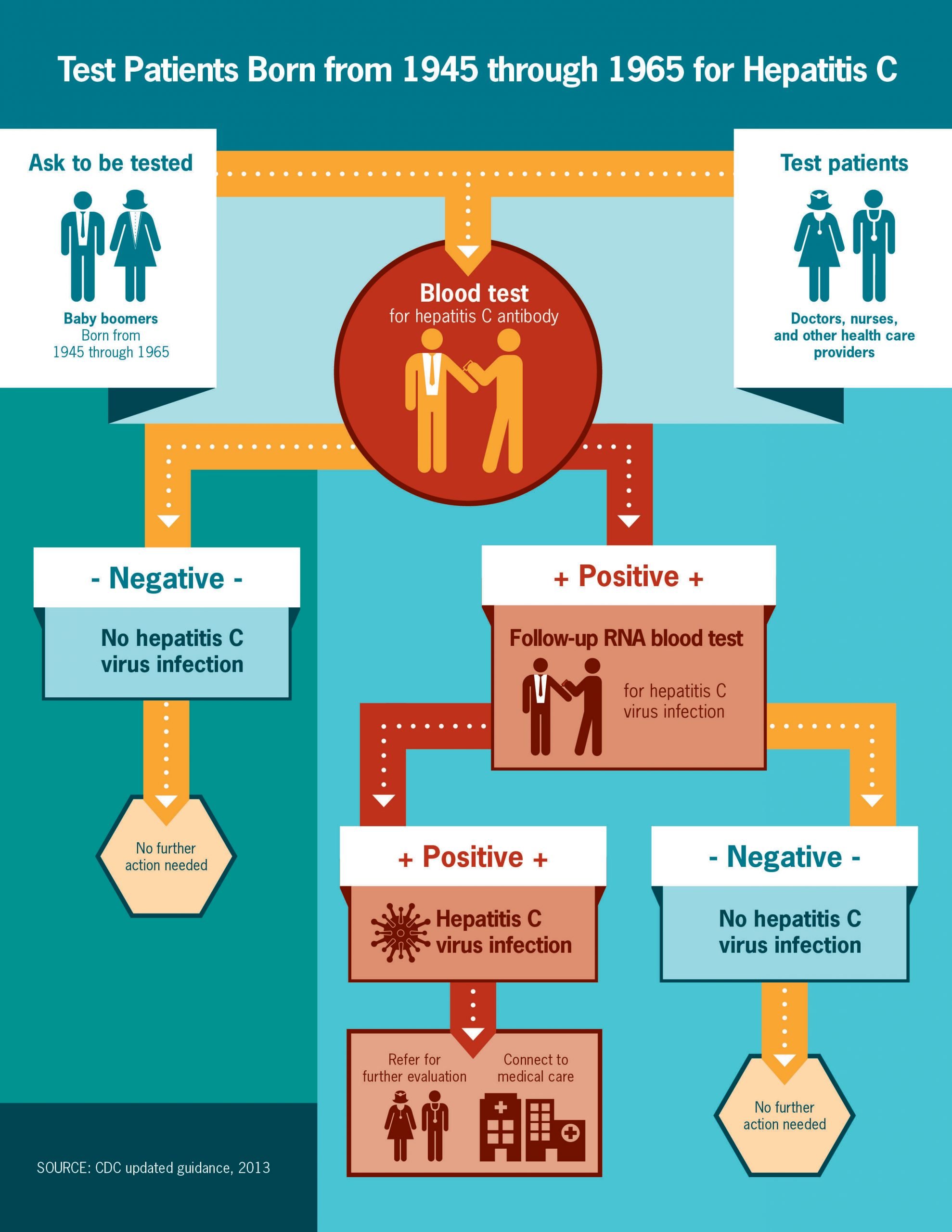
How Hepatitis C Is Diagnosed
To determine a hepatitis C diagnosis, your doctor will:
- Get your medical history .
- Perform a physical exam, especially checking for changes in skin color, swelling in your lower extremities, and tenderness in your abdomen.
- Order certain diagnostic blood tests.
The first diagnostic tool in the screening process is a blood test that screens for HCV antibodies proteins the body produces in response to the virus. An enzyme immunoassay is used to perform this test.
A negative result for the antibody test means that youve never had HCV in your blood, while a positive result means you were exposed to the virus at some point in your life. Up to a quarter of people spontaneously clear the virus from their blood within six months of contracting it.
Because EIA sometimes produces false-positive results, a test called recombinant immunoblot assay may be used to confirm that you have the HCV antibody. This test is not necessary for most patients, and it is more commonly performed by blood banks to check for the virus in donated blood.
A negative EIA result may just mean that your body has not yet produced the HCV antibody , and you may need to be tested again in a few months.
If you have a positive antibody test, your doctor will then use another blood sample to conduct a qualitative polymerase chain reaction test or a process called transcription-mediated amplification , which looks for the presence or absence of RNA of HCV in your blood.
Hepatitis B And C Prevention Screening And Treatment
Hepatitis B is a potentially life-threatening liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus . It is a major global health problem. It can cause chronic infection and puts people at high risk of death from cirrhosis and liver cancer. Hepatitis C is a liver disease caused by the hepatitis C virus : the virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness.
A vaccine against hepatitis B has been available since 1982. The vaccine is 95% effective in preventing infection and the development of chronic disease and liver cancer due to hepatitis B. Catch-up vaccination of older individuals and vaccination of groups of higher risk of infection have been implemented in many LAC countries. Groups at higher risk of infection include people who inject drugs, men who have sex with men, sexual partners of people living with HIV, prisoners, and others such as recipients of blood products and health-care workers.
There is currently no vaccine for HCV. Hence, there is an even greater need to intensify current efforts to screen for and prevent HCV transmission. WHO recommends a screening test for those considered at high risk of infection followed by another test for those who screen positive, to establish whether they have chronic hepatitis C infection.
| . |
Read Also: Hepatitis B Titer Lab Test
How Do I Prepare For Covid
There are a number of things you can do to be ready for COVID-19. Prepare a COVID-Ready KitA COVID-Ready Kit will help prepare you or someone in your household test positive for COVID-19 and you need to isolate at home.Your COVID-Ready Kit should include:
- A thermometer
- Pain relief
- Two weeks supply of your regular medications
- A plan for who can look after your children, pets, or people in your care if you have to go to hospital.
- Masks, hand sanitiser and gloves
- A plan for how youll get food and essentials
- Phone numbers for services and people outside your home you can call for help
- Stay-at-home activities
- COVID Care Plan
Prepare a COVID Care PlanThis will help you outline important information about you, your health, and others in your household. You can share the COVID Care Plan with your doctor, other health workers, hospital staff or friends and family members.
Treatment: Chronic Hepatitis C
The latest drug to be approved by the FDA is glecaprevir and pibrentasvir . This medication offers a shorter treatment cycle of 8 weeks for adult patients with all types of HCV who donât have cirrhosis and who have not been previously treated. The length of treatment is longer for those who are in a different disease stage. The prescribed dosage for this medicine is 3 tablets daily.
There are several other combination drugs available, as well as some single drugs that may be used in combination. Your doctor will choose the right one for you depending on the type of hepatitis C you have, how well your liver is functioning and any other medical problems you may have. Also be sure to discuss your insurance coverage since these medications are expensive.
Don’t Miss: Which Hepatitis Is Not Curable
Preventing Hepatitis B Or C
There are vaccines available to prevent hepatitis B. The vaccines are free for babies and children under 18 years, and some adults. Talk with your doctor or nurse to find out more.
There is no vaccine against hepatitis C. To prevent spreading or catching hepatitis B or C:
- Always use condoms during sex.
- Cover cuts and scratches.
- Do not share toothbrushes, razors or other personal items.
- Do not share needles, syringes or other injecting equipment, including those used for skin piercing and tattooing.
- Be careful about blood contact, for example, when playing a contact sport.
- Get advice from your doctor if you are likely to have contact with blood or body fluids at work.
- Do not donate blood if you have hepatitis B or C.
Poor Infection Control For Tattooing And Piercing
The notes that HCV may be transmitted by receiving tattoos or piercings from unregulated settings with poor infection control standards.
Commercially licensed tattooing and piercing businesses are generally thought to be safe.
More informal settings may not have adequate safeguards to help avoid the spread of infections. Receiving a tattoo or piercing in settings such as in a prison or in a home with friends carries a of HCV transmission
Also Check: How Long Does Hepatitis C Last
Tests To Diagnose Hepatitis C
How is Hepatitis C diagnosed?
There are two main blood tests typically used to diagnose Hepatitis C. First, youll have a screening test that shows if youve ever had Hepatitis C at some point in your life. If this test is positive, youll have a second test to see if you have Hepatitis C now. These blood tests are described below:
Hepatitis C antibody test
This is the screening test used by doctors to show whether or not you have ever been exposed to Hepatitis C at some time in your life, by detecting antibodies in your blood. Antibodies are substances your body makes to fight off all kinds of infections. If you were ever infected with Hepatitis C, your body would have made antibodies to fight the virus.
If the test result is:
- Negative, it means you have not been exposed to Hepatitis C and further testing is usually not needed.
- Positive, you have had Hepatitis C at some point. However, it does not tell you whether you have it now. Youll need to see your doctor for another test the Hepatitis C RNA test to determine if the virus is still active and present in your blood.
Hepatitis C RNA Qualitative Test
This test will determine whether or not you are currently infected with Hepatitis C. It is often called the PCR test because of the process used . It looks for the genetic material of the Hepatitis C virus in your blood.
If the test result is:
Hepatitis C RNA Quantitative Test
How Can You Prevent Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B: Vaccination is the best way to prevent all of the ways that hepatitis B is transmitted. People with HIV who do not have active HBV infection should be vaccinated against it. In addition to the 3-dose series of hepatitis B vaccine given over 6 months, as of 2017, there is a 2-dose series given over 1 month.
Hepatitis C: No vaccine exists for HCV and no effective pre- or postexposure prophylaxis is available. The best way to prevent hepatitis C infection is to never inject drugs or to stop injecting drugs by getting into and staying in drug treatment. If you continue injecting drugs, always use new, sterile needles or syringes, and never reuse or share needles or syringes, water, or other drug preparation equipment.
Also Check: How Can Someone Contract Hepatitis C
Whos Most At Risk Of Hepatitis B
People at highest risk of hepatitis B include:
- people born or brought up in a country where the infection is common
- babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B
- people who have ever injected drugs
- anyone who has had unprotected sex, including anal or oral sex particularly people who have had multiple sexual partners, people who have had sex with someone in or from a high-risk area, men who have sex with men, and commercial sex workers
- close contacts, such as family members, of someone with a long-term hepatitis B infection
The risk of getting hepatitis B for travellers going to places where the infection is common is generally considered to be low if these activities are avoided.
Your GP can arrange for you to have a blood test to check for hepatitis B and have the hepatitis B vaccination if youâre at a high risk.