What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis C
Treatment for hepatitis C is with antiviral medicines. They can cure the disease in most cases.
If you have acute hepatitis C, your health care provider may wait to see if your infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
If your hepatitis C causes cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Treatments for health problems related to cirrhosis include medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If your hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
What Drugs Treat And Cure Hepatitis C
The treatment of chronic hepatitis C has gone through several generations of medications. Not long ago, treatment was limited to interferon alpha-2b or pegylated interferon alpha-2b , and ribavirin . Interferon and pegylated interferon need to be injected under the skin , while ribavirin is taken by mouth. This combination therapy is infrequently used today, being recommended for only the least common genotypes of hepatitis C virus .
Since 2010, direct-acting antiviral drugs have been in use. The second generation of antivirals for HCV was the protease inhibitors telaprevir and boceprevir , both taken by mouth. These were used in combination with the earlier drugs to increase effectiveness . These drugs are also no longer in common use, and have been replaced by better options.
As more has been learned about how hepatitis C virus multiplies within the liver cells, new drugs continue to be developed to interfere with this multiplication at different stages. As such, we no longer think in terms of generations of drugs, but rather categories of action. Research and development of these direct-acting antivirals continue, with new agents coming to market every few months. Each category is improved and expanded by the addition of new drugs, which are safer and more effective.
Currently available and commonly used direct-acting antiviral drugs include:
- simeprevir
- Muscle aches
Alterations Of Lipid Metabolism
Lipids are required for the HCV replication and particles assembly. As mentioned above, HCV can modify the host serum lipid profile and this modification can provoke the steatosis. The steatosis is more frequent and more severe in patients with HCV gt 3 and it is correlated with a high HCV RNA levels. On one hand, in HCV-infected patients, the steatosis can be considered as a marker of the liver disease progression and, on the other hand, as an indication of the reduced response to therapy. However, if it is not metabolic or alcoholic steatosis, an efficient antiviral therapy is capable to reduce it.
Read Also: Is Hepatitis Ca Sexually Transmitted Disease
Distinctive Properties Of Hdv
The HDV particle is approximately 36 nm in diameter and composed of an RNA genomeassociated with HDAg, surrounded by an envelope of HBsAg. The HDV genome is aclosed circular RNA molecule of 1679 nucleotides and resembles those of thesatellite viroids and virusoids of plants and similarly seems to be replicatedby the host RNA polymerase II with autocatalytic cleavage and circularization ofthe progeny genomes via trans-esterification reactions. Consensus sequences of viroids which are believed to beinvolved in these processes also are conserved in HDV. Unlike the plant viroids,HDV codes for a protein, HDAg.
This is encoded in an open reading frame in the antigenomic RNA but four otheropen reading frames which are also present in the genome do not appear to beutilized. The antigen, which contains a nuclear localization signal, wasoriginally detected in the nuclei of infected hepatocytes and may be detected inserum only after stripping off the outer envelope of the virus withdetergent.
How Do Doctors Treat The Complications Of Hepatitis C
If hepatitis C leads to cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Doctors can treat the health problems related to cirrhosis with medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If you have cirrhosis, you have an increased chance of liver cancer. Your doctor may order an ultrasound test to check for liver cancer.
If hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know You Have Hepatitis B
Do I Have To Have Drug Treatment
The choice is up to you and your doctor. The decision to use drug therapy can be hard to make because of the potential side effects. Your doctor will closely monitor your symptoms and the amount of the virus in your body. He or she will also consider your overall health. This includes looking at blood test results. All are important factors to consider before you and your doctor start drug treatment for your hepatitis C.
What Happens At The Start Of The Disease
Hepatitis C can spread through the body through blood contamination. The virus mostly impacts the liver as it processes many of the bodys contaminated fluids.
A common sign of hepatitis is bruising or bleeding easily. You may also experience fatigue and a poor appetite. Jaundice may occur due to the liver becoming weak, causing the skin or eyes to turn yellow in color.
You may also notice swelling in your legs and the buildup of fluid in the abdomen. These problems may develop even if you start losing weight. Your urine may also become dark in color. The dark tone may persist even if you are hydrated.
You May Like: Should I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
What If I’m Pregnant And I Have Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be passed from a mother to her child during pregnancy and during delivery. Per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , approximately 6 of every 100 infants born to HCV-infected mothers become infected with the virus. The risk is two to three times greater when the mother has HIV as well.
You and your doctor should discuss and decide if you should receive treatment for hepatitis C during your pregnancy.
What Are The Common Types Of Viral Hepatitis
Although the most common types of viral hepatitis are HAV, HBV, and HCV, some clinicians had previously considered the acute and chronic phases of hepatic infections as “types” of viral hepatitis. HAV was considered to be acute viral hepatitis because the HAV infections seldom caused permanent liver damage that led to hepatic failure. HBV and HCV produced chronic viral hepatitis. However, these terms are outdated and not currently used as frequently because all of the viruses that cause hepatitis may have acute phase symptoms . Prevention techniques and vaccinations have markedly reduced the current incidence of common viral hepatitis infections however, there remains a population of about 1 to 2 million people in the U.S. with chronic HBV, and about 3.5 million with chronic HCV according to the CDC. Statistics are incomplete for determining how many new infections occur each year the CDC documented infections but then goes on to estimate the actual numbers by further estimating the number of unreported infections .
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis C
Types D, E, and G Hepatitis
Individuals who already have chronic HBV infection can acquire HDV infection at the same time as they acquire the HBV infection, or at a later time. Those with chronic hepatitis due to HBV and HDV develop cirrhosis rapidly. Moreover, the combination of HDV and HBV virus infection is very difficult to treat.
- HIV patients
- People with hemophilia who receive blood clotting factors
Read Also: How To Find Out If You Have Hepatitis
What Is The Treatment For Viral Hepatitis
Treatment of acute viral hepatitis and chronic viral hepatitis are different. Treatment of acute viral hepatitis involves resting, relieving symptoms, and maintaining an adequate intake of fluids. Treatment of chronic viral hepatitis involves medications to eradicate the virus and taking measures to prevent further liver damage.
Acute hepatitis
In patients with acute viral hepatitis, the initial treatment consists of relieving the symptoms of nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain . Careful attention should be given to medications or compounds, which can have adverse effects in patients with abnormal liver function . Only those medications that are considered necessary should be administered since the impaired liver is not able to eliminate drugs normally, and drugs may accumulate in the blood and reach toxic levels. Moreover, sedatives and “tranquilizers” are avoided because they may accentuate the effects of liver failure on the brain and cause lethargy and coma. The patient must abstain from drinking alcohol since alcohol is toxic to the liver. It occasionally is necessary to provide intravenous fluids to prevent dehydration caused by vomiting. Patients with severe nausea and/or vomiting may need to be hospitalized for treatment and intravenous fluids.
Chronic hepatitis
Medications for chronic hepatitis C infection include:
- oral daclatasvir
Medications for chronic hepatitis B infection include:
- oral entecavir
- oral tenofovir
Fulminant hepatitis
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis C
You are more likely to get hepatitis C if you
- Have injected drugs
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you probably will not have symptoms until it causes complications. This can happen decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Signs And Symptoms Cdc
Hbv And Hepatocellular Carcinoma
When tests for HBsAg became widely available, regions of the world where thechronic carrier state is common were found to be coincident with those wherethere is a high prevalence of primary liver cancer. Furthermore, in these areas,patients with tumor almost invariably are seropositive for HBsAg. A prospectivestudy in Taiwan revealed that 184 cases of hepatocellular carcinoma occurred in3,454 carriers of HBsAg at the start of the study, but only 10 such tumors arosein the 19,253 control males who were HBsAg negative.
How Many People Have Hepatitis C
During 2013-2016 it was estimated that about two and half million people were chronically infected with HCV in the United States. The actual number may be as low as 2.0 million or as high as 2.8 million.Globally, hepatitis C is a common blood-borne infection with an estimated 71 million people chronically infected according to the World Health Organization .
Also Check: Difference Between Hiv And Hepatitis
What Is Chronic Viral Hepatitis
Patients infected with HBV and HCV can develop chronic hepatitis. Doctors define chronic hepatitis as hepatitis that lasts longer than 6 months. In chronic hepatitis, the viruses live and multiply in the liver for years or decades. For unknown reasons, these patients’ immune systems are unable to eradicate the viruses, and the viruses cause chronic inflammation of the liver. Chronic hepatitis can lead to the development over time of extensive liver scarring , liver failure, and liver cancer. Liver failure from chronic hepatitis C infection is the most common reason for liver transplantation in the U.S. Patients with chronic viral hepatitis can transmit the infection to others with blood or body fluids as well as infrequently by transmission from mother to newborn.
How Does Hepatitis C Affect The Liver
When infected, the liver becomes inflamed, which may cause the healthy, soft tissues in the liver to harden and scar. If not stopped, inflammation and scarring can lead to serious liver diseases such as cirrhosis of the liver or liver tumors. If the damage is severe enough, the liver may not perform all of its functions normally.
Also Check: What Is Autoimmune Hepatitis C
Contact Us Today For Hepatitis C Treatment
If you need help treating or detecting hepatitis C, contact us at Health Services of North Texas in Denton, TX. We also have offices in Plano, and Wylie, TX, so you can receive the treatment you require whether you are in Denton or Collin County. Contact us today to learn more about how our services work and what you can expect from treatment.
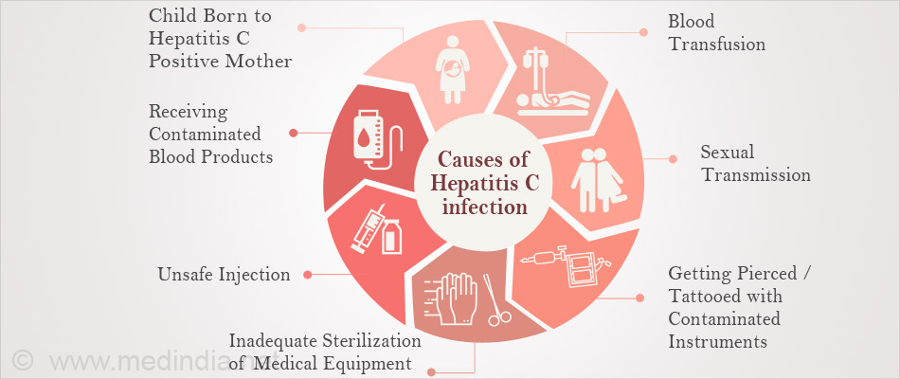
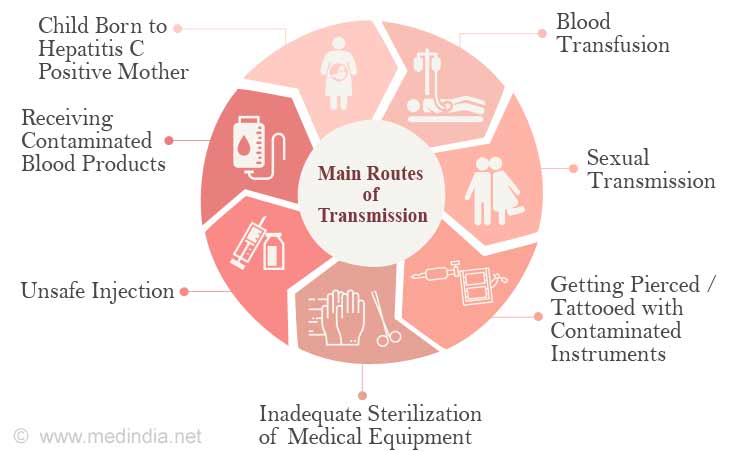
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis C
People more likely to get hepatitis C are those who
- have injected drugs
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- have hemophilia and received clotting factor before 1987
- have been on kidney dialysis
- have been in contact with blood or infected needles at work
- have had tattoos or body piercings
- have worked or lived in a prison
- were born to a mother with hepatitis C
- are infected with HIV
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have or had sex with men
In the United States, injecting drugs is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.13
Recommended Reading: How To Get Hepatitis A Virus
Can Hepatitis C Be Prevented Or Avoided
The only way to prevent hepatitis C is to avoid coming in contact with an infected persons blood. Always have protected sex . Dont do intravenous drugs. Dont share personal care items with a person who has hepatitis C. If youre a health care worker, follow your workplaces standard safety practices.
How Long Does It Last
Hepatitis A can last from a few weeks to several months.
Hepatitis B can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious, life-long condition. More than 90% of unimmunized infants who get infected develop a chronic infection, but 6%10% of older children and adults who get infected develop chronic hepatitis B.
Hepatitis C can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious, life-long infection. Most people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop chronic hepatitis C.
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C Infection
Treatment And Medication For Hepatitis C
If you have acute hepatitis C, there is no recommended treatment. If your hepatitis C turns into a chronic hepatitis C infection, there are several medications available.
Interferon, peginterferon, and ribavirin used to be the main treatments for hepatitis C. They can have side effects like fatigue, flu-like symptoms, anemia, skin rash, mild anxiety, depression, nausea, and diarrhea.
Now youâre more likely to get one of these medications:
Find out more on treatment options for hepatitis C.
What Causes Hepatitis In General

- Virus and other infections
- Autoimmune response
- Ischemia
- Metabolic disorders
- An acute illness caused by the hepatitis A virus .
- Transmitted through food and water contaminated by feces of infected people.
Read Also: How Do You Get Hepatitis Ab And C
What Is Viral Hepatitis
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is a vital organ that processes nutrients, filters the blood, and fights infections. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can cause hepatitis. However, hepatitis is often caused by a virus. In the United States, the most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C.
Extrahepatic Manifestations Associated With The Hcv Infection
At least, one clinically significant extrahepatic manifestation occurs in 38% to 76% of HCV infected patients with chronic HCV. The most frequent associated pathology is a mixed cryoglobulinemia. It is detected in 19% to 50% of HCV infected patients, while only 15% of them are symptomatic. The cryoglobulins are immunoglobulins which precipitate at a temperature below 37 °C. They are produced by HCV activated B cells. The cryoglobulins deposed in small and medium vessels are the cause of systemic vasculitis which can manifest in level joint, skin, renal or peripheral nerves. Other observed extrahepatic manifestations are the following: lymphoma, thyroid disorders, diabetes, xerostomia and xerophthalmia. The HCV infection cure leads to a gradual decrease of the cryoglobulin level in serum, followed by the remission of cryoglobulin-related symptoms and pathologic lesions. Interestingly, as a result of treatment the incidence of type 2 diabetes is also reduced by approximately two thirds.
Read Also: How To Manage Hepatitis C
Cost Of Hepatitis C Medicines
The newer direct-acting antiviral medicines for hepatitis C can be costly. Most government and private health insurance prescription drug plans provide some coverage for these medicines. Talk with your doctor about your health insurance coverage for hepatitis C medicines.
Drug companies, nonprofit organizations, and some states offer programs that can help pay for hepatitis C medicines. If you need help paying for medicines, talk with your doctor. Learn more about financial help for hepatitis C medicines.
Getting Tested Is The Only Way To Know If You Have Hepatitis C
A blood test called a hepatitis C antibody test can tell if you have been infected with the hepatitis C viruseither recently or in the past. If you have a positive antibody test, another blood test is needed to tell if you are still infected or if you were infected in the past and cleared the virus on your own.
- Are 18 years of age and older
- Are pregnant
- Currently inject drugs
- Have ever injected drugs, even if it was just once or many years ago
- Have HIV
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Are on hemodialysis
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis C Virus Ab