People With Hepatitis C Should Not Eat
- Calories : Increasing calories means gaining weight or being obese, while increasing the risk of diabetes. To cut calories, limit foods: high in fat, processed, canned, and fast foods.
- Salt: Salty foods can lead to water retention, thus increasing blood pressure, which is extremely dangerous for people with cirrhosis.
- Sugar : Foods that contain sugar are often high in fat, which can easily cause weight gain.
- Raw or unpasteurized products: Sushi or other raw foods may contain bacteria that aggravate hepatitis C. You should also avoid raw eggs, unpasteurized milk and cheese.
Recommended Reading: Antiviral Drugs For Hepatitis A
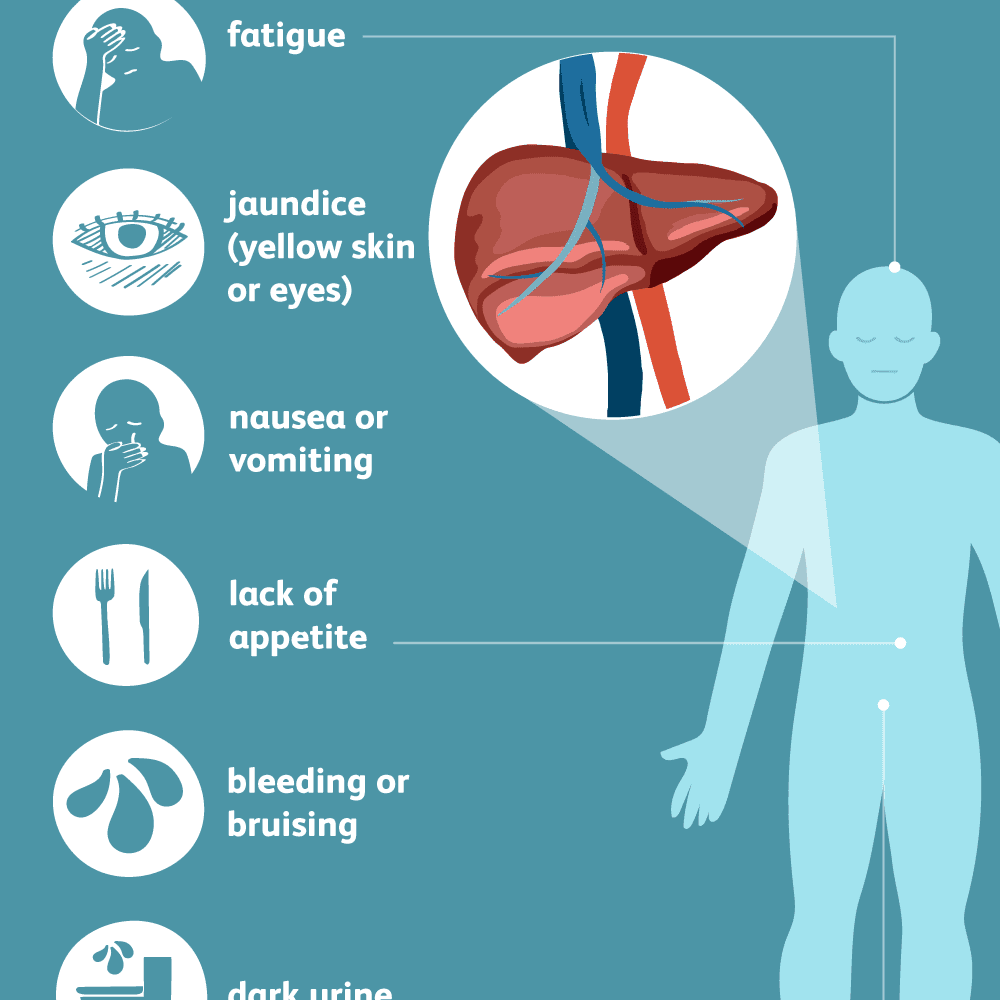
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Hcv Infection
Most people with HCV have no symptoms. But even without symptoms, they can develop health problems decades later and can still pass the disease to others.
If symptoms do happen, it’s usually when the disease is very advanced. Symptoms can be similar to those of hepatitis A and hepatitis B and include:
- jaundice
- fever
- darker than usual urine or gray-colored stools
Additional Tests You Might Need
Once youve been diagnosed with Hepatitis C, your doctor will likely order a number of tests to find out about the health of your liver and decide on a treatment plan thats most appropriate for you.
Hepatitis C genotype
The Hepatitis C genotype refers to a specific strain or type of the Hepatitis C virus. There are six major types of Hepatitis C around the world: genotypes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. In the United States, genotypes 1, 2, and 3 are common:
- Genotype 1: Most Americans with Hepatitis C have this type
- Genotype 2: About 10% of Americans with Hepatitis C have this type
- Genotype 3: About 6% of Americans with Hepatitis C have this type
The genotype of Hepatitis C does not change over time, so you only need to get tested once.
Genotype tests are done before a person starts treatment. Hepatitis C treatment works differently for different genotypes, so knowing your genotype helps your doctor choose the best treatment for you.
Testing for Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B
Your doctor may test to see if your body is immune to Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B. If these tests show no prior exposure or protection, he or she will recommend that you be vaccinated against these two viruses to eliminate the chance of becoming infected.
Liver function tests or liver enzymes
- ALT
- AST
Liver function tests also include ALP and total bilirubin, among other things.
Tests to measure liver scarring or fibrosis
- Liver Biopsy
- Elastography
- Serum markers
Imaging tests
Also Check: Most Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Most people infected with hepatitis C have no symptoms. Some people with an acute hepatitis C infection may have symptoms within 1 to 3 months after they are exposed to the virus. These symptoms may include
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you most likely will have no symptoms until complications develop, which could be decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
Diagnostic Tests For The Hepatitis C Virus:
You can be infected with the hepatitis C virus and have no symptoms. Your doctor could find it when he checks your blood and sees that your level of certain liver enzymes is high. If that happens, hell follow up with other tests to confirm you have the disease. Who Should Get Screened for Hepatitis C? Some doctors say you should get tested at least once no matter what.
Definitely, get screened if any of these things apply to you:
Were born between 1945 and 1965. Currently using or injecting drugs. Ever injected drugs even if it was just once or a long time ago. Have abnormal alanine aminotransferase levels . Had a blood transfusion, blood components, or an organ transplant before July 1992. Got clotting factor concentrates made before 1987. Received blood from a donor who later tested positive for the hepatitis C virus. Health care workers, first responders, and others whose work exposes them to HCV-infected needles. Children born to women with HCV.
Why Should You Get Tested?
You can have hep C with no symptoms. The test is quick and easy. Youll protect family and friends. Treatment can suppress the virus and maybe even cure you. Early treatment prevents cirrhosis and liver failure. Hepatitis C Testing and DiagnosisDoctors will start by checking your blood for Anti-HCV antibodies: These are proteins your body makes when it finds the hep C virus in your blood. They usually show up about 12 weeks after infection.
How long does it take to get results?
Reactive or positive:
Read Also: How Is Hepatitis A Caused
Research And Statistics: Who Has Hepatitis C How Many People Have Hepatitis C
Health officials reported 2,967 cases of acute hepatitis C in 2016, but the CDC estimates that the actual number of acute cases is 13.9 times the number of reported cases in any year. The CDC put the real number of acute hepatitis C cases in 2016 at an estimated 41,200.
Despite these estimates, “we really do not know how many people are infected with HCV,” Dr. Branch says, adding that the U.S. estimates come from specific datasets that “do not include prisoners or the homeless and have too small a sample size to yield precise data.”
The Journal of Infectious Diseases
It’s unclear how many people fail to get treatment in time and die from HCV-related issues. According to the CDC, there were 18,153 reported deaths related to HCV, but this is likely an underestimate.
“HCV may be causing 3 to 5 times more deaths than we know,” Branch says. “Better information about the number of HCV-related deaths would help make HCV testing and treatment more of a priority.”
Getting Tested Is The Only Way To Know If You Have Hepatitis C
A blood test called a hepatitis C antibody test can tell if you have been infected with the hepatitis C viruseither recently or in the past. If you have a positive antibody test, another blood test is needed to tell if you are still infected or if you were infected in the past and cleared the virus on your own.
- Are 18 years of age and older
- Are pregnant
- Currently inject drugs
- Have ever injected drugs, even if it was just once or many years ago
- Have HIV
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Are on hemodialysis
Recommended Reading: How Much Is A Hepatitis C Test
North America And Western Europe
The most common malignant tumors in the liver represent metastases from tumors which originate elsewhere in the body. Among cancers that originate from liver tissue, HCC is the most common primary liver cancer. In the United States, the US surveillance, epidemiology, and end results database program, shows that HCC accounts for 65% of all cases of liver cancers. As screening programs are in place for high-risk persons with chronic liver disease, HCC is often discovered much earlier in Western countries than in developing regions such as sub-Saharan Africa.
Acute and chronic hepatic porphyrias and tyrosinemia type I are risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma. The diagnosis of an acute hepatic porphyria should be sought in patients with HCC without typical risk factors of hepatitis B or C, alcoholic liver cirrhosis, or hemochromatosis. Both active and latent genetic carriers of acute hepatic porphyriasare at risk for this cancer, although latent genetic carriers have developed the cancer at a later age than those with classic symptoms. Patients with acute hepatic porphyrias should be monitored for HCC.
The incidence of HCC is relatively lower in the Western Hemisphere than in Eastern Asia. However, despite the statistics being low, the diagnosis of HCC has increased since the 1980s and it is continuing to increase, making it one of the rising causes of death due to cancer. The common risk factor for HCC is hepatitis C, along with other health issues.
What Is Viral Hepatitis
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is a vital organ that processes nutrients, filters the blood, and fights infections. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can cause hepatitis. However, hepatitis is often caused by a virus. In the United States, the most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: What Is Mild Hepatic Steatosis
How Can A Person Identify A Hep C Rash
The rash and itching that is associated with symptoms for Hep C may look like an extreme case of dermatitis, although it is generally also accompanied by the joint pain and even mild jaundice. This condition comes from the body trying to process toxins through the skin, since the liver function has been compromised. While the rash will often be an obvious sign, it is usually accompanied by abdominal discomfort as the liver struggles to process impurities.
Symptoms Of A Chronic Infection
If the hepatitis C infection progresses to a chronic infection , it can take years before symptoms develop. Symptoms of advanced liver disease caused by long-term chronic infection can include: jaundice fluid build-up and blood in stool or vomit. Sleep disturbances, depression, weight loss, dry or itchy skin, and brain fog also occur in people with chronic hepatitis C but the cause of these symptoms remains uncertain.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis C Contagious Sexually
With Spike In Hepatitis C Virus Infections Cdc Recommends Screening For All Adults
This page was fact checked by our expert Medical Review Board for accuracy and objectivity. Read more about our editorial policy and review process.
All adults age 18 and older should be screened for hepatitis C virus infection at least once in their lifetime, while women should be screened during every pregnancy, say new U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommendations.
These latest recommendations, published on April 10, 2020, expand CDCs 2012 call for one-time HCV screening of all baby boomers, adults born from 1945 through 1965, along with people of any age with certain risk factors. This group includes injection drug users, dialysis patients, people with HIV, children born to mothers with HCV, and incarcerated people, among others. Individuals with any ongoing risk should be screened for HCV periodically, according to the CDC.
The new recommendations do not apply in areas of the U.S. where less than 0.1% of adults have HCV infections, says the CDC. However, no U.S. state currently meets this criterion.
HCV and screeningMost often transmitted by intravenous drug users sharing needles, HCV causes the liver infection hepatitis C. Less commonly, the virus is spread via sexual contact, unregulated tattooing, needlestick injuries in healthcare workers, and from mothers to babies during pregnancy or childbirth.
What Are The Side Effects Of Treatments For Hepatitis C Infection

Side effects of interferon or pegylated interferon
- The most common side effects of interferon or pegylated interferon include fever, flu-like symptoms, and depression. Patients must be monitored closely for depression. Risk of suicide is a reason to avoid interferons.
- Interferons also reduce white blood cell and/or red blood cell counts . This may cause increased susceptibility to infection. Interferons also increase the risk of certain cancers. Death rarely occurs as a result of therapy, but may occur from progression of liver failure in patients with advanced cirrhosis.
Side effects of ribavirin
- Ribavirin most commonly causes anemia due to destruction of red blood cells . This can be severe enough that people with heart disease may suffer a heart attack from insufficient blood flow, so people with heart disease should not receive this drug. Anemia improves with a reduction in the dose of ribavirin. Injected growth factor that stimulates the production of red blood cells often is used to improve the anemia associated with ribavirin. Ribavirin also accumulates in the testicles and ovaries and causes birth defects in animals. Although no birth defects have been reported in humans, both men and women should use contraceptive measures to avoid pregnancy during and for at least six months after ribavirin treatment.
Side effects of DAAs
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis B Caused By
How Is It Spread
Hepatitis A is spread when a person ingests fecal mattereven in microscopic amountsfrom contact with objects, food, or drinks contaminated by feces or stool from an infected person.
Hepatitis B is primarily spread when blood, semen, or certain other body fluids- even in microscopic amounts from a person infected with the hepatitis B virus enters the body of someone who is not infected. The hepatitis B virus can also be transmitted from:
- Birth to an infected mother
- Sex with an infected person
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles, syringes, and even medical equipment, such as glucose monitors
- Sharing personal items such as toothbrushes or razors
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
Hepatitis C is spread when blood from a person infected with the Hepatitis C virus even in microscopic amounts enters the body of someone who is not infected. The hepatitis C virus can also be transmitted from:
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles and syringes
- Receiving a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
- Birth to an infected mother
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis C
People more likely to get hepatitis C are those who
- have injected drugs
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- have hemophilia and received clotting factor before 1987
- have been on kidney dialysis
- have been in contact with blood or infected needles at work
- have had tattoos or body piercings
- have worked or lived in a prison
- were born to a mother with hepatitis C
- are infected with HIV
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have or had sex with men
In the United States, injecting drugs is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.13
Read Also: Genotype 2a Hepatitis C Virus
Is Screening For Hepatitis C Recommended During Pregnancy
There is a 4%-7% risk of transmitting HCV from mother to infant with each pregnancy. Currently, there is no CDC recommendation for routine hepatitis C screening during pregnancy, and there is no currently recommended medicine to prevent transmission from mother to infant . However, CDC is monitoring research findings and may make recommendations in the future as evidence arises.
While data is still limited, a recent study of over 1,000 cases in the United Kingdom found that 11% of infants had been infected at birth, and that these infants were likely to develop cirrhosis in their early 30s. The case for screening for HCV during pregnancy includes the potential to safely treat mothers during pregnancy with direct-acting antiviral agents to treat the mother before cirrhosis develops, prevent infant transmission, and prevent transmission to others. Children born to HCV-infected mothers may also be offered treatment at an early age to prevent cirrhosis, as well as transmission to others. Coordination of care between multiple specialists will be important to accomplish these goals.
Children of HCV-infected mothers may be screened for hepatitis C as early as 1-2 months of age using hepatitis C viral load or PCR testing . Antibodies to hepatitis C passed from the mother to child will be present for up to 18 months, so children should be tested for HCV antibody no earlier than this.
Cdc Recommendations For Hepatitis C Screening Among Adults In The United States
- Universal hepatitis C screening:
- Hepatitis C screening at least once in a lifetime for all adults aged 18 years and older, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is less than 0.1%*
- Hepatitis C screening for all pregnant women during each pregnancy, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is less than 0.1%*
- Any person who requests hepatitis C testing should receive it, regardless of disclosure of risk, because many persons may be reluctant to disclose stigmatizing risks
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis C And Hiv The Same
Chronic Hepatitis C: What Are The Signs And Symptoms
Even when an acute infection becomes chronic, it can be years before a person receives a diagnosis, thus delaying treatment. In fact, the majority of people with chronic hepatitis C are asymptomatic until the liver becomes severely damaged, often decades after exposure, says Dr. Adalja.
It’s common for people to unknowingly carry HCV until they go through a blood screening or other examination for reasons unrelated to hepatitis C.
However, chronic hepatitis C is a serious issue that can result in long-term health problems, including liver damage, liver cancer, liver failure, and death.