What Research Is Ongoing To Prevent And Treat Cirrohsis Of The Liver
Progress in the management and prevention of cirrhosis continues. Research is ongoing to determine the mechanism of scar formation in the liver and how this process of scarring can be interrupted or even reversed. Newer and better treatments for viral liver disease are being developed to prevent the progression to cirrhosis. Prevention of viral hepatitis by vaccination, which is available for hepatitis B, is being developed for hepatitis C. Treatments for the complications of cirrhosis are being developed or revised, and tested continually. Finally, research is being directed at identifying new proteins in the blood that can detect liver cancer early or predict which patients will develop liver cancer.
Alcohol And Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Alcohol
Alcohol is a very common cause of cirrhosis, particularly in the Western world. Chronic, high levels of alcohol consumption injure liver cells. Thirty percent of individuals who drink daily at least eight to sixteen ounces of hard liquor or the equivalent for fifteen or more years will develop cirrhosis. Alcohol causes a range of liver diseases, which include simple and uncomplicated fatty liver , more serious fatty liver with inflammation , and cirrhosis.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Whos At Risk For Hepatitis C
You might be more likely to get it if you:
- Inject or have injected street drugs
- Were born between 1945 and 1965
- Got clotting factor concentrates made before 1987
- Received a blood transfusion or solid organ transplants before July 1992
- Got blood or organs from a donor who tested positive for hepatitis C
- Are on dialysis
- Get a body piercing or tattoo with nonsterile instruments
Read Also: Can Hepatitis Cause Low Platelets
What Is The Prognosis And Life Expectancy Of Hepatitis C Patient
Hepatitis C infographic from hcv.guidelinecentral.com
Hepatitis C is a very serious condition that not only affects the liver, but it is a powerful disease that can have other significant complications and problems within the body. Many people could be infected and living with it and not even know at first because the symptoms are initially mild. However, as Hepatitis C continues to grow and progress within the body it can lead to onset liver disease and cirrhosis. The important thing for anyone is to be able to understand not only what the disease is, but also how they can take precautions to protect against it.
The Final Stage Of Fibrosis Is Cirrhosis
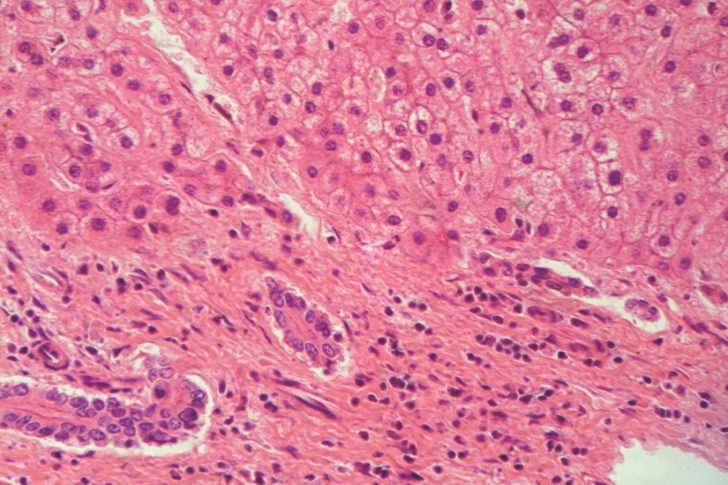
Cirrhosis is where your liver is severely scarred and permanently damaged. While the word cirrhosis is most commonly heard when people discuss alcohol-induced liver disease, cirrhosis is caused by many forms of liver disease.
While fibrosis is reversible there is a point where the damage becomes too great and the liver cannot repair itself. There is no treatment that can cure cirrhosis. If possible, treating the underlying cause of cirrhosis may keep your cirrhosis from getting worse and help prevent liver failure. Successful treatment may slowly improve some of your liver scarring. It is important to avoid things that could damage your liver further like alcohol, certain medications and fatty food. Treatment for someone with cirrhosis often means managing the symptoms of cirrhosis and preventing further damage to avoid liver failure. Doctors treat liver failure with a liver transplant. Someone with cirrhosis is at a very high risk of developing liver cancer. It is very important to receive routine liver cancer surveillance if you have cirrhosis most people who develop liver cancer have evidence of cirrhosis. Doctors also treat liver cancer with a transplant. It is important to note, people often live with cirrhosis for a long time before the option of liver transplant is discussed.
You May Like: Hepatitis A Shots At Costco
Prevention Is The Best Medicine
Even though hepatitis C rarely spreads within a household, if you or a family member have the disease, it’s wise to take precautions to prevent its spread especially if anyone in your home is immune compromised, or has cuts or open sores that increase the risk of infection.
In general, use these common sense preventive tips:
- Unless you are in a long-term, monogamous relationship, practice safe sex.
- Clean up spilled or dried blood with a bleach-based cleaning solution and wear rubber gloves.
- Do not share razors.
- Do not share toothbrushes. “Though hepatitis C is not transmitted through saliva, there might be blood on the toothbrush,” Reau says.
Note that hepatitis C is not transmitted by sharing eating utensils, hugging, kissing, coughing or sneezing.
It’s Different Than Hepatitis A And B
Each form of hepatitis has its own specific virus that spreads and is treated differently. “Hepatitis simply means inflammation of the liver, or that the virus has an affinity for hurting the liver,” Reau says.
- Hepatitis A is an acute, short-term infection that often does not require treatment.
- Hepatitis B hides deep in the body and, like hepatitis C, is treated in a variety of ways, from antiviral medications to liver transplants.
“The viruses are different, but all of them should be taken very seriously since they can lead to significant liver disease and even death,” she adds.
Read Also: How To Prevent Hepatitis A
What Is The Prognosis And Life Expectancy For Cirrhosis Of The Liver
The prognosis and life expectancy for cirrhosis of the liver varies and depends on the cause, the severity, any complications, and any underlying diseases.
- In compensated cirrhosis, patients have not developed any major complications and the average survival rate is more than 12 years.
- The prognosis for is worse for patients who have decompensated cirrhosis and have developed complications such as ascites, variceal hemorrhage, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, hepatocellular carcinoma, hepatorenal syndrome, or hepatopulmonary syndrome. Patients with decompensated cirrhosis often require liver transplantation and in those who are unable to receive an organ transplant, life expectancy may be less than 6 months.
Sometimes The Infection Goes Away On Its Own
Acute hepatitis is C is a short-term illness that occurs within the first six months after being exposed to the virus. Like the human papillomavirus , early acute hepatitis C can clear on its own without treatment this happens about 25% of the time.
However, it’s more likely that the virus will remain in your body longer than six months, at which point it’s considered to be chronic hepatitis C infection.
“Being younger or a woman tends to be a factor in whether the virus clears on its own, and genetics may play a role,” Reau says. “But we can’t determine with certainty which people are certain to clear the infection and which aren’t.”
Read Also: How Do You Get Hepatitis A And B
What Are Treatment Options For Cirrhosis
Preventing further damage to the liver
Consume a balanced diet and one multivitamin daily. Patients with PBC with impaired absorption of fat-soluble vitamins may need additional vitamins D and K.
Avoid drugs that cause liver damage. All patients with cirrhosis should avoid alcohol. Most patients with alcohol-induced cirrhosis experience an improvement in liver function with abstinence from alcohol. Even patients with chronic hepatitis B and C can substantially reduce liver damage and slow the progression towards cirrhosis with abstinence from alcohol.
Avoid nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs . Patients with cirrhosis can experience worsening of liver and kidney function with NSAIDs.
Eradicate hepatitis B and hepatitis C virus by using anti-viral medications. Not all patients with cirrhosis due to chronic viral hepatitis are candidates for drug treatment. Some patients may experience serious deterioration in liver function and/or intolerable side effects during treatment. Thus, decisions to treat viral hepatitis have to be individualized, after consulting with doctors experienced in treating liver diseases .
Suppress the immune system with drugs such as prednisone and azathioprine to decrease inflammation of the liver in autoimmune hepatitis.
Why Does Cirrhosis Cause Problems
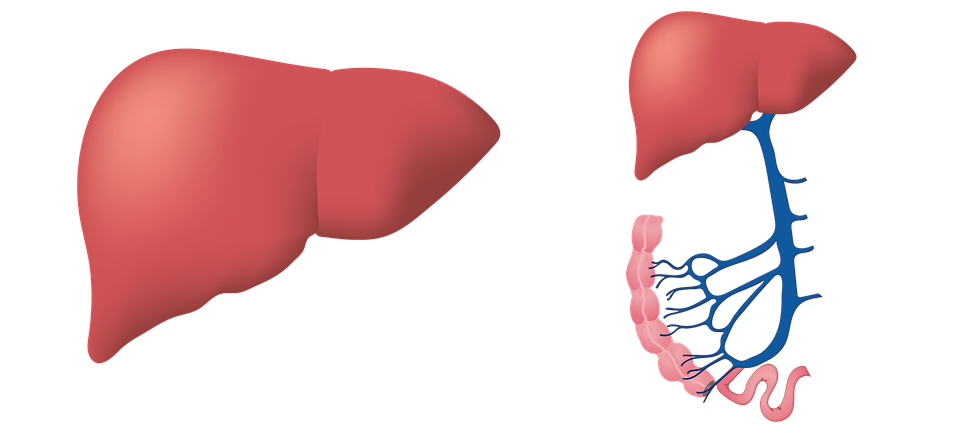
The liver is an important organ in the body. It performs many critical functions, two of which are producing substances required by the body, for example, clotting proteins that are necessary in order for blood to clot, and removing toxic substances that can be harmful to the body, for example, such as drugs. The liver also has an important role in regulating the supply of glucose and lipids that the body uses as fuel. In order to perform these critical functions, the liver cells must be working normally, and they must have a close proximity to the blood because the substances that are added or removed by the liver are transported to and from the liver by the blood.
Don’t Miss: Where To Get Hepatitis B Test
Treatment For Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis Complications
Patients suspected of having spontaneous bacterial peritonitis usually will undergo paracentesis. The fluid that is removed is examined for white blood cells and cultured for bacteria. Culturing involves inoculating a sample of the ascites into a bottle of nutrient-rich fluid that encourages the growth of bacteria, thus facilitating the identification of even small numbers of bacteria. Blood and urine samples also are often obtained for culturing because many patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis also will have infections in their blood and urine. Many doctors believe the infection may have begun in the blood and the urine and spread to the ascitic fluid to cause spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Most patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis are hospitalized and treated with intravenous antibiotics such as cefotaxime . Patients usually treated with antibiotics include:
- Ascites fluid cultures that contain bacteria.
- Patients without bacteria in their blood, urine, and ascitic fluid but who have elevated numbers of white blood cells in the ascitic fluid . Elevated neutrophil numbers in ascitic fluid often mean there is a bacterial infection. Doctors believe the lack of bacteria with culturing in some patients with increased neutrophils is due either to a very small number of bacteria or ineffective culturing techniques.
Did You Know That Hepatitis Simply Means Inflammation Of The Liver
Inflammation is the bodys natural response to injury and an important part of healing or immune response. Think about when you get a cut or injury to your skin. The area around the wound becomes swollen or inflamed. Seeing the swelling is not the only way you experience the inflammatory phase. You may also experience pain, redness, or the wound may feel warm to the touch. Under the skin, your body is hard at work to stop the bleeding and prevent infection. Blood vessels near the wound widen, or dilate, making more room for special healing and repair cells, or cells in the wounded area. These cells remove damaged cells and harmful substances and allow the rest of the healing process to continue. Inflammation is essential to fight infection.
Inflammations Role in Repairing Damaged CellsThe liver recognizes and replaces its own damaged or broken-down cells while still performing all of its vital functions. Just as inflammation is required to get rid of toxic substances, inflammation is part of repairing damaged liver cells. Damaged liver cells and immune cells both send out messages to activate specific repair cells which travel to the site of the injury. These repair cells release something called collagen, a fiber, which stiffens the tissue around the cells, protects the surviving cells and allows healing to occur. In a healthy liver, this repair process is very closely regulated and when no longer needed the extra collagen will disperse and the liver returns to normal.
Read Also: Hepatitis C How Is It Transmitted
Hepatitis C And Liver Cancer: What To Know
Several viruses besides HPV have been linked to cancer, includinghepatitis C, which is linked to liver cancer.
If you think HPV is the only virus that causes cancer, think again. Several other viruses have been linked to cancer, including hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is the most common blood-borne infection in the United States. Its also the leading cause of liver cancer.
About 30 percent of people who get exposed to the hepatitis C virus will clear it on their own. The rest will go on to have chronic hepatitis C.
This ongoing infection causes inflammation in the liver. This extended inflammation can cause scarring, called cirrhosis, and can ultimately lead to liver cancer.
Chronic hepatitis C also increases the risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and head and neck cancers.
Unlike hepatitis A and B, there is no vaccine against hepatitis C, and there are few if any symptoms, says Harrys Torres, M.D., associate professor of Infectious Diseases.
Its a silent infection, he says. And its a very clever virus that mutates very fast, so it has been difficult to develop a vaccine.
Knowing the risk factors and getting screened are your best defenses against cancers caused by hepatitis C. Treatment of this virus can reduce your risk of liver cancer by 75%.
Risk factors
About 75% of those infected with hepatitis C in the United States are baby boomers people born between 1945 and 1965.
Other risk factors for hepatitis C infection include:
Life Expectancy Among Patients With Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection Cirrhosis
- Date:
- JAMA – Journal of the American Medical Association
- Summary:
- Patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection and advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis who attained sustained virological response had survival comparable with that of the general population, whereas patients who did not attain SVR had reduced survival, according to a study.
Patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection and advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis who attained sustained virological response had survival comparable with that of the general population, whereas patients who did not attain SVR had reduced survival, according to a study in the November 12 issue of JAMA.
Almost three million people in the United States are chronically infected with the hepatitis C virus . The life expectancy of patients with chronic HCV infection is reduced compared with the general population, largely attributable to the development of cirrhosis, liver failure and cancer. Studies have shown that the risk of all-cause death is lower among patients with chronic HCV infection and advanced hepatic fibrosis if sustained virological response is attained, but comparisons have been limited to those without SVR, according to background information in the article.
Story Source:
Recommended Reading: Hiv Hepatitis B And C
The Local Homeless Ill
We had 55 people in this evening, the sessions seem to be reliably in the 50s every week, so this brings new challenges. The hall is not that big really so with 20 volunteers also is can seem pretty crowded.
Having the larger of numbers of people coming in each week now it is very intensive in the respect of peoples individual needs. Some people are happy just to come in eat and leave where others want to sit and chat. The variety of problems that our clients are experiencing are so varied that we have to be on our guard all the time at each session at the same time as showing kindness and compassion. Someone could walk through the door in crisis and with suicidal thoughts down to emotions of fear as they have just lost their job and frightened how they are going to pay their bills. Every person to us is just as important regardless of who they are and whatever their need is. We will always do our best to help in whatever way we are able and if we cannot help, we will signpost to someone or an organisation who can.
How Fibrosis Develops
When someone has liver disease, their liver enters into a very dangerous cycle. Persistent inflammation, or hepatitis, sends nonstop signals to repair cells to continue depositing collagen. The extra collagen stiffens around the tissue like it is supposed to in the healthy liver but, instead of a signal being released to stop the inflammation and discard the extra collagen, the inflammation continues, and even more collagen is deposited, leading to more stiffening. This is how fibrosis develops.
When repetitive damage or long-lasting inflammation occurs, collagen and other proteins build-up between liver cells, forming scar tissue. Scar tissue can block or limit blood flow within the liver, starving and killing healthy liver cells, causing more scar tissue to form. Unlike healthy liver cells, scar tissue cannot function or repair itself. As fibrosis advances it can impact the livers ability to function, limit its ability repair itself and restrict blood flow. Over time, the scars in the liver will continue to build and replace healthy tissue. Gradually, the scars snake out farther, covering more of the healthy liver and grow together, or bridge, creating or bands of scar tissue. Fibrosis also restricts blood flow. When doctors want to determine how severe the scarring is, they examine the impact on the portal blood flow. The portal vein brings all the blood from the intestines to the liver to be processed.
Cirrhosis
Recommended Reading: Royal Canin Hepatic Wet Dog Food
Causes Of Hepatitis C
You can become infected with hepatitis C if you come into contact with the blood of an infected person.
Other bodily fluids can also contain the virus, but blood contains the highest level of it. Just a small trace of blood can cause an infection. At room temperature, it’s thought the virus may be able survive outside the body in patches of dried blood on surfaces for up to several weeks.
The main ways you can become infected with the hepatitis C virus are described below.
Blood And Vessel Problems
People with hepatitis C often get a condition called cryoglobulinemia. This happens when certain proteins in your blood stick together in cold weather. They can build up in vessels and block blood flow, which causes swelling and damage. The condition can affect your skin, organs, nerves, and joints.
Hepatitis C also can cause problems with blood itself. You may not make enough white blood cells, which fight infections, or platelets, which help your blood clot.
The infection can also make you bruise easily or get red or purple spots under your skin. Those are signs of a bleeding disorder called immune thrombocytopenic purpura.
Don’t Miss: How Dangerous Is Hepatitis C