Estimates Of Hepatitis D Virus Prevalence At National Regional And Global Levels
Our search returned 3518 records, and 634 of these met the inclusion criteria . In total, 332155 individuals of the general populations from 48 countries and regions and 271629 HBsAg-positive carriers from 83 countries and regions were included . For estimating the global prevalence, we calculated that the pooled prevalence of HDV is 0.80% in the general population and 13.02% among HBsAg-positive carriers, corresponding to 4860 million infections worldwide . China, India, and Nigeria are the leading countries in this respect . Regionally, HDV is highly prevalent in central Asia, eastern Europe, tropical and central Latin America, as well as central and west sub-Saharan Africa . Asia followed by Africa are predominant with respect to global HDV burden. Hepatitis D virus infection is especially prevalent in low-income and lower-middle-income countries, but concomitantly data from these resource-limited countries are relatively limited .
Global prevalence of hepatitis D virus infection. General population hepatitis B virus surface antigens-positive carriers. Blank means HDV-pooled prevalence is not applicable due to lacking HDV epidemiological data. First 10 counties for the estimates of HDV burden were listed, respectively.
Hepatitis D Coinfection Vs Superinfection: What Is The Difference
Hepatitis D is one of the least-discussed but most fascinating of all hepatitis viruses. Tirst discovered in 1977, hepatitis D is considered to be the very smallest disease-causing virus in humans.
This particle is so small and so simple that it is not able to cause an infection on its own. Instead, hepatitis D needs hepatitis B to replicate and infect the liver. Once the virus enters a liver cell, it suppresses the replication of the hepatitis B virus and hijacks some parts hepatitis B coded for its own assembly.
This disease is spread via contact with infected blood, and using IV drugs unsafely or being exposed to other bodily fluids are two of the main ways of contracting hepatitis D. Although it isn’t very common, the infection can be passed from mother to child during childbirth as well.
It is estimated that there are around 20 million people currently living with hepatitis D worldwide. The symptoms of this disease aren’t different from those of other hepatitis viruses, both infectious and non-infectious. They include, among others:
- Pain in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen
- Pale stool
- Weight loss
- Jaundice
Metabolic And Autoimmune Changes
Another factor to consider is the down-regulation of the Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor and guanine binding proteins. These proteins are involved in the regulation of the mitogen activated protein kinase pathway, which is frequently implicated in cancer. A lower availability of Triosephosphate Isomerase and Pyruvate Carboxylase, which lead to an abnormal retention of lipids may also be responsible for microvesicular steatosis during HDV infection.
Furthermore, Wedemeyer et al suggest that hepatitis D is an immune mediated disease, noting a rise in CD4+ T cells in individuals with a HDV infection. Although the role of the hosts immune system seems unlikely, various autoantibodies have been detected in infected patients. Prominent amongst them is liver-kidney microsomal antibody type 3, directed against uridine diphosphate glucoronyl transferase. The disruption of metabolism in this way could contribute to HCC. Indeed Hanahan et al have already labeled some changes in cellular metabolism as hallmarks of cancer.
You May Like: Early Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
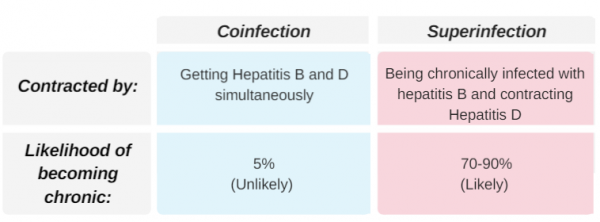
Hepatitis Delta: Coinfection Vs Superinfection
By Sierra Pellechio, Hepatitis Delta Connect Coordinator
Hepatitis delta is an aggressive form of hepatitis that can only exist alongside hepatitis B. This means that all hepatitis B patients are at risk for hepatitis delta, but so are people who have not received the hepatitis B vaccination series.
If contracted, 70-90% of people with chronic hepatitis B will go on to also develop a chronic hepatitis delta infection called a superinfection. Approximately 70% of these cases will progress to cirrhosis , compared to 15-30% of those infected only with the hepatitis B virus.
Due to the likelihood of liver complications, hepatitis B patients should be aware of potential exposures to hepatitis delta. The virus is spread the same way as hepatitis B, through direct blood-to-blood contact and unprotected sex with an infected person. It is important to be aware that blood contact could also occur by exposure to unsafe blood transfusions, unsterile medical or dental equipment, and the sharing of razors or toothbrushes with an infected person due to the possibility of infected blood entering the body.
The good news is that the hepatitis B vaccine series can prevent both viruses in people who are not already infected. Once completed, the vaccine can provide a lifetime of protection!
For more information about hepatitis B/delta coinfection, please visit www.hepdconnect.org or email us at .
Receptor Interaction And The Consequence Of Hbv Integration
Liver tropism and hepatic receptors of HBV and HDV
The liver tropism of HBV and HDV is primarily determined by a specific interaction of an extended receptor binding domain in the preS-1-part of the HBV L-protein and the hepatic NTCP receptor. NTCP interaction of HBV and HDV requires prior attachment to heparan sulphate proteoglycans . This mandatory step presumably triggers the release of the otherwise hidden preS-receptor binding site. HSPG-requirement explains how neutralising anti-HBsAg-specific antibodies, although they do not directly interfere with preS/NTCP-interaction, block entry and control infection.
NTCP exclusively locates at the basolateral/sinusoidal membrane of differentiated, polarised hepatocytes. NTCP-expression ceases when differentiated hepatocytes proliferate. NTCP is also downregulated in transformed cell lines of hepatic origin such as HepG2, HuH7 and Hep3B. Thus, proliferating normal hepatocytes, transformed hepatoma cells, and probably also tumour cells in HCC lack NTCP and do not support entry of HBV and HDV. Though, proliferating cells support spread of HDV RNA activated state) but loose HBV cccDNA . A deeper understanding of these peculiar differences of HDV and its helper HBV will be crucial for understanding persistence and is important for the development of successful therapeutic interventions.
Studying HDV replication in vitro
Consequences of HBV integration and clonal expansion of integrants
Recommended Reading: How Does One Contact Hepatitis C
Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis D
The incubation period for HDV depends on whether it is a co-infection or superinfection as the HBV surface antigens are necessary for HDV replication. Therefore in co-infection it depends on when there is sufficient surface antigens while with superinfection it is about 6 to 9 weeks. With co-infection, acute hepatitis occurs but it is self limiting. With superinfection, a severe acute hepatitis will arise. Some HBV carriers may not even be aware of the HBV infection until the onset of hepatitis following the inoculum of HDV. However those patients with chronic hepatitis B will report an aggravation of the condition. The clinical features may include :
- Jaundice
How Can Hepatitis D Be Treated
The treatment of this disease depends on the form the disease takes. If an acute form of the infection is present, specific therapy usually isn’t needed. The chronic form of the disease, on the other hand, requires intense therapy. Although interferon therapy is available, unfortunately, the response to this therapy is low. Liver transplantation is an option, if an acute liver failure occurs, or in the case of cirrhosis.
As for prevention, there is unfortunately no vaccine to protect you from hepatitis D. However, since the hepatitis D virus relies on the presence of the hepatitis B virus to cause an infection, a vaccine for hepatitis B can protect us from this form of viral hepatitis as well.
The other ways of staying safe from the infection, aside from immunization, include always using new, sterile needles , practicing safe sex and only receiving blood transfusions at facilitates that have tested for the presence of hepatitis D. Since even the smallest amounts of infected blood can cause an infection, it is also advised not to share personal equipment, such as razors or toothbrushes.
The good news is that there are fewer people infected with hepatitis D now than there were in the 1980s. There are several reasons for this, such as regular testing of the blood used for transfusions and increased popularity of condom use, but overall, the worldwide use of the hepatitis B vaccine is considered to be the main reason for the lowered number of people affected.
Read Also: Cost Of Medication For Hepatitis C
New Therapeutic Approaches Targeting Hbsag
Apart from the above-mentioned therapies, any new therapeutic that leads to functional cure in HBV monoinfected patients could be helpful in HBV/HDV coinfected ones. RNA interference and antisense oligonucleotides showed substantial declines of HBsAg in few weeks of administration in the absence of peg-IFN, suggesting a potential role also in the treatment of coinfected patients.
Open Questions And Future Directions
-
Can hepatitis D virus establish transcriptionally silenced but reactivatable episomes in hepatocytes as an additional mechanism of persistence?
-
To what extent do the eight HDV genotypes differ in replication efficacy and sensitivity against the upcoming novel treatments?
-
Do HDV-targeted therapies lead to a restoration of HDV-specific immunity?
-
Are these restored immune responses required for treatment response? Are they required for prevention of viral relapse? Of note, there may be differences in treatment regimens that are associated with alanine aminotransferase flares combination therapy) compared with treatment regimens without ALT flares .
-
How can a synergistic potential of antiviral drugs and immune-modulators be translated into curative regimens?
-
Are there baseline or on-treatment predictors to sustained HDV virological response for the different treatment strategies?
-
Is a sustained HDV virological response without hepatitis B surface antigen loss a realistic and achievable aim for treatment regimens without IFNs?
-
Are drugs aiming at HBsAg loss effective and safe in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus/HDV coinfection?
-
Last but not least, since HDV is prevalent in low-income countries and migrant populations, it will be important to establish new concepts to foster diagnosis and access to care.
Recommended Reading: What Are The First Signs Of Hepatitis C
Section Iv: Stability And Viability
DRUG SUSCEPTIBILITY: Susceptible to alfa interferon Footnote 1.
SUSCEPTIBILITY TO DISINFECTANTS: Unknown however, other hepatitis viruses are susceptible to 1-2% glutaraldehyde, 6-10% hydrogen peroxide, 8-12% formaldehyde, iodophores , chlorine compounds , and 0.5-3% phenolic compoundsFootnote 6.
PHYSICAL INACTIVATION: Unknown however, other hepatitis viruses can be inactivated by moist heat and dry heat Footnote 6.
SURVIVAL OUTSIDE HOST: Can survive in blood and blood products under the conditions used for the storage of such productsFootnote 1.
Factors Influencing Hepatitis D Progression
Many factors can influence the outcome of hepatitis D, the single most important being the pattern of infection with HBV, for instance, coinfection versus superinfection as described above.
The severity of hepatitis D is influenced by the HDV genotype. HDV isolates show up to 39% heterogeneity, and the different sequences have been classified into eight HDV genotypes . Although infection with multiple genotypes may occur in patients at high risk of repeated exposure such as injecting drug users, a single genotype usually predominates with > 10% of the viral load being represented by the minor strain . In the Western world, where most natural history studies detailed in the previous paragraph have been conducted, HDV genotype 1 is prevailing . In Taiwan, where the predominant genotype is 2, acute HDV infection evolves less frequently toward acute liver failure, and even chronic hepatitis D seems less rapidly progressive . On the other hand, infection with genotype 3, which is prevalent in South America, induces a severe form of hepatitis. Indeed, severe outbreaks of acute hepatitis D with a high incidence of liver failure have been reported among the Yucpa Indians of Venezuela , the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta in Colombia , and some areas of the Brazilian and Peruvian Amazonian forest. A viral factor potentially involved in influencing disease outcome is the occurrence of specific HDAg species that have been reported in acute liver failure cases .
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Adults
Symptoms Of Hepatitis D
- Have had sexual contact with someone who has hepatitis D
- Work in health care or a related field
- Are on dialysis
- Are a man who has sex with men
- Receive many blood transfusions or blood products
Additionally, babies born to a parent with hepatitis D are more likely to contract the disease. It’s rare for the disease to get passed from parent to child during birth, but it does happen.
Hepatocellular Carcinoma In Hdv Infection
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the second most common cause of cancer-related death in men worldwide. Persistent HDV replication and hepatic inflammation end up with cirrhosis and HCC formation. Active replication of both HBV and HDV may be associated with a more progressive disease pattern leading to early cirrhosis and HCC. Wu et al described three phases of HDV superinfection: acute phase, active HDV replication and suppression of HBV with high alanine transaminase levels chronic phase, decreasing HDV and reactivating HBV with moderate ALT levels and late phase, development of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma caused by replication of either virus or remission resulting from the marked reduction of both viruses. Therefore, HBV replication, in spite of being inhibited by HDV, appears to play a major role sustaining HDV pathogenicity.
Hepatic decompensation, rather than development of liver cancer, is the first clinical endpoint that develops during the course of HDV infection. A clinical study has suggested that HCC in HDV infection may be a secondary effect of severe necroinflammation leading to cirrhosis. In this study, decreased liver size was noticed more in cases of HDV HCC compared to an HBV monoinfection group where the liver size was normal or increased. HDV patients had lower platelets and larger varices on endoscopy as an indirect evidence of more severe portal hypertension. HCC presented at an earlier TNM stage compared with HBV monoinfection.
Don’t Miss: List Of Hepatitis C Medications
Hepatitis D Virus Infection Presents A Distinct Epidemiological Profile Among Hepatitis B Virus Patients
There are hardly data that comprehensively capture how and to what extent HDV contributes to severe liver diseases. It is interesting to note that the prevalence of HDV infection in HBsAg-positive patients is very distinct between different forms of liver pathology. Among acute HBV patients, the rate of HDV infection is much higher in FH compared with less symptomatic cases of AH . In chronic HBV patients, HDV infection rates are low in asymptomatic carrier , but they are high in CH , cirrhosis , and HCC . Comparison of symptomatic chronic HBV patients with asymptomatic controls of the same population yielded an OR for HDV infection of 3.56 , 6.75 , and 5.61 for CH, cirrhosis, and HCC, respectively . The pooled OR of these severe liver diseases is 4.55 , and thus HDV infection is significantly linked to more serious pathology in HBV patients.
The epidemiological profile of hepatitis D virus infection. Prevalence of HDV among acute hepatitis B virus patients. Prevalence of HDV among chronic HBV patients. Forest plot of HDV prevalence among patients with chronic liver diseases compared with asymptomatic controls. Data are pooled from a random-effects model. ASC, asymptomatic carrier CH, chronic hepatitis CI, confidence interval FH, fulminant hepatitis HBsAg, HBV surface antigen HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma.
Towards Therapeutics And A Better Understanding Of Hdv
A better understanding of the molecular events underlying HCC development following HDV infection is vital to not only the approach to the virus but also for the development of new drugs, which can target specific parts of the pathways involved if not the virus itself and prevent development of HCC in patients infected with HDV. For example the targeted inhibition of STAT3 with a decoy 15-mer double-stranded oligonucleotide, which corresponds to the STAT3 response element in the c-fos promoter region, has been experimentally proven to abrogate head and neck cancer growth and could eventually be used to prevent or treat HCC as well.
Cyclophilins are a class of proteins localized in various cellular compartments, involved in metabolism and homeostasis and are upregulated during inflammation and cancer. Cyclophilin A , in the cytoplasm, is involved in the virus life cycle, while extracellular CypA and CypB are pro-inflammatory in nature. Cyclosporins are potential cyclophilin inhibitors and could have therapeutic potential for the treatment of virus induced liver diseases. Indeed cyclosporin A has been shown to inhibit HBV and HDV entry via sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide. There is a direct interaction between the drug and the NTCP receptor , with overlap at the preS1 domain . CsA also has immunosuppressive effects, exercised via cyclophilin dependent inhibition of calcineurin.
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis B And Hiv The Same
Pathogenesis Of Hepatitis D
HDV only replicates in the liver, and therefore pathologic changes are limited to this organ. Liver damage in HDV infection is thought to be mostly immune mediated, although initial data from experimentally infected chimpanzees had suggested a direct cytopathic effect of HDV on hepatocytes, particularly during the primary infection . It was observed that in acute hepatitis D, infected hepatocytes were undergoing degenerative changes characterized by shrunken eosinophilic cytoplasm and pyknotic nuclei, with minimal inflammatory cells in the liver parenchyma, consistent with a cytopathic hepatocellular damage. These findings were reported both in vitro and in human studies . The small isoform of HDAg expressed was suggested to be responsible for this direct cytopathic effect of HDV . However, other results and in vivo observations, such as the presence of inflammatory cells surrounding the infected hepatocytes and the presence of various autoantibodies in the serum of patients, argue for a mostly immune-mediated liver damage. On the other hand, because HBV replication is usually suppressed by HDV, liver damage is believed to be induced mostly by HDV rather than by HBV.
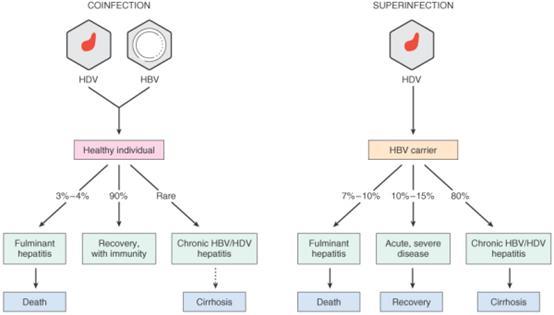
Different Infection Patterns Of Hepatitis D Virus Infection Result In Distinct Outcomes
Two major HDV infection patterns, coinfection and superinfection, provoke different outcomes . The majority of HBV-HDV-coinfected patients spontaneously recover from HDV infection , but only a minor proportion of superinfected patients recover . In contrast, only a relatively small proportion of coinfected patients develop chronic disease , but a substantial proportion of superinfected patients progress to chronic disease . The OR to recover or become chronically infected after HDV coinfection are 5.05 and 0.05 , respectively, relative to HDV superinfection. Stratification according to the pattern of viral infection reveals that most patients are HDV dominant or HBV-HDV codominant , with only a small fraction of patients being HBV dominant . Thus, patients with HBV infection will clearly benefit from measures that prevent further HDV infection.
You May Like: How Can You Contact Hepatitis B