Infants Born To Mothers Who Have Hepatitis B: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
Protecting Your Baby
Infants born to women with hepatitis B must receive accurate doses of hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin to ensure complete protection. In order to protect these infants, medications should be given immediately after birth in the delivery room or within the first 12-24 hours of life*.
* See Testing and Treatment During Pregnancy section for details. Please note that testing of all pregnant women for hepatitis B is a global recommendation.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Infants
The World Health Organization recommends that infants born to hepatitis B positive mothers receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth, and ideally a dose of hepatitis B immunoglobulin . These shots must be followed by the additional vaccine doses given on the recommended schedule. In the U.S., infants should follow a 1 month and 6-month schedule for the additional two doses.
4-Dose Combination Vaccine Series for Infants
How To Get Vaccinated Against Hepatitis B
All babies in the UK born on or after 1 August 2017 are given 3 doses of hepatitis B-containing vaccine as part of the NHS routine vaccination schedule.
These doses are given at 8, 12 and 16 weeks of age.
Babies at high risk of developing hepatitis B infection from infected mothers are given extra doses of the hepatitis B vaccine at birth, 4 weeks and 1 year of age.
If you think you’re at risk and need the hepatitis B vaccine, ask your GP to vaccinate you, or visit any sexual health or genitourinary medicine clinic.
If your job places you at risk of hepatitis B infection, it’s your employer’s responsibility to arrange vaccination for you, rather than your GP. Contact your occupational health department.
Concurrent Administration Of Vaccines
HB-containing vaccines may be administered concomitantly with other vaccines or with HBIg. Different injection sites and separate needles and syringes must be used for concurrent parenteral injections.
Refer to Timing of Vaccine Administration in Part 1 for additional information about concurrent administration of vaccines.
Also Check: How Can You Get Infected With Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B Vaccination In Pregnancy
Hepatitis B infection in pregnant women may result in severe disease for the mother and chronic infection for the baby.
This is why the hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for pregnant women who are in a high-risk category.
There’s no evidence of any risk from vaccinating pregnant or breastfeeding women against hepatitis B.
And, as it’s an inactivated vaccine, the risk to the unborn baby is likely to be negligible .
Why Is The Hepb Vaccine Recommended
People who dont know they’re infected can spread the hepatitis B virus. So it cant be avoided just by being careful. That’s why health experts recommend that all babies get the vaccine right from birth.
The HepB injection usually creates long-term immunity. Most infants who get the HepB series are protected from hepatitis B infection beyond childhood, into their adult years.
Eliminating the risk of infection also decreases risk for cirrhosis of the liver, chronic liver disease, and liver cancer.
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B Virus
Aboriginal And Torres Strait Islander People
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people are recommended to:
- have their risks and vaccination status for hepatitis B reviewed
- receive testing for previous hepatitis B virus infection
- receive vaccination if non-immune
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people have a higher risk of acquiring new hepatitis B virus infection than non-Indigenous Australians.2,3
Adult-formulation hepatitis B vaccine should be given in a 3-dose schedule.
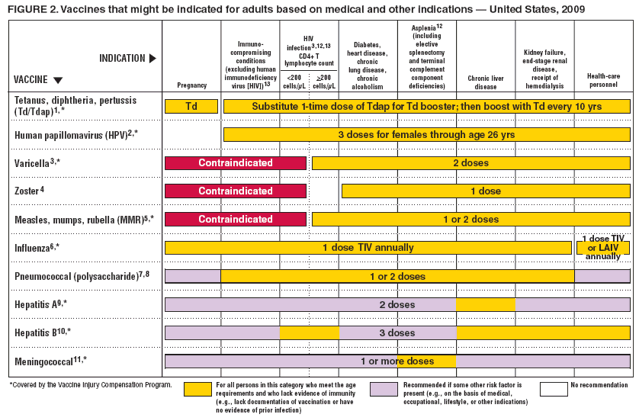
Children with HIV are recommended to receive 3 doses of hepatitis B vaccine using an adult formulation. This is double the recommended dose for children. In a limited number of studies, children who were immunocompromised responded better when given higher doses in a 3-dose schedule.4,5
Levels of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen should be checked after the vaccination course. See Serological testing after hepatitis B vaccination.
Adults with HIV are recommended to receive larger-than-usual doses of hepatitis B vaccine. They should receive 2 injections of the standard adult dose on each occasion at 0, 1, 2 and 6 months. Limited studies in adults with HIV have revealed an improved and accelerated serological response to a schedule that consists of 4 double doses.6,7
A 3-dose schedule at 6, 8 and 12 months after transplant is required using:
What Is The Morphology Of Hbv
HBV is an oncogenic DNA virus that belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family. The discovery of the etiologic agent of hepatitis B remains a remarkable scientific achievement. It was discovered in 1965 by Dr Blumberg, who won the Nobel Prize in Medicine for his discovery in 1976 . HBV virus, initially called the Dane particle, is a 42-nm virus . HBV is composed of a nucleocapsid core, surrounded by an outer lipoprotein coat . The virus contains 3 primary structural antigens: surface , core , and e . HBsAg is produced in excess amounts and found in the blood of infected individuals in the form of spherical and tubular particles . These immunogenic, but noninfectious, subviral particles lack genomic DNA and paved the way to develop hepatitis B vaccines . HBV is divided into 4 major phenotypic subtypes based on antigenic epitopes presented on its envelope proteins, and comprises 10 major genotypes that differ at the nucleotide level across full-length genotypes by> 8% . The HBV genotypes have distinct virological characteristics and geographical distributions however, the licensed HBV vaccines are effective against all genotypes .
A, Electron micrograph of hepatitis B virus : Dane particles and spherical and tubular surface antigen particles . Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. As a work of the U.S. federal government. B, A simplified figure of the HBV particle and surface antigens.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Definition Of Hepatitis B
What Is Hepatitis B
Viral hepatitis type B caused by the hepatitis B virus is a serious, potentially life-threatening disease that can be prevented by vaccination. Most people that are HBV infected remain asymptomatic and do not know their hepatitis status for many years. Only some individuals newly infected with HBV have symptoms . The symptoms can include extreme fatigue, abdominal pain, nausea, and jaundice. Most available scientific evidence suggests that HBV is not directly cytopathic, but that liver damage is caused by the cellular response to viral proteins in infected hepatocytes . For many people, hepatitis B is a short-term illness as clinical signs and symptoms of acute hepatitis B usually resolve within 1 to 3 months . Fulminant liver failure occurs in approximately 0.5% to 1.0% of adults with reported acute hepatitis B. In a subset of persons, the HBV can also cause a chronic liver infection that can later develop into cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma . The course of chronic HBV infection is dynamic with different clinical phases, each of which potentially lasts for decades . Most of the disease burden associated with HBV infection occurs among persons with chronic infection .
Which Adults Should Be Vaccinated Against Hepatitis B
According to CDC recommendations, adults in the following groups are recommended to receive hepatitis B vaccine:
General
- All people age 18 years and younger.
- Anyone 19 years and older who wants to be protected from hepatitis B.
People at risk for infection by sexual exposure
- Sex partners of people who are hepatitis B surface antigen -positive.
- Sexually active people who are not in long-term, mutually monogamous relationships.
- People seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually transmitted disease.
- Men who have sex with men.
People at risk for infection by percutaneous or permucosal exposure to blood or body fluids
- Current or recent illegal injection drug users.
- Household contacts of people who are HBsAg-positive.
- Residents and staff of facilities for developmentally challenged people.
- Healthcare and public safety workers with reasonably anticipated risk for exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids.
- People with end-stage renal disease, including predialysis, hemo-, peritoneal- and home-dialysis patients.
Others
- International travelers to regions with intermediate or high levels of endemic HBV infection.
- People with chronic liver disease.
- People with HIV infection.
- People with diabetes who are age 19 through 59 years. For those age 60 and older, clinicians should make a determination of need for
- vaccination based on their patients’ situation.
In a future issue, we will review the various hepatitis B serologic tests, who needs testing, and when they need it .
You May Like: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Ql Reactive
Preparations Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis B vaccine is produced using recombinant DNA technology. A plasmid containing the gene for hepatitis B surface antigen is inserted into common bakers yeast, which then produces HBsAg. The HBsAg is harvested and purified. This vaccine cannot cause hepatitis B virus infection because no potentially infectious viral DNA or complete viral particles are produced during this process.
Single-antigen and a combination formulation that combines hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines are available. Two single-antigen vaccines, Engerix-B® and Recombivax HB®, are conjugated with aluminum. A newer formulation, HepB-CpG , uses the immune-stimulating adjuvant, cytidine-phosphate-guanosine oligodeoxynucleotide .
Indications For Hepatitis B Vaccine
HepB vaccine also is indicated for adults who have not been previously vaccinated when any of the following is present:
-
A desire for protection from hepatitis B in people who have not been previously vaccinated
-
A sexually active lifestyle in people who are not in a long-term, mutually monogamous relationship
-
Need for evaluation or treatment of a sexually transmitted disease
-
Current or recent use of illicit injection drugs
-
Sex between men
-
Employment in which workers may be exposed to blood or other potentially infectious body fluids
-
Diabetes in people < 60 years and sometimes in those 60 years
-
End-stage renal disease
-
HIV infection
-
A chronic liver disorder
-
Household contact and/or sexual contact with people who are positive for hepatitis B surface antigen
-
Travel to endemic areas
-
Time spent in correctional facilities or in facilities that provide sexually transmitted disease treatment, HIV testing and treatment, drug abuse treatment and prevention services, services to injection-drug users or men who have sex with men, or care for patients with developmental disabilities or with end-stage renal disease
-
Pregnant women if at risk of infection or severe outcome resulting from infection during pregnancy
The combination HepA and HepB vaccine can be used in people 18 years who have indications for either hepatitis A or hepatitis B vaccine and who have not been previously vaccinated with one of the vaccine components.
Read Also: Do I Have Hepatitis B
Transmission Symptoms And Treatment
How is HBV transmitted?
HBV is transmitted through activities that involve percutaneous or mucosal contact with infectious blood or body fluids , including
- sex with an infected partner
- injection-drug use that involves sharing needles, syringes, or drug-preparation equipment
- birth to an infected mother
- contact with blood from or open sores on an infected person
- exposures to needle sticks or sharp instruments and
- sharing certain items with an infected person that can break the skin or mucous membranes , potentially resulting in exposure to blood.
How long does HBV survive outside the body?
HBV can survive outside the body and remains infectious for at least 7 days .
What should be used to clean environmental surfaces potentially contaminated with HBV?
Any blood spills should be disinfected using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 10 parts of water. Gloves should be worn when cleaning up any blood spills.
Who is at risk for HBV infection?
The following populations are at increased risk for becoming infected with HBV:
- Infants born to infected mothers
- Sex partners of infected people
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household contacts or sexual partners of known people with chronic HBV infection
- Health-care and public-safety workers at risk for occupational exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- Hemodialysis patients
Who should be screened for HBV?
CDC recommends that the following people be screened for HBV :
- fever,
People At Occupational Risk

Hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for people who work in any occupation that involves any of:
- direct patient care
- handling human tissue, blood or body fluids
- handling used needles or syringes
These people should also routinely follow standard precautions against exposure to human tissue, blood or body fluids.19
The risk to people in certain occupations differs considerably between settings in different parts of Australia. Workers who have an increased risk of acquiring hepatitis B include:
- healthcare workers
- police, members of the armed forces, emergency services staff and staff of correctional facilities, if they are assigned to duties that may involve exposure to human tissue, blood or body fluids
- funeral workers, embalmers and other workers who have regular contact with human tissue, blood or body fluids, or used needles or syringes
- staff involved in both residential and non-residential care of people with developmental disabilities, because of the high prevalence of markers of past or current infection in people in this setting16-18
- workers who perform skin penetration procedures, such as tattooists and body-piercers
Early childhood educators and carers are normally at minimal risk of hepatitis B transmission. The local public health authority can provide advice about risk if needed.
Adult-formulation hepatitis B vaccine should be given in a 3-dose schedule. See Table. Monovalent hepatitis B vaccines for adolescents and adults in Vaccines, dosage and administration.
Recommended Reading: Just Food For Dogs Hepatic
Why Do You Need A Hepatitis B Shot
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that cant be transferred person-to-person unless you have contact with an infected persons bodily fluids. Annual infection rates of HBV are going down in the United States thanks to vaccines. So you might be wondering if you or your child needs a shot to protect against hepatitis B.
Measles Mumps And Rubella Vaccination
Routine vaccination
- No evidence of immunity to measles, mumps, or rubella: 1 dose
- Evidence of immunity: Born before 1957 , documentation of receipt of MMR vaccine, laboratory evidence of immunity or disease
Special situations
- Pregnancy with no evidence of immunity to rubella: MMR contraindicated during pregnancy after pregnancy , 1 dose
- Nonpregnant women of childbearing age with no evidence of immunity to rubella: 1 dose
- HIV infection with CD4 count 200 cells/mm3 for at least 6 months and no evidence of immunity to measles, mumps, or rubella: 2-dose series at least 4 weeks apart MMR contraindicated for HIV infection with CD4 count < 200 cells/mm3
- Severe immunocompromising conditions: MMR contraindicated
- Students in postsecondary educational institutions, international travelers, and household or close, personal contacts of immunocompromised persons with no evidence of immunity to measles, mumps, or rubella: 2-dose series at least 4 weeks apart if previously did not receive any doses of MMR or 1 dose if previously received 1 dose MMR
- Health care personnel:
- Born in 1957 or later with no evidence of immunity to measles, mumps, or rubella: 2-dose series at least 4 weeks apart for measles or mumps or at least 1 dose for rubella
- Born before 1957 with no evidence of immunity to measles, mumps, or rubella: Consider 2-dose series at least 4 weeks apart for measles or mumps or 1 dose for rubella
Don’t Miss: Can You Catch Hepatitis C From Sex
Transporting Storing And Handling Vaccines
Transport according to National Vaccine Storage Guidelines: Strive for 5.87 Store at +2°C to +8°C. Do not freeze. Protect from light.
Infanrix hexa must be reconstituted. Add the entire contents of the syringe to the vial and shake until the pellet completely dissolves. Use reconstituted vaccine as soon as practicable. If it must be stored, hold at room temperature for no more than 8 hours.
Us Infant Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Infants
Since 1991, ALL medically stable infants with a birth weight of at least 2,000 g in the U.S. are recommended to receive the first dose of hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth. The additional 2 doses are given at 1 month and 6 months of age.
4-Dose Vaccine Combination Series for Infants
Combination vaccines, such as the pentavalent and hexavalent vaccines, include protection against 5 or 6 diseases, including hepatitis B. The first shot is usually given at 6 weeks of age, but in order to protect infants from hepatitis B beginning at birth, a monovalent or single dose of the hepatitis B vaccine is also recommended within 24 hours of birth. The hepatitis B vaccine series can then be completed with the pentavalent or hexavalent vaccine with the recommended schedule.
You May Like: Do They Have A Cure For Hepatitis C
Accelerated Us Children And Adult Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
In some instances, it may be necessary to vaccinate within a short period of time to ensure protection before travel. There are accelerated schedules to provide the highest level of protection over a short period of time. Individuals who need an accelerated schedule must have a booster dose at 1 year to ensure long-term protection. Note that the 2-dose Heplisav-B vaccine will also ensure maximum protection over a 1-month period without the need for a booster dose at 1 year.
4-Dose Vaccine Series for Children and Adults
Engerix-B is a 3-dose vaccine that can be given on an accelerated, four-dose schedule, with 3 shots administered within 2 months, and a booster dose at 1 year to provide maximum long-term protection.
4-Dose Combination Hepatitis A and B Vaccine Series
Twinrix is a 4-dose vaccine that can be given on an accelerated schedule to provide protection against hepatitis A and B. Three doses are administered within 1 month, followed by a booster shot at 1 year. This is a common choice of vaccine for those travelling on short-notice outside the U.S. It is important to complete the booster dose at 1 year, to ensure long-term protection.
2-Dose Vaccine Series