Treatments For Different Genotypes
DAAs are the most common treatment that directly targets the hepatitis C virus. A person may also need to take other medications, depending on the genotype of the virus and any complications of the infection.
The best treatment option tends to depend on whether or not the person has cirrhosis. The options below apply to people who have not previously received treatment for hepatitis C.
The following medications are recommended for genotypes 1a and 1b:
- elbasvir and grazoprevir
- ledipasvir and sofosbuvir
- glecaprevir and pibrentasvir
- sofosbuvir and velpatasvir
If a person has genotype 2 or 3, a healthcare provider may choose to prescribe glecaprevir and pibrentasvir or sofosbuvir and velpatasvir.
For people who have genotype 4, they may prescribe glecaprevir and pibrentasvir, sofosbuvir and velpatasvir, elbasvir and grazoprevir, or ledipasvir and sofosbuvir.
For people with genotypes 5 or 6, they may describe a combination of these medications. As one study paper concludes, developing more effective treatments and a better understanding of the prevalence of the condition will require more research.
The right treatment varies from person to person. When recommending a course of action, a healthcare provider will take into consideration previous treatments, medical history, overall health, and any complications of hepatitis C.
Do Genotypes Change Over Time
A viruss genotype usually stays the same. Genetic changes, or mutations, can occur at random or in response to the environment. Some mutations are harmless, but others can affect how well a patient responds to treatment. New HCV treatments include more than one drug to prevent drug resistance from happening by targeting more than one step in the virus life cycle. However, if patients miss treatment doses, this can lead to genetic mutations, which cause resistance to HCV treatment .
HARDER TO TREAT GENOTYPE 3
Genotype 3 is the second most common HCV subtype in the world, particularly in Northern Europe, South Asia, and Southeast Asia. It can pose more difficult health problems for people with HCV, including more rapid progression of liver disease, increased rates of steatosis , and a higher risk for cancer . Genotype 3 has been associated with unique characteristics, such as how it creates resistance to insulin and how it causes the liver to break down fats, which make it harder to treat with DAAs.
People infected with genotype 3 are the most challenging to treat if they:
- have previously tried treatment
- have cirrhosis, and
- have , which is a life-threatening condition leading to liver failure.
Genotype 3 often requires longer treatment and does not achieve strong cure rates. There are lower cure rates in patients with cirrhosis.
Zeroing In On The Hepatitis C Virus
The era of direct-acting antivirals that specifically target HCV began in 2011 with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval of the first protease inhibitors. These drugstelaprevir and boceprevir, along with several similar drugs approved latertargeted the HCV protease that is critical for viral replication. When used in conjunction with peginterferon and ribavirin, protease inhibitors yielded SVR rates of up to 75 percent. However, this triple therapy was accompanied by additional side effects to those already present with peginterferon and ribavirin. Nevertheless, the success of HCV-specific protease inhibitors showed that the virus had vulnerabilities that could be exploited by a well-designed and properly administered drug.
More new anti-HCV drugs were developed and tested over the next several years. These new drugs included sofosbuvir and dasabuvir, which interfered with the activity of the HCV polymerase, an enzyme that is responsible for the viral replication. Members of a second class of drugs, ledipasvir and daclatasvir, targeted the NS5A region of the virus, which makes a structural protein critical for viral replication. Many of these drugs were initially tested in conjunction with peginterferon and ribavirin, or in combination with a protease inhibitor. Generally, the results were SVR rates of at least 80 percent.
Also Check: Do I Have Hepatitis C
Questions For Your Doctor
When you visit the doctor, you may want to ask questions to get the information you need to manage your hepatitis C. If you can, have a family member or friend take notes. You might ask:
Study Population And Hcv Viral Load
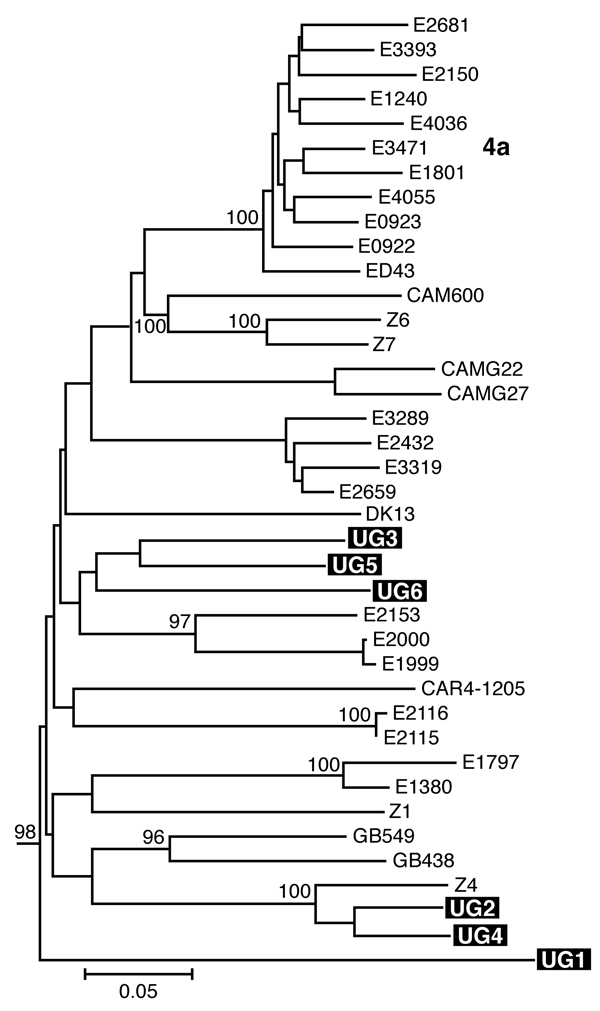
The Centre Pasteur of Cameroon is the reference laboratory for HIV and Hepatitis in Cameroon. As part of this role, patients are routinely referred to CPC for viral load and genotyping. Data reported here were collected in the framework of these routine activities and no additional parameter was assessed.
From January to December 2016, all samples received at CPC for HCV genotyping and viral load were included. Demographic data were recorded for all patients. The HCV viral loads were determined using the Abbott RealTime HCV assay and the Abbott m2000 platforms according to the manufacturers instructions. Briefly, 0.5mL plasma sample was used for RNA extraction on the Abbott m2000sp followed by amplification using the m2000rt. The detection limit was 12IU/mL.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Is Caused By
Assessing The Severity Of The Infection
If you are found to have virus present then other tests may be advised to check on the extent of inflammation or damage to the liver. For example:
- Blood tests called liver function tests. These measure the activity of chemicals and other substances made in the liver. This gives a general guide as to whether the liver is inflamed and how well it is working. See the separate leaflet called Liver Function Tests. Other blood tests will also be done for various reasons. For example, tests to check for other illnesses which can be passed on in the same way, such as HIV or hepatitis B. Also tests of other functions of the liver, such as the ability of blood to clot properly, and levels of iron stores.
- An ultrasound scan of the liver.
- Other tests may be done if cirrhosis or other complications develop.
- There are other specialised blood tests being developed which assess the development and severity of cirrhosis.
- A small sample of the liver taken to look at under the microscope used to be recommended before considering treatment. However, this is no longer routine prior to treatment. See the separate leaflet called Liver Biopsy.
Viral Hepatitis Definition And Overview
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Many illnesses and conditions can cause inflammation of the liver, for example, drugs, alcohol, chemicals, and autoimmune diseases. Many viruses, for example, the virus causing mononucleosis and the cytomegalovirus, can inflame the liver. Most viruses, however, do not attack primarily the liver the liver is just one of several organs that the viruses affect. When most doctors speak of viral hepatitis, they are using the definition that means hepatitis caused by a few specific viruses that primarily attack the liver and are responsible for about half of all human hepatitis. There are several hepatitis viruses they have been named types A, B, C, D, E, F , and G. As our knowledge of hepatitis viruses grows, it is likely that this alphabetical list will become longer. The most common hepatitis viruses are types A, B, and C. Reference to the hepatitis viruses often occurs in an abbreviated form The focus of this article is on these viruses that cause the majority of human viral hepatitis.
Hepatitis viruses replicate primarily in the liver cells. This can cause the liver to be unable to perform its functions. The following is a list of major functions of the liver:
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Blood Test Results
How Genotypes Affect Treatment
Medications known as direct acting antivirals, or DAAs, stop the hep C virus from making copies of itself. Some DAAs appear to work well on all hepatitis C genotypes. Others work on only one or some.
Your doctor will probably prescribe some combination of these medications:
- Velpatasvir
Some pills combine two drugs into one pill.
You’ll probably take these meds for anywhere from 8 to 12 weeks. But they may not be right for everyone because of things like cost or other illnesses.
Your specific genotype can tell your doctor important things about how to use those medications, what to watch for, and other drugs you might need.
For example, you may have a higher chance for cirrhosis if you have genotype 1.
Genotype 3, the second most common subtype worldwide, may not respond as well to DAAs alone. In addition, this type might suggest that:
- Liver cancer is more likely.
- Insulin resistance might happen. When your body resists or doesn’t respond to insulin as well as normal, you have a higher chance of heart disease and diabetes.
- You might need longer, more challenging treatment
Your doctor might adjust or change your DAA treatment if you have:
Show Sources
American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases: âInitial Treatment of Adults with HCV Infection,â âHCV Guidance: Recommendations for Testing, Managing, and Treating Hepatitis C.â
CDC: âHepatitis C Questions and Answers for the Public.â
Infohep.org: âHepatitis C treatment factsheet: Harvoni .â
Clinical Significance Of Hepatitis C Genotypes
Genotype generally has not been found in epidemiological studies to play a large rolein liver disease progression due to HCV. Rather, genotype is of clinical importanceprincipally as a factor in selecting the appropriate HCV medications for treatment. Please see the HCV Treatment Considerations for more information.
Don’t Miss: Interesting Facts About Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C Has Different Genotypes What Does This Mean
HCV is a single-stranded RNA virus. That means the genetic code of each virus particle is contained within one continuous piece of the nucleic acid RNA.
Every strand of a nucleic acid is made up of a chain of building blocks. The sequence of these blocks determines the proteins that an organism requires, whether its a virus, plant, or animal.
Unlike HCV, the human genetic code is carried by double-stranded DNA. The human genetic code goes through strict proofreading during the process of DNA replication.
Random changes to the human genetic code occur at a low rate. Thats because most mistakes of DNA replication are recognized and corrected.
In contrast, HCVs genetic code isnt proofread when its replicated. Random mutations occur and stay in the code.
HCV reproduces very quickly up to 1 trillion new copies per day. So, certain parts of HCV genetic code are highly varied and change frequently, even within a single person with an infection.
Genotypes are used to identify particular strains of HCV. Theyre based on differences in particular regions of the viral genome. There are additional branching subcategories within a genotype. They include subtype and quasispecies.
Retreatment Of Persons With Prior Peginterferon And Ribavirin Failure
The latest version of the AASLD-IDSA HCV Guidance no longer provides specific recommendations for retreatment of persons with a history of peginterferon plus ribavirin therapy, with or without an earlier generation direct-acting antiviral agent . The AASLD-IDSA HCV Guidance notes that these individuals respond to retreatment similar to treatment-naïve persons, thus implying the treatment approach should be the same as with treatment-naïve individuals. Although the pool of persons with a history of failure with a peginterferon-based regimen who need retreatment is small and diminishing, there are some individuals with this treatment history who need retreatment and may require special consideration that differs from that of treatment-naïve individuals. The following outlines a few of these key considerations based on available data and previous guidance that should be noted when retreating an individual with a history of prior treatment failure with peginterferon plus ribavirin, with or without an earlier generation DAA . Note that except for the 8-week option of glecaprevir-pibrentasvir , when retreating these individuals with first-line DAA combinations that have pangenotypic activity , the treatment will be the same as their treatment-naïve counterparts.
You May Like: How Do You Contact Hepatitis C
Eu Clears Gilead’s Hepatitis C Therapy Sovaldi
Regions first all-oral treatment approved to treat the virus
Gilead Sciences has been granted approval by the European Commission for Sovaldi, getting a green light for the first all-oral treatment for chronic hepatitis C virus in the EU.
The European regulator approved Sovaldi for use both in combination with pegylated interferon alpha and ribavirin in patients with hepatitis C genotypes 1, 4, 5 or 6, and as an interferon-free regimen alongside ribavirin alone in patients with hepatitis C genotypes 2 or 3 or those awaiting a liver transplant.
Gilead’s drug – which is the first compound in the NS5B polymerase inhibitor class to be registered – was approved for the same indication in the US in December 2013, and analysts are already predicting that it could reach blockbuster sales levels of $1bn or more by the end of this year and $5bn or more at peak.
One reason for the anticipated rapid take-up of Sovaldi is that hepatitis C patients have been delaying treatment – a phenomenon known as ‘warehousing’ – in anticipation of the availability of more effective and tolerable new therapies.
Despite the fact that hepatitis C is curable, there is a pressing need for new and improved therapies because “many hepatitis C virus patients have not currently achieved a cure and often progress to end-stage liver disease or liver cancer,” he added.
BMS is hoping to position daclatasvir alongside sofosbuvir as the basis of an all-oral, interferon-free regimen of choice for hepatitis C.
Hbeag Seroconversion And Hbsag Seroclearance
HBeAg seroconversion and HBsAg seroclearance are the most important steps in the natural progression of HBV infection, and the annual incidence of these are 12% and 2%, respectively. Earlier HBeAg seroconversion is generally accepted as a positive outcome. Conversely, delayed seroconversion, or its absence, after recurrent hepatitis attacks may indicate progression of chronic hepatitis to LC. Following their study in Taiwanese patients, Lin et al reported that spontaneous HBeAg seroconversion in patients with genotype C was lower than that in genotype B patients . HBeAg seroconversion rate in genotype B patients is lower than genotype C patients, and a more lengthy persistence of HBV replication explains why LC and HCC development was found in patients with this genotype.
Read Also: Hepatitis A B C Symptoms
How Is Genotype Determined
A simple blood test can be used to determine your hepatitis C genotype. The test doesnt have to be repeated because once someone has been infected with HCV, the genotype remains the same. It is possible to be infected by more than one HCV genotype. However, this occurs rarely.
Learn more about recommended treatment based on HCV genotype.
How Common Is Hepatitis C
The exact number of people infected is not known. There are around 200,000 people chronically infected with hepatitis C in the UK. Worldwide, over 180 million people are infected. Rates of infection have been relatively stable in recent years, but deaths from hepatitis C have reduced, thought to be because treatment options have become better.
Most cases are in people who inject illegal drugs. It is estimated that up to half of injecting drug users become infected with hepatitis C.
You May Like: What Is Non Reactive Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C Testing And Diagnosis
Doctors will start by checking your blood for:
Anti-HCV antibodies: This blood test is the first — and sometimes only — one you may get. Also called the ELISA screen, it checks for antibodies that your body releases to fight the virus. These are proteins your body makes when it finds the hep C virus in your blood. They usually show up about 12 weeks after infection. Your test will be either negative or positive for antibodies. It usually takes a few days to a week to get results, though a rapid test is available in some places.
What the results mean
Negative . This is when your blood shows no signs of HCV antibodies. Most of the time, thatâs because you never came in contact with the virus and you do not have hep C.
Sometimes, your negative result can be false, meaning you have HCV. That may happen if you:
- Took the test too soon after your exposure. This test checks for only HCV antibodies, which can take several months to appear.
- Have HIV, a donated organ, or other conditions that weaken your immune system, which can suppress your antibodies
- Get hemodialysis for kidney problems
If youâve been exposed in the last 6 months, youâll need to be retested.
Positive . This means youâve been infected with HCV. But false positives are surprisingly common. More than 1 in 5 people who test positive donât actually have hepatitis C. Possible reasons include:
What the results mean
Determination Of Hcv Genotypes And Subtypes
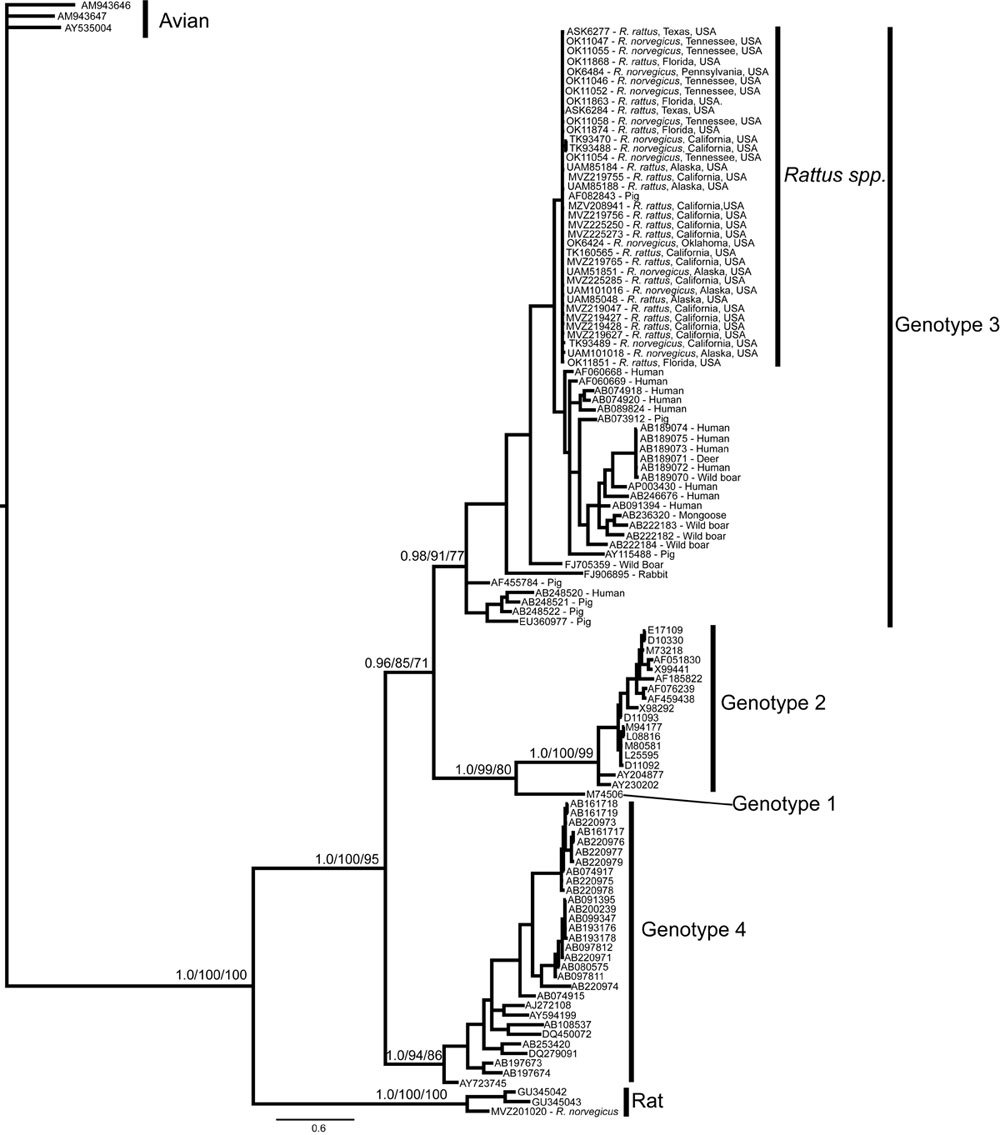
Nucleotides sequences obtained in both regions were aligned by ClustalW with reference sequences representing HCV genotypes and subtypes retrieved from Genbank . Phylogenetic trees were further constructed in MEGA 6.06 software by the neighbor-joining method with the Kimura two-parameter method for computing evolutionary distances . Robustness of the tree topologies was estimated by bootstrap analysis with 1000 pseudo-replicate data sets, and only bootstrap values > 70 were considered significant.
Don’t Miss: Hep C Without Hepatic Coma Meaning
Response To Interferon Therapy
An interferon-sensitive region in the nonstructural portion of the HCV genome has been identified in Japanese patients infected with genotype 1b . However, studies from the United States and Europe failed to confirm these findings . The significance of these findings is not known, and the clinical application of such an expensive and labor-intensive procedure to predict the response to treatment is impractical.
Do You Need Vaccinations Before Traveling Abroad
The CDC divides travel vaccinations into three categories: 1) routine, 2) recommended, and 3) required. The only vaccine classified as “required” by International Health Regulations is the yellow fever vaccination for travel to certain countries in sub-Saharan Africa and tropical South America.
“Routine” vaccinations are those that are normally administered, usually during childhood, in the United States. These include immunizations against:
- tetanus
You May Like: Does Hepatitis C Affect The Liver