What Type Of Doctor Treats Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is treated by either a gastroenterologist, a hepatologist , or an infectious disease specialist. The treatment team may include more than one specialist, depending on the extent of liver damage.Surgeons who specialize in surgery of the liver, including liver transplantation, are part of the medical team and should see patients with advanced disease early, before the patient needs a liver transplant. They may be able to identify issues that need to be addressed before surgery can be considered. Other persons who can be helpful in managing patients include dietitians to consult on nutritional issues and pharmacists to assist with management of drugs.
Can You Die From Hepatitis C
Complications from untreated hepatitis C, including cirrhosis and liver cancer, can be fatal, though HCV itself is rarely fatal.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , people who develop cirrhosis from HCV have a
more than half of people with an HCV infection will develop chronic hepatitis C. Chronic hepatitis C is long term and can lead to permanent cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Chronic hepatitis C usually has no symptoms. People with chronic hepatitis C may not even know they have it. But once symptoms appear, it means that damage to the liver has already begun.
Medications Used To Treat Hepatitis C
The HCV Medications section on this website provides detailed information for each of the Food and Drug Administration -approved medications listed in the treatment recommendations, including links to the full prescribing information and to patient assistance programs. The DAAs exert their action at specific steps in the HCV life cycle. There are three major classes of DAA medications: nonstructural proteins 3/4A protease inhibitors, NS5A inhibitors, and NS5B polymerase inhibitors the NS5B polymerase inhibitors include the nucleoside analogs and nonnucleoside analogs. Adherence with the treatment regimen is of paramount importance. Thus, individuals should receive detailed counseling regarding the importance of adherence prior to starting therapy, as well as intensive monitoring and follow-up during therapy.
Don’t Miss: Life Insurance For Hepatitis B Carrier
Genotypes Of Hepatitis C
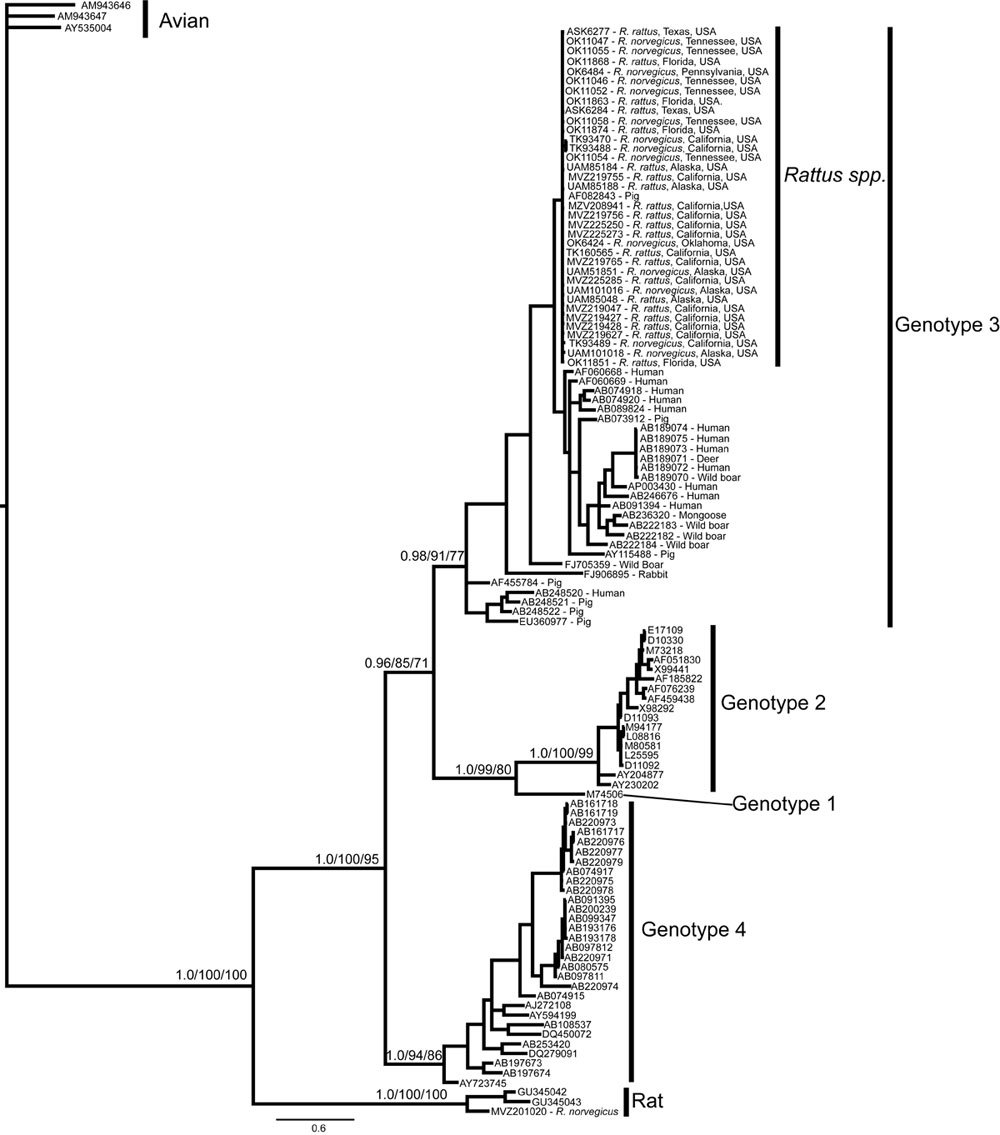
Which genotype of hepatitis C somebody has dictates what treatment is available to them. If you are living with genotype 3, then there is evidence that liver disease might progress more quickly.
The ability of the virus to mutate has resulted in the existence of different genetic variations of HCV. These are called genotypes. The different genotypes are often, but not exclusively, related to different parts of the world.
Genotypes 1, 2 and 3 have a worldwide distribution. Types 1a and 1b are the most common, accounting for about 60% of global infections. They predominate in Northern Europe and North America and in Southern and Eastern Europe and Japan. Genotype 2 is less frequently represented than type 1. Genotype 3 is endemic in south-east Asia. Genotype 4 is principally found in the Middle East, Egypt, and central Africa. Type 5 is almost exclusively found in South Africa. The most common genotypes found in the UK are 1 and 3.
It is still unclear whether or not the type of virus affects the progression of the disease. If it does it is not thought to present any real cause for concern. However, HCV genotype does influence response to treatment. If you are considering treatment it is very important to know which genotype you are actually infected with.
Clinical Significance Of Hepatitis C Genotypes
Genotype generally has not been found in epidemiological studies to play a large rolein liver disease progression due to HCV. Rather, genotype is of clinical importanceprincipally as a factor in selecting the appropriate HCV medications for treatment. Please see the HCV Treatment Considerations for more information.
You May Like: What Form Of Hepatitis Is Sexually Transmitted
What Medications Cure Hepatitis C Infection
Interferons, for example, Roferon-A and Infergen, and pegylated interferons such as Peg-IntronT, Pegasys, were mainstays of treatment for years. Interferons produced sustained viral response of up to 15%. Later, peglatedll forms produced SVR of 50%-80%. These drugs were injected, had many adverse effects, required frequent monitoring, and were often combined with oral ribavirin, which caused anemia. Treatment durations ranged up to 48 weeks.
Direct-acting anti-viral agents are antiviral drugs that act directly on hepatitis C multiplication.
Characteristics And Demographics Of Patients With Novel Hcv Subtypes
Of the 19 patients infected with novel HCV subtypes, 12 patients were enrolled in France . Of the remaining 7 patients, 2 patients each were enrolled in Great Britain and the United States, 1 patient was enrolled in each of Canada, India, and Taiwan. The overrepresentation of patients from France was particularly apparent for patients with novel genotype 2 and genotype 4 subtypes, where 6 of 9 patients and 4 of 5 patients, respectively, were from France. Of the patients from France with novel genotype 2 subtypes, the majority were black . There was a difference in gender between the subtypes, as the majority of patients with novel genotype 2 subtypes were male , but for the other novel subtypes, the majority were female .
You May Like: Medications Used To Treat Hepatitis C
What Are Hepatitis C Genotypes
A variable for those with chronic hepatitis C virus is the genotype, or the strain of the virus when they contracted an infection. The genotype is determined by a blood test.
The genotype doesnt necessarily play a role in progression of the virus, but rather as a factor in selecting the right medications for treating it.
According to the
Whats The Difference Between Hepatitis C Genotypes
As mentioned, the different HCV genotypes and subtypes have different distributions throughout the world.
Genotype 1 is the most common HCV genotype in the United States. Its found in nearly 75 percent of all HCV infections in the country.
Most of the remaining people in the United States with HCV infection carry genotypes 2 or 3.
The HCV genotype isnt absolutely related to the rate of liver damage, or the likelihood of eventually developing cirrhosis. However, it can help predict the outcome of treatment.
The genotype can help predict the outcome of anti-HCV therapy with interferon-based treatment regimens. Genotype has also helped to determine treatment.
In some formulations, the recommended doses of ribavirin and pegylated interferon are for people with specific HCV genotypes.
Recommended Reading: When Do Hepatitis C Symptoms Appear
Genotypes And Hcv Genetic Heterogeneity As Epidemiologic Markers
Because of geographic clustering of distinct HCV genotypes, genotyping may be a useful tool for tracing the source of an HCV outbreak in a given population. Examples include tracing the source of HCV infection in a group of Irish women to contaminated anti-D immunoglobulins . All of these women were infected with HCV genotype 1b, a genotype identical to the isolate obtained from the implicated batch of anti-D immunoglobulin. Hohne et al. used genotyping to trace the sources of outbreaks in Germany . More recently, genotyping and molecular characterization of HCV isolates provided evidence for a patient-to-patient transmission of HCV during colonoscopy . The index case as well as the two other infected patients had HCV genotype 1b. Nucleotide sequencing of the NS3 region showed that the three patients had the same isolate , strongly suggesting a common source of infection.
Although Zein et al. found no association between HCV genotypes and the mode of HCV acquisition in their population, others have provided evidence for such an association . It has been suggested that genotypes 3a and 1a are closely associated with intravenous drug use and that genotype 1b is seen more often in patients who acquired HCV through blood transfusion. This information may be useful in tracing sources of HCV epidemics.
Progression To Lc Or Hcc
In a meta-analysis investigating the correlation between HBV genotypes and HCC, HCC detection was 12% for genotype B, and 25% for genotype C . Moreover, a correlation between genotype C patients and more severe liver diseases has been reported. Conversely, genotype A and genotype C have a similar HCC risk. In accordance with previous studies, another meta-analysis showed that HCC development was associated more with genotype C patients than with patients with the other HBV genotypes.
A study carried out in South Korea showed that HBV mutations were significantly related to HCC in CHB patients infected by genotype C, especially in major histocompatibility complex class II-restricted regions. In the prec/C region, there are six and seven types of mutations that are related to HCC, and these define HBeAg serostatus. The results showed that HBV variants in the C region could lead to HCC progression in chronic patients infected by genotype C by the immune escape pathway against the CD4 T-cell-mediated immune response. Therefore, it was concluded that HCC-related hepatitis B core antigen mutations and HBeAg serostatus could be used as diagnostic markers for early diagnosis of liver disease progression, including HCC. Interestingly, many studies reported that HCC development was observed in patients at an advanced age with genotype C, whereas this occurred earlier in genotype B patients.
You May Like: Hepatomegaly With Diffuse Hepatic Steatosis
Approach To Choosing Hcv Genotype 3 Treatment Regimen
When considering treatment of persons with chronic HCV genotype 3, five major factors influence the choice and duration of therapy: cirrhosis status, prior treatment experience, coexistent renal disease, drug interactions, and medication cost and/or insurance considerations. With certain regimens for treatment-experienced and/or cirrhotic patients, pretreatment NS5A resistance may also influence both the choice of regimen and duration of therapy. The following treatment recommendations are based on the 2013 AASLD/AST Evaluation for Liver Transplantation Guidelines for initial treatment of adults with HCV genotype 3 and for retreatment of adults in whom prior therapy failed, including those with HCV genotype 3.
How Is Hepatitis C Diagnosed
Blood tests for hepatitis C
There are several blood tests for the diagnosis of hepatitis C infection. Blood can be tested for antibody to hepatitis C . It takes about 8-12 weeks on average, and up to 6 months, for antibodies to develop after the initial infection with hepatitis C, so screening for antibodies may miss a few newly infected individuals. Having antibodies is not an absolute indication of active, multiplying hepatitis C virus, but if the antibody test is positive , the statistical probability of active infection is greater than 99%.
Several tests are available to measure the amount of hepatitis C virus in a person’s blood . The hepatitis C virus’s RNA can be identified by a type of test called polymerase chain reaction that detects circulating virus in the blood as early as 2-3 weeks after infection, so it can be used to detect suspected acute infection with hepatitis C early infection. It also is used to determine whether active hepatitis is present in someone who has antibodies to hepatitis C, and to follow the viral load during treatment.
Blood tests are also performed to identify the genotypes of HCV. Genotypes respond differently to different treatment, so this information is important in selection of the most appropriate treatment regimen.
Estimation of liver fibrosis using blood tests also is quite reliable in diagnosing clinically significant scarring these include FIB-4, FibroSure, Fibrotest, and aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index .
Don’t Miss: Royal Canin Feline Hepatic Diet
Why Do People Have Different Genotypes
A person of any racial or ethnic group can carry any genotype or subtype. However, some may be more prevalent in some racial or ethnic groups than others. In the United States, over 90% of African Americans, compared to 67% of Caucasians, carry genotype 1.
People who travel between regions where different genotypes are more common can be exposed to different HCV genotypes, leading to a mixed infection. HCV is transmitted through contact with blood, such as through contaminated blood products or medical equipment, blood transfusions, kidney dialysis, or the sharing of drug injection equipment, such as syringes, or non-injection equipment, such as pipes, spoons, cotton balls, or straws for snorting drugs.
Willowbrook State School Experiments
A New York University researcher named Saul Krugman continued this research into the 1950s and 1960s, most infamously with his experiments on mentally disabled children at the Willowbrook State School in New York, a crowded urban facility where hepatitis infections were highly endemic to the student body. Krugman injected students with gamma globulin, a type of antibody. After observing the temporary protection against infection this antibody provided, he then tried injected live hepatitis virus into students. Krugman also controversially took feces from infected students, blended it into milkshakes, and fed it to newly admitted children.
Read Also: How Is Hepatitis B Virus Transmitted
Which Treatment Works For Each Genotype
- All Genotypes: see Epclusa fact sheet
- Genotypes 1 through 4: see Sovaldi, Viekira XR and Technivie, Harvoni, Olysio fact sheets
- Genotypes 1 or 4: see Zepatier fact sheet
- Genotypes 2 or 3: see Sovaldi, Daklinza fact sheets
- Genotype 6: see Harvoni fact sheets
Ribavirin causes birth defects and miscarriage. HCV treatment regimens that include RBV should not be used by pregnant women or by male partners of pregnant women. RBV stays in a persons body for months, so women and their male partners should avoid pregnancy until six months after stopping it .
This fact sheet is current as of December 2016. It is recommended to be read alongside the Adherence and HCV Diagnostics fact sheets. Always check for updated information.
Whats The Outlook For Hep C Thats Developed Into Cirrhosis Or Liver Cancer
Hepatitis C can lead to cirrhosis, especially if left untreated. Without treatment, cirrhosis can lead to liver cancer and liver failure.
Treating cirrhosis and liver cancer typically requires a liver transplant. A transplant can cure both cancer and liver function impairment. But a transplant is only available for a small number of people.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Is Curable Or Not
What Are The Most Common Hepatitis C Virus Genotypes
HCV genomic analysis by means of an arduous gene sequencing of many viruses has led to the division of HCV into six genotypes based on homology. Numerous subtypes have also been identified. Arabic numerals denote the genotype, and lower-case letters denote the subtypes for lesser homology within each genotype.
Molecular differences between genotypes are relatively large, and they have a difference of at least 30% at the nucleotide level. The major HCV genotype worldwide is genotype 1, which accounts for 40%-80% of all isolates. Genotype 1 also may be associated with more severe liver disease and a higher risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Genotypes 1a and 1b are prevalent in the United States, whereas in other countries, genotype 1a is less frequent. Genotype details are as follows:
Within a region, a specific genotype may also be associated with a specific mode of transmission, such as genotype 3 among persons in Scotland who abuse injection drugs.
References
World Health Organization. Hepatitis C: fact sheet. Available at . Updated: October 2017 Accessed: January 23, 2018.
Frank C, Mohamed MK, Strickland GT, et al. The role of parenteral antischistosomal therapy in the spread of hepatitis C virus in Egypt. Lancet. 2000 Mar 11. 355:887-91. .
Kim A. Hepatitis C virus. Ann Intern Med. 2016 Sep 6. 165 :ITC33-ITC48. .
Bonkovsky HL, Mehta S. Hepatitis C: a review and update. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001 Feb. 44:159-82. .
Clinical Importance Of Hbv Genotypes
A greater understanding of the relationship between HBV genotypes, progression of hepatitis B disease, and clinical outcomes has developed over time. Clinical outcomes of chronic HBV infections are variable, and many viral factors, such as host factors, HBV genotype, specific viral mutations, viral load, and quantitative HBsAg levels are important in their prediction. HBV genotypes in viral factors are not only predictive of clinical progression, but are also related to interferon – treatment response. In a study comparing genotypes B and C, alanine aminotransferase levels were higher in patients with genotype C. However, the reason for this is not yet known. The primary clinical and virological features among HBV genotypes are shown in Table .
Read Also: Can You Catch Hepatitis C From Your Own Blood
Amplification Rate Of Core And Ns5b Regions
A positive amplification was obtained in at least one genomic region for all the samples with similar amplification rate in the two genomic regions . Three hundred and forty six samples were positive in the core region while 338 were positive in the NS5B region. Three hundred and fifteen samples were positive in both regions , 31 samples positive in core region only and 23 samples positive in the NS5B region only .
Table 2 Amplification rate of Core and NS5B regions
Hepatitis C And Health
How can health-care personnel avoid exposure to HCV?
Avoiding occupational exposure to blood is the primary way to prevent transmission of bloodborne illnesses among health-care personnel. To promote blood safety in the workplace, health-care personnel should consult infectious-disease control guidance from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health and from CDC. Depending on the medical procedure involved, Standard Precautions may include the appropriate use of personal protective equipment .
What is the risk of acquiring hepatitis C after being accidentally exposed to HCV-contaminated blood or body fluids in the workplace?
Although sharps injuries have decreased in recent decades due to improved prevention measures, they continue to occur, placing health-care personnel at risk for several bloodborne pathogens like hepatitis C. A recent analysis of several studies revealed an overall 0.2% risk for infection among those exposed to HCV-antibody-positive blood through needlestick or sharps injuries . Updated guidelines for management and treatment of hepatitis Cexternal icon are available to provide guidance for health-care personnel who become infected via exposure to contaminated blood at the workplace.
Other than needlesticks, do other exposures place health-care personnel at risk for hepatitis C?
Should HCV-infected health-care personnel be restricted in their work?
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Adults