Complications Of Hepatitis C
If the infection is left untreated for many years, some people with hepatitis C will develop scarring of the liver .
Over time, this can cause the liver to stop working properly.
In severe cases, life-threatening problems, such as liver failure, where the liver loses most or all of its functions, or liver cancer, can eventually develop.
Treating hepatitis C as early as possible can help reduce the risk of these problems happening.
How Hepatitis C May Be Eradicated
The Nobel Laureates discovery of the hepatitis C virus was a landmark achievement in the ongoing battle against viral diseases that paved the way for highly sensitive blood tests for the virus as well as the rapid development of antiviral drugs that can cure the disease, the Nobel committee said in its statement announcing the winners.
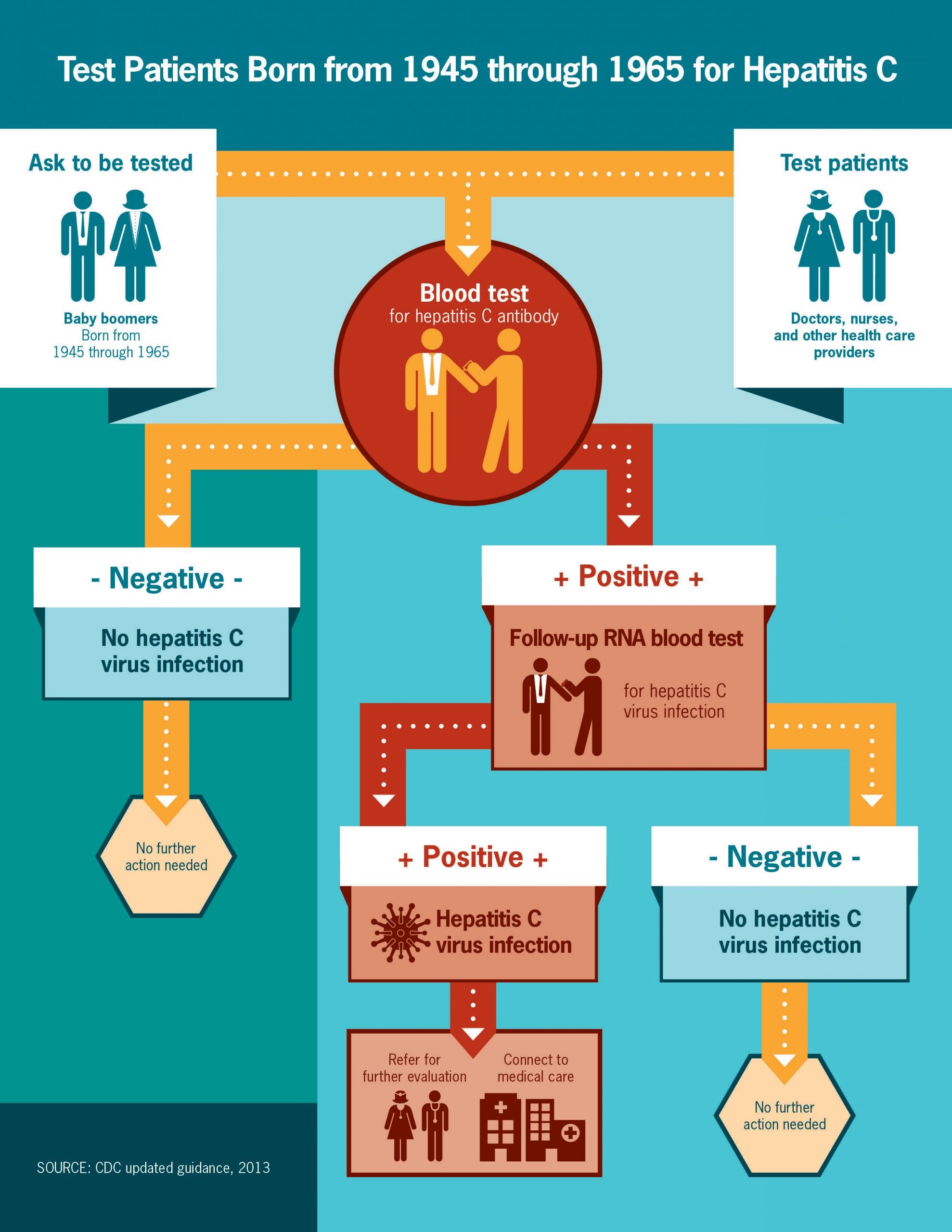
Hepatitis C is diagnosed in two processes, according to the World Health Organization . First, a blood test for hepatitis C antibodies identifies people who have been infected. Then, if that test is positive, a second blood test is used to confirm if people have a chronic infection.
People with chronic hepatitis C can get an additional workup including a liver biopsy or noninvasive tests to assess the extent of liver damage and diagnose conditions like fibrosis and cirrhosis, according to the WHO.
Antiviral medicines can cure more than 95 percent of people with hepatitis C infections, according to the WHO. The trouble is that many people cant access testing or afford medicines, particularly in the developing world.
To achieve this goal , international efforts facilitating blood testing and making antiviral drugs available across the globe will be required.
Pamela Anderson Cured Of Hepatitis C: What You Should Know About The Virus
Pamela Anderson has announced shes been cured of hepatitis C after living with the virus for 16 years.
The actress and model, 48, took to Instagram to share her good news. I am CURED!!! – I just found out #nomorehepc,” she wrote in the caption. “I pray anyone living with hep C can qualify or afford treatment. It will be more available soon. I know treatment is hard to get still…#dontlosehope.
Hepatitis C can be a debilitating and even fatal condition, but it can also be asymptomatic for years before it causes problems. That’s why it can go entirely unnoticed for years. In fact, of the estimated 2.7 million people in the United States who have hep C, three in four don’t know they’re infected, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention .
Many, many more people have never even heard of it. Below, we outline the need-to-know facts on the condition.
Read Also: What Are The Ways You Can Get Hepatitis C
Hcv Pseudotype Virus Particles
The HCV pseudotyped particles were constructed with chimeric genes expressing HCV envelope E1 and E2 proteins and the transmembrane and cytoplasmic tail of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein. The pseudotyped particles allowed a detailed study of the role of HCV receptors in the early steps of HCV infection in Huh7 cells and primary human hepatocytes. The system is useful for testing of new antiviral drugs.
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis C
Doctors treat hepatitis C with antiviral medicines that attack the virus and can cure the disease in most cases.
Several newer medicines, called direct-acting antiviral medicines, have been approved to treat hepatitis C since 2013. Studies show that these medicines can cure chronic hepatitis C in most people with this disease. These medicines can also cure acute hepatitis C. In some cases, doctors recommend waiting to see if an acute infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
Your doctor may prescribe one or more of these newer, direct-acting antiviral medicines to treat hepatitis C:
You may need to take medicines for 8 to 24 weeks to cure hepatitis C. Your doctor will prescribe medicines and recommend a length of treatment based on
- which hepatitis C genotype you have
- how much liver damage you have
- whether you have been treated for hepatitis C in the past
Your doctor may order blood tests during and after your treatment. Blood tests can show whether the treatment is working. Hepatitis C medicines cure the infection in most people who complete treatment.
Hepatitis C medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Check with your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Can You Get Rid Of It
What Is Chronic Hepatitis C
Doctors refer to hepatitis C infections as either acute or chronic:
- An acute HCV infection is a short-term illness that clears within 6 months of when a person is exposed to the virus.
- A person who still has HCV after 6 months is said to have a chronic hepatitis C infection. This is a long-term illness, meaning the virus stays in the body and can cause lifelong illness. An estimated 3.2 million people in the U.S. have chronic HCV.
Preventive Measures For Hcv Infection
Treatment options for hepatitis C are expensive, noncurative, and out of reach for the majority of people living in less-developed countries. Hence, prevention of infection remains an important public health goal.
HCV has a high mutation rate and multiple genotypes, which have challenged the development of an HCV vaccine. As a result, the primary means of prevention include infection-control practices in health care settings , the screening and testing of blood and organ donors, and viral inactivation in plasma-derived products. The development in the 1990s of highly effective assays to screen for HCV in donor blood greatly reduced the transmission of the virus in health care settings.
Risk-reduction counseling may help prevent the transmission of HCV among individuals who inject drugs.
Also Check: How Do You Hepatitis B
Symptoms Of Hcv Infection
About 70 to 80 percent of individuals who contract HCV show no symptoms of acute hepatitis. When present, symptoms of acute illness may include fever, malaise, nausea, jaundice, arthralgia , dark urine, pale stools, and abdominal pain. Acute symptoms typically subside within several weeks. In very rare instances, primarily when another chronic liver disease is present, acute illness culminates in fulminant hepatic failure.
In roughly 70 to 90 percent of persons infected with HCV, the virus persists in the liver following the acute phase of infection. In the majority of cases, chronic infection is asymptomatic for decades. The infection may be noticed only after routine blood tests reveal elevated levels of liver enzymes, by which time liver function has begun to decline. Symptomatic patients may experience fatigue, nausea, anorexia, myalgia , arthralgia, weakness, and weight loss. Complications arising from chronic HCV infection include cirrhosis , liver failure, and liver cancer.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Most people infected with hepatitis C have no symptoms. Some people with an acute hepatitis C infection may have symptoms within 1 to 3 months after they are exposed to the virus. These symptoms may include
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you most likely will have no symptoms until complications develop, which could be decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
Also Check: Chronic Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma Hcc
Virus Production In Huh751 Cells
Taking advantage of the JFH-1 genome and a highly permissive Huh7.5-derived cell line designated Huh7.5.1, Zhong et al. made the perplexing observation that transfected cells released up to 105 focus-forming units per ml, as determined by the average number of HCV protein -positive foci detected by immunofluorescence analysis of cells infected with the highest virus dilution. This number is 50-fold higher as compared to a previous study that also used the same JFH-1 isolate but naïve Huh-7 cells as well as another Huh-7 cell clone . The difference appears to be due at least in part to the higher permissiveness of Huh7.5.1 cells, but what renders these cells more permissive, and which stage of the replication cycle is affected? Different scenarios can be envisioned: Huh7.5 cells have a defect in the RIG-I pathway, making them less responsive to intracellular dsRNA, generated during virus replication and inducing an antiviral program . The reduced efficiency of the host cell’s innate defenses could explain the higher permissiveness. Alternatively, Huh7.5.1 cells may display a higher density of virus receptors allowing attachment and entry to proceed with greatly enhanced efficiency. Also, virus assembly and egress could be more efficient in this particular host cell.
Virus Release And Extracellular Particles
Analysis of cell supernatant by gradient density centrifugation demonstrated that the MVs subpopulations are different, depending on the cell line. It is known, that MVs are intensively released by primary hepatocytes and immortalized cells of hepatic origin. The release from hepatocytes might be increased by an undergoing lipotoxicity. Thus, MVs are actively used by the hepatocytes as delivery system and the amounts of MVs might be increased in response to lipotoxicity and likely other complications. In this regard, we speculate that during acute phase of infection the virus can trigger the MV release and that might be an additional pathway for the virus. How MVs containing virus particles can influence HCV distribution along the density gradient? In fact, MV containing different amount of viruses may contribute to observed diversity of buoyant densities of HCV, especially when plasma is investigated.
It is known, that the diffusion of spherical particle through a viscous liquid is dependent on the particle diameter. It is described by Stokes-Einstein equation:
Math.
D = diffusion constant, k = Boltzmann constant, T = temperature , = solvent viscosity, r = radius of spherical particle.
Another parameter that influences the diffusion is the mass of spherical particle and the equation counting these parameters looks as follows:
Math.
where: D = diffusion = radius of the spherical particle M = mass of the particle = viscosity of the medium.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatic Metastatic Disease
Who Is Most At Risk Of Contracting Hepatitis C
You have a high risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- use or have used injection drugs even if it was just once or many years ago
- have received blood or blood products or an organ transplant before July 1990 in Canada
- have been in jail or
- have been injected or scratched during vaccination, surgery, blood transfusion or a religious/ceremonial ritual in regions where hepatitis C is common.
You have a high moderate risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- have tattoos or body piercing
- have multiple sexual partners
- have a sexually transmitted infection , including HIV or lymphogranuloma venereum
- have experienced traumatic sex or rough sex or have used sex toys or fisting that can tear body tissue
- have vaginal sex during menstruation
- have received a kidney treatment
- have received an accidental injury from a needle or syringe
- have another infectious disease
- were born to a hepatitis C infected mother or
- have a sexual partner infected with hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is NOT passed from person to person by:
- coughing, sneezing
- breastfeeding unless your nipples are cracked and bleeding or
- oral sex, unless blood is present.
Alterations Of Lipid Metabolism
Lipids are required for the HCV replication and particles assembly. As mentioned above, HCV can modify the host serum lipid profile and this modification can provoke the steatosis. The steatosis is more frequent and more severe in patients with HCV gt 3 and it is correlated with a high HCV RNA levels. On one hand, in HCV-infected patients, the steatosis can be considered as a marker of the liver disease progression and, on the other hand, as an indication of the reduced response to therapy. However, if it is not metabolic or alcoholic steatosis, an efficient antiviral therapy is capable to reduce it.
You May Like: When Was Hepatitis C Discovered
Questions For Your Doctor
When you visit the doctor, you may want to ask questions to get the information you need to manage your hepatitis C. If you can, have a family member or friend take notes. You might ask:
Treatment And Medication For Hepatitis C
If you have acute hepatitis C, there is no recommended treatment. If your hepatitis C turns into a chronic hepatitis C infection, there are several medications available.
Interferon, peginterferon, and ribavirin used to be the main treatments for hepatitis C. They can have side effects like fatigue, flu-like symptoms, anemia, skin rash, mild anxiety, depression, nausea, and diarrhea.
Now youâre more likely to get one of these medications:
Find out more on treatment options for hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: Cost Of Medicine For Hepatitis C
Identification Of The Hepatitis C Virus
HCV was first recognized in 1989 using recombinant technology to create peptides from an infectious serum that were then tested against serum from individuals with non-A, non-B hepatitis. This approach resulted in the isolation of a section of the HCV genome. Subsequently, the entire HCV genome was sequenced. HCV is a member of the family of flaviviridae. Flaviviruses are positive, single-stranded RNA viruses. The HCV genome encodes a gene for production of a single polypeptide chain of approximately 3000 amino acids. This polypeptide gives rise to a number of specific proteins. The Env proteins are among the most variable parts of the peptide chain and are associated with multiple molecular forms in a single infected person. The mutations affecting this portion of the HCV genome seem to be critical for escape of the virus from the host immune response. The HCV protein NS5a contains an interferon-response element. Evidence from several studies suggest that mutational variation in the HCV genome encoding this protein are associated with resistance to interferon, the main antiviral agent used in treatment of HCV. Other proteins encoded by the HCV genome include the NS3 region that codes for a protease and the NS5b region that codes for an RNA polymerase. Drugs that target the HCV protease or polymerase are now undergoing trials as therapeutic agents to treat HCV infection.
Stuart C. Ray, David L. Thomas, in, 2015
How Is The Hepatitis C Virus Spread
Blood-to-blood contact with blood containing the virus spreads HCV infection. The infection may spread in the following ways:
- Sharing equipment for snorting, smoking or injection of drugs, such as needles and syringes, straws and pipes, with someone living with HCV
- Exposure to blood and/or blood products, including receiving a transfusion of blood or a blood product in a country where the blood supply is not tested for HCV. In Canada, this applies to blood and blood products received before 1992
- An accidental poke with a needle or syringe used by someone living with hepatitis C
- From a mother to her baby before or during birth
- Skin-piercing events such as tattoos, body piercing, acupuncture or electrolysis, if the equipment is contaminated with the virus
Other, less common ways HCV is spread is through:
- Sexual intercourse, especially if blood or open sores are present
- Sharing toothbrushes, dental floss, razors, nail files or other items, which could have tiny amounts of blood on them
There is a very low risk of spreading the virus through other body fluids like semen or vaginal secretions. This risk increases if blood is present in these secretions.
There is no vaccine to prevent people from getting HCV infection.
Read Also: Hepatitis C And Kidney Failure
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis C
Treatment for hepatitis C is with antiviral medicines. They can cure the disease in most cases.
If you have acute hepatitis C, your health care provider may wait to see if your infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
If your hepatitis C causes cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Treatments for health problems related to cirrhosis include medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If your hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Hcv Infection
Hepatitis C can be a “silent but deadly” infection. Most people with HCV have no symptoms. But even without symptoms, they can develop health problems decades later and can still pass the disease to others.
When symptoms do happen , they can be similar to those of hepatitis A and hepatitis B and include:
- jaundice
- fever
- nausea, vomiting, and lack of appetite
- belly pain
- joint pain
You May Like: Transplanting Hepatitis C Positive Kidneys
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis C
You are more likely to get hepatitis C if you:
- Have injected drugs
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you probably will not have symptoms until it causes complications. This can happen decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
Envelope Proteins E1 And E2

Glycoproteins E1 and E2 are type 1 transmembrane proteins that are forming the envelope of the virus particle .3B). E1 an E2 are cleaved from the precursor in ER by the cellular SP. The glycoproteins contained large hydrophilic ectodomains and 30 aa long transmembrane domains . The TMD is responsible for an anchoring of the envelope proteins in the membrane of the ER and their ER retention. The ectodomains of both glycoproteins are heavily glycosylated. The E1 has 4-5 and the E2 – 11 putative N-glycosylation sites, respectively. Interestingly, the glycosylation sites are rather conserved in each genotype, but the number of glycosylation sites varies between the genotypes. Its worth mentioning, that some of the glycans are engaged in folding and formation of the E1-E2 heterodimer complexes on the surface of the virion. These complexes are essential for the interaction with cellular receptors and helps to promote the virus-to-cell fusion.
You May Like: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Saliva