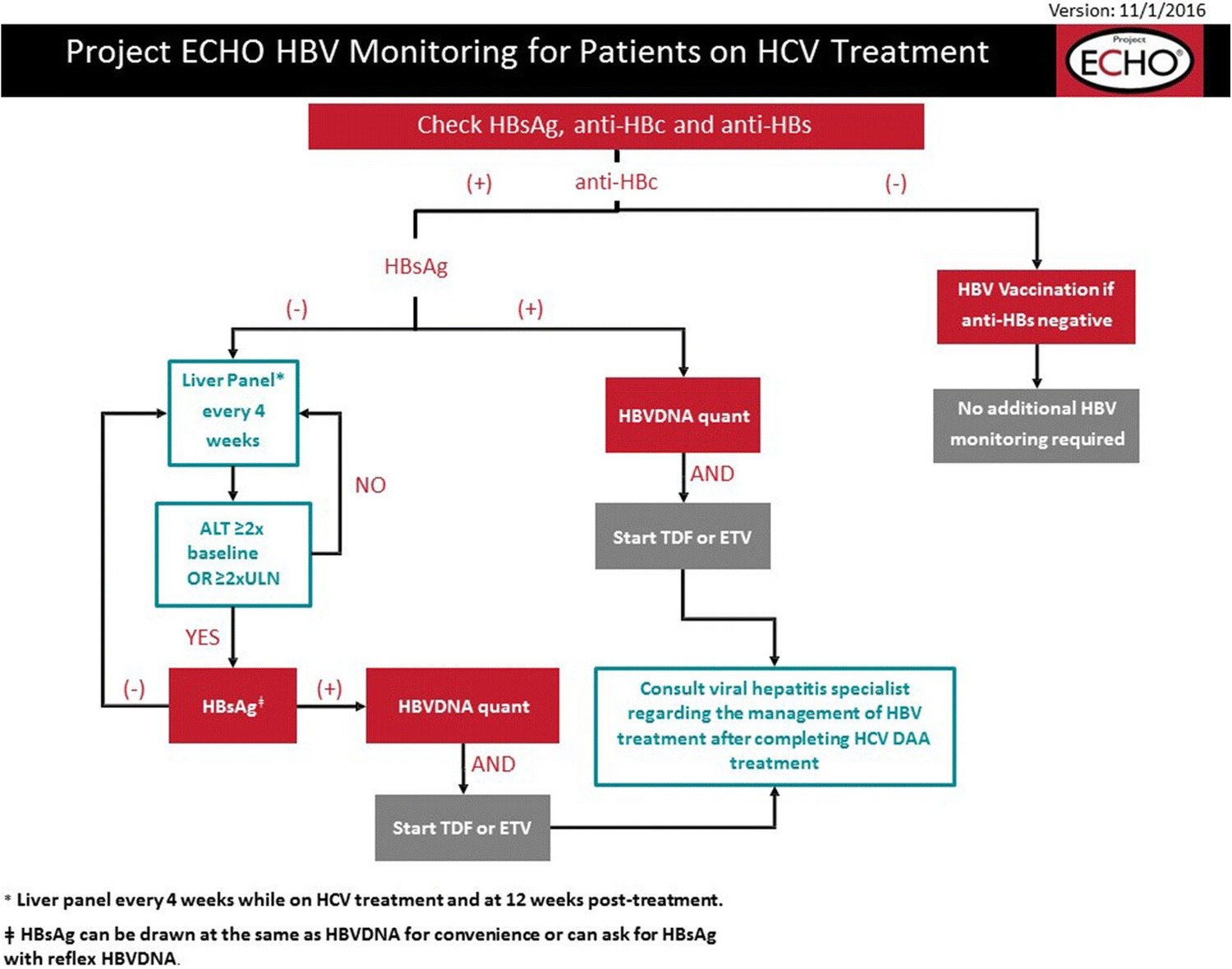
Reactivation Risk In Anti
Table 1 American Gastroenterological Association classification of reactivation risk in HBsAg/anti-HBc patients Full size table
The risk of HBV reactivation can be assessed based on positivity for HBV serum biomarkers and the type, duration, combination of agents, and dosing of immunosuppressive or chemotherapeutic agents . HBV reactivation risk can be as high as 4070% in anti-HBc-only, patients who are undergoing chemotherapy with B cell depleting antibodies like rituximab .
Noting that reactivation after immunosuppressive therapy is associated with significant morbidity and mortality, the AGA recommends antiviral prophylaxis for patients classified as at either moderate or high risk for reactivation for low-risk patients, there is no prophylaxis recommendation monitoring is per provider preference but seemingly sufficient . Entecavir and tenofovir prodrugs should be used as first-line prophylaxis or therapy due to their stronger antiviral potency and high threshold for resistance.
What Do Hepatitis B Test Results Mean
Hepatitis B test results help determine if HBV infection is negative or positive, and if positive, whether the infection is acute or chronic, or if recovery is complete. A combination of results are considered to identify and classify HBV infection status.
The following are some interpretations of hepatitis B test results:
Table: Hepatitis B test results and interpretations
| Test |
|---|
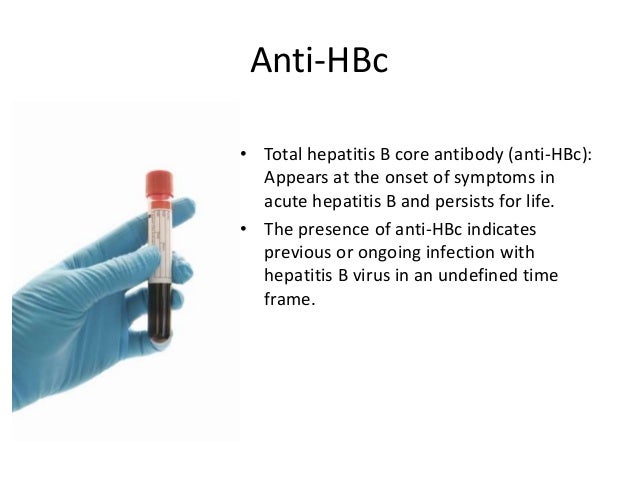
Hepatitis B Core Antibody Total Blood Test
A Hepatitis B Core Antibody Total Blood Test is used to find out if you are infected with the hepatitis B virus.
Also Known As: Anti-HBc Antibody to Hepatitis B Core Antigen HBcAb Total
Methodology: Immunochemiluminometric assay
Preparation: No fasting required. Stop biotin consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection.
Test Results: 2-3 days. May take longer based on weather, holiday or lab delays.
Also Known As: Anti-HBc Antibody to Hepatitis B Core Antigen HBcAb Total
Methodology: Immunoassay
Preparation: No fasting required. Stop biotin consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection.
Test Results: 2-3 days. May take longer based on weather, holiday or lab delays.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vaccine Information Sheet
Don’t Miss: How Do You Prevent Hepatitis C
Being Tested For Hepatitis B Core Antibody
The hepatitis B core antibody test is part of a screening panel for hepatitis B, which also will include hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B surface antibody . These three tests look for acute and chronic infections.
Tests may be ordered if you have symptoms of hepatitis, such as jaundice , fever, fatigue, pale stools, dark urine, nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite. In this case, the hepatitis B core antibody IgM test may be used, as it shows an early stage of infection.
This test may be ordered if you are being screened for hepatitis B because you are donating blood or wish to become an organ donor. Hepatitis B can be transmitted by blood or through organ transplants, so donors are tested to prevent infecting recipients. Its possible to have had the infection with only mild symptoms, so many people dont realize they have had hepatitis B.
People who are part of populations at risk for hepatitis B infection will be screened. Screening is also often done for pregnant people, infants, people sharing a home with hepatitis B patients, people who may have been exposed by needlestick injuries or body fluids, and for people with HIV .
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis B testing is typically prescribed by a doctor and performed in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Taking a hepatitis B test requires a blood sample, which can be collected by a health care professional.
For laboratory-based testing, blood is drawn from a patients vein. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
You May Like: What Are The First Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Read Also: How Can You Get Hepatitis A And B
What Tests Will You Have To Do
Hepatitis B
You can be tested for hepatitis B at your VA medical center. This test is done by taking a sample of your blood.
Your provider may recommend the following tests:
Hepatitis B surface antibody If this test is positive, it means that:
- you have antibodies against hepatitis B and are safe from getting the disease
- you were either vaccinated against hepatitis B or exposed to it at some point in your lifetime
Hepatitis B core antibody If the test is positive, it means that:
- you have been exposed to hepatitis B and have developed an antibody to only part of the virus
- they will do more tests to find out if you currently have the disease
Hepatitis B surface antigen If the test is positive, it means that:
- you currently have hepatitis B infection
- you can spread the virus to others
Hepatitis B e antigen If the test is positive, it means that:
- you may have active hepatitis B and should be followed closely by your provider and possibly take hepatitis B medications
- you may be very contagious to others
Mutant Viruses And Chronic Infection
Anti-HBe-positive patients in the reactivated phase of the disease are also referred to as the HBeAg-negative viremic group. Genomic analyses has revealed that such patients carry natural mutants of the virus that have either reduced levels or complete abrogation of HBeAg production. These variants are selected at the time of, or soon after, seroconversion, and become dominant during the reactivation phase. The most common precore mutation is the G1896A substitution, which creates a premature stop codon in the precursor protein from which HBeAg is elaborated. This mutation affects the stem of the encapsidation signal, but leads to stronger base pairing with the A1896 change in genotypes with a T at position 1858 of the precore region, such as B, C, D, and E. The double mutation affecting the core promoter region is thought to result in decreased transcription of the precore mRNA, with a knockon effect on HBeAg production, while pgRNA production remains the same or is even upregulated. It is now apparent that additional mutations in this region may contribute to this phenotype.
Geoffrey M. Dusheiko, in, 2003
Recommended Reading: How Do You Catch Hepatitis
Hbcab Or The Hepatitis B Core Antibody Test
The hepatitis B core antibody is produced by your immune system after infection by the hepatitis B virus, and it can persist for life. It is a sign that you either have an new, active hepatitis B infection or that you acquired hepatitis B in the past.
HBcAb is an immune system response to a protein in the core of the virus, and it is only present if you have been infected, rather than immunized against the virus. It is part of a routine screening panel of tests for hepatitis B. If your rest results turn out to be positive, your healthcare provider will order further tests to determine the stage of the infection: acute or chronic .
Also Known As: anti-HBc, HBcAb
What Are Some Of The Proven Ways To Prevent Hepatitis B
Healthcare providers stand by vaccination as a reliable prevention measure known to be effective to all age groups- adults, infants, and children. Therefore, close family members and sexual partners of infected persons must get tested and avail HBV vaccination to protect themselves. Medications have also been in use to prevent chronic HBV infection. Additionally, the power of vaccination of sexual partners and close family people cannot be overemphasized in aiding protection against the disease. Apart from vaccination, a few pointers to prevent hepatitis B Infection: Always make sure needles used for acupuncture, body piercing, tattoos, and ear piercing are sterile. Sanitary napkins and tampons need to be disposed of in a hygienic manner. Adopt effective hygiene upon exposure to contaminated blood like washing your hands well using soap. Avoid exposure of wounds to contamination. Avoid direct contact with blood and bodily fluids.
Read Also: Hepatic Cirrhosis Of The Liver
Negative But Other Hepatitis Tests Are Positive
Your HBsAb test may be negative even when other hepatitis B tests are positive, showing active or chronic infection. Further testing is necessary, especially for the hepatitis B surface antigen , which shows that the virus itself is circulating in your bloodstream and that you have an active or chronic infection.
You May Like: Treatment To Cure Hepatitis C
Epidemiology Of Hbv Reactivation
When combined with chemotherapy, the HBV reactivation rate during rituximab treatment has been reported to be 20%-55% overall and 3% in hepatitis B surface antigen negative patients. HBV reactivation can be caused by chemotherapy alone. However, rituximab more easily induces HBV reactivation independently upon combined treatment with chemotherapy or steroid treatment. The frequency of HBV reactivation is also higher with combination treatments including rituximab compared to chemotherapy alone or a combination chemotherapy and steroid treatment. Risk factors for HBV reactivation in patients receiving chemotherapy include being male, lack of HBs antibody, HBs antigen positivity, presence of a precore mutant, HBV-DNA level, anthracycline/steroid use, transplantation, second/third line treatment, youth, and the presence of lymphoma. However, when rituximab is used, the risk factors for HBV reactivation are narrowed to a lack of HBs antibody, youth, and being male. All the above reports are retrospective analyses of patients who were HBs antigen positive and who therefore were subject to prophylactic nucleoside analog therapy. In the future, patient groups must be identified who tend to experience reactivation even when receiving such therapy.
Also Check: How Can You Get Hepatitis C From Someone
Read Also: How Do You Get Hepatitis From Drinking
Hepatitis B Core Antibody Blood Test Igm
A Hepatitis B Core Antibody Blood Test, IgM, measures HBcAb which is an antibody produced in response to the core-antigen, a component of the Hepatitis B virus.
Also Known As: Anti-HBc, IgM, Antibody to Hepatitis B Core Antigen, IgM, HBcAb, IgM.
Methodology: Immunochemiluminometric assay
Preparation: No fasting required. Stop biotin consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection.
Test Results: 1-2 days. May take longer based on weather, holiday or lab delays.
Also Known As: Anti-HBc, IgM, Antibody to Hepatitis B Core Antigen, IgM, HBcAb, IgM.
Methodology: Immunoassay
Preparation: No fasting required. Stop biotin consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection.
Test Results: 1-2 days. May take longer based on weather, holiday or lab delays.
Hepatitis B Core Antigen Total Test
Hepatitis B Core Antigen Total, also known as Anti-HBc, HBcAb Total test is a blood test to detect acute and chronic Hepatitis B virus infections. The tests look for different signs of infection such as the Antigens, made by the viruses Antibodies, made by the body to fight the infection and Hepatitis B DNA, which is the genes of the virus and confirms its presence. The test detects both Hepatitis antibodies IgM and IgG,, and Hepatitis B core antigen. Those who had Hepatitis B vaccine will not have the core antibody in their blood.
No special preparation or fasting required. Biotin or Vitamin-B supplement consumption should be stopped at least 72 hours prior to the collection. About 2 ml of blood sample is taken from the vein in the arm. An elastic band is wrapped on the upper arm to restrict blood flow. This makes the veins visible and makes inserting the needle easy. The spot is cleaned with alcohol. The needle is inserted and when sufficient blood is collected, the armband is removed. The needle is withdrawn and the spot is pressed with a cotton swab.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Spread Through Sweat
Why Do I Need This Test
You may need this test if your healthcare provider suspects you have a liver infection caused by HBV. You may also need this test if you have symptoms of hepatitis B. Symptoms usually start slowly. Many people have no symptoms or only feel like they have a mild case of the flu. You may not have symptoms until the infection is chronic or severe.
The most common symptom is extreme tiredness. Other symptoms may include:
-
Nausea
-
Belly pain
-
Swelling and confusion. This is in extreme cases.
You may also have this test if you have a history that puts you at risk for being in contact with the virus. Risk factors for hepatitis B infection include:
-
Having sex with someone infected with the virus
-
Living in close contact with someone who has the virus
-
Being a man who has sex with men
-
Being a child born to a mother who has the virus
-
Sharing needles for intravenous drug use
-
Working in a healthcare center where you are exposed to blood
-
Getting a blood transfusion or organ transplant. This is less common with active screening.
What Does Hepatitis B Core Antibody Positive Mean
Hepatitis B is an inflammation of the liver caused by a virus. Signs of hepatitis include tiredness or fatigue, fevers, loss of appetite, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, headache, itchy skin, muscle soreness , jaundice , dark urine, and light stools.Here are some hepatitis B facts:
1. HBV infections will occur in one out of every 20 people at some time in the United States
2. Your risk of HBV is greater if you have sex with someone who has HBV.
3. Your risk is greater if you have a job that places you in contact with human blood.
4. Your risk is greater if you travel to areas where HBV is common.
Some people who donate blood get a letter from the blood bank saying that they are hepatitis B core antibody positive. Dont panic. This does not mean that you have hepatitis B, but you should get a more thorough screening. There are three blood tests that are used to diagnose hepatitis B: hepatitis B surface antigen, hepatitis B surface antibody, and hepatitis B core antibody positive. If your blood tests show that you are hepatitis B core body positive, it means that you either have a present infection or that you were infected in the past. There is a possibility of having a false hepatitis B core antibody positive. Blood banks only screen for hepatitis B core antibody positive and not for surface antigens or antibodies.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis C Spread Through Saliva
Recommended Reading: Hep C Without Hepatic Coma
Counseling Practices That Educate Support And Motivate Clients Undergoing Screening
Clients might need help deciding whether to get screened, understanding the test results, and determining their next steps. Even when services offered through the substance abuse treatment program are limited, discussing testing with clients presents an opportunity for counselors to motivate clients for change by confronting substance use and by making choices that improve their overall health. However, this may also be true when services are offered on-site through substance abuse treatment programs. A study at one methadone clinic that offered hepatitis screening and vaccination revealed that although the majority of clients completed screening , only 54.7 percent of clients who lacked for hepatitis A received vaccinations and only 2.9 percent of clients who lacked immunity for received vaccinations .
The Consensus Panel makes the following general recommendations while recognizing that, in some programs, the counselors role may be limited:
You May Like: Is Hepatitis C Caused By A Virus Or Bacteria
About Our Hepatitis B Core Antibody Test Igm
This blood test detects IgM antibodies to hepatitis B core antigen to indicate an acute hepatitis B infection. After infection with HBV, the IgM antibody is the first antibody produced by the body to fight off the virus.
The recommended minimum window period for Hepatitis B Core Antibody, IgM is:
- 6 weeks post potential exposure hepatitis B can occasionally be detected as early as 3 weeks post-exposure. For the most accurate results, we recommend getting tested after 6 weeks.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Is Caused By
Acute Hepatitis B Infection
High titers of immunoglobulin M anti-HBc, thought to be predominantly a thymus-independent response, appears early in the course of acute HBV infection, together with HBsAg and HBeAg . Anti-pre-S1 may also occur early in the course of infection. This is accompanied by a vigorous major histocompatibility complex class I restricted cytolytic T lymphocyte response against multiple epitopes throughout the structural and nonstructural proteins of the virus. The CTLs, by direct lysis of infected hepatocytes, are thought to be important in clearance of the virus. There is also some evidence for a role in viral elimination of the cytokines interferon γ and tumor necrosis factor α .
Figure 2. The natural history of acute HBV infection. HBsAg and HBeAg can be detected early in the serum, prior to the onset of clinical hepatitis. Antibody to pre-S1 can sometimes be detected during this early phase. AST (aspartate aminotransferaseis an indication of lysis of infected hepatocytes.
There is a strong MHC class II restricted T helper cell proliferative response to the nucelocapsid antigens, HBcAg and HBeAg, but not to the envelope proteins, during the early phase of acute hepatitis B. The association of recovery with the presence of the MHC class II locus DRB1*-1302 supports an important role for the CD4 response in recovery.
Louis M. Katz MD, Roger Y. Dodd PhD, in, 2013
Surface Antigen And Antibody
Hepatitis B surface antigen
The hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein found on the surface of HBV it is the firstserum to be detected following initial infection. Whilst it is the first antigen to appear, it is important to note, there is a window period of up to 200 days between the first exposure to HBV and the detection of HBsAg in the serum.2
HBsAgseroconversion is the development of antibodies against HBsAg it indicates the clearance of HBsAg and the resolution of infection.5 The presence of HBsAg always implies activeinfection, whilst persistence of HBsAg for more than six months indicates chronic infection.5
Antibody to Hepatitis B surface antigen
Anti-HBs is the antibody produced by the host in response to HBsAg . The presence of anti-HBs without HBsAg indicates two possible scenarios: either previous, cleared infection or vaccination against hepatitis B virus distinguishing between these two scenarios is possible with further serological testing. Anti-HBs remains in serum for life and indicates immunity to HBV.
Recommended Reading: Who Should Be Tested For Hepatitis C