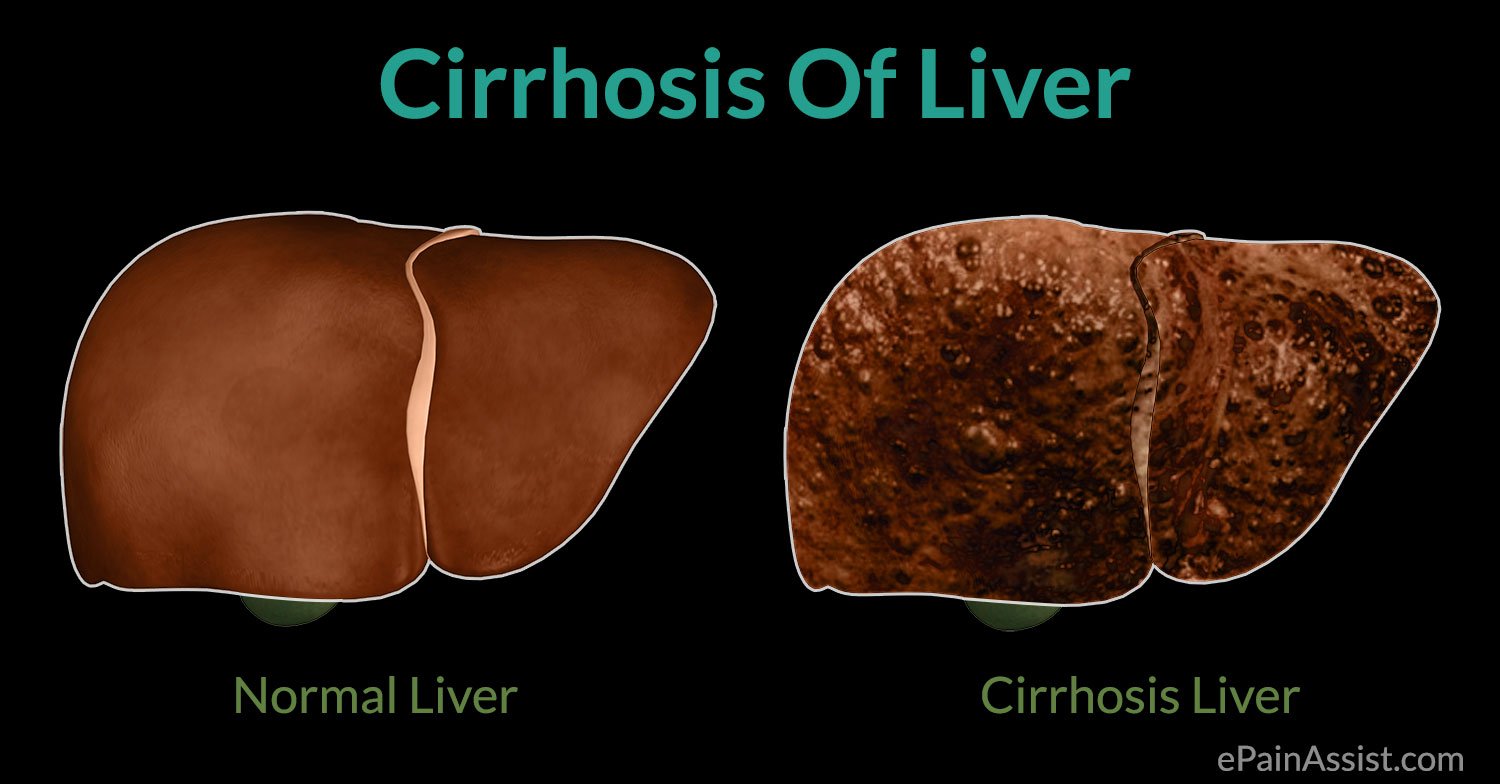
What Are Symptoms Of Cirrhosis Of The Liver
Many people with cirrhosis have no symptoms during the early phases of the disease. Symptoms are caused by either of 2 problems:
- Gradual failure of the liver to carry out its natural functions
- Distortion of the liver’s usual shape and size because of scarring
The most common symptoms of cirrhosis are as follows:
- Tiredness or even exhaustion
- Weakness
- Loss of appetite leading to weight loss
- Loss of sex drive
Symptoms may not appear until complications of cirrhosis set in. Many people do not know they have cirrhosis until they have a complication.
- Jaundice – Yellowing of the skin and eyes from the deposition of bilirubin in these tissues. Bilirubin is a product of the breakdown of old blood cells in the liver.
Cirrhosis can be caused by a number of conditions, including long-standing inflammation, poisons, infections, and heart disease, as well as chronic alcoholism and chronic hepatitis, the most common causes. For 30-50 percent of cirrhosis cases, however, no cause can be found. Often, the progress toward liver failure is slow and gradual. There is no cure for cirrhosis, but removing the cause can slow the sidease. If the damage is not too devere, the liver can heal itself over time.
Chronic alcoholism: Alcohol can poison all living cells, causing liver cells to become inflamed and die.
Hepatitis: Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver from any cause, but it usually refers to a viral infection of the liver.
How Is Cirrhosis Of The Liver Treated
While there is no cure for cirrhosis, your doctor may recommend various treatments to help slow the scarring and relieve symptoms. First, your doctor may try to treat the underlying disease that is the cause of cirrhosis through medication, weight loss or alcohol treatment programs. To treat the symptoms of cirrhosis itself, your doctor may recommend:
- Lifestyle changes including, diet changes such as a low-sodium or plant-based diet, and discontinuing the use of alcohol.
- Medications, such as antibiotics, may be prescribed in order to avoid infections as well as vaccinations for viral hepatitis, pneumonia and influenza to help you avoid possible illnesses that can cause infections. Your doctor may also prescribe medication to help reduce toxins in the blood.
- Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt , a procedure to treat the portal hypertension caused by cirrhosis. An interventional radiologist places a small tube into the liver to help bypass blood flow into the liver by directing it back towards the heart.
- SurgeryIn severe cases, a liver transplant may be needed. A liver transplant replaces the damaged liver with a healthy one from a donor.
When Should I Call 911 Or Go To The Emergency Room
If you have cirrhosis and experience the following, call 911:
- Your poop are black and tarry or contain blood .
- You are vomiting blood.
- You have muscle tremors or shakiness.
- You are confused, irritable, disoriented, sleepy, forgetful or foggy.
- You have a change in your level of consciousness or alertness you pass out.
Don’t Miss: How Can You Get Hepatitis B
Impact Of Sleep Disturbances In Liver Cirrhosis
Sleep disturbances have been shown to negatively impact QoL in cirrhotic patients and have been measured in the majority of studies by the SF-36,,, or the Chronic Liver Disease Questionnaire., For example, QoL in patients with liver cirrhosis is worse than QoL in healthy controls, for both the Physical Component Summary and the Mental Component Summary. Samanta et al, in a study comparing 100 cirrhotic patients with minimal HE or no HE, showed that minimal HE was associated with poor sleep and EDS, but also that sleep disturbances aggravate neuropsychiatric impairment. Sleep disturbances have also been shown to negatively impact psychological distress and depression.
Drug Hepatotoxicity In The Patient With Cirrhosis
The institution of any new medical therapy warrants the performance of more frequent liver chemistries patients with liver disease can ill afford to have drug-induced liver disease superimposed on their condition. Medications associated with drug-induced liver disease include the following:
-
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Child
Primary Goals In Management Ofcompensated Cirrhosis
- Treatment of the etiology of the underlying liver disease, for example:
- Antiviral treatment of HCV or HBV
- Abstinence from alcohol
What Research Is Ongoing To Prevent And Treat Cirrohsis Of The Liver
Progress in the management and prevention of cirrhosis continues. Research is ongoing to determine the mechanism of scar formation in the liver and how this process of scarring can be interrupted or even reversed. Newer and better treatments for viral liver disease are being developed to prevent the progression to cirrhosis. Prevention of viral hepatitis by vaccination, which is available for hepatitis B, is being developed for hepatitis C. Treatments for the complications of cirrhosis are being developed or revised, and tested continually. Finally, research is being directed at identifying new proteins in the blood that can detect liver cancer early or predict which patients will develop liver cancer.
Don’t Miss: How Does A Person Contract Hepatitis
How Is Cirrhosis Of The Liver Diagnosed And Evaluated
If your doctor suspects you have cirrhosis, one or more of the following imaging tests may be performed:
Other tests include:
- Biopsy: Part of the liver tissue is sampled and examined by a pathology doctor to analyze the extent of liver damage. The biopsy is often done by a radiologist using ultrasound guidance and is minimally invasive.
- Liver function test: This test involves analyzing the blood for particular enzymes that signal that liver damage is present.
What Is Passive Hepatic Congestion
Passive hepatic congestion, also known as congested liver in cardiac disease, describes the stasis of blood in the hepatic parenchyma, due to impaired hepatic venous drainage, which leads to the dilation of central hepatic veins and hepatomegaly.
Also to know is, what does a congested liver mean?
Congestive hepatopathy, is liver dysfunction due to venous congestion, usually due to congestive heart failure. The paler areas are unaffected surrounding liver tissue. When severe and longstanding, hepatic congestion can lead to fibrosis if congestion is due to right heart failure, it is called cardiac cirrhosis.
Additionally, what are signs and symptoms of cardiac cirrhosis? Patients with cardiac cirrhosis are usually asymptomatic. This condition is usually suggested from abnormal liver function tests. Common symptoms are due to heart failure like shortness of breath, leg swelling, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea and orthopnea.
Also question is, how does congestion affect the liver?
Such congestion increases pressure in the inferior vena cava and other veins that carry blood to it, including the hepatic veins . If this pressure is high enough, the liver becomes engorged with blood and malfunctions.
Is cardiac cirrhosis reversible?
You May Like Also
You May Like: How To Cure Hepatitis C Naturally
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Liver Cancer
When liver cancer is in the early stages, you may have no symptoms at all. If your liver is swollen, you might notice the following symptoms: You may have:
- A lump below the rib cage or pain on the right side of the abdomen, or pain near the right shoulder.
- Jaundice .
- Dark-colored urine.
- Bloating.
Remember, though, that liver cancer is only one of the reasons that a liver can be swollen.
Surveillance For Hepatocellular Carcinoma
The incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma has risen in the United States. The practice guidelines of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases recommend that patients with cirrhosis undergo surveillance for HCC with ultrasonography every 6 months. The discovery of a liver nodule should prompt the performance of a 4-phase CT scan or an MRI scan . Lesions that enhance in the arterial phase and exhibit “washout” in the delayed phases are highly suggestive of HCC.
Many authors contend that the combination of arterial enhancement and washout on CT scanning or MRI offers greater diagnostic power for HCC than does guided liver biopsy. Indeed, guided liver biopsies have a 20-30% false negative rate in making the diagnosis of HCC. Current guidelines support the use of CT scanning and MRI in confirming the presence of HCC. Biopsy is not required in order to define a lesion as HCC. However, CT scanning or ultrasonographically guided liver biopsy may be useful when a noduleâs enhancement characteristics are not typical for HCC.
Patients with a diagnosis of HCC and no evidence of extrahepatic disease, as determined by chest and abdominal CT scans and by bone scan, should be offered curative therapy. Commonly, this therapy entails liver resection surgery for patients with Child Class A cirrhosis and an accelerated course to liver transplantation for patients with Child Class B or C cirrhosis.
Also Check: How Long Is A Hepatitis C Shot Good For
Did You Know That Hepatitis Simply Means Inflammation Of The Liver
Inflammation is the bodys natural response to injury and an important part of healing or immune response. Think about when you get a cut or injury to your skin. The area around the wound becomes swollen or inflamed. Seeing the swelling is not the only way you experience the inflammatory phase. You may also experience pain, redness, or the wound may feel warm to the touch. Under the skin, your body is hard at work to stop the bleeding and prevent infection. Blood vessels near the wound widen, or dilate, making more room for special healing and repair cells, or cells in the wounded area. These cells remove damaged cells and harmful substances and allow the rest of the healing process to continue. Inflammation is essential to fight infection.
Inflammations Role in Repairing Damaged CellsThe liver recognizes and replaces its own damaged or broken-down cells while still performing all of its vital functions. Just as inflammation is required to get rid of toxic substances, inflammation is part of repairing damaged liver cells. Damaged liver cells and immune cells both send out messages to activate specific repair cells which travel to the site of the injury. These repair cells release something called collagen, a fiber, which stiffens the tissue around the cells, protects the surviving cells and allows healing to occur. In a healthy liver, this repair process is very closely regulated and when no longer needed the extra collagen will disperse and the liver returns to normal.
Esophageal And Gastric Variceal Bleeding
For portal hypertension, nonselective beta blockers such as propranolol or nadolol are commonly used to lower blood pressure over the portal system. In severe complications from portal hypertension, transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting is occasionally indicated to relieve pressure on the portal vein. As this shunting can worsen hepatic encephalopathy, it is reserved for those patients at low risk of encephalopathy. TIPS is generally regarded only as a bridge to liver transplantation or as a palliative measure. Balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration can be used to treat gastric variceal bleeding.
You May Like: What Kind Of Doctors Treat Hepatitis C
Causes And Things That Make It More Likely
Cirrhosis always develops because of another liver problem or disease. If you don’t treat the cause of your cirrhosis, it’ll get worse, and over time your healthy liver cells won’t be able to keep up. You might start to get tired, feel like you don’t want to eat, and lose weight without trying. After a while, your liver may not be able to work well or at all.
It’s important to know the cause of your cirrhosis so you can get the right treatment and keep it from getting worse. The most common causes are:
Alcohol abuse. If you have a drinking problem, it’s important to get help. Alcohol harms your liver. Talk to your doctor. They may refer you to a treatment program.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Obesity raises your chances of this condition. If your cirrhosis is caused by this disease, you may improve your liver health if you lose weight and keep your blood sugar levels under control.
Hepatitis B or hepatitis C. Medicines for these diseases can stop more damage from happening to your liver.
Other conditions that can lead to cirrhosis include:
- Some infections, including syphilis and brucellosis
- Bad reactions to certain medications
Is Cirrhosis Of The Liver Hereditary
Cirrhosis is fibrosis, a form of scarring within your liver. This is also the end-stage type of scarring brought about by various liver diseases in addition to conditions such as hepatitis. Each time the liver gets harmed as a result of long-lasting problems inside of this vital organ, our livers attempt to repair by itself. Cirrhosis will ultimately become a liver failure, where in fact, the liver stops working, which may be deadly. On the other hand, it often takes many years in terms of this condition to reach this grave. Furthermore, treatment can help hamper its progression.
You May Like: Where Do You Get Hepatitis C
If I Have Ascites How Can I Best Take Care Of Myself
People with ascites should work with a dietitian to plan a sodium-restricted diet. Check food labels, and avoid high-sodium foods.
You can use several salt substitutes. However, avoid substitutes with potassium, since the medicine you may be taking for ascites can also increase potassium. A dietitian can help you plan a healthy diet and provide recommendations for salt alternatives.
In addition, you should:
- Take your diuretics as prescribed.
- Record your weight every day.
- Stop drinking alcohol, which can cause further liver damage.
- Treat hepatitis B or C if necessary.
How Is Cirrhosis Of The Liver Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will first ask about your medical history and over-the-counter and prescription drug use. They will also ask about any supplements or herbal products you may take. Your provider may suspect you have cirrhosis if you have a long history of alcohol abuse, injectable drug abuse or have had hepatitis B or C and have the symptoms listed in this article.
To diagnosis cirrhosis, your provider will perform a physical exam and may order one or more of the following tests:
- Physical exam: Your doctor will examine you, looking for the signs and symptoms of cirrhosis including: the red, spider-like blood vessels on your skin yellowing of your skin or whites of your eyes bruises on your skin redness on your palms swelling, tenderness or pain in your abdomen enlarged firmer-feeling, bumpy texture to the lower edge of your liver .
- Blood tests: If your doctor suspects cirrhosis, your blood will be checked for signs of liver disease. Signs of liver damage include:
- Lower than normal levels of albumin and blood clotting factors .
- Raised levels of liver enzymes .
- Higher level of iron .
- Presence of autoantibodies .
- Raised bilirubin level .
- High white blood cell count .
- High creatinine level .
- Lower levels of sodium .
- Raised level of alpha-fetoprotein .
In addition, other blood work will include a complete blood count to look for signs of infection and anemia caused by internal bleeding and a viral hepatitis test to check for hepatitis B or C.
Read Also: How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis B
Effectiveness Of He Treatment On Sleep Disturbances
Non-absorbable disaccharides
Lactulose and lactitol aim to decrease ammonia absorption from the gut and are effective for improving HE.,, Treatment improves neurocognition and QoL. A recent work from Singh et al, comparison of cirrhotic patients without HE and those with minimal HE who were given lactulose for 3 months, showed that HE treatment led to improvements in EDS , sleep quality , and QoL .
Rifaximin
Rifaximin is a non-absorbable oral antibiotic currently recommended for the treatment of refractory HE and to maintain remission of these episodes. Its mechanism of action is complex and is thought to involve a decrease in the load of pathogenic microbial flora. Rifaximin improves neurocognitive function and QoL in HE., With regard to sleep, we have compared 15 recurrent HE patients before and after a rifaximin course. No changes in subjective nighttime sleep quality and daytime sleepiness were observed. REM sleep amounts were increased on PSG, but no changes were observed for EDS or the need for naps, despite improvements in HE scores.
Probiotics and l-ornithine l-aspartate
These medications have been proved to improve HE and QoL., However, no specific studies are currently focused on sleep disturbances.
Liver transplant
Treating And Managing The Effects Of Cirrhosis
Another aspect of treatment is to deal with the complications of cirrhosis as early as possible. For this reason your doctor may suggest you have regular tests to identify problems even before you notice any symptoms. You may also be given other drugs to reduce blood pressure, to prevent and treat infections and to help support your bodys functions.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis B Curable Or Treatable
Portal Hypertension And Variceal Bleeding
Medicines including beta blockers such as propranolol can reduce the risk of bleeding and reduce the severity of any bleed, should it occur. If there is a serious bleed, initial treatment is to replace the fluid and then to identify and correct the cause of bleeding. There are several techniques aimed at stemming the bleeding which involve endoscopy.
One of these is called banding, where a single vein is sucked into a ring at the end of the endoscope. A small band is then placed around the base of the varix which will control the bleeding.
Injection sclerotherapy is also used and involves injecting a substance into the veins of the gullet to induce clotting and scar tissue that will help stop the veins from bleeding.
If bleeding can not be stopped by endoscopy, a Sengstaken tube is passed down the throat into the stomach. This device has two balloons which once inflated, put pressure on the varices and help control the bleeding. People are heavily sedated for this procedure.
If bleeding still cannot be controlled a procedure to lower pressure in the portal vein called a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunt may be needed. In this procedure a metal tube is passed across your liver to join two large veins . This creates a bypass so the blood flows straight into the hepatic vein relieving the pressure which causes the varices.