Is Hepatitis Testing Recommended For People With Hiv
Yes. Everyone living with HIV should be tested for HBV and HCV when they are first diagnosed with HIV and begin treatment. People living with HIV who have ongoing risk factors for getting hepatitis B or hepatitis C should be tested annually.
In addition, new HCV screening recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention call for:
- One-time screening for all adults 18 years and older
- Screening of all pregnant women during every pregnancy
- Testing for all persons with risk factors, with testing continued periodic testing those with ongoing risk.
How Do You Treat Hepatitis B
Like hepatitis A, medical treatment for acute hepatitis B is focused on getting plenty of rest and fluids and eating a healthy diet, although sometimes antiviral drugs are recommended for severe cases to help prevent liver failure. Patients with chronic hepatitis B may be given an oral antiviral drug to control the viral infection and minimize liver damage. These drugs are effective, but they rarely cure chronic hepatitis B. Therefore, these medications often have to be taken for life.
Screening For Viral Hepatitis
The purpose of screening for viral hepatitis is to identify people infected with the disease as early as possible, even before symptoms and transaminase elevations may be present. This allows for early treatment, which can both prevent disease progression and decrease the likelihood of transmission to others.
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A causes an acute illness that does not progress to chronic liver disease. Therefore, the role of screening is to assess immune status in people who are at high risk of contracting the virus, as well as in people with known liver disease for whom hepatitis A infection could lead to liver failure. People in these groups who are not already immune can receive the hepatitis A vaccine.
Those at high risk and in need of screening include:
- People with poor sanitary habits such as not washing hands after using the restroom or changing diapers
- People who do not have access to clean water
- People in close contact with someone who has hepatitis A
- People who use illicit drugs
- People with liver disease
- People traveling to an area with endemic hepatitis A
The presence of anti-hepatitis A IgG in the blood indicates past infection with the virus or prior vaccination.
Hepatitis B
The CDC, WHO, USPSTF, and ACOG recommend routine hepatitis B screening for certain high-risk populations. Specifically, these populations include people who are:
Other
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B and C
Hepatitis D
Hepatitis E
Alcoholic hepatitis
Also Check: How Often Should You Be Tested For Hepatitis C
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis
Treatment for hepatitis depends on which type you have and whether it is acute or chronic. Acute viral hepatitis often goes away on its own. To feel better, you may just need to rest and get enough fluids. But in some cases, it may be more serious. You might even need treatment in a hospital.
There are different medicines to treat the different chronic types of hepatitis. Possible other treatments may include surgery and other medical procedures. People who have alcoholic hepatitis need to stop drinking. If your chronic hepatitis leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
If I Have Hepatitis How Can I Avoid Giving It To Someone Else
For hepatitis A, one of the best things you can do is wash your hands a lot. That will keep the virus out of food and drinks.
If you have hepatitis B and C, you need to find ways to keep others from making contact with your blood. Follow these tips:
- Cover your cuts or blisters.
- Carefully throw away used bandages, tissues, tampons, and sanitary napkins.
- Don’t share your razor, nail clippers, or toothbrush.
- If your blood gets on objects, clean them with household bleach and water.
- Don’t breastfeed if your nipples are cracked or bleeding.
- Don’t donate blood, organs, or sperm.
- If you inject drugs, don’t share needles or other equipment.
Show Sources
Also Check: What Happens If You Have Hepatitis B
Spread Of The Disease
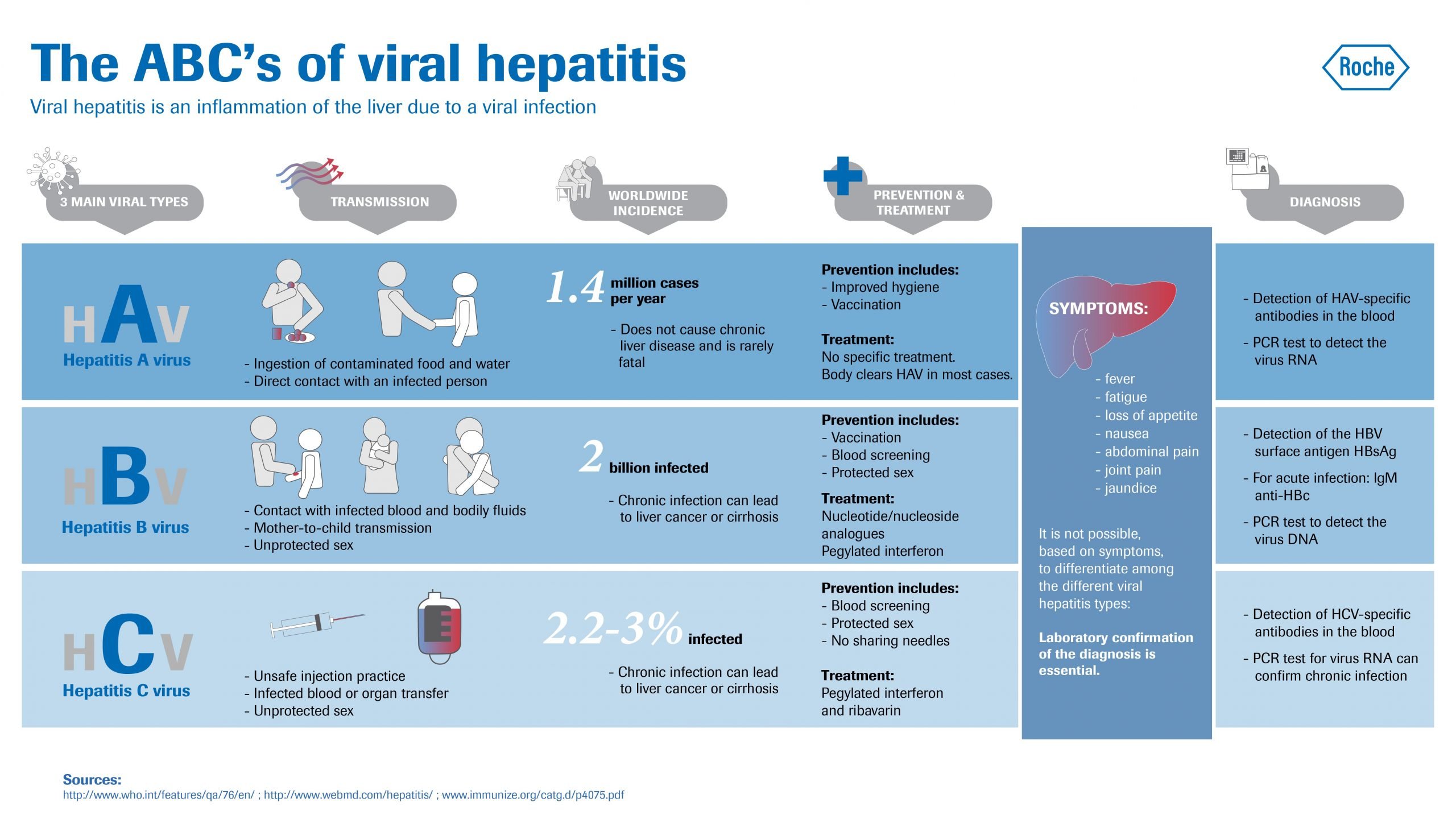
Hepatitis A virus characteristically spreads through the ingestion of contaminated food and water whereas Hepatitis B, C and D usually take place due to parenteral contact with contaminated body fluids like blood . Furthermore, Hepatitis B can get transmitted from an infected mother to baby at birth due to the possible mixing of blood and also by unprotected sexual intercourse.
How Do You Get Hepatitis B
In the U.S., people usually get hepatitis B infection through sexual transmission or intravenous drug use. In other parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, such as Southeast Asia, mother-to-child transmission at birth is the most common way people get infected. Unlike hepatitis A infection, hepatitis B has the potential to become a chronic infection that requires lifelong management.
Also Check: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Oral Sex
Hepatitis A B And C: Whats The Difference
Hepatitis is often caused by a virus that comes in different strains. The most common strains of hepatitis are hepatitis A, B, and C. They all are contagious, but they differ primarily by the way they are spread.
Table: Differences among hepatitis A, B, and C
Table: Differences among hepatitis A, B, and C
Do You Need Vaccinations Before Traveling Abroad
The CDC divides travel vaccinations into three categories: 1) routine, 2) recommended, and 3) required. The only vaccine classified as “required” by International Health Regulations is the yellow fever vaccination for travel to certain countries in sub-Saharan Africa and tropical South America.
“Routine” vaccinations are those that are normally administered, usually during childhood, in the United States. These include immunizations against:
- tetanus
Recommended Reading: How Much Is A Hepatitis C Test
What Are The Common Types Of Viral Hepatitis
Although the most common types of viral hepatitis are HAV, HBV, and HCV, some clinicians had previously considered the acute and chronic phases of hepatic infections as “types” of viral hepatitis. HAV was considered to be acute viral hepatitis because the HAV infections seldom caused permanent liver damage that led to hepatic failure. HBV and HCV produced chronic viral hepatitis. However, these terms are outdated and not currently used as frequently because all of the viruses that cause hepatitis may have acute phase symptoms . Prevention techniques and vaccinations have markedly reduced the current incidence of common viral hepatitis infections however, there remains a population of about 1 to 2 million people in the U.S. with chronic HBV, and about 3.5 million with chronic HCV according to the CDC. Statistics are incomplete for determining how many new infections occur each year the CDC documented infections but then goes on to estimate the actual numbers by further estimating the number of unreported infections .
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis C
Types D, E, and G Hepatitis
Individuals who already have chronic HBV infection can acquire HDV infection at the same time as they acquire the HBV infection, or at a later time. Those with chronic hepatitis due to HBV and HDV develop cirrhosis rapidly. Moreover, the combination of HDV and HBV virus infection is very difficult to treat.
- HIV patients
- People with hemophilia who receive blood clotting factors
Do I Need A Hepatitis Panel
Few reasons that have prompted your healthcare provider to order the hepatitis panel for you are: You have exhibited some acute symptoms of hepatitis and the type of virus A, B, or C is not known. You carry an elevated risk of hepatitis infection due to recent exposure and a hepatitis panel may be recommended to determine the type of virus behind the hepatitis infection. Your doctor may ask you to undergo the test even in the absence of symptoms. If you show signs of liver damage, then the hepatitis panel test is a must for you. Some of the overriding symptoms that prompt a hepatitis panel test are: Loss of appetite Illegal drugs
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis C And Is It Curable
How Are Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Spread From Person To Person
Like HIV, the hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses spread:
- From mother to child: Pregnant women can pass these infections to their infants. HIV-HCV coinfection increases the risk of passing on hepatitis C to the baby.
- Sexually: Both viruses can also be transmitted sexually, but HBV is much more likely than HCV to be transmitted sexually. Sexual transmission of HCV is most likely to happen among gay and bisexual men who are living with HIV.
Acute Vs Chronic Infection

Doctors distinguish between chronic and acute infection with hepatitis viruses. Acute infection is a short-term condition, lasting under six months. Chronic infection is a long-term condition, lasting more than six months.
Hepatitis B infection can be either acute or chronic. Most people who get acute hepatitis B dont end up progressing to chronic hepatitis B. By contrast, acute hepatitis C tends to develop into chronic hepatitis C. Approximately 7585 percent of adults newly infected with hepatitis C develop a chronic infection, according to the CDC . Others clear the infection.
When you get acute hepatitis C you may or may not have symptoms. Most cases of acute hepatitis C are asymptomatic, meaning people dont notice the symptoms. Symptoms are only noticeable in 15 percent of cases of acute hepatitis C.
Read Also: What Is The Best Medication For Hepatitis B
How Does It Affect The Body
The incubation period for hepatitis B can range from . However, not everyone who has acute hepatitis B will experience symptoms.
About 95 percent of adults completely recover from hepatitis B. However, hepatitis B can also become chronic.
The risk of chronic hepatitis B is greatest in those who were exposed to HBV as young children. Many people with chronic hepatitis B dont have symptoms until significant liver damage has occurred.
In some people whove had hepatitis B, the virus can reactivate later on. When this happens, symptoms and liver damage may occur. People with a weakened immune system and those being treated for hepatitis C are at a higher risk for HBV reactivation.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Some people with hepatitis do not have symptoms and do not know they are infected. If you do have symptoms, they may include:
- Joint pain
- Jaundice, yellowing of your skin and eyes
If you have an acute infection, your symptoms can start anywhere between 2 weeks to 6 months after you got infected. If you have a chronic infection, you may not have symptoms until many years later.
Also Check: How Can You Pass Hepatitis C
What Is Viral Hepatitis
Viral hepatitis is an inflammation of your liver that’s caused by a virus. There are five types, but the most common ones in the U.S. are hepatitis A, B, and C. All of them affect your liver. Some of the symptoms are similar, but they have different treatments.
Hepatitis A. This type won’t lead to long-term infection and usually doesn’t cause any complications. Your liver heals in about 2 months. You can prevent it with a vaccine.
Hepatitis B. Most people recover from this type in 6 months. Sometimes, though, it causes a long-term infection that could lead to liver damage. Once you’ve got the disease, you can spread the virus even if you don’t feel sick. You won’t catch it if you get a vaccine.
Hepatitis C. Many people with this type don’t have symptoms. About 80% of those with the disease get a long-term infection. It can sometimes lead to cirrhosis, a scarring of the liver. There’s no vaccine to prevent it.
What Are The Risk Factors
Some people are at an increased risk for contracting HAV, including:
- people traveling to areas of the world where hepatitis A is common
- men who have sex with men
- people who use injectable or noninjectable drugs
- caregivers for those who have hepatitis A
- people who are experiencing homelessness
- people living with a child whos been adopted from an area where hepatitis A is common
Don’t Miss: How Can A Person Get Hepatitis C
What Are The Symptoms And Signs Of Viral Hepatitis
The period of time between exposure to hepatitis and the onset of the illness is called the incubation period. The incubation period varies depending on the specific hepatitis virus. Hepatitis A virus has an incubation period of about 15 to 45 days Hepatitis B virus from 45 to 160 days, and Hepatitis C virus from about 2 weeks to 6 months.
Many patients infected with HAV, HBV, and HCV have few or no symptoms of illness. For those who do develop symptoms of viral hepatitis, the most common are flu-like symptoms including:
How Is Viral Hepatitis Prevented
Prevention of hepatitis involves measures to avoid exposure to the viruses, using immunoglobulin in the event of exposure, and vaccines. Administration of immunoglobulin is called passive protection because antibodies from patients who have had viral hepatitis are given to the patient. Vaccination is called active protection because killed viruses or non-infectious components of viruses are given to stimulate the body to produce its own antibodies.
Avoidance of exposure to viruses
Prevention of viral hepatitis, like any other illness, is preferable to reliance upon treatment. Taking precautions to prevent exposure to another individual’s blood , semen , and other bodily secretions and waste will help prevent the spread of all of these viruses.
Use of immunoglobulins
Immune serum globulin is human serum that contains antibodies to hepatitis A. ISG can be administered to prevent infection in individuals who have been exposed to hepatitis A. ISG works immediately upon administration, and the duration of protection is several months. ISG usually is given to travelers to regions of the world where there are high rates of hepatitis A infection and to close or household contacts of patients with hepatitis A infection. ISG is safe with few side effects.
Hepatitis A
Individuals at increased risk of acquiring hepatitis A are:
Some local health authorities or private companies may require hepatitis A vaccination for food handlers.
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for:
Read Also: Is Hiv The Cause Of Hepatitis B
What Is Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A viral infection is transmitted from one person to another faeco-orally ). Moreover, certain unprotected sexual practices are also known to increase the spread of HAV in general.
A higher incidence can be seen in developing countries mainly with poor hygiene and sanitation measures. However, the World Health Organization has taken lots of measures to bring down this rate of affected individuals. Introducing various protocols and vaccines have proven to be effective in controlling the transmission of the virus.
The incubation period of hepatitis A is around 24 weeks. Patients will experience fever, malaise, loss of appetite, loose stools, nausea, abdominal discomfort, dark color urine, and jaundice.
Infections caused this way are usually mild to moderate in severity, and most affected individuals will reach a full recovery and acquire a lifelong immunity to further HAV infections. HAV infections can become severe rarely it can be a life-threatening condition for patients who are immune-compromised.
It is important to know that infections caused by hepatitis A can not be easily distinguished clinically from other types of acute viral hepatitis. However, an accurate diagnosis is usually made by doing an antibody test which will show HAV-specific Immunoglobulin G antibodies in the blood.
Furthermore, a reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction can be used to detect the hepatitis A virus RNA, but it requires advanced laboratory techniques.
feco oral route
How Do You Treat Hepatitis C
When Dr. Fried started treating hepatitis C in 1990, the cure rate was 7 percent. Treatments have evolved since then, leading to a 95 percent cure rate. The treatment course includes taking one to a few pills a day for 12 to 24 weeks, and the medicines have few side effects. Hepatitis C is the only chronic viral infection that you can routinely cure, thanks to these new medicines.
Read Also: Natural Cure For Hepatitis A
What Is Acute Fulminant Hepatitis
Rarely, individuals with acute infections with HAV and HBV develop severe inflammation, and the liver fails . These patients are extremely ill with the symptoms of acute hepatitis already described and the additional problems of confusion or coma , as well as bruising or bleeding . In fact, up to 80% of people with acute fulminant hepatitis can die within days to weeks therefore, it is fortunate that acute fulminant hepatitis is rare. For example, less than 0.5% of adults with acute infection with HBV will develop acute fulminant hepatitis. This is even less common with HCV alone, although it becomes more frequent when both HBV and HCV are present together.
How To Protect Yourself Against Hepatitis C
Unfortunately, there is no vaccine available for hepatitis C, but you can protect yourself by avoiding behaviors such as sharing needles and syringes. In addition, the CDC recommends people born between 1945 and 1965 get tested for hepatitis C. Testing is also recommended for people who were treated for blood-clotting problems before 1987 and recipients of blood transfusions or donated organs before 1992.
The UNC Liver Center has a clinic in Chapel Hill that specializes in hepatitis B and C, incorporating the latest clinical trials and most up-to-date therapies. Treatment for hepatitis is also available at our locations in Asheville, High Point, Raleigh and Wilmington. To learn more, call 966-2516.
Michael Fried, MD, is the director of the UNC Liver Center and a professor of medicine at the UNC School of Medicine.
Also Check: Hepatitis B And C Test